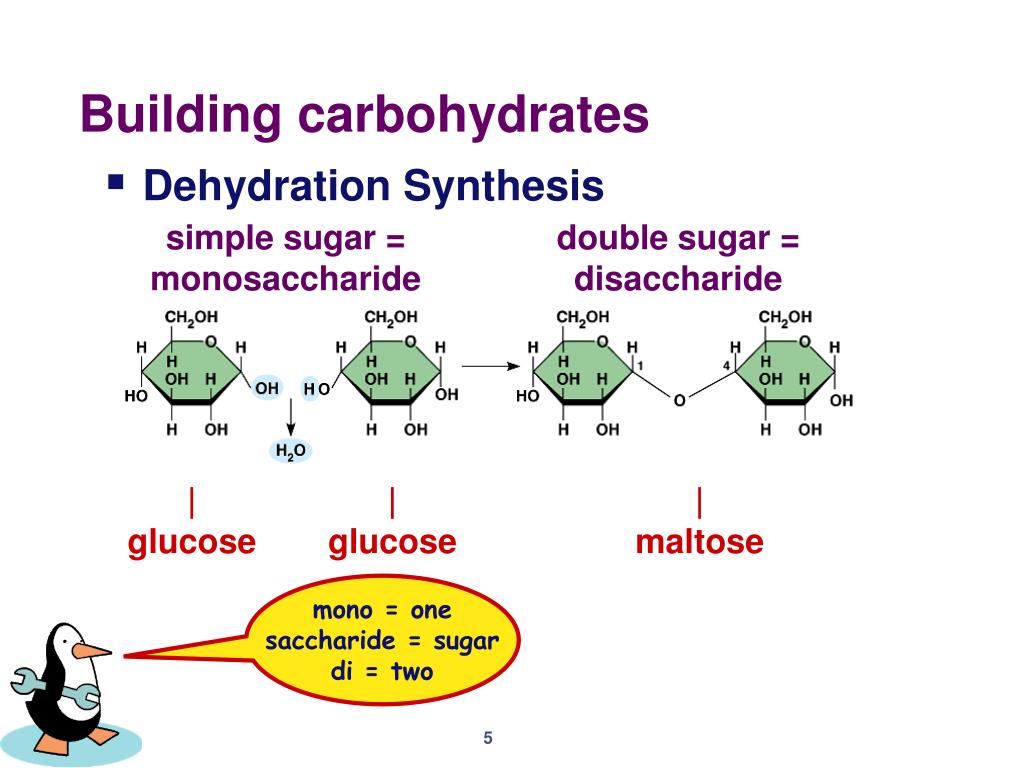
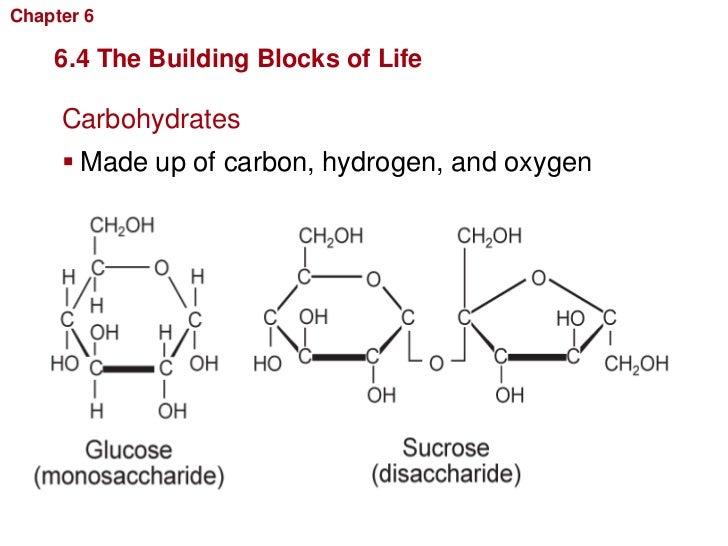
Building Blocks Of Carbohydrates
Building Blocks Of Carbohydrates - Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a. Carbohydrates are classified into three subtypes: The basic building block of carbohydrates is the monosaccharide, which consists of six carbon atoms. Explore the types of carbohydrates, such as monosaccharides, disaccharides, and. Find out the differences between monosaccharides, disaccharides and. Explore the conformations, anomers, cyclic forms, oxidation, reduction and condensation. Cells are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms, from microscopic bacteria to towering trees and complex animals. Carbohydrates provide energy to the. This amounts less than 130 grams of carbohydrates per day, compared to a typical daily intake of 225 to 325 grams of carbs in a standard diet. Learn about the names and structures of carbohydrates, the polyfunctional compounds in nature. Learn about the three main classes of carbohydrates: Carbohydrates provide energy to the body, particularly through glucose, a simple sugar that is a component of starch and an ingredient in many staple foods. Carbohydrates provide energy to the. Learn about the structure and classification of carbohydrates, the chemical building blocks of life. Carbohydrates are, in fact, an essential part of our diet; Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a. Carbohydrates are classified into three subtypes: Learn about the different types of carbohydrates, such as monosaccharides, disaccharides, starches, glycogen and fiber, and how they affect the body. Learn about the biological building blocks of carbohydrates, their structure, classification, and functions. Cells are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms, from microscopic bacteria to towering trees and complex animals. Sugars, or carbohydrates, on the other hand, are among the body's main sources of energy. Proteins are the workhorses of our cells and their main building blocks. Learn what carbohydrates are, why they are important and how they are structured. Carbohydrates are a fundamental component of life, providing energy and serving as structural building blocks in various organisms. These building. These building blocks come together to create chains, which in turn create different types of. Proteins are the workhorses of our cells and their main building blocks. This amounts less than 130 grams of carbohydrates per day, compared to a typical daily intake of 225 to 325 grams of carbs in a standard diet. Carbohydrates provide energy to the. Learn. These building blocks come together to create chains, which in turn create different types of. Explore the conformations, anomers, cyclic forms, oxidation, reduction and condensation. Grains, fruits, and vegetables are all natural sources of carbohydrates. Find out the differences between monosaccharides, disaccharides and. Cells are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms, from microscopic bacteria to towering trees and. Sugars, or carbohydrates, on the other hand, are among the body's main sources of energy. Learn about the biological building blocks of carbohydrates, their structure, classification, and functions. Carbohydrates are formed in green plants by photosynthesis, which is the chemical combination, or fixation, of carbon dioxide and water by utilization of energy from the absorption of visible. Carbohydrates are composed. Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a. Proteins are the workhorses of our cells and their main building blocks. The basic building block of carbohydrates is the monosaccharide, which consists of six carbon atoms. This amounts less than 130 grams of carbohydrates per day, compared to a typical daily intake of 225 to 325 grams of carbs. This amounts less than 130 grams of carbohydrates per day, compared to a typical daily intake of 225 to 325 grams of carbs in a standard diet. Proteins are the workhorses of our cells and their main building blocks. Learn what carbohydrates are, why they are important and how they are structured. Carbohydrates provide energy to the body, particularly through. Cells are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms, from microscopic bacteria to towering trees and complex animals. Carbohydrates are classified into three subtypes: Sugars, or carbohydrates, on the other hand, are among the body's main sources of energy. This amounts less than 130 grams of carbohydrates per day, compared to a typical daily intake of 225 to 325. Carbohydrates are formed in green plants by photosynthesis, which is the chemical combination, or fixation, of carbon dioxide and water by utilization of energy from the absorption of visible. Carbohydrates are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a. This amounts less than 130 grams of carbohydrates per day, compared to a typical daily intake of 225 to 325 grams. Carbohydrates are formed in green plants by photosynthesis, which is the chemical combination, or fixation, of carbon dioxide and water by utilization of energy from the absorption of visible. Learn about the structure and classification of carbohydrates, the chemical building blocks of life. Carbohydrates are a fundamental component of life, providing energy and serving as structural building blocks in various. These building blocks come together to create chains, which in turn create different types of. Carbohydrates are formed in green plants by photosynthesis, which is the chemical combination, or fixation, of carbon dioxide and water by utilization of energy from the absorption of visible. Proteins are the workhorses of our cells and their main building blocks. Carbohydrates are a fundamental. Explore the types of carbohydrates, such as monosaccharides, disaccharides, and. Did you know that the building blocks of carbohydrates are called monosaccharides? Understanding cell biology is crucial for. Learn what carbohydrates are, why they are important and how they are structured. These building blocks come together to create chains, which in turn create different types of. Find out the differences between monosaccharides, disaccharides and. Carbohydrates are, in fact, an essential part of our diet; Learn about the biological building blocks of carbohydrates, their structure, classification, and functions. Sugars, or carbohydrates, on the other hand, are among the body's main sources of energy. Monosaccharides are the simplest and smallest units of carbohydrates, with. Learn about the structure and classification of carbohydrates, the chemical building blocks of life. Learn about the three main classes of carbohydrates: Carbohydrates provide energy to the body, particularly through glucose, a simple sugar that is a component of starch and an ingredient in many staple foods. This amounts less than 130 grams of carbohydrates per day, compared to a typical daily intake of 225 to 325 grams of carbs in a standard diet. Carbohydrates are classified into three subtypes: Proteins are the workhorses of our cells and their main building blocks.The Essential Components Of Carbohydrates' Building Blocks
PPT Carbohydrates PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6987875
PPT Orgo C licker Review PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Biochemistry notes students
2 Biological Building Blocks Carbohydrates Basicmedical Key
PPT Carbohydrates PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2427741
2 Monomeric building blocks of lignocellulose for carbohydrates
2 Biological Building Blocks Carbohydrates Basicmedical Key
Building Blocks of Carbohydrates Types, Properties & Functions
Organic molecules
Explore The Conformations, Anomers, Cyclic Forms, Oxidation, Reduction And Condensation.
Learn About The Names And Structures Of Carbohydrates, The Polyfunctional Compounds In Nature.
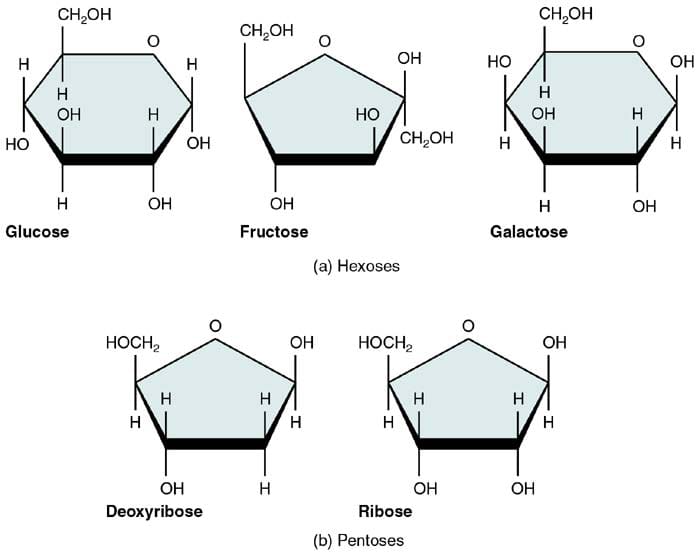
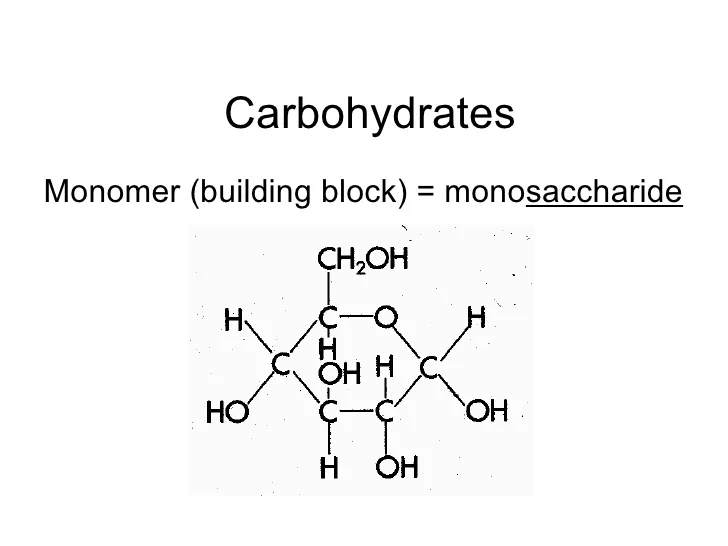
The Basic Building Block Of Carbohydrates Is The Monosaccharide, Which Consists Of Six Carbon Atoms.
Learn About The Different Types Of Carbohydrates, Such As Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, Starches, Glycogen And Fiber, And How They Affect The Body.
Related Post: