Ammonia Build Up Liver Failure
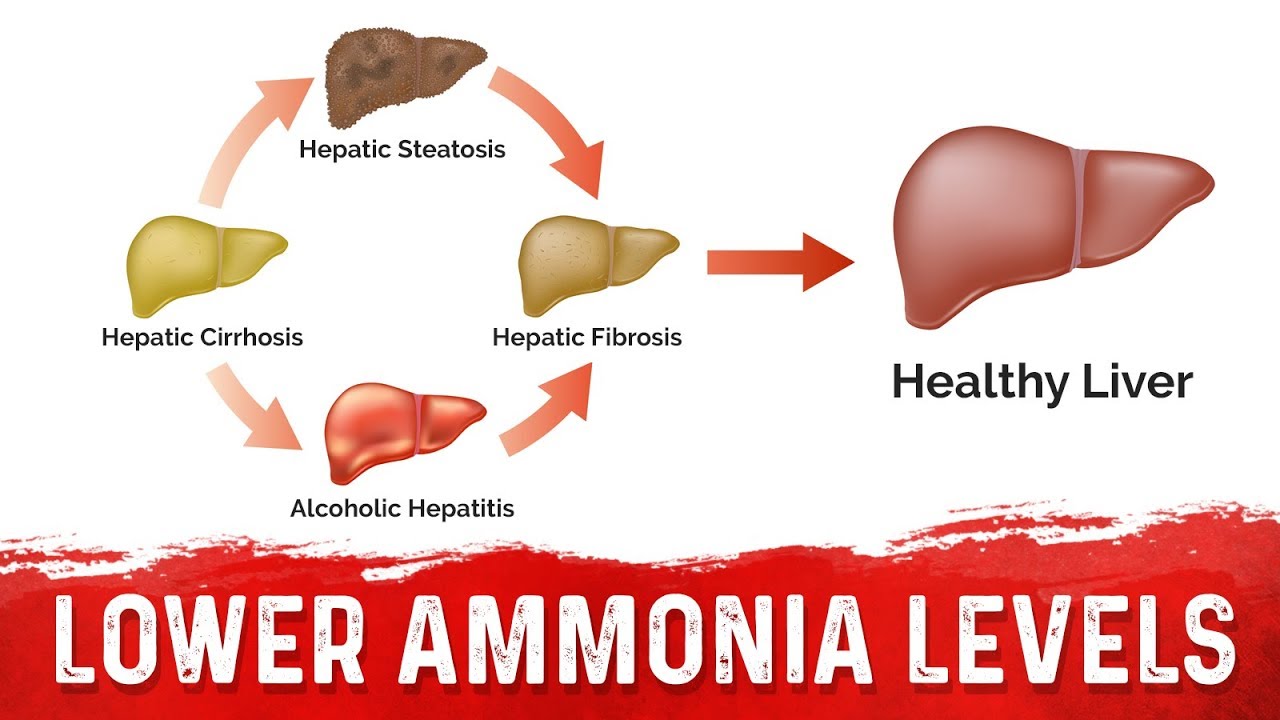
Ammonia Build Up Liver Failure - If there’s an issue with any part of the urea cycle or your liver’s ability to process ammonia, ammonia can build up in your blood, causing hyperammonemia. These can help determine whether or not your liver disease is. Ammonia is a potent neurotoxin, and. Research indicates various factors contribute to elevated ammonia levels. This can sometimes happen if you have kidney or liver failure. Ammonia toxicity, indicated by elevated serum ast and alt levels, points to liver damage and impaired protein metabolism, as corroborated by studies on ammonia toxicity in. When the liver is unable to effectively filter toxins, substances like ammonia can build up in the bloodstream. Hyperammonaemia frequently results from hepatic dysfunction, while rarer causes include urea cycle defects (ucd), drugs, and infections. Serum ammonia may have prognostic value in liver failure. However, when the liver is not functioning properly due to disease or damage, ammonia can build up in the bloodstream. Background acute liver failure (alf) is an emergent condition that requires intensive care and manifests in particular by significant elevation in serum ammonia level. Research indicates various factors contribute to elevated ammonia levels. Serum ammonia may have prognostic value in liver failure. Ammonia, also known as nh3, is a waste product that bacteria in your intestines primarily make when digesting protein. These can range from liver dysfunction to hereditary metabolic disorders. Hyperammonaemia frequently results from hepatic dysfunction, while rarer causes include urea cycle defects (ucd), drugs, and infections. But with certain conditions, that flow. This can sometimes happen if you have kidney or liver failure. It can also happen if you have a urea cycle problem or a. Elevated ammonia levels can lead to neurological disturbances,. A serum ammonia test measures the concentration of ammonia in the. But ammonia will build up in your body if you can't get rid of urea. Normally, ammonia is processed in your liver, where it’s transformed into another waste product called urea. If you have liver cirrhosis, you should know some factors to consider including normal ammonia levels. However, when. The urea is then carried to your kidneys, where it’s eliminated in your urine (pee). When the liver is damaged, the detoxification process may be disturbed and. Ammonia is a potent neurotoxin, and. It can also happen if you have a urea cycle problem or a. But ammonia will build up in your body if you can't get rid of. These can range from liver dysfunction to hereditary metabolic disorders. Background acute liver failure (alf) is an emergent condition that requires intensive care and manifests in particular by significant elevation in serum ammonia level. If you have liver cirrhosis, you should know some factors to consider including normal ammonia levels. A serum ammonia test measures the concentration of ammonia in. In many cases, the problem occurs in adults with cirrhosis, an advanced stage of liver disease when scar. If there’s an issue with any part of the urea cycle or your liver’s ability to process ammonia, ammonia can build up in your blood, causing hyperammonemia. Key findings from recent studies reveal:. Serum ammonia may have prognostic value in liver failure.. But with certain conditions, that flow. However, when the liver is not functioning properly due to disease or damage, ammonia can build up in the bloodstream. In many cases, the problem occurs in adults with cirrhosis, an advanced stage of liver disease when scar. When the liver is unable to effectively filter toxins, substances like ammonia can build up in. When the liver is damaged, the detoxification process may be disturbed and. Have a high suspicion for he in patients with known liver disease or acute liver failure, who present with confusion, and check an ammonia level. These can range from liver dysfunction to hereditary metabolic disorders. When your liver is healthy and functioning normally, it turns ammonia into a. In many cases, the problem occurs in adults with cirrhosis, an advanced stage of liver disease when scar. Normally, ammonia is processed in your liver, where it’s transformed into another waste product called urea. Have a high suspicion for he in patients with known liver disease or acute liver failure, who present with confusion, and check an ammonia level. Elevated. The degree of elevation may. Elevated ammonia levels can lead to neurological disturbances,. Background acute liver failure (alf) is an emergent condition that requires intensive care and manifests in particular by significant elevation in serum ammonia level. Ammonia toxicity, indicated by elevated serum ast and alt levels, points to liver damage and impaired protein metabolism, as corroborated by studies on. If there’s an issue with any part of the urea cycle or your liver’s ability to process ammonia, ammonia can build up in your blood, causing hyperammonemia. When the liver is unable to effectively filter toxins, substances like ammonia can build up in the bloodstream. Normally, ammonia is processed in your liver, where it’s transformed into another waste product called. In many cases, the problem occurs in adults with cirrhosis, an advanced stage of liver disease when scar. Ammonia, also known as nh3, is a waste product that bacteria in your intestines primarily make when digesting protein. If there’s an issue with any part of the urea cycle or your liver’s ability to process ammonia, ammonia can build up in. It can also happen if you have a urea cycle problem or a. A serum ammonia test measures the concentration of ammonia in the. High ammonia levels are commonly associated with liver disease. If there’s an issue with any part of the urea cycle or your liver’s ability to process ammonia, ammonia can build up in your blood, causing hyperammonemia. This can sometimes happen if you have kidney or liver failure. When your liver is healthy and functioning normally, it turns ammonia into a waste product called urea, which is then flushed out of your body in your urine. Hyperammonaemia frequently results from hepatic dysfunction, while rarer causes include urea cycle defects (ucd), drugs, and infections. Ammonia is a potent neurotoxin, and. But with certain conditions, that flow. Normally, ammonia is processed in your liver, where it’s transformed into another waste product called urea. When the liver is damaged, the detoxification process may be disturbed and. But ammonia will build up in your body if you can't get rid of urea. Background acute liver failure (alf) is an emergent condition that requires intensive care and manifests in particular by significant elevation in serum ammonia level. The urea is then carried to your kidneys, where it’s eliminated in your urine (pee). Elevated ammonia levels can lead to neurological disturbances,. Ammonia, also known as nh3, is a waste product that bacteria in your intestines primarily make when digesting protein.How to Lower Your Ammonia From Liver Cirrhosis Ammonia Toxicity In
PPT Liver Function Tests (LFTs) PowerPoint Presentation ID2622690
Mechanistic insight, diagnosis, and treatment of ammonia‐induced
GRAPHIC
The lipopolysaccharideTLR4 axis regulates hepatic glutaminase 1
The Story of Ammonia in Liver Disease An Unraveling Continuum
The Story of Ammonia in Liver Disease An Unraveling Continuum
The Story of Ammonia in Liver Disease An Unraveling Continuum
The Story of Ammonia in Liver Disease An Unraveling Continuum
Novel AmmoniaLowering Agents for Hepatic Encephalopathy Clinics in
Have A High Suspicion For He In Patients With Known Liver Disease Or Acute Liver Failure, Who Present With Confusion, And Check An Ammonia Level.
The Degree Of Elevation May.
Serum Ammonia May Have Prognostic Value In Liver Failure.
Drinking Alcohol If You Have A Large Belly Or Diabetes More Than Doubles The Risk Of Serious Liver Damage, While Having High Blood Pressure And Drinking Nearly Doubles The Risk, A.
Related Post: