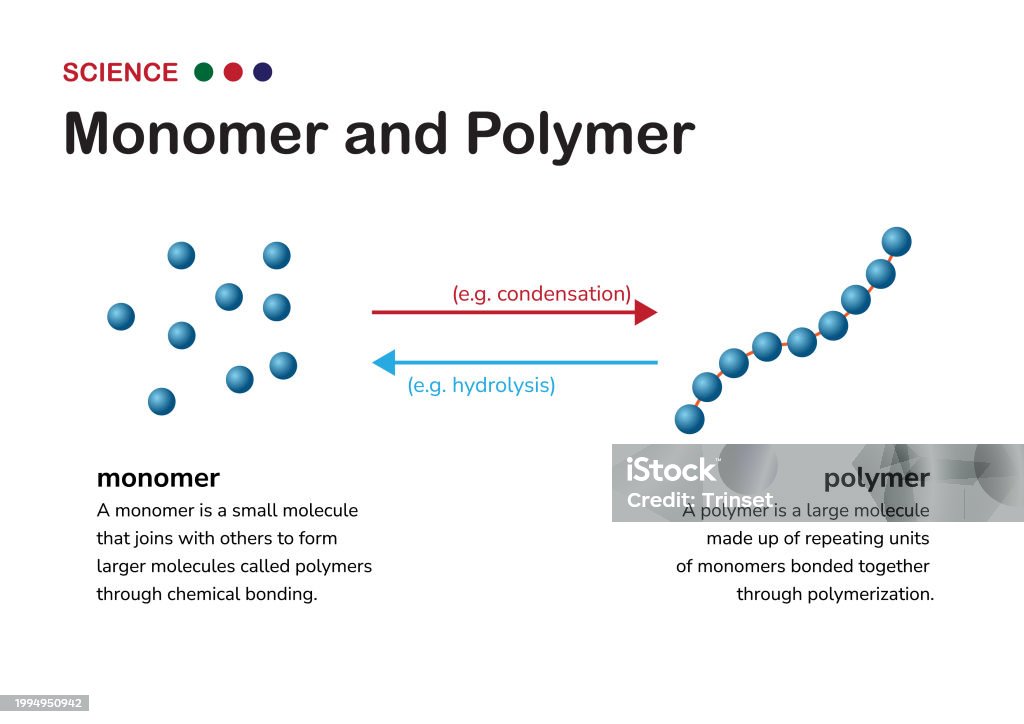
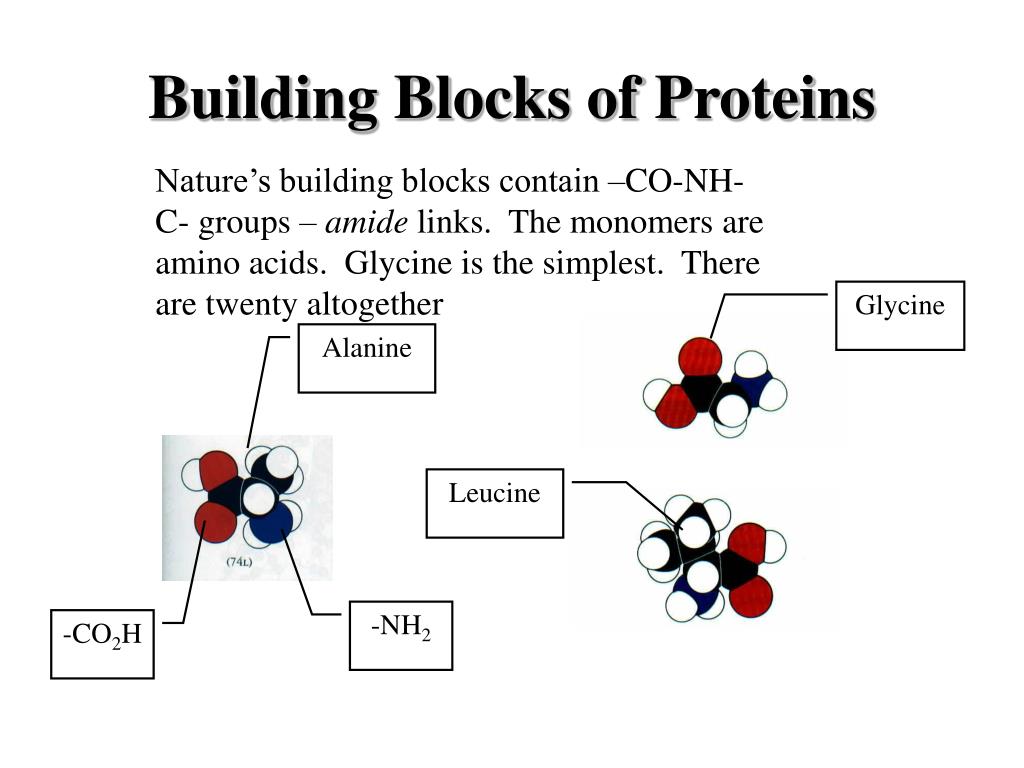
Building Blocks Of Polymers
Building Blocks Of Polymers - Low molecular weight compared to polymers (typically <500 g/mol) Extant biopolymers provide information on prebiotic chemistry. Monomers are small, single molecules that can join together to form a larger structure known as a polymer. A polymer (/ ˈ p ɒ l ɪ m ər / [4] [5]) is a substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. As a living organism develops, the relative level of 14 c in its body is equal to the concentration of 14 c in the atmosphere. Notably, the double bonds between carbons increase the chances for chemical reactions that enable polymerization. Key characteristics of monomers include: Each class of macromolecule has its own specific type of monomer, contributing to the unique properties of the resulting polymer. Reactive functional groups (e.g., double bonds, hydroxyl groups) that allow polymerization; Since a significant amount of ia can be obtained from. Wang and de pablo knew what it takes to imbue stretchability into materials—long polymers with bendable molecular chains—and also knew what molecular structures were required for an organic material to emit light very efficiently. Each class of macromolecule has its own specific type of monomer, contributing to the unique properties of the resulting polymer. Long chains of similar repeating subunits joined by common bond types ex: It is effectively impossible to generate a completely aligned polymer crystal, but there is still a thermodynamic driving force for the alignment of polymer chains below the crystallization temperature t c.to gain partial crystalline character even in the presence of. Polymers, the ubiquitous compounds that constitute the backbone of countless materials in our daily lives, are truly fascinating entities. When an organism dies, it is no. As a living organism develops, the relative level of 14 c in its body is equal to the concentration of 14 c in the atmosphere. One of the simplest and most common techniques of applying thin polymers films onto wafers is spin coating. Polymers are massive molecules made up of a long chain of identical, tiny particles called monomers. Monomers are small, single molecules that can join together to form a larger structure known as a polymer. One of the simplest and most common techniques of applying thin polymers films onto wafers is spin coating. A carbon ring opens at a double bond to create a polymer chain that grows as each. In these direct synthesis models, biology incorporated and has maintained prebiotic building blocks and polymers; A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar. From the plastic bottles we use to the fibers in our clothing, from the coatings on our cars to the adhesives that hold things together, polymers are everywhere. Generally, these approaches rely on identifying. What are the building blocks of polymers? Polymers most biologically important molecules are polymers: Dreiling used dhf, a circular monomer with a double bond, as a. A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds, much as a train consists of a chain of cars. In these direct synthesis models, biology incorporated and has maintained prebiotic building blocks and polymers; Monomers are the building blocks of polymers, and their chemical structure determines the properties of the resulting. Located in the central heart of the beautiful neighborhood offering a serene atmosphere with its beautiful tree canopies. The molecular building blocks of the polymer backbone contain functional groups, or clusters of atoms that serve as reactive sites for modification. Notably, the double bonds between carbons increase the chances for chemical reactions that enable polymerization. Polymers are massive molecules made. Since a significant amount of ia can be obtained from. Low molecular weight compared to polymers (typically <500 g/mol) [6] due to their broad spectrum of properties, [7] both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Generally, these approaches rely on identifying. Dreiling used dhf, a circular monomer with a double bond, as a building. Long chains of similar repeating subunits joined by common bond types ex: They set out to create new polymers that integrated both properties. [6] due to their broad spectrum of properties, [7] both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Monomers are small, single molecules that can join together to form a larger structure known. What are the building blocks of polymers? Monomers are small, single molecules that can join together to form a larger structure known as a polymer. In these direct synthesis models, biology incorporated and has maintained prebiotic building blocks and polymers; Today, let’s dive into the world of plastics, uncovering their fascinating versatility and the myriad ways they’ve transformed our lives.. Since a significant amount of ia can be obtained from. Today, let’s dive into the world of plastics, uncovering their fascinating versatility and the myriad ways they’ve transformed our lives. Polysaccharides, proteins, nucleic acids lipids are not the common bond types are unique to each molecule peptide bonds join proteins, phosphodiester bonds join One of the simplest and most common. Monomers are small, single molecules that can join together to form a larger structure known as a polymer. Dreiling used dhf, a circular monomer with a double bond, as a building block for two successive polymerizations, the second of which. Reactive functional groups (e.g., double bonds, hydroxyl groups) that allow polymerization; Here is all that you wanted to know about. For example, amino acids serve as the building blocks for proteins, while monosaccharides make up carbohydrates. Wang and de pablo knew what it takes to imbue stretchability into materials—long polymers with bendable molecular chains—and also knew what molecular structures were required for an organic material to emit light very efficiently. Low molecular weight compared to polymers (typically <500 g/mol) As. It is effectively impossible to generate a completely aligned polymer crystal, but there is still a thermodynamic driving force for the alignment of polymer chains below the crystallization temperature t c.to gain partial crystalline character even in the presence of. Long chains of similar repeating subunits joined by common bond types ex: From the plastic bottles we use to the fibers in our clothing, from the coatings on our cars to the adhesives that hold things together, polymers are everywhere. The building blocks of polymers are monomers. When an organism dies, it is no. A polymer (/ ˈ p ɒ l ɪ m ər / [4] [5]) is a substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Here is all that you wanted to know about polymers, the building blocks of plastics or highly stable chain like macromolecules known to be a very essential part of the society starting from the packing material to the interiors of cars, from clinical instruments to the everyday use articles. Wang and de pablo knew what it takes to imbue stretchability into materials—long polymers with bendable molecular chains—and also knew what molecular structures were required for an organic material to emit light very efficiently. Located in the central heart of the beautiful neighborhood offering a serene atmosphere with its beautiful tree canopies. Polymers are massive molecules made up of a long chain of identical, tiny particles called monomers. Notably, the double bonds between carbons increase the chances for chemical reactions that enable polymerization. Low molecular weight compared to polymers (typically <500 g/mol) For example, amino acids serve as the building blocks for proteins, while monosaccharides make up carbohydrates. Since a significant amount of ia can be obtained from. Key characteristics of monomers include: Monomers are small, single molecules that can join together to form a larger structure known as a polymer.Monomers are the building blocks of larger molecules called polymers. A
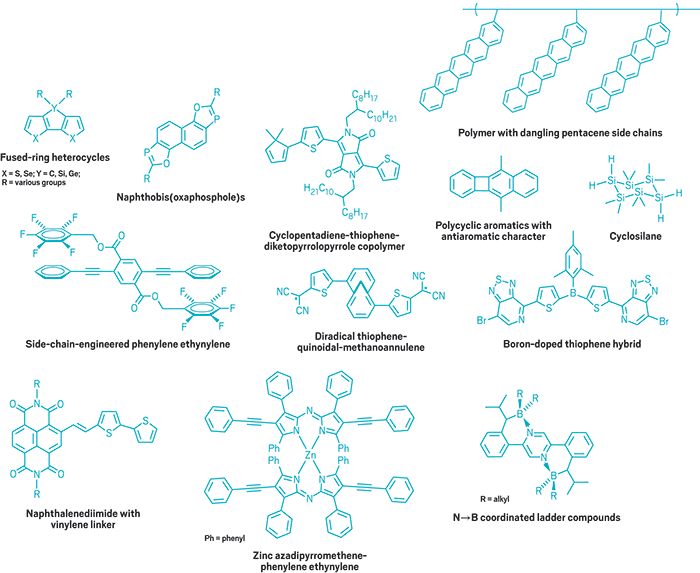
Chemists build a zoo of new polymer building blocks
Understanding Chemistry From Monomer To Polymer Monomers The Building
Scheme 1. (a) Chemical Structure of Building Blocks and (b) Probable
Building Polymers Monomers are the building blocks of larger molecules
PPT Polymer Properties and Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free
Macromolecules Biomolecules Building Blocks of Life Monomers Build
Example of some of the main polymer building blocks (A) employed for
Chemists build a zoo of new polymer building blocks
Segmental dynamics of different building blocks of conjugated polymers
Extant Biopolymers Provide Information On Prebiotic Chemistry.
Reactive Functional Groups (E.g., Double Bonds, Hydroxyl Groups) That Allow Polymerization;
Generally, These Approaches Rely On Identifying.
Synthesis Of Functional Organic Materials.
Related Post: