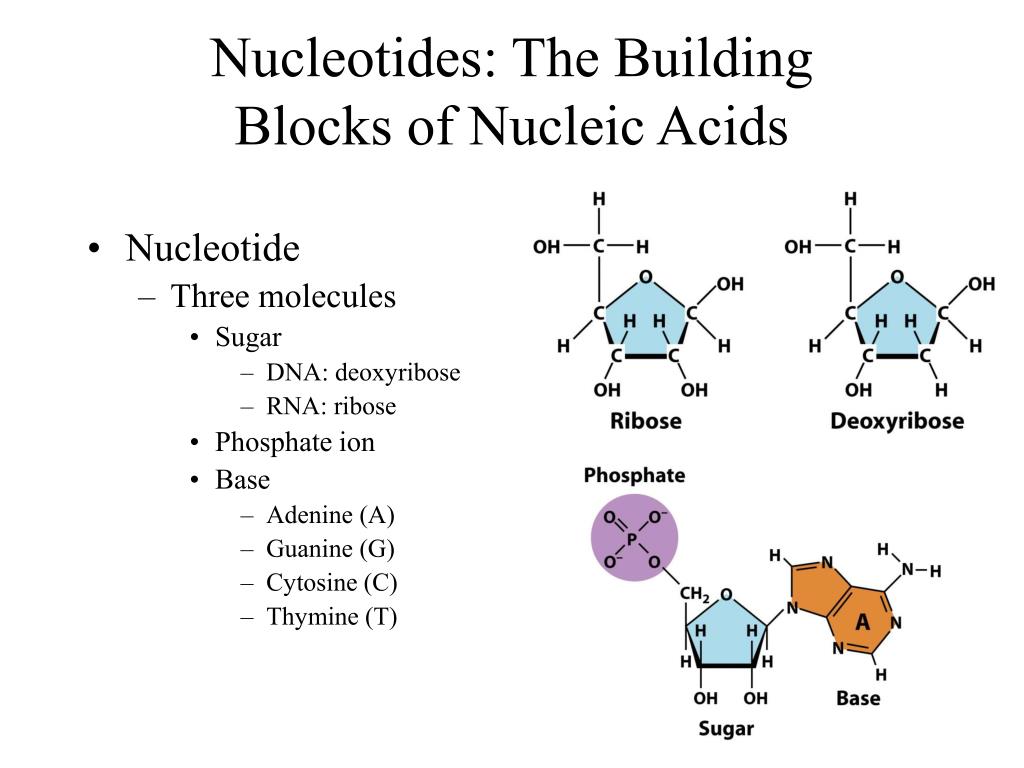
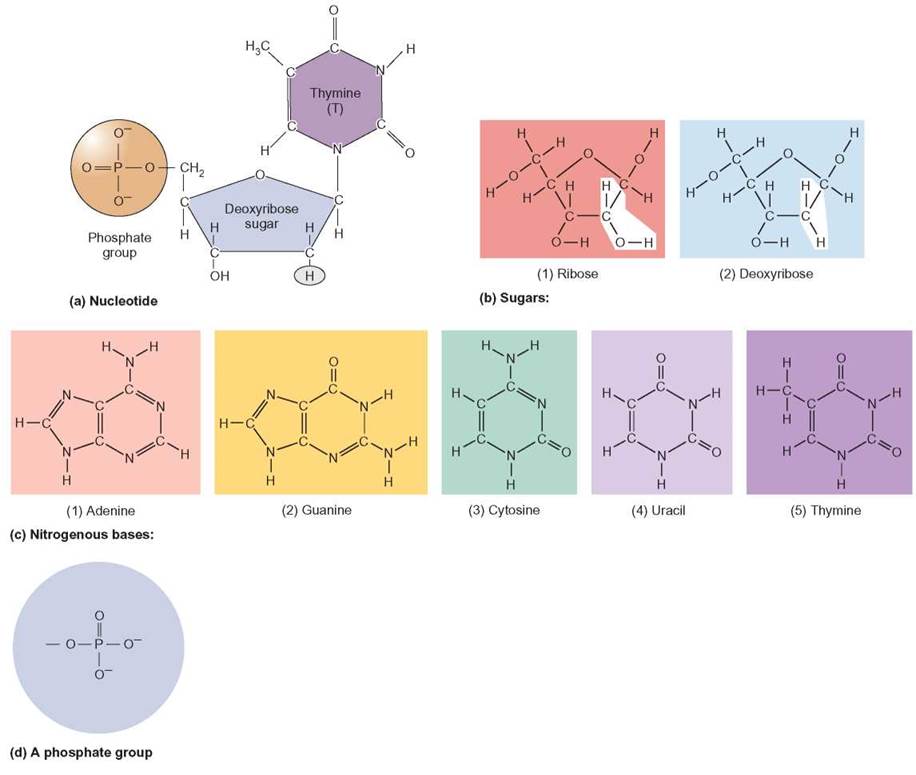
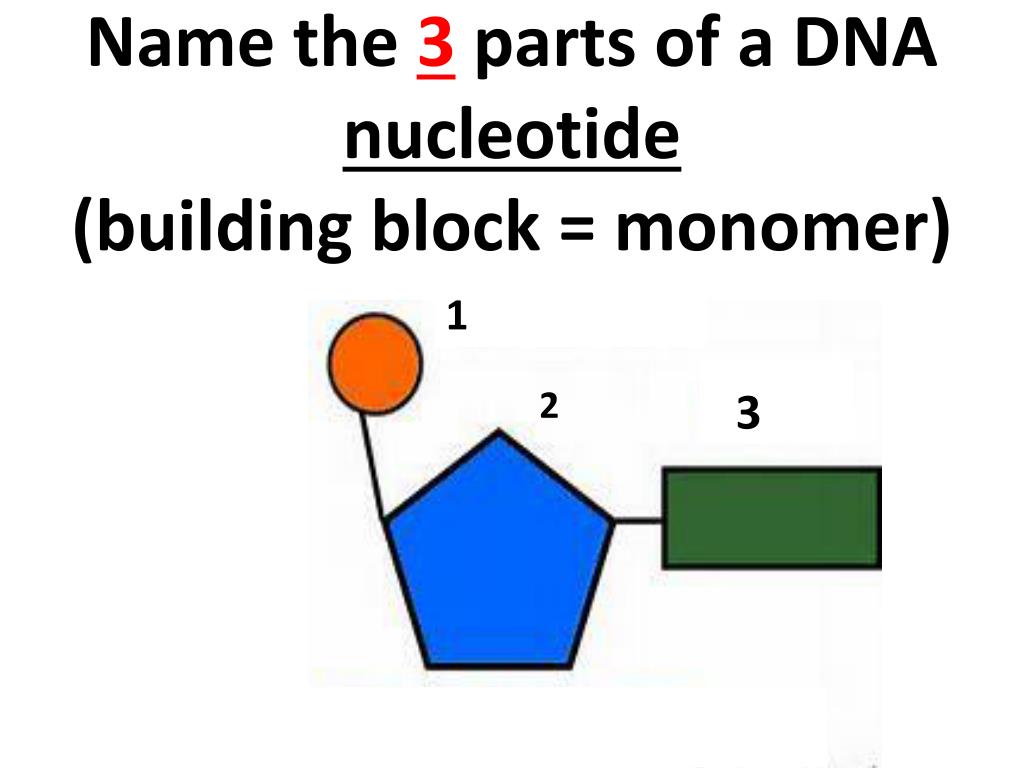
Building Blocks Monomers Are Nucleotides
Building Blocks Monomers Are Nucleotides - These monomers consist of a sugar molecule, a. Nucleic acids are long chains of. Nucleotides are nucleosides with one or more phosphate groups attached, forming nucleotide monophosphates, diphosphates, or triphosphates. These molecular building blocks are fundamental to dna, encoding the information necessary for growth, development, and reproduction in living organisms. The building blocks of dna are nucleotides. Nucleic acid monomers, or nucleotides, are the fundamental building blocks of the genetic material found in all living organisms. Nucleotides joined together by covalent bonds called phosphodiester linkages form nucleic acid molecules. Nucleotides are organic molecules that serve as the basic structural (monomer) units for dna and rna, which, as we know, are the building blocks responsible for all life on earth. The phosphate is attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose and the. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the building blocks (monomers) of nucleic acids are, the molecule that is formed by linking together monomers called. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. The phosphate is attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose and the. What are the monomers of dna? Nucleotides are nucleosides with one or more phosphate groups attached, forming nucleotide monophosphates, diphosphates, or triphosphates. Nucleic acids are long chains of. Building blocks are linked by bonds that have high intrinsic activation energies of hydrolysis,. Lipid molecules serve as storage of biological energy and provide the building blocks for biological membranes. Like all macromolecules nucleic acids are made of building blocks or monomers. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are nucleic acids. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Comprising a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base, nucleotides are the monomers of nucleic acids. Differences in sugars and nitrogenous bases. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Lipid molecules serve as storage of biological energy and provide the building blocks for biological membranes. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of nucleic acids, which include dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) and. They are like building blocks. Monomers of nucleic acids are ____. The nitrogenous base and pentose sugar are the fundamental building blocks of nucleic acids, the monomers. What are the monomers of dna? The monomers (building blocks) of dna are called nucleotides. These monomers polymerize to form complex and crucial. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. They are like building blocks. Organic molecules that serve as the monomers, or subunits, of nucleic acids like dna and rna. Nucleotides are organic molecules that serve as the basic structural (monomer) units for dna and rna, which, as we know, are the building blocks responsible for all life on earth. The building blocks of nucleic acids, nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a five. Organic molecules that serve as the monomers, or subunits, of nucleic acids like dna and. Nucleotides a nucleotide is a nucleic acid monomer consisting of a nitrogen base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. The building blocks of dna are nucleotides. The monomers (building blocks) of dna are called nucleotides. Comprising a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base, nucleotides are the monomers of nucleic acids. Differences between dna and rna nucleotides. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the building blocks (monomers) of nucleic acids are, the molecule that is formed by linking together monomers called. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are nucleic acids. Comprising a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base, nucleotides are the monomers of nucleic acids. Dna and rna structures have 3. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of nucleic acids, which include dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) and rna (ribonucleic acid). Nucleic acid monomers, or nucleotides, are the fundamental building blocks of the genetic material found in all living organisms. The building blocks of nucleic acids, nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a five. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. These molecular. Building blocks are linked by bonds that have high intrinsic activation energies of hydrolysis,. Nucleic acids are long chains of. They are like building blocks. These monomers consist of a sugar molecule, a. These monomers polymerize to form complex and crucial. The monomers (building blocks) of dna are called nucleotides. The building blocks of nucleic acids, nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a five. They are like building blocks. Differences between dna and rna nucleotides. Nucleotides a nucleotide is a nucleic acid monomer consisting of a nitrogen base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. These molecular building blocks are fundamental to dna, encoding the information necessary for growth, development, and reproduction in living organisms. The distinction between dna and rna nucleotides lies in their sugar components. Monomers of nucleic acids are ____. Nucleic acid monomers, or nucleotides, are the fundamental building blocks of the genetic material found in all living organisms. The nitrogenous base. Dna nucleotides contain deoxyribose, lacking. What are the monomers of dna? Nucleotides are organic molecules that serve as the basic structural (monomer) units for dna and rna, which, as we know, are the building blocks responsible for all life on earth. Dna and rna structures have 3 main differences.the. Building blocks are linked by bonds that have high intrinsic activation energies of hydrolysis,. Nucleotides are nucleosides with one or more phosphate groups attached, forming nucleotide monophosphates, diphosphates, or triphosphates. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. The nitrogenous base and pentose sugar are the fundamental building blocks of nucleic acids, the monomers. Differences between dna and rna nucleotides. Nucleotides joined together by covalent bonds called phosphodiester linkages form nucleic acid molecules. The phosphate is attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose and the. These monomers polymerize to form complex and crucial. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are long chains of. Nucleic acid monomers, or nucleotides, are the fundamental building blocks of the genetic material found in all living organisms. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of nucleic acids, which include dna (deoxyribonucleic acid) and rna (ribonucleic acid).PPT DNA and DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Macromolecules Biomolecules Building Blocks of Life Monomers Build
Biology…. The study of life. ppt download
Building Blocks (Monomers) Are Nucleotides at bradmwilliamso blog
PPT Classical and Modern PowerPoint Presentation ID143901
What Are the Monomer Building Blocks of Dna ElysekruwTyler
Nucleic Acids Organic Molecules—The Molecules of Life CORNERSTONES
Two MORE Organic Biomolecules Proteins and Nucleic Acids ppt download
Monomers Definition, Types, Structure, Examples
PPT DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis PowerPoint Presentation, free download
An Anion Of Phosphoric Acid, I.e.,.
The Building Blocks Of Dna Are Nucleotides.
Comprising A Sugar, A Phosphate Group, And A Nitrogenous Base, Nucleotides Are The Monomers Of Nucleic Acids.
Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like The Building Blocks (Monomers) Of Nucleic Acids Are, The Molecule That Is Formed By Linking Together Monomers Called.
Related Post:
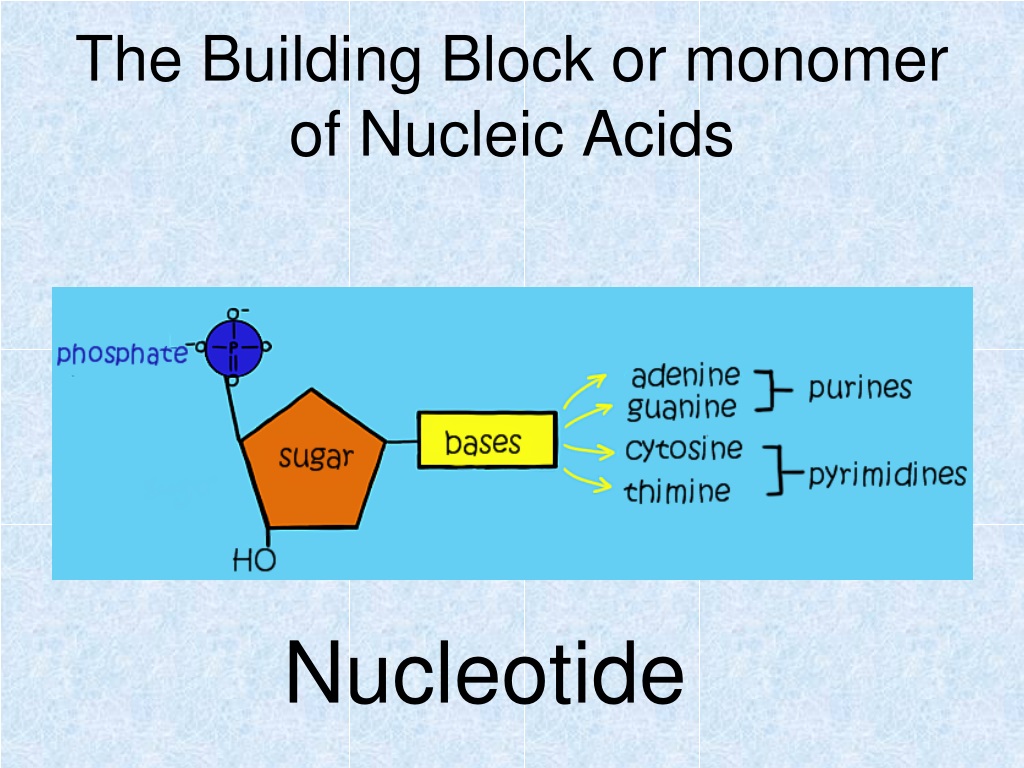

+of+nucleic+acids..jpg)