Building Blocks Monomers Are Amino Acids
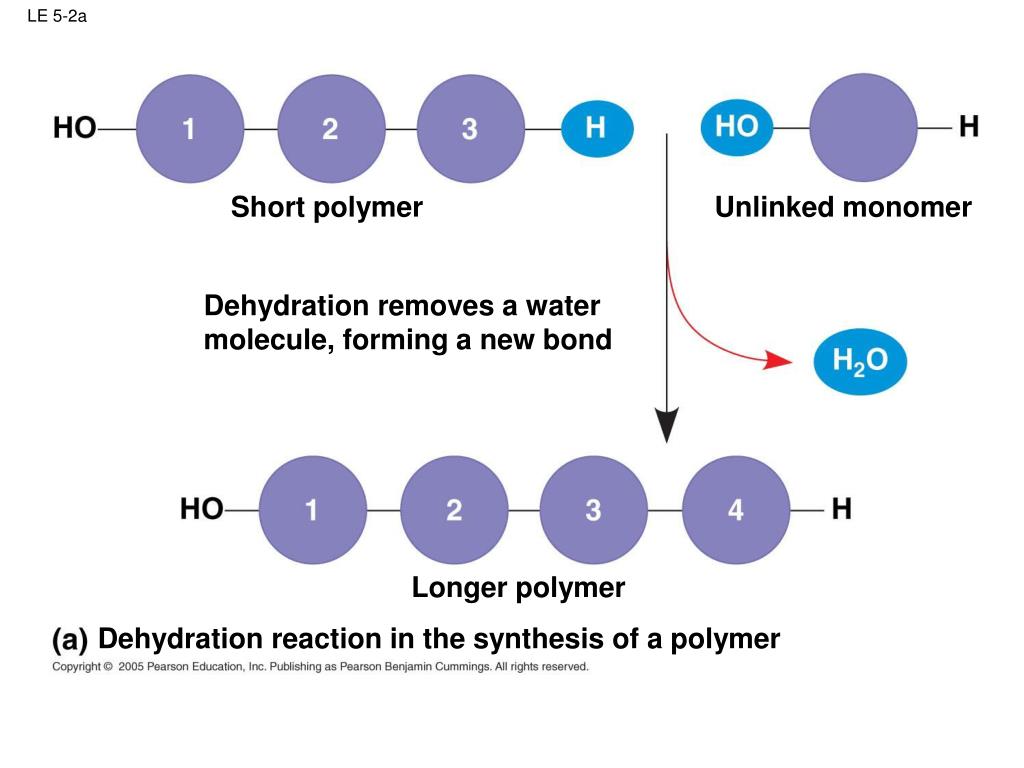
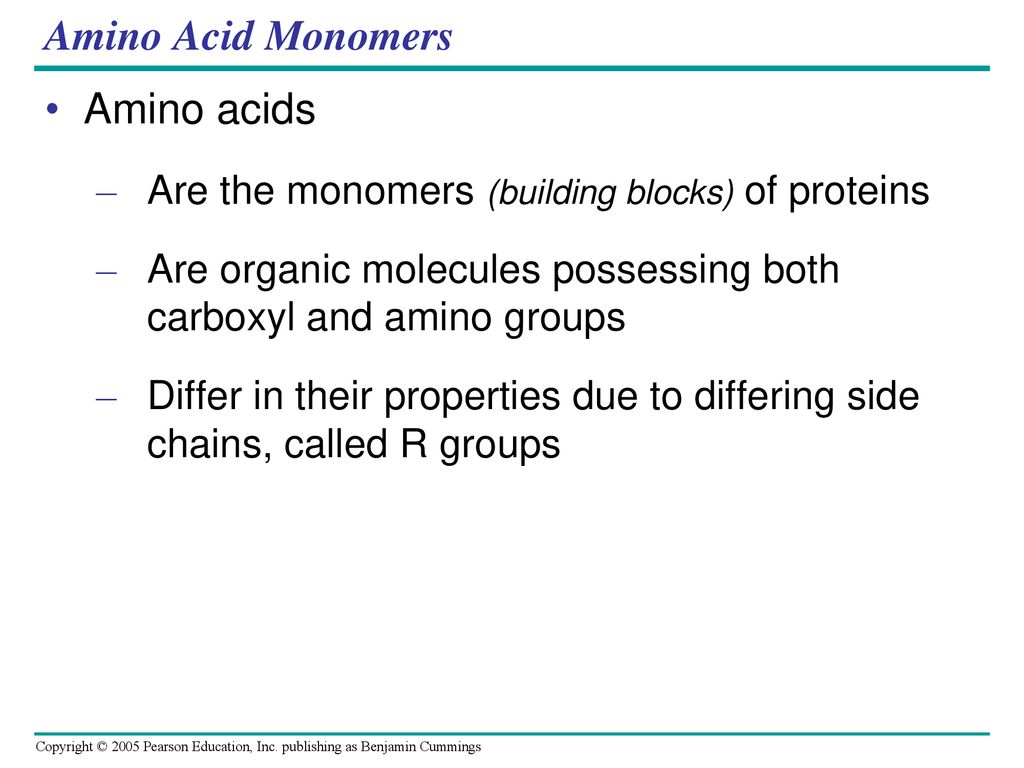
Building Blocks Monomers Are Amino Acids - These polymers are composed of small building blocks that are linked together in. Amino acids are the fundamental building blocks of proteins, characterized by their unique structure. There are 20 building blocks, or monomers, that are used to build proteins. The building blocks of proteins are amino acids, which are small organic molecules that consist of an alpha (central) carbon atom linked to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom,. Amino acids are small molecules that contain a central carbon atom, called the alpha carbon, which is attached to. Proteins, in other words, which consist of one or more polypeptide chains folded up into a specific 3d conformation—proteins are composed of amino acids. What do proteins do for the body?. The building blocks of proteins (monomers) are amino acids. Proteins are polymers composed of monomers called amino acids. The primary structure of a protein, a peptide chain, is made of amino. The building blocks of proteins are amino acids, which are small organic molecules that consist of an alpha (central) carbon atom linked to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom,. Drag the labels to the appropriate blanks on the diagram. A residue is a monomer that results when two or more amino acids combine and remove water molecules. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Each of these polypeptide chains is made up of amino acids, which are joined together in a detailed, deliberate and specific order. That makes amino acids absolutely. They have been found in: Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Each amino acid has a central carbon that is linked to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and an. Proteins, in other words, which consist of one or more polypeptide chains folded up into a specific 3d conformation—proteins are composed of amino acids. The building blocks of proteins (monomers) are amino acids. Each amino acid has a central carbon that is linked to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and an. Amino acids can best be described as the construction blocks from which protein is made. These organic compounds, characterized by. Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, which are indispensable to nearly all biological processes. There are 20 common amino acids that combine in various sequences to. That makes amino acids absolutely. Proteins, in other words, which consist of one or more polypeptide chains folded up into a specific 3d conformation—proteins are composed of amino acids. Amino acids are. The building blocks of proteins (monomers) are amino acids. That makes amino acids absolutely. Proteins, in other words, which consist of one or more polypeptide chains folded up into a specific 3d conformation—proteins are composed of amino acids. Amino acids are small molecules that contain a central carbon atom, called the alpha carbon, which is attached to. The first few. Proteins, in other words, which consist of one or more polypeptide chains folded up into a specific 3d conformation—proteins are composed of amino acids. What do proteins do for the body?. Each of these polypeptide chains is made up of amino acids, which are joined together in a detailed, deliberate and specific order. Amino acids 5 many of the most. There are over 700 types of amino acids that have been discovered in nature. What do proteins do for the body?. The building blocks of proteins are amino acids, which are small organic molecules that consist of an alpha (central) carbon atom linked to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom,. There are 20 common amino acids that. They have been found in: Proteins are polymers composed of monomers called amino acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Amino acids are small molecules that contain a central carbon atom, called the alpha carbon, which is attached to. What do proteins do for the body?. The building blocks of proteins are amino acids, which are small organic molecules that consist of an alpha (central) carbon atom linked to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom,. Amino acids can best be described as the construction blocks from which protein is made. They have been found in: That makes amino acids absolutely. The primary structure. The building blocks of proteins (monomers) are amino acids. These organic compounds, characterized by. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. A residue is a monomer that results when two or more amino acids combine and remove water molecules. The first few amino acids were discovered in the early 1800s. There are 20 common amino acids that combine in various sequences to. These organic compounds, characterized by. Proteins are polymers composed of monomers called amino acids. The building blocks of proteins (monomers) are amino acids. They have been found in: Proteins are polymers composed of monomers called amino acids. The building blocks of proteins (monomers) are amino acids. The building blocks of proteins are amino acids, which are small organic molecules that consist of an alpha (central) carbon atom linked to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom,. They are small organic molecules consisting of an amino group,. These polymers are composed of small building blocks that are linked together in. The primary structure of a protein, a peptide chain, is made of amino. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Amino acids can best be described as the construction blocks from which protein is made. A residue is a monomer that results when two or more amino acids combine and remove water molecules. Drag the labels to the appropriate blanks on the diagram. That makes amino acids absolutely. There are 20 building blocks, or monomers, that are used to build proteins. These organic compounds, characterized by. The first few amino acids were discovered in the early 1800s. Each amino acid has a central carbon that is linked to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and an. What do proteins do for the body?. The building blocks of proteins (monomers) are amino acids. Proteins, in other words, which consist of one or more polypeptide chains folded up into a specific 3d conformation—proteins are composed of amino acids. The building blocks of proteins are amino acids, which are small organic molecules that consist of an alpha (central) carbon atom linked to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom,. Amino acids are small molecules that contain a central carbon atom, called the alpha carbon, which is attached to.Solved Amino acids are building blocks [monomers] of
the study of the molecules that make up living things ppt download
Monomers Definition, Types, Structure, Examples
PPT Polymer Monomer (basic building block *) Protein 20 amino acids
Proteins The multitaskers. ppt download
Organic Molecules Category Building blocks of the cell (monomer) ppt
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules ppt download
Proteins & Enzymes. ppt download
PPT Polymer Monomer (basic building block *) Protein 20 amino acids
PROTEINS. ppt download
Amino Acids Are The Fundamental Building Blocks Of Proteins, Characterized By Their Unique Structure.
Amino Acids Are The Monomers That Make Up Proteins.
Amino Acids Are The Building Blocks Of Proteins, Which Are Indispensable To Nearly All Biological Processes.
Amino Acids 5 Many Of The Most Important Macromolecules In Living Systems Are Polymers.
Related Post:
![Solved Amino acids are building blocks [monomers] of](https://media.cheggcdn.com/study/acd/acd6c50d-3d31-475b-98d2-5c5d892d3e55/image)
+called+amino+acids.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)