Basic Building Blocks Of Carbohydrates
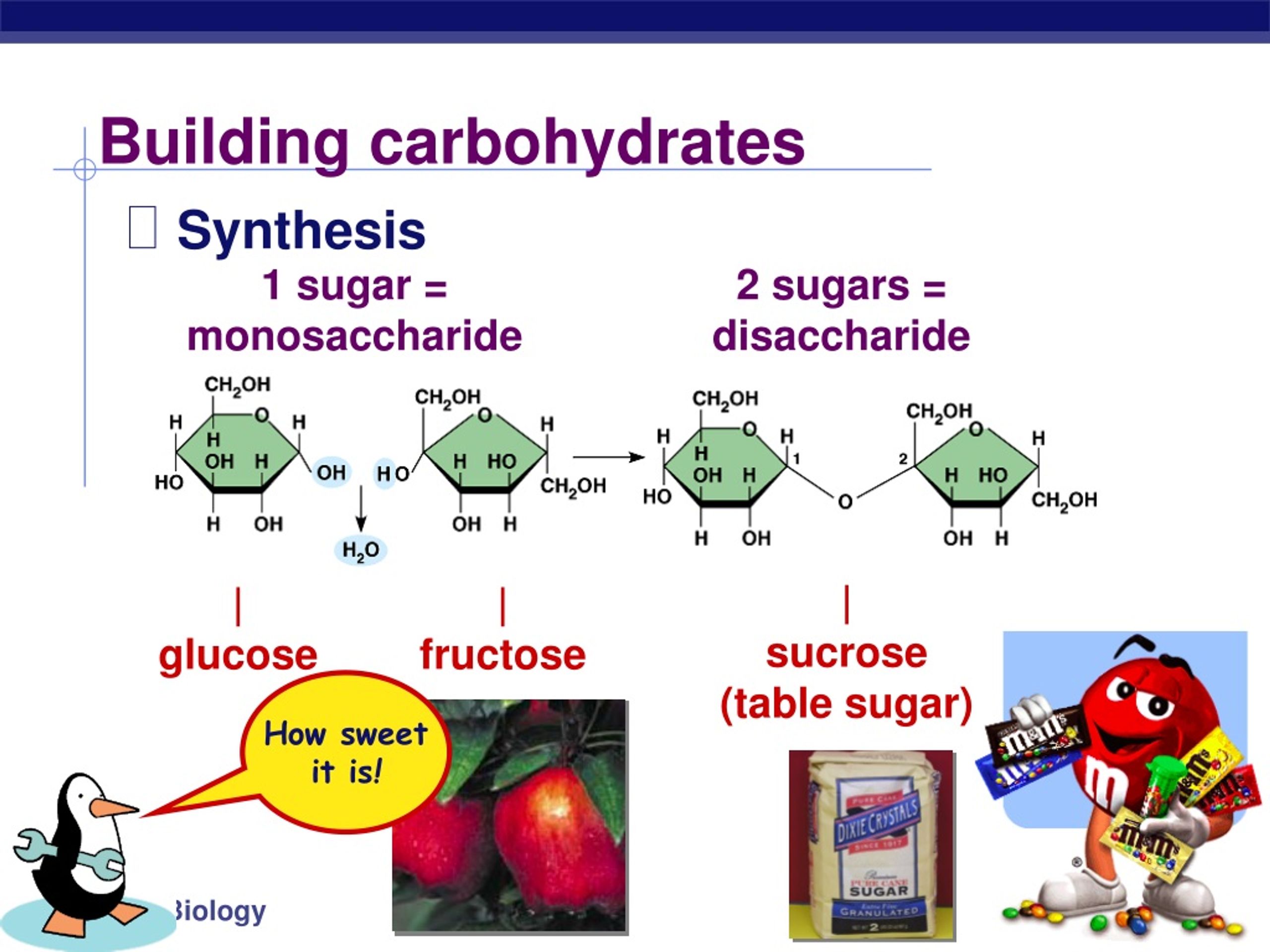
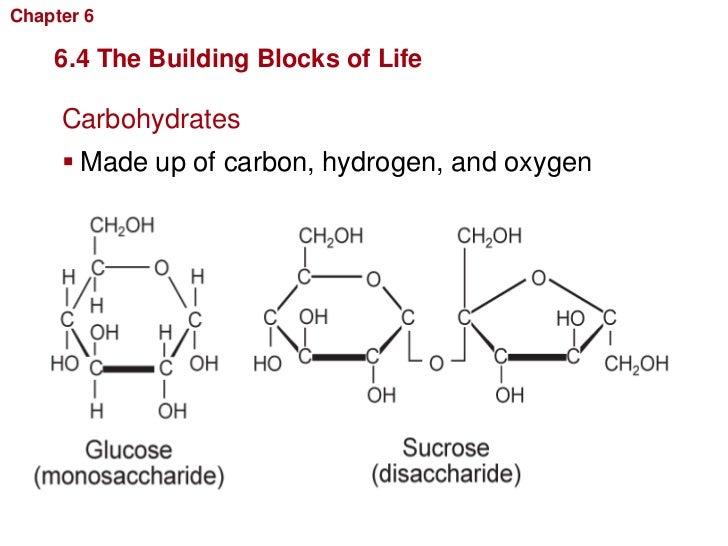
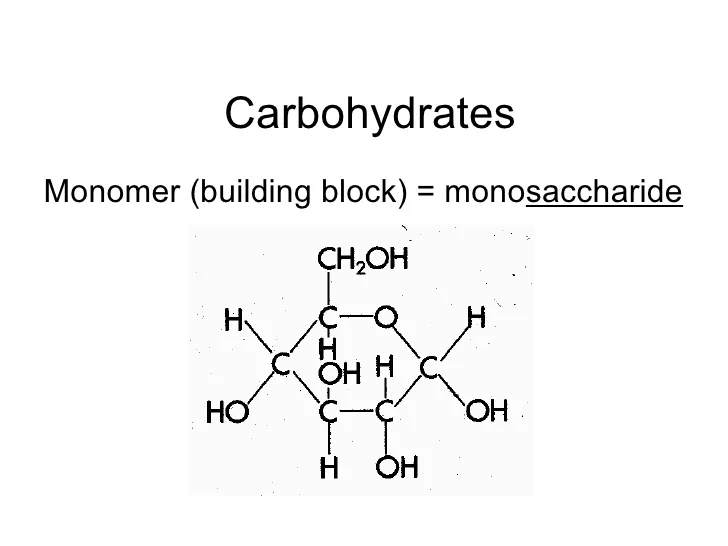
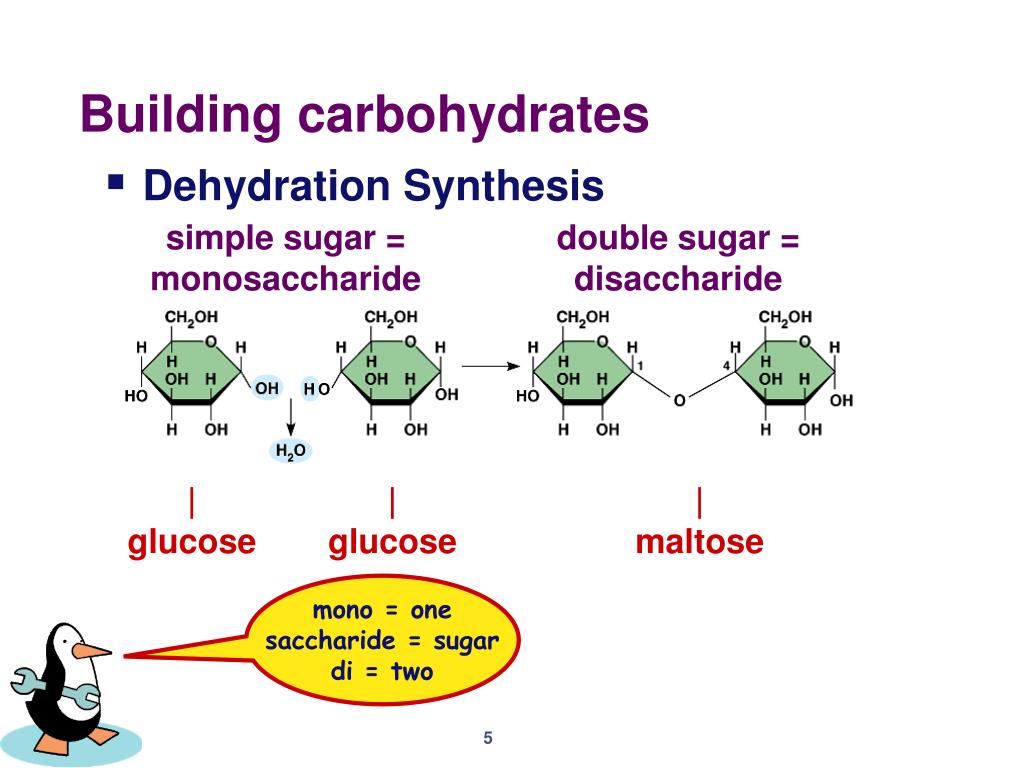
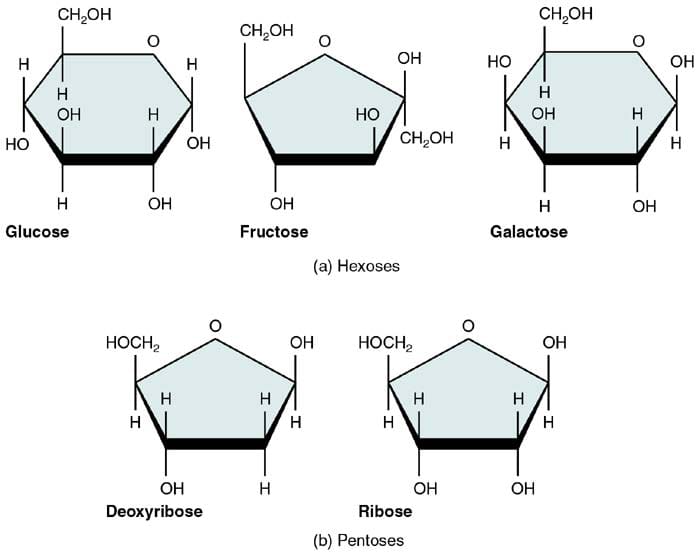
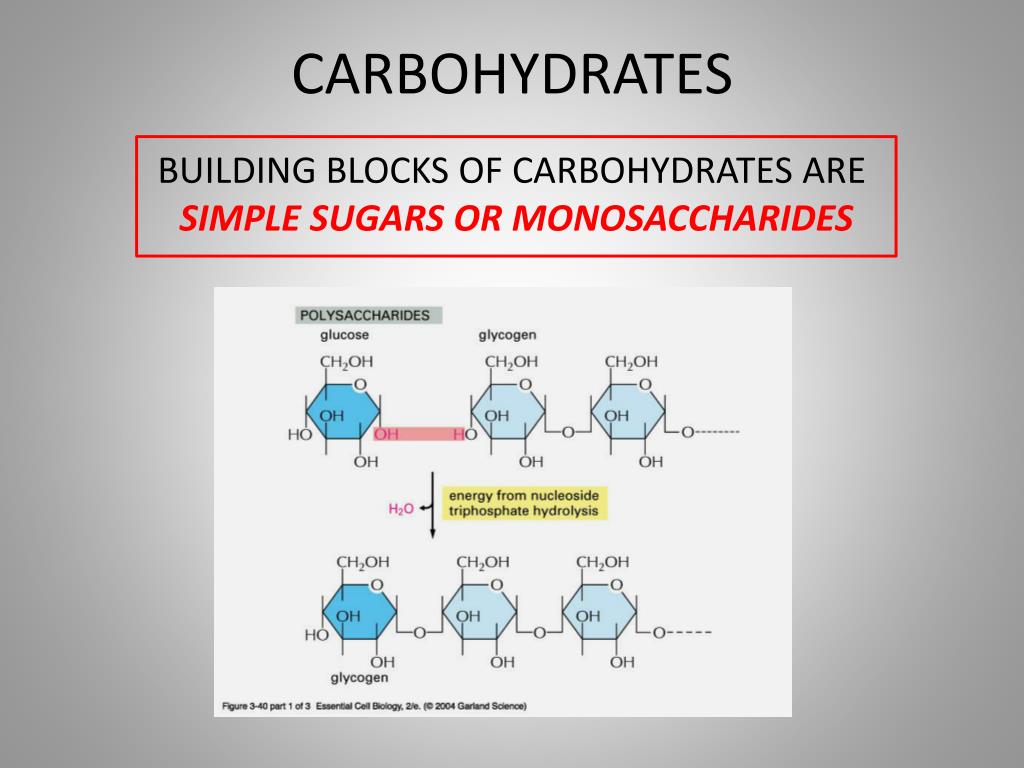
Basic Building Blocks Of Carbohydrates - Monosaccharides, often referred to as simple sugars, are the most basic form of carbohydrates. These building blocks come together to create chains, which in turn create different types of carbohydrates. Monomers bind with another monomer to. Centers for disease control and prevention. Of course, they play an important role in energy storage and transport. Glucose, fructose and galactose are examples of monosaccharides. Based on sugar units, carbohydrates are classified into three types: They contain atoms that combine together to form molecules. At the most basic level, all organisms are made of a combination of elements. Sugars, polysaccharides and fibers are the main answers. Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. When you break two molecules apart you have to add? The general empirical structure for carbohydrates is (ch2o)n. They contain atoms that combine together to form molecules. The predominant carbohydrates encountered in the body are structurally related to the aldotriose glyceraldehyde and to the ketotriose dihydroxyacetone. Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen learn. Do you know carbohydrates building blocks? Like most biochemical compounds, carbohydrates are built of small repeating units, or monomers, which form bonds with each other to make larger molecules, called polymers. Carbohydrates are important energy source required for various metabolic activities and may bind to proteins and lipids that play important roles in cell interactions. The basic biochemistry of living organisms can, therefore, be understood regarding the morphology and physiology of the four biological macromolecules: Do you know carbohydrates building blocks? Monosaccharides, often referred to as simple sugars, are the most basic form of carbohydrates. Based on sugar units, carbohydrates are classified into three types: What are the building blocks of carbohydrates? Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like monosaccaride, disaccharide, polysaccharide and more. Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen learn. Monomers bind with another monomer to. These molecules are the building blocks for more complex carbohydrates and. Monosaccharides, often referred to as simple sugars, are the most basic form of carbohydrates. A monomer is the simplest molecule that forms the basic unit of polymers and thus is considered as the building blocks of polymers. The building blocks of carbohydrates are monosaccharides. These molecules are the building blocks for more complex carbohydrates and. They are also crucial parts of important. Carbohydrates consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The general empirical structure for carbohydrates is (ch2o)n. A monomer is the simplest molecule that forms the basic unit of polymers and thus is considered as the building blocks of polymers. Houses the cell's genetic material (dna). The general empirical structure for carbohydrates is (ch2o)n. Carbohydrates are important energy source required for various metabolic activities and may bind to proteins and lipids that play important roles in cell. Like most biochemical compounds, carbohydrates are built of small repeating units, or monomers, which form bonds with each other to make larger molecules, called polymers. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like monosaccaride, disaccharide, polysaccharide and more. Carbohydrates consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. These building blocks come together to create chains, which in turn create different types. Glucose, fructose and galactose are examples of monosaccharides. They are organic compounds organized in the form of. Carbohydrates are one of the major classes of biological molecules. They contain atoms that combine together to form molecules. The building blocks of carbs are sugars, starches and fiber, inning accordance with the u.s. Carbohydrates consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. But how do they affect the body? Carbohydrates are one of the building blocks of the body, that interact with molecules of other organic compounds like fats, proteins and nucleic acids, for proper functioning of a healthy. A monomer is the simplest molecule that forms the basic unit of polymers and thus is. Do you know carbohydrates building blocks? Centers for disease control and prevention. Carbohydrates are the body's primary. Carb is short for carbohydrate, one of the main nutrients (along with fats and proteins) that you must consume to fuel your body. The building blocks of carbohydrates are monosaccharides. These molecules are the building blocks for more complex carbohydrates and. The building blocks of carbohydrates are monosaccharides. Houses the cell's genetic material (dna). Carbohydrates are one of the major classes of biological molecules. Carbohydrates consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Like most biochemical compounds, carbohydrates are built of small repeating units, or monomers, which form bonds with each other to make larger molecules, called polymers. Composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins, carbohydrates, and cholesterol. Of course, they play an important role in energy storage and transport. Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen learn. These have the molecular formula of c. Of course, they play an important role in energy storage and transport. Monosaccharides, often referred to as simple sugars, are the most basic form of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are the body's primary. Houses the cell's genetic material (dna). Glucose, fructose and galactose are examples of monosaccharides. When you break two molecules apart you have to add? The basic biochemistry of living organisms can, therefore, be understood regarding the morphology and physiology of the four biological macromolecules: Sugars, polysaccharides and fibers are the main answers. What are the building blocks of carbohydrates? The general empirical structure for carbohydrates is (ch2o)n. The predominant carbohydrates encountered in the body are structurally related to the aldotriose glyceraldehyde and to the ketotriose dihydroxyacetone. Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Thus, monosaccharides are the building blocks of carbohydrates. The building blocks of carbohydrates are monosaccharides. Carbohydrates are one of the building blocks of the body, that interact with molecules of other organic compounds like fats, proteins and nucleic acids, for proper functioning of a healthy. In this article, we will learn about carbohydrate structure and properties of the three main carbohydrate classes:PPT Carbohydrates PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2427741
2 Biological Building Blocks Carbohydrates Basicmedical Key
PPT Carbohydrates PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID463401
Biochemistry notes students
Organic molecules
2 Biological Building Blocks Carbohydrates Basicmedical Key
basic building blocks of carbohydrates
PPT Carbohydrates PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6987875
Building Blocks of Carbohydrates Types, Properties & Functions
PPT BASIC CHEMISTRY AND BIOCHEMISTRY PowerPoint Presentation, free
A Monomer Is The Simplest Molecule That Forms The Basic Unit Of Polymers And Thus Is Considered As The Building Blocks Of Polymers.
Composed Of A Phospholipid Bilayer With Embedded Proteins, Carbohydrates, And Cholesterol.
Centers For Disease Control And Prevention.
Carbohydrates Are Important Energy Source Required For Various Metabolic Activities And May Bind To Proteins And Lipids That Play Important Roles In Cell Interactions.
Related Post: