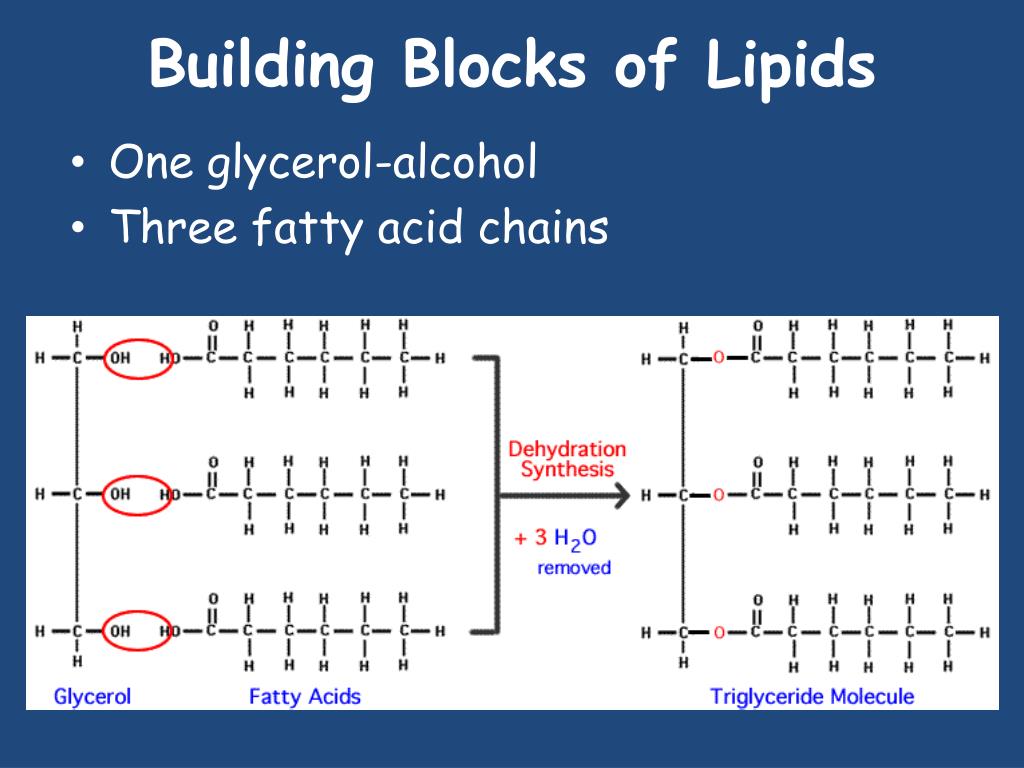
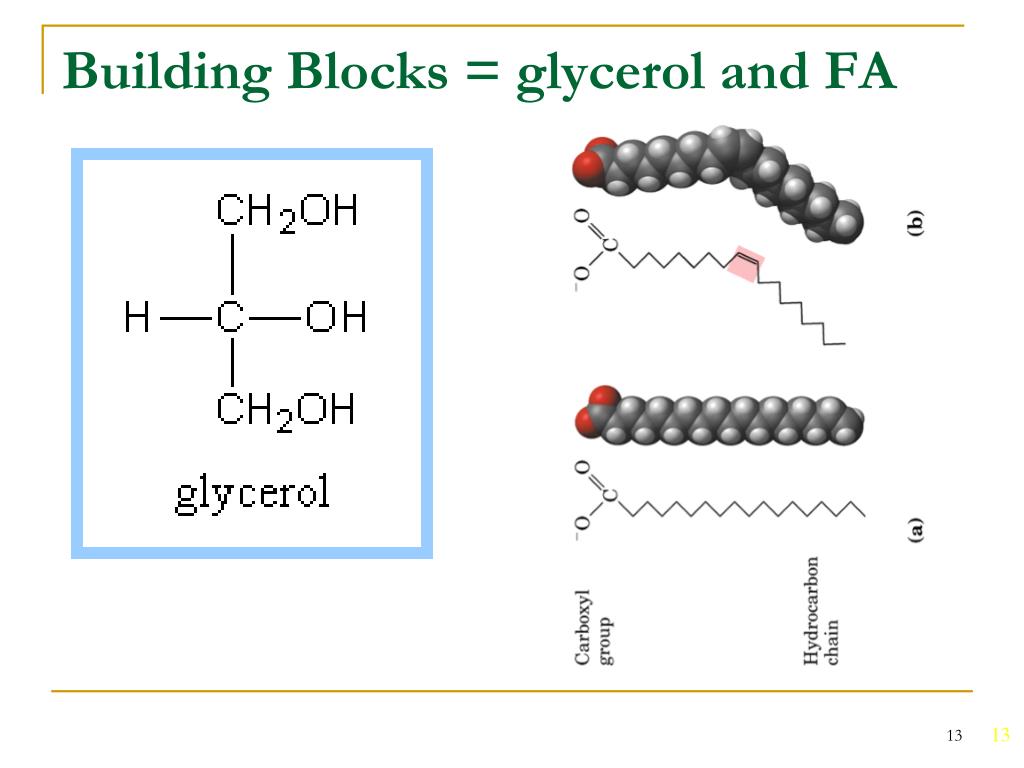
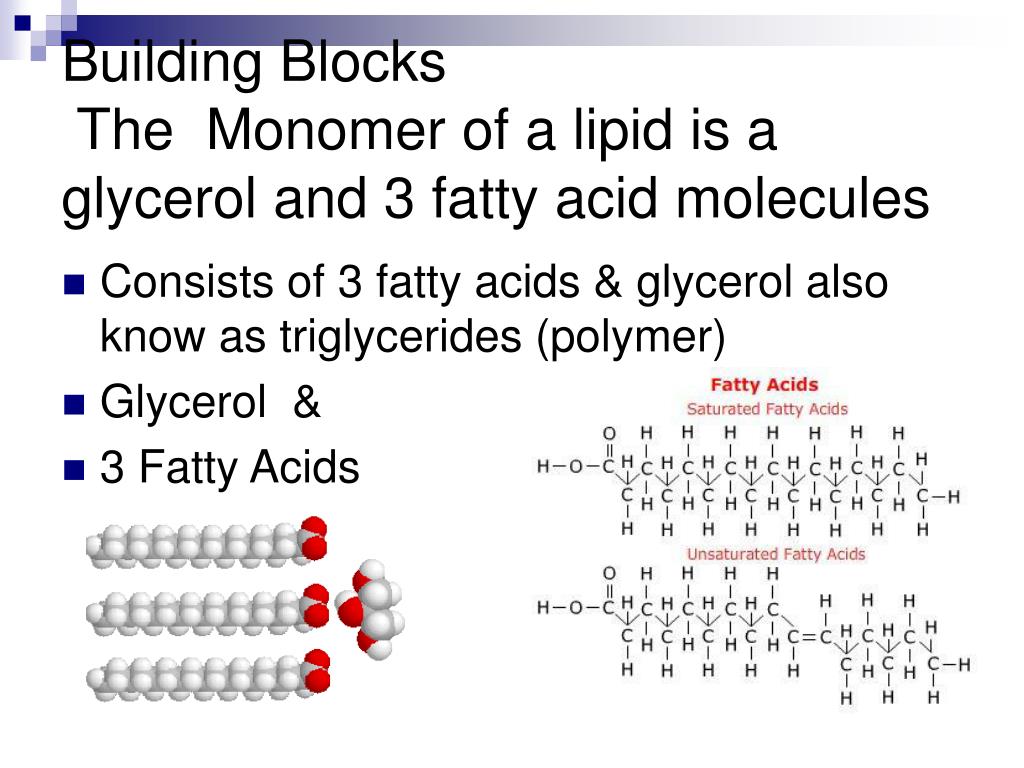
Building Blocks Are Glycerol And Fatty Acids
Building Blocks Are Glycerol And Fatty Acids - This pairing is essential because it’s the building block for more complex. Mixing these two monomers, fatty acids, and glycerol, results in a dynamic duo, or what we technically call a lipid. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. Fatty acids are building blocks in several other types of lipids. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. Fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks of triacylglycerols. Fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks of triacylglycerols. Glycerol and fatty acids are two building blocks of fat molecules. Cells link together via dehydration synthesis and are broken apart by hydrolysis. Glycerol acts as the backbone, while fatty acids attach to it to form triglycerides, the most common type of fat. To form a triglyceride, a glycerol molecule is. Glycerol acts as the backbone, while fatty acids attach to it to form triglycerides, the most common type of fat. Glycerol and fatty acids are the building blocks of fat. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. To form a triacylglycerol, a glycerol molecule is joined by three fatty acid chains (figure 5.1.2 5.1. Cells link together via dehydration synthesis and are broken apart by hydrolysis. Fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks of triacylglycerols. Mixing these two monomers, fatty acids, and glycerol, results in a dynamic duo, or what we technically call a lipid. This pairing is essential because it’s the building block for more complex. Glycerol and fatty acids are two building blocks of fat molecules. In this article, we explain why you need fatty acids in your diet and where you can find them. To form a triglyceride, a glycerol molecule is. Glycerol is a thick, smooth, syrupy compound that is often used in the food industry. Mixing these two monomers, fatty acids, and glycerol, results in a dynamic duo, or what we technically call. Glycerol is not a lipid but it forms the. Glycerol and fatty acids are two building blocks of fat molecules. Glycerol and fatty acids are the building blocks of fat. Fatty acids are the building blocks of the fat in our bodies and in the food we eat. A fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. Explain how the building blocks of glycerol and fatty acids are combined and how they are decomposed. To form a triacylglycerol, a glycerol molecule is joined by three fatty acid chains (figure 5.1.2 5.1. Mixing these two monomers, fatty acids, and glycerol, results in a dynamic duo, or what we technically call a lipid. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol). Fatty acids have a long chain of hydrocarbons with a carboxyl group attached and. To form a triacylglycerol, a glycerol molecule is joined by three fatty acid chains (figure 5.1.2 5.1. Glycerol is a thick, smooth, syrupy compound that is often used in the food industry. They have a long chain of hydrocarbons to which a carboxyl (carboxylic acid) group. Fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks of triacylglycerols. Fatty acids are the building blocks of the fat in our bodies and in the food we eat. Glycerol and fatty acids are two building blocks of fat molecules. Lipids are also the building blocks of many hormones and are an important constituent of all cellular membranes. Fatty acids and. Fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks of triglycerides. Fatty acids have a long chain of hydrocarbons with a carboxyl group attached and. Fatty acids are the building blocks of the fat in our bodies and in the food we eat. Glycerol is a thick, smooth, syrupy compound that is often used in the food industry. Glycerol is an. A fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. To form a triglyceride, a glycerol molecule is. Glycerol and fatty acids are the building blocks of fat. Fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks of triacylglycerols. Fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks of triacylglycerols. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. To form a triglyceride, a glycerol molecule is. Glycerol is a thick, smooth, syrupy compound that is often used in the food industry. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and. Glycerol is not a lipid but it forms the. Fatty acids are building blocks in several other types of lipids. Explain how the building blocks of glycerol and fatty acids are combined and how they are decomposed. Fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks of triacylglycerols. To form a triacylglycerol, a glycerol molecule is joined by three fatty acid chains (figure 5.1.2 5.1. Triacylglycerols are composed of fatty. Explain how the building blocks of glycerol and fatty acids are combined and how they are decomposed. Fatty acids have a long chain of hydrocarbons with a carboxyl group attached and. Triacylglycerols are composed of fatty acids and glycerol. This pairing is essential because it’s the building block for more complex. Glycerol and fatty acids are two building blocks of. This pairing is essential because it’s the building block for more complex. Glycerol and fatty acids are the building blocks of fat. Cells link together via dehydration synthesis and are broken apart by hydrolysis. Mixing these two monomers, fatty acids, and glycerol, results in a dynamic duo, or what we technically call a lipid. Glycerol acts as the backbone, while fatty acids attach to it to form triglycerides, the most common type of fat. In this article, we explain why you need fatty acids in your diet and where you can find them. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. To form a triglyceride, a glycerol molecule is. Lipids are also the building blocks of many hormones and are an important constituent of all cellular membranes. Glycerol is a thick, smooth, syrupy compound that is often used in the food industry. A fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. Fatty acids have a long chain of hydrocarbons with a carboxyl group attached and. Fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks of triacylglycerols. A fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (oh) groups. Triacylglycerols are composed of fatty acids and glycerol.Organic Molecules Chapter ppt download
Chapter 2 Test Review. ppt download
PPT Lipids & Nucleic Acids PowerPoint Presentation, free download
PPT Water and Biochemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download
PPT Organic Molecules PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5504895
PPT Lipids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1151469
Monday, September 12th Bell Work Identify the “building blocks” in the
Organic Molecule Building Block carbohydrates simple sugars lipids
Lipids Monomer/Building blocks Glycerol and Fatty acid chains. Each
Concept 5.3 Lipids include fats and steroids.. Lipids Group of organic
Glycerol Is Not A Lipid But It Forms The.
Fatty Acids And Glycerol Are The Building Blocks Of Triglycerides.
Lipids Include Fats, Oils, Waxes, Phospholipids, And.
Fatty Acids Are The Building Blocks Of The Fat In Our Bodies And In The Food We Eat.
Related Post:
.jpg)