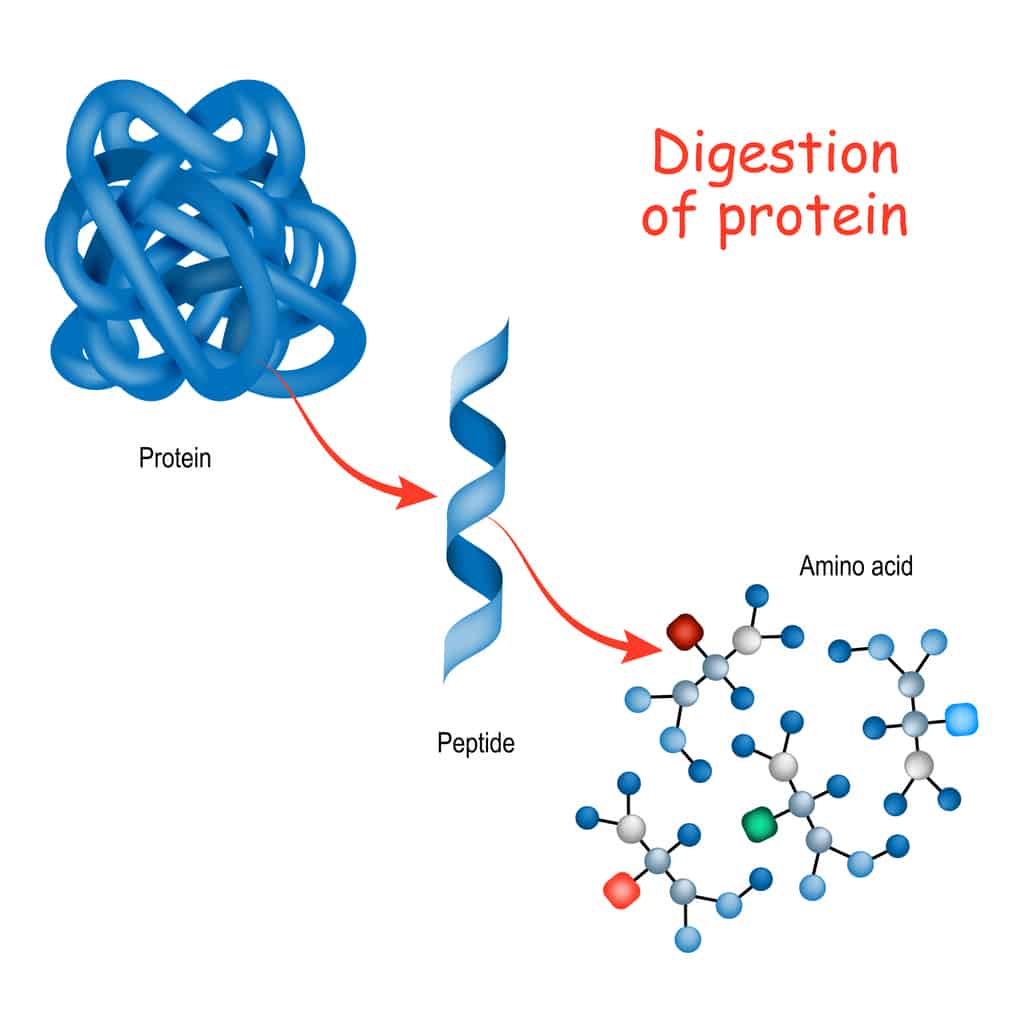
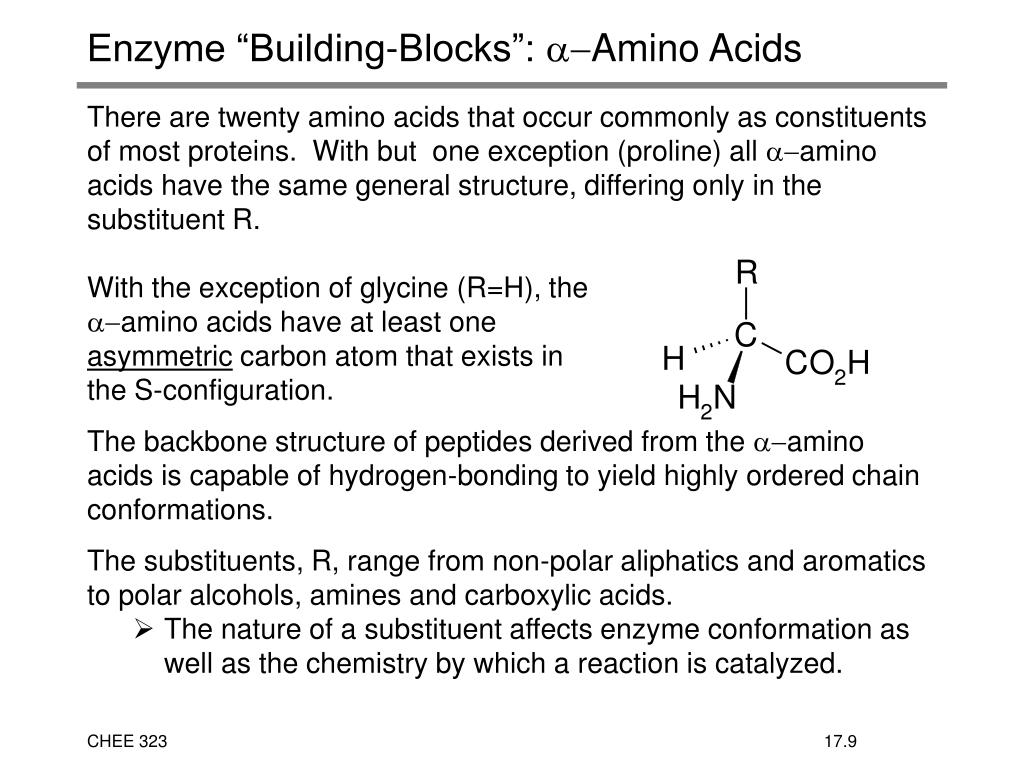
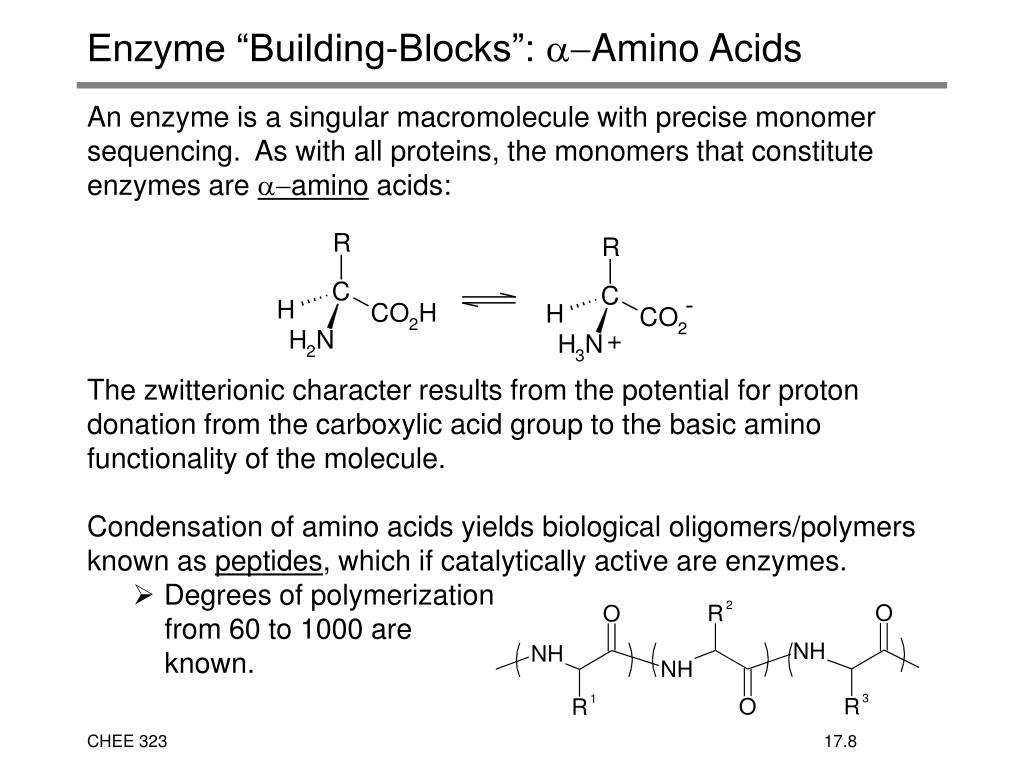
Building Blocks Of An Enzyme
Building Blocks Of An Enzyme - Dna stores the directions for building proteins in a. No chemical reaction can occur without what? In this perspective, we aim to highlight challenges and opportunities of biosynthetic investigations on noncanonical natural product pathways that utilize primary. Proteins serve as structural support, biochemical catalysts, hormones, enzymes, building blocks, and initiators of cellular death. Enzymes, which are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions, are composed of monomers or building blocks, which are small organic molecules known as amino acids. Enzymes play vital roles in biochemical reactions and metabolic processes within living organisms. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like do most enzymes consist of carbohydrate, protein, or lipid?, what are the building blocks (monomers). In this article, we'll explore the basics of enzymes, their composition, and their diverse applications, including their role in ethanol fermentation. Enzymes are essential proteins that play a crucial role in various biological processes, including cell division and metabolism. The ability of enzymes to act as catalysts depends on what? What happens if the shape of an. Enzymes are proteins, having primary, secondary, tertiary. A molecule enzymes interact with. Enzymes have complex, irregular shapes that are made up of hundreds of amino acids. Phosphate, glycerol, and fatty acids. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined to form. The steps must occur at what? Proteins serve as structural support, biochemical catalysts, hormones, enzymes, building blocks, and initiators of cellular death. What are the building blocks of enzymes? They are composed of monomers or. Enzymes play vital roles in biochemical reactions and metabolic processes within living organisms. Enzymes are proteins, having primary, secondary, tertiary. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined to form. The ability of enzymes to act as catalysts depends on what? What kind of biomolecule are the building blocks of enzymes? Phosphate, glycerol, and fatty acids. Enzymes are protein macromolecules that play a crucial role in the body's chemical reactions. Coenzymes are organic helper molecules with a basic atomic structure of carbon and hydrogen, essential for. Enzymes are proteins, having primary, secondary, tertiary. These proteins are made up of amino acids, a set of building blocks that. No chemical reaction can occur without what? In this perspective, we aim to highlight challenges and opportunities of biosynthetic investigations on noncanonical natural product pathways that utilize primary. Coenzymes are organic helper molecules with a basic atomic structure of carbon and hydrogen, essential for. These proteins are made up of amino acids, a set of building blocks that. Enzymes are. Enzymes have complex, irregular shapes that are made up of hundreds of amino acids. What makes an enzyme specific? Each of these building blocks needs to be placed perfectly or else the enzyme will slow. They are composed of monomers or. What gives an enzyme its specific shape. What kind of biomolecule are the building blocks of enzymes? What are the building blocks of enzymes? Chang, michelle cy | abstract: They are composed of monomers or. In this article, we'll explore the basics of enzymes, their composition, and their diverse applications, including their role in ethanol fermentation. What happens if the shape of an. Enzymes have complex, irregular shapes that are made up of hundreds of amino acids. Proteins serve as structural support, biochemical catalysts, hormones, enzymes, building blocks, and initiators of cellular death. What makes an enzyme specific? In this perspective, we aim to highlight challenges and opportunities of biosynthetic investigations on noncanonical natural product pathways. What are the building blocks of enzymes? Coenzymes are organic helper molecules with a basic atomic structure of carbon and hydrogen, essential for. This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of enzymes. Their functions are diverse and essential for maintaining life processes. Enzymes are essential proteins that play a crucial role in various biological processes, including. The ability of enzymes to act as catalysts depends on what? The building blocks of enzymes are amino acids, which are the basic building blocks of proteins. Enzymes are proteins that provide the instructions to build enzymes, which are proteins composed of amino acid strands. No chemical reaction can occur without what? This will also help you to draw the. What are the building blocks of enzymes? What kind of biomolecule are the building blocks of enzymes? These proteins are made up of amino acids, a set of building blocks that. Their functions are diverse and essential for maintaining life processes. Enzymes, which are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions, are composed of monomers or building blocks, which are small organic. Phosphate, glycerol, and fatty acids. What are the building blocks of enzymes? Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like which suffix usually makes up the end of an enzyme's name?, what are the building blocks (monomers) of an enzyme?, the. Enzymes play vital roles in biochemical reactions and metabolic processes within living organisms. No chemical reaction can occur. This will also help you to draw the structure and diagram of enzymes. Dna stores the directions for building proteins in a. In this perspective, we aim to highlight challenges and opportunities of biosynthetic investigations on noncanonical natural product pathways that utilize primary. They are composed of monomers or. They can be further defined by their four. Enzymes are protein macromolecules that play a crucial role in the body's chemical reactions. The building blocks of an enzyme are: Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like do most enzymes consist of carbohydrate, protein, or lipid?, what are the building blocks (monomers). What makes an enzyme specific? In this article we will discuss about the structure of enzymes. Enzymes are essential proteins that play a crucial role in various biological processes, including cell division and metabolism. In this article, we'll explore the basics of enzymes, their composition, and their diverse applications, including their role in ethanol fermentation. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like which suffix usually makes up the end of an enzyme's name?, what are the building blocks (monomers) of an enzyme?, the. Enzymes have complex, irregular shapes that are made up of hundreds of amino acids. The steps must occur at what? A molecule enzymes interact with.Enzymes that break down food compounds into their basic building blocks
Protein The Building Block of Life EatPlantBased
PPT Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID594577
Newly discovered enzyme “square dance” helps generate DNA building
[Solved] Enzymes are composed of what kind of chemical building blocks
Biochemistry (2)100 N/A 256 Part 1 Building Blocks of the Cell NEL
Solved The building blocks of an enzyme are Select one O a.
Solved The building blocks of an enzyme arephosphate,
Example structures and strategic application of enzyme classes that
PPT Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID594577
Enzymes Have Complex, Irregular Shapes That Are Made Up Of Hundreds Of Amino Acids.
Coenzymes Are Organic Helper Molecules With A Basic Atomic Structure Of Carbon And Hydrogen, Essential For.
The Building Blocks Of Enzymes Are Amino Acids, Which Are The Basic Building Blocks Of Proteins.
Enzymes Are Proteins, Having Primary, Secondary, Tertiary.
Related Post: