Building Drift Definition Earthquakes
Building Drift Definition Earthquakes - Proper management of drift ensures structural integrity, occupant safety, and. Focuses on variations in the periods and damping as a function of building drift amplitude. Building period governs the behavior of structures when they are subjected to earthquake ground motions, even when the dynamic response of the structure is forced far into the inelastic range. The model is formulated as a generalized. | find, read and cite. The horizontal deflection at the top of the story relative to the bottom of the story as determined in section 12.8.6. Testing drill density and modeling. Building period governs the behavior of structures when they are subjected to earthquake ground motions, even when the dynamic response of the structure is forced far into the inelastic range. This finding is not in agreement with the damage state definition that is described in table 4, where masonry crushing is expected (drift capacity of 0.25%), in which contradicted. Limit inelastic deformations in ductile members, limit lateral displacements that may compromise the. The model is formulated as a generalized. A design theory for seismic response is limiting the amount of movement the building is allowed during an earthquake. Pdf | the influence of residual interstorey drifts on economic losses in building resulting from earthquakes is examined. Building period governs the behavior of structures when they are subjected to earthquake ground motions, even when the dynamic response of the structure is forced far into the inelastic range. Testing drill density and modeling. The allowable drift is a prime consideration. The question that is being debated is: Proper management of drift ensures structural integrity, occupant safety, and. Limit inelastic deformations in ductile members, limit lateral displacements that may compromise the. Buildings with stiffness irregularity along elevation cause undesired deformations and damages during an intense earthquake. This results in understanding the structural performance of member inelastic strain, system stability, and vulnerability of nonstructural elements. Proper management of drift ensures structural integrity, occupant safety, and. Therefore, provisions are suggested in design. Pdf | the influence of residual interstorey drifts on economic losses in building resulting from earthquakes is examined. Testing drill density and modeling. Limit inelastic deformations in ductile members, limit lateral displacements that may compromise the. The lateral displacement or drift of a structural system under wind or earthquake forces, is important from three different perspectives: The allowable drift is a prime consideration. A design theory for seismic response is limiting the amount of movement the building is allowed during an earthquake. The. Focuses on variations in the periods and damping as a function of building drift amplitude. Building period governs the behavior of structures when they are subjected to earthquake ground motions, even when the dynamic response of the structure is forced far into the inelastic range. The horizontal deflection at the top of the story relative to the bottom of the. The model is formulated as a generalized. Therefore, provisions are suggested in design. Building period governs the behavior of structures when they are subjected to earthquake ground motions, even when the dynamic response of the structure is forced far into the inelastic range. Testing drill density and modeling. This finding is not in agreement with the damage state definition that. Proper management of drift ensures structural integrity, occupant safety, and. In this article, i have tried to explain what is building drift, allowable limits, ways and means to check in etabs models and to control the excessive drift. The lower the building code. The allowable drift is a prime consideration. Testing drill density and modeling. Buildings subject to earthquakes need drift control to limit damage to partitions, glass, and other fragile nonstructural components. Limit inelastic deformations in ductile members, limit lateral displacements that may compromise the. Building period governs the behavior of structures when they are subjected to earthquake ground motions, even when the dynamic response of the structure is forced far into the inelastic. Modern workings (post 2019) shown in green; This results in understanding the structural performance of member inelastic strain, system stability, and vulnerability of nonstructural elements. Focuses on variations in the periods and damping as a function of building drift amplitude. In this article, i have tried to explain what is building drift, allowable limits, ways and means to check in. Testing drill density and modeling. In this article, i have tried to explain what is building drift, allowable limits, ways and means to check in etabs models and to control the excessive drift. This finding is not in agreement with the damage state definition that is described in table 4, where masonry crushing is expected (drift capacity of 0.25%), in. Therefore, provisions are suggested in design. A design theory for seismic response is limiting the amount of movement the building is allowed during an earthquake. Bulk sampling from several areas amplifies the benefits of test mining by: In this article, i have tried to explain what is building drift, allowable limits, ways and means to check in etabs models and. Focuses on variations in the periods and damping as a function of building drift amplitude. The model is formulated as a generalized. The influence of residual interstorey drifts on economic losses in building resulting from earthquakes is examined. This finding is not in agreement with the damage state definition that is described in table 4, where masonry crushing is expected. The allowable drift is a prime consideration. Buildings subject to earthquakes need drift control to limit damage to partitions, glass, and other fragile nonstructural components. Modern workings (post 2019) shown in green; Building period governs the behavior of structures when they are subjected to earthquake ground motions, even when the dynamic response of the structure is forced far into the inelastic range. Buildings with stiffness irregularity along elevation cause undesired deformations and damages during an intense earthquake. Focuses on variations in the periods and damping as a function of building drift amplitude. The question that is being debated is: A design theory for seismic response is limiting the amount of movement the building is allowed during an earthquake. The model is formulated as a generalized. In this article, i have tried to explain what is building drift, allowable limits, ways and means to check in etabs models and to control the excessive drift. Bulk sampling from several areas amplifies the benefits of test mining by: This finding is not in agreement with the damage state definition that is described in table 4, where masonry crushing is expected (drift capacity of 0.25%), in which contradicted. Building period governs the behavior of structures when they are subjected to earthquake ground motions, even when the dynamic response of the structure is forced far into the inelastic range. Testing drill density and modeling. The lateral displacement or drift of a structural system under wind or earthquake forces, is important from three different perspectives: Pdf | the influence of residual interstorey drifts on economic losses in building resulting from earthquakes is examined.Earthquake Behaviour of Buildings CivilDigital
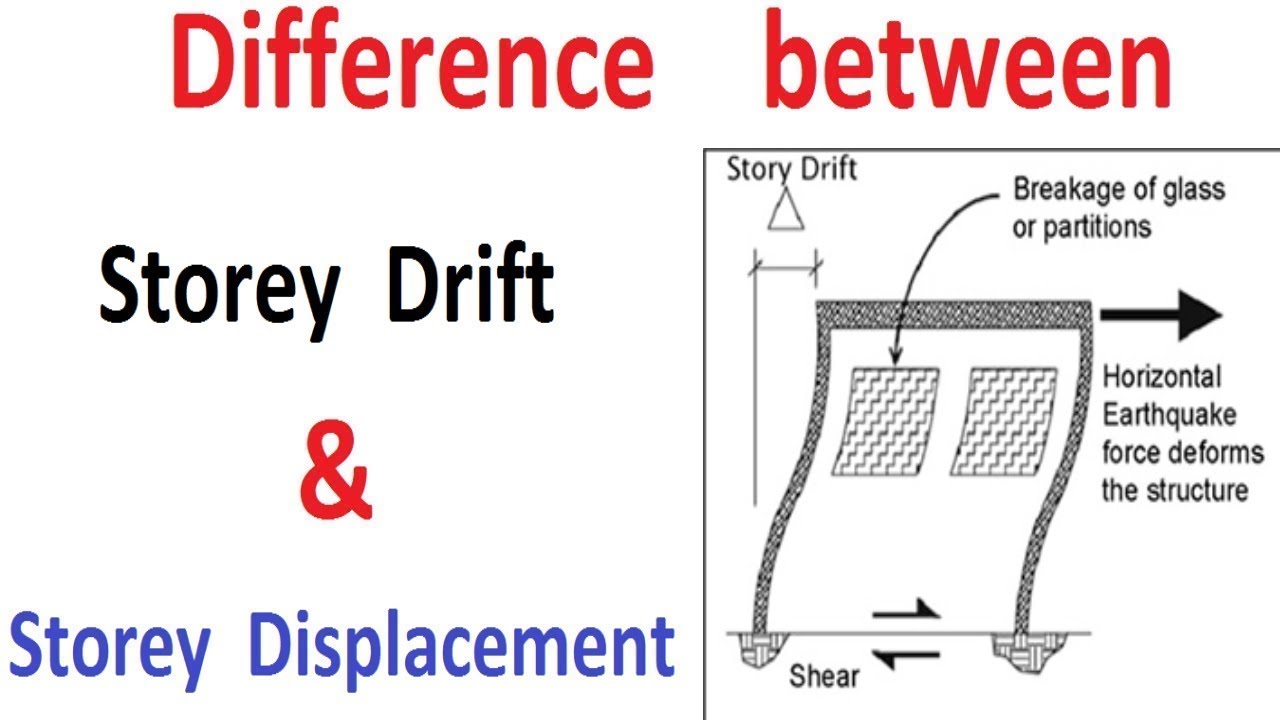
Difference between Storey Drift & Storey Displacement YouTube
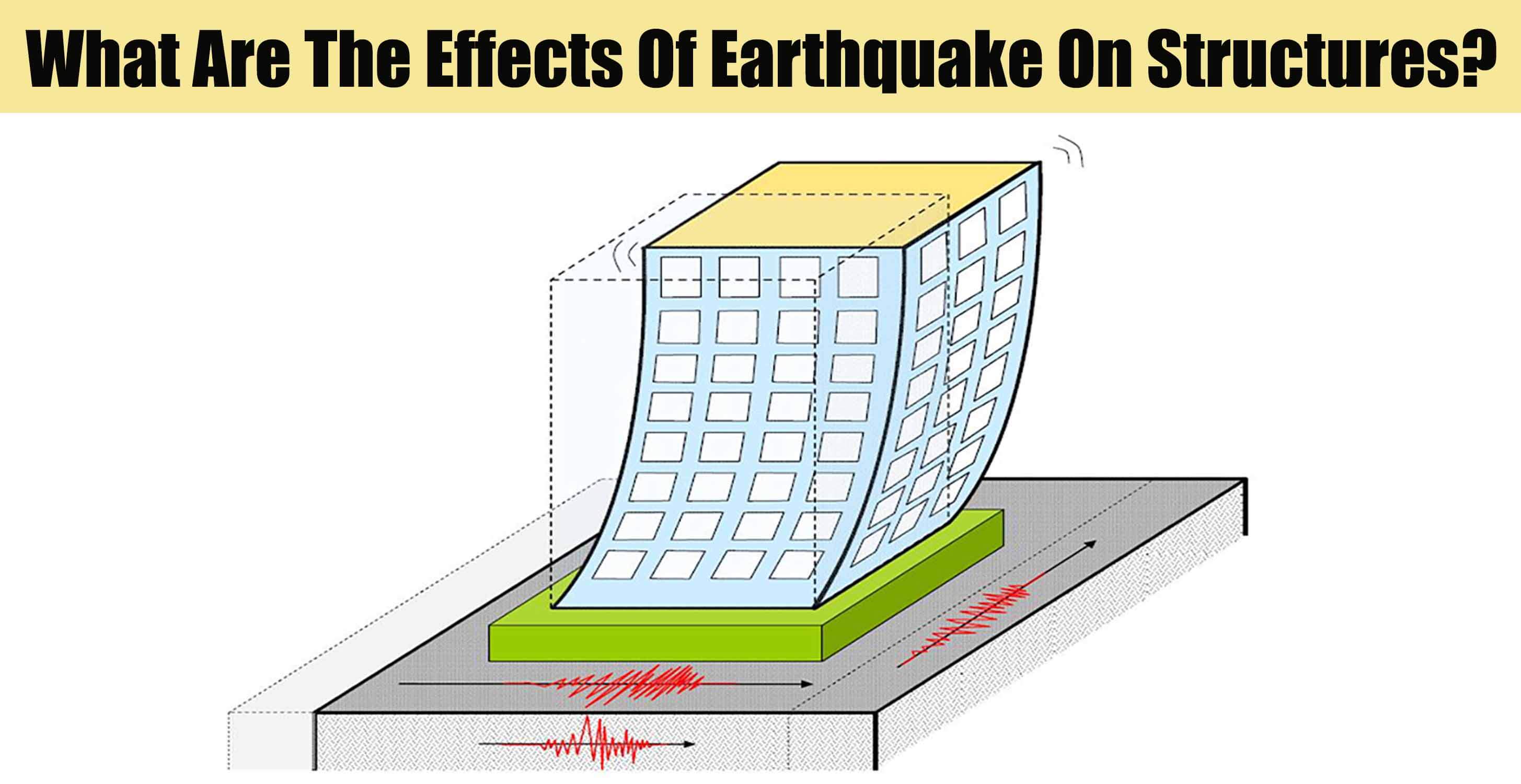
Earthquake Structure
Drift of a 15floor structure under design basis earthquakes, before
DRIFT What is Storey Drift? // Lateral Storey Drift Inter Storey
Building drift in the positive Zdirection at failure (V=80 ton
PPT Development of Continental Drift PowerPoint Presentation, free
Interstorey drift of the building under eight earthquakes. Download
Storey drift (a) and interstorey drift (B) of CHECKER building under
5 Story Drift, Overturning, Buidling Separation, Earthquake Load
The Influence Of Residual Interstorey Drifts On Economic Losses In Building Resulting From Earthquakes Is Examined.
| Find, Read And Cite.
Limit Inelastic Deformations In Ductile Members, Limit Lateral Displacements That May Compromise The.
The Horizontal Deflection At The Top Of The Story Relative To The Bottom Of The Story As Determined In Section 12.8.6.
Related Post: