Building Blocks For Macromolecules
Building Blocks For Macromolecules - These macromolecules play diverse roles in biological systems, ranging from catalyzing chemical reactions and transporting oxygen to providing immunity against. The findings contradict the classic view that microtubules are typically similar building blocks in every cell, while regulatory proteins confer unique structure and function,. A building block of a macromolecule, this is small chemical unit that makes up a polymer. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and more. Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids are the essential building blocks of the human body. These four macromolecules play crucial roles in the structure, function,. Have students create different macromolecules by bonding the structures together. Up to 24% cash back macromolecules •large organic molecules. Because these biological macromolecules all involve carbon. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are the 3 building blocks of all living things that we will focus on this unit. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen building blocks: Dehydration synthesis creates the building blocks of life; Amylose, glycogen and cellulose all consist of glucose; Up to 24% cash back macromolecules •large organic molecules. Have students create different macromolecules by bonding the structures together. Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids are the essential building blocks of the human body. Macromolecules are critical for building cells, storing energy, transmitting genetic information, and performing biochemical. •made up of smaller “building blocks” called monomers. Help your students visualize their macromolecules with these simple chemical structures. Supramolecular ordered networks are formed through directional interactions of uniform macromonomer building blocks. In the intricate tapestry of life, macromolecules stand as the essential building blocks, the fundamental units that shape our biological existence. Living things are made of four types of molecules, known as macromolecules. Dehydration synthesis creates the building blocks of life; These macromolecules are proteins, nucleic acids (dna and rna), lipids (fats) and. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are the 3. Amylose, glycogen and cellulose all consist of glucose; Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen building blocks: In the intricate tapestry of life, macromolecules stand as the essential building blocks, the fundamental units that shape our biological existence. Living things are made of four types of molecules, known as macromolecules. Have students create different macromolecules by bonding the structures together. Have students create different macromolecules by bonding the structures together. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and more. Building blocks provides shared office and coworking. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are the 3 building blocks of all living things that we will focus on this unit. Amylose, glycogen and cellulose all consist of glucose; The findings contradict the classic view that microtubules are typically similar building blocks in every cell, while regulatory proteins confer unique structure and function,. Macromolecules are critical for building cells, storing energy, transmitting genetic information, and performing biochemical. Up to 24% cash back macromolecules •large organic molecules. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are the 3 building blocks of all living things. These are called macromolecules because they are large. The monomer of carbohydrates is a monosaccharide, the monomer of lipids is a fatty acid, the. Now it has been shown that, rather than. The findings contradict the classic view that microtubules are typically similar building blocks in every cell, while regulatory proteins confer unique structure and function,. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen building. •made up of smaller “building blocks” called monomers. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen building blocks: Because these biological macromolecules all involve carbon. Have students create different macromolecules by bonding the structures together. Amylose, glycogen and cellulose all consist of glucose; These macromolecules are proteins, nucleic acids (dna and rna), lipids (fats) and. Living things are made of four types of molecules, known as macromolecules. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are the 3 building blocks of all living things that we will focus on this unit. •made up of smaller “building blocks” called monomers. These four macromolecules play crucial roles in the. These four macromolecules play crucial roles in the structure, function,. Have students create different macromolecules by bonding the structures together. These macromolecules play diverse roles in biological systems, ranging from catalyzing chemical reactions and transporting oxygen to providing immunity against. Because these biological macromolecules all involve carbon. Why are macromolecules essential for life? Living things are made of four types of molecules, known as macromolecules. The monomer of carbohydrates is a monosaccharide, the monomer of lipids is a fatty acid, the. These are called macromolecules because they are large. Building blocks is the engine to help you grow, the fuel to inspire you, and the vehicle to push your business beyond the boundaries.. The monomer of carbohydrates is a monosaccharide, the monomer of lipids is a fatty acid, the. •made up of smaller “building blocks” called monomers. Living things are made of four types of molecules, known as macromolecules. These macromolecules are proteins, nucleic acids (dna and rna), lipids (fats) and. Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids are the essential building blocks of. Have students create different macromolecules by bonding the structures together. A building block of a macromolecule, this is small chemical unit that makes up a polymer. These are called macromolecules because they are large. In the intricate tapestry of life, macromolecules stand as the essential building blocks, the fundamental units that shape our biological existence. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and more. These macromolecules are proteins, nucleic acids (dna and rna), lipids (fats) and. Building blocks is the engine to help you grow, the fuel to inspire you, and the vehicle to push your business beyond the boundaries. Dehydration synthesis creates the building blocks of life; Building blocks provides shared office and coworking. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen building blocks: Living things are made of four types of molecules, known as macromolecules. Supramolecular ordered networks are formed through directional interactions of uniform macromonomer building blocks. These four macromolecules play crucial roles in the structure, function,. These macromolecules are the basic chemical building blocks from which all organisms are composed. Amylose, glycogen and cellulose all consist of glucose; •made up of smaller “building blocks” called monomers.Unit 2 Biochemistry 2.4 Macromolecules. ppt download
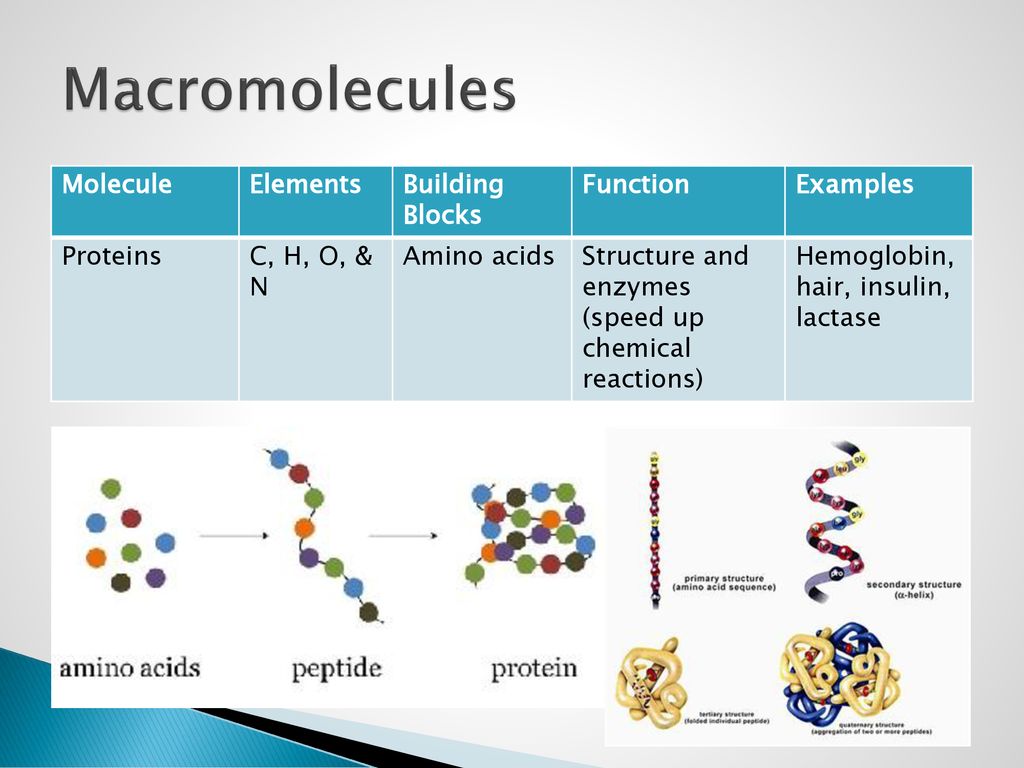
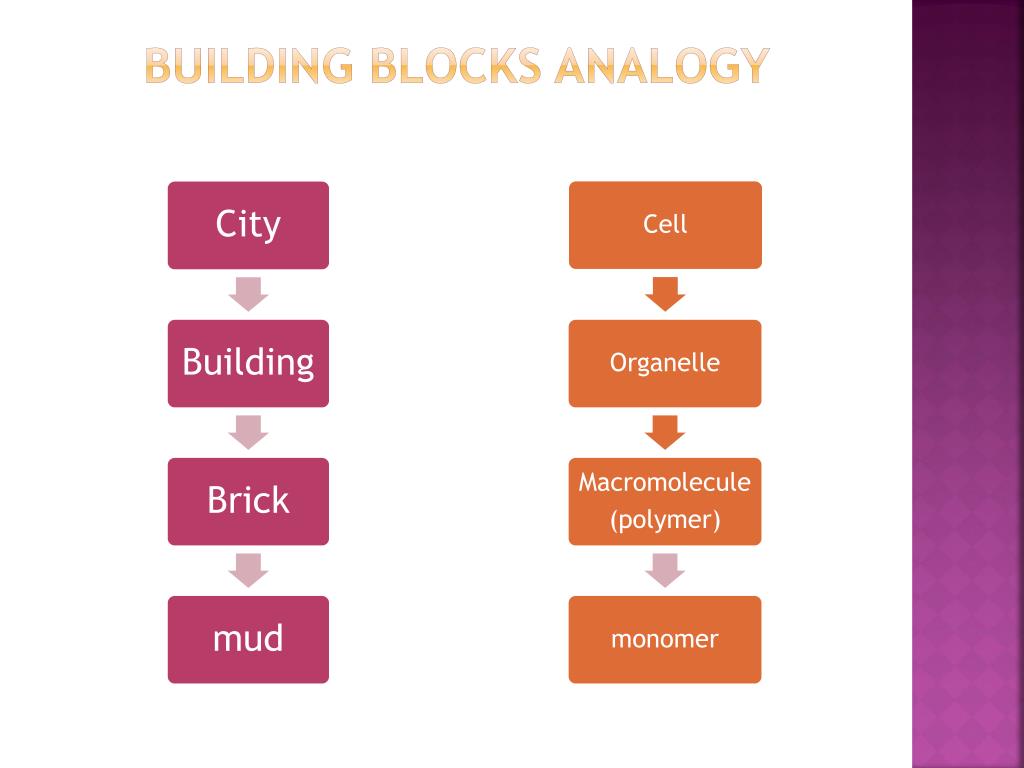
PPT Macromolecules Building blocks of life PowerPoint Presentation
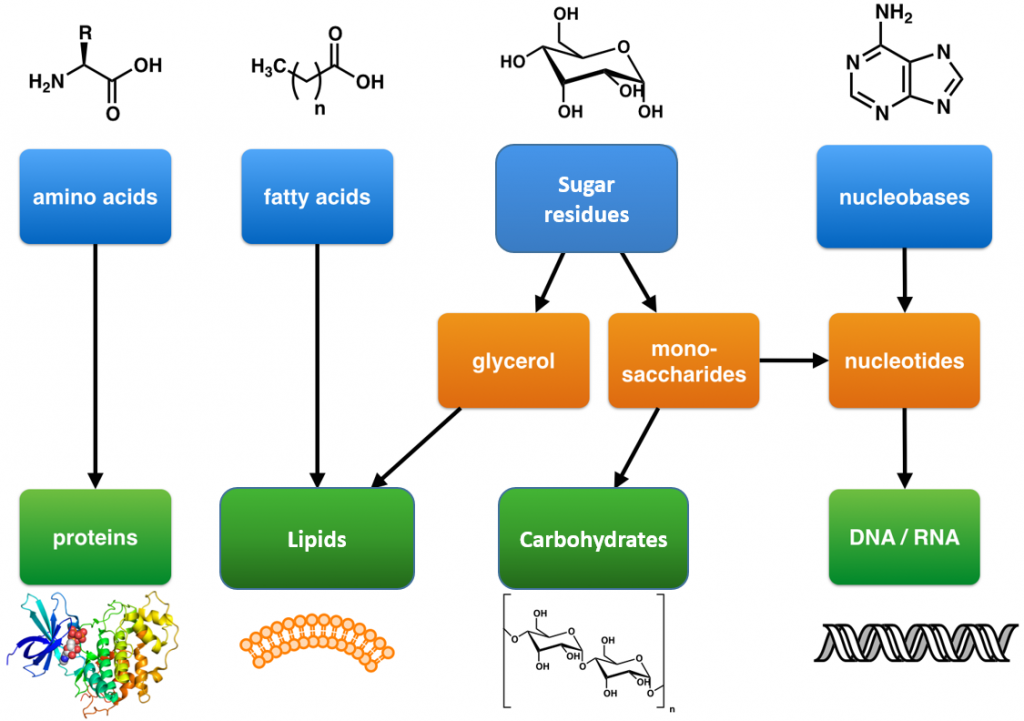
Some examples of "building blocks" (BBs) in biological macromolecules
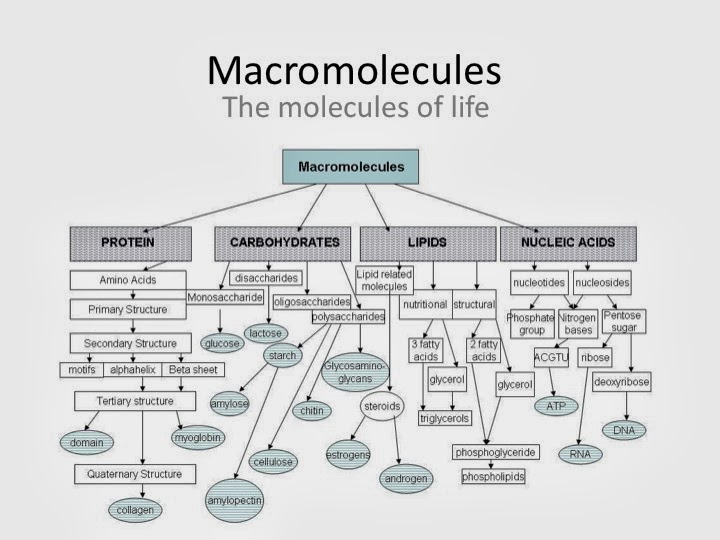
CH103 Chapter 8 The Major Macromolecules Chemistry
Mr. Maxey's Biology Blog The Building Blocks of Life Macromolecules
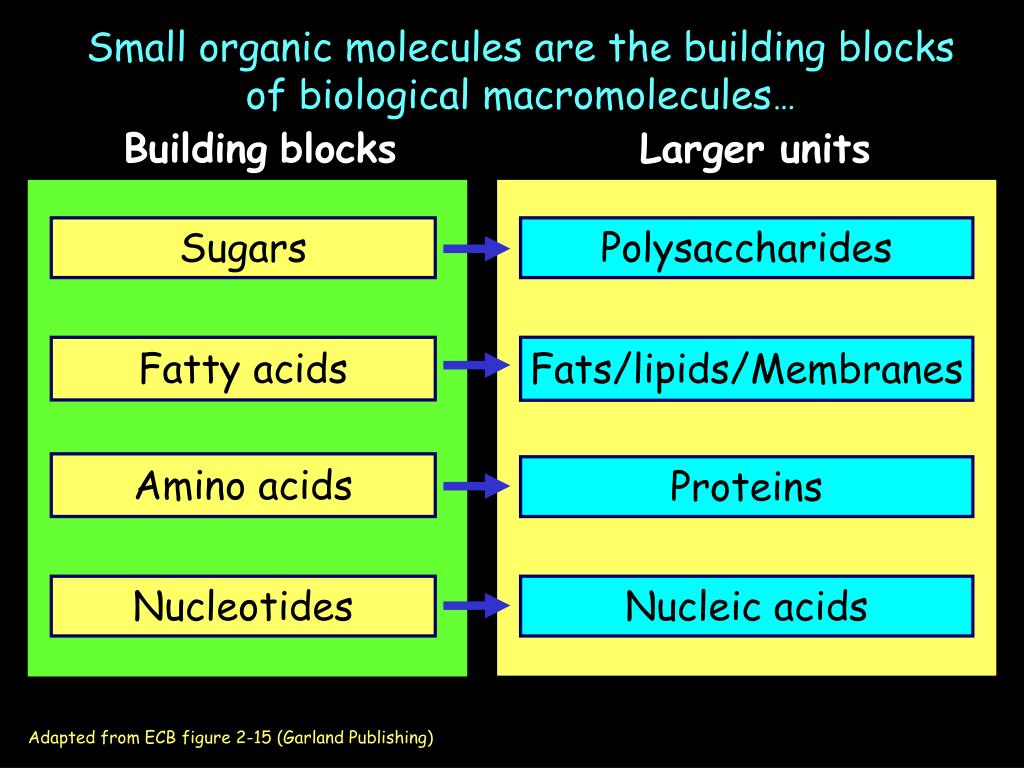
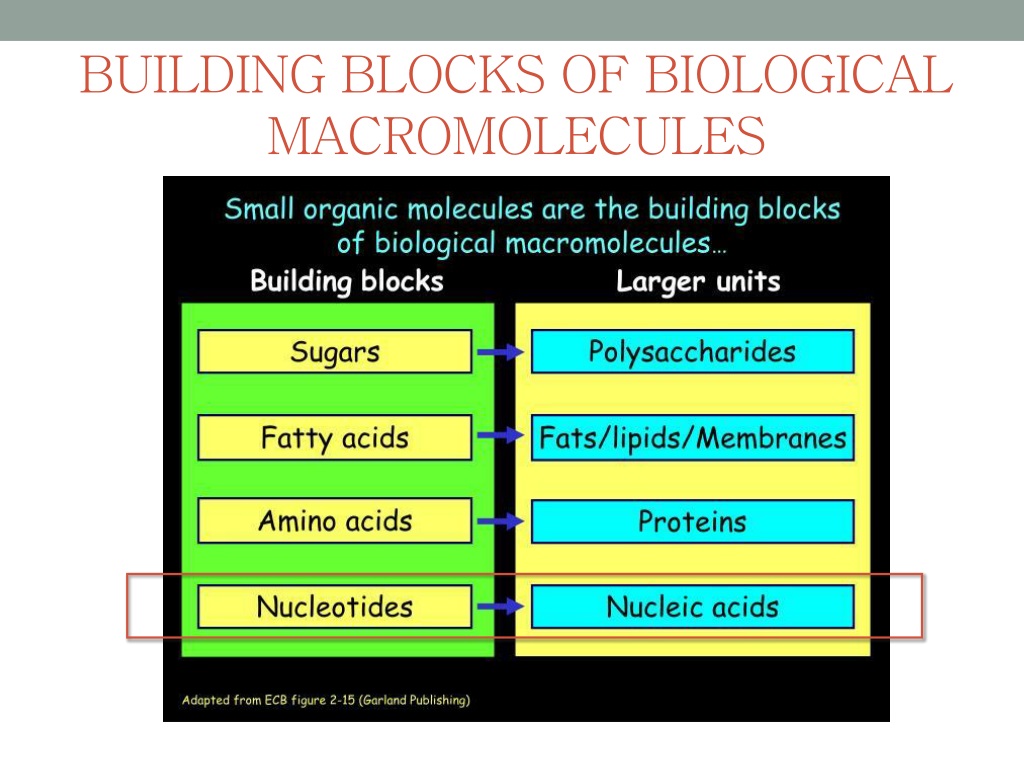
PPT Small organic molecules are the building blocks of biological
PPT MACROMOLECULES PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6388389
PPT BIOCHEMISTRY COURSE Pharmacy biomedical preview program, Summer
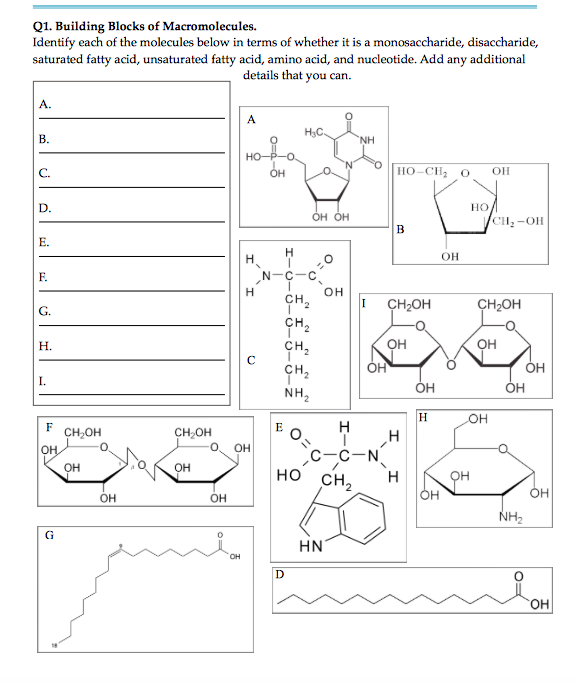
Solved Q1. Building Blocks of Macromolecules. Identify each
Building Blocks of Life 28 Macromolecules Activities Teaching Expertise
Why Are Macromolecules Essential For Life?
Now It Has Been Shown That, Rather Than.
Macromolecules Are Critical For Building Cells, Storing Energy, Transmitting Genetic Information, And Performing Biochemical.
The Monomer Of Carbohydrates Is A Monosaccharide, The Monomer Of Lipids Is A Fatty Acid, The.
Related Post: