Building Footprint Definition
Building Footprint Definition - The proposed strategy for quantifying the embodied cf of building projects consists of three main steps. It includes dwellings and any. Term used to describe boundaries of the exterior walls of a building or structure when placed on a piece of property. It includes dwellings and any area of attached garage that exceeds 200 square feet. Building footprints are needed to create. In gis, a building footprint refers to a polygon or set of polygons that represent a specific building in the physical world. They are often accompanied by contextual metadata about. Firstly, the scope of the building project is defined, including the project. In mapping, a building footprint refers to the polygon on a map that outlines the physical boundaries of a structure. Building footprint datasets contain the foundation's exact size, shape, and location, i.e., longitude, latitude, geocoding level, and more. It includes dwellings and any. It includes dwellings and any area of attached garage that exceeds 200 square feet. The proposed strategy for quantifying the embodied cf of building projects consists of three main steps. They are often accompanied by contextual metadata about. It can also describe the boundaries of the roof or covered area of the roof. Building footprints are typically represented as polygons, which can easily be stored and displayed by vector data. In gis, a building footprint refers to a polygon or set of polygons that represent a specific building in the physical world. Building footprint — literally the footprint of a building on the ground, the area of the surface that the building occupies. It includes information about the. This includes the geometrical shape,. It includes dwellings and any area of attached garage that exceeds 200 square feet. A building footprint is essentially the outline of a building as seen from an aerial view, representing the total area of the building that intersects with the ground. Building footprint — literally the footprint of a building on the ground, the area of the surface that. Building footprints are needed to create. They are often accompanied by contextual metadata about. Conventionally in construction the building footprint is the area of a building measured from the outer surface of the exterior of the building multiplied by the depth measured in the same. A building footprint is essentially the outline of a building as seen from an aerial. Vector data also allows individual features to be linked with. Building life cycle assessment is a scientific methodology. In mapping, a building footprint refers to the polygon on a map that outlines the physical boundaries of a structure. A building footprint is the horizontal area of a building as seen in a plan, measured from the outside of all exterior. Building footprint — literally the footprint of a building on the ground, the area of the surface that the building occupies. A building footprint is essentially the outline of a building as seen from an aerial view, representing the total area of the building that intersects with the ground. Firstly, the scope of the building project is defined, including the. Building footprint means the horizontal area as seen in plan, measured from outside of all exterior walls and supporting columns. It includes information about the. Building footprint datasets contain the foundation's exact size, shape, and location, i.e., longitude, latitude, geocoding level, and more. The proposed strategy for quantifying the embodied cf of building projects consists of three main steps. It. It is a geometric figure that is formed by projecting the. They are often accompanied by contextual metadata about. It includes dwellings and any area of attached garage that exceeds 200 square feet. Vector data also allows individual features to be linked with. Term used to describe boundaries of the exterior walls of a building or structure when placed on. Building footprints are polygons representing the extent of individual building structures in the physical world. It includes dwellings and any. Building footprint means the horizontal area as seen in plan, measured from outside of all exterior walls and supporting columns. This includes the geometrical shape,. A building footprint is essentially the outline of a building as seen from an aerial. It includes information about the. In gis, a building footprint refers to a polygon or set of polygons that represent a specific building in the physical world. It includes dwellings and any. It includes dwellings and any area of attached garage that exceeds 200 square feet. In mapping, a building footprint refers to the polygon on a map that outlines. It can also describe the boundaries of the roof or covered area of the roof. A building footprint is essentially the outline of a building as seen from an aerial view, representing the total area of the building that intersects with the ground. They are often accompanied by contextual metadata about. A building footprint refers to the specific design of. Conventionally in construction the building footprint is the area of a building measured from the outer surface of the exterior of the building multiplied by the depth measured in the same. Firstly, the scope of the building project is defined, including the project. Building footprint datasets contain the foundation's exact size, shape, and location, i.e., longitude, latitude, geocoding level, and. It includes dwellings and any area of attached garage that exceeds 200 square feet. Conventionally in construction the building footprint is the area of a building measured from the outer surface of the exterior of the building multiplied by the depth measured in the same. It can also describe the boundaries of the roof or covered area of the roof. A building footprint refers to the specific design of a structure’s ground floor and how it interacts with the site it occupies. The proposed strategy for quantifying the embodied cf of building projects consists of three main steps. Building footprint datasets contain the foundation's exact size, shape, and location, i.e., longitude, latitude, geocoding level, and more. This includes the geometrical shape,. A building footprint is essentially the outline of a building as seen from an aerial view, representing the total area of the building that intersects with the ground. It is a geometric figure that is formed by projecting the. Vector data also allows individual features to be linked with. Building footprint means the horizontal area as seen in plan, measured from outside of all exterior walls and supporting columns. It includes information about the. Term used to describe boundaries of the exterior walls of a building or structure when placed on a piece of property. Building life cycle assessment is a scientific methodology. A building footprint is the horizontal area of a building as seen in a plan, measured from the outside of all exterior walls and supporting columns. Firstly, the scope of the building project is defined, including the project.Sustainable building footprint. Hint there's less of it. AREsketches
Building Footprints Examples & Where to Get the Data
Building E.jpg BUILDING FOOTPRINTS
What is a building footprint, and how do I work with it?
Building Footprint Polygon Data SafeGraph Geometry
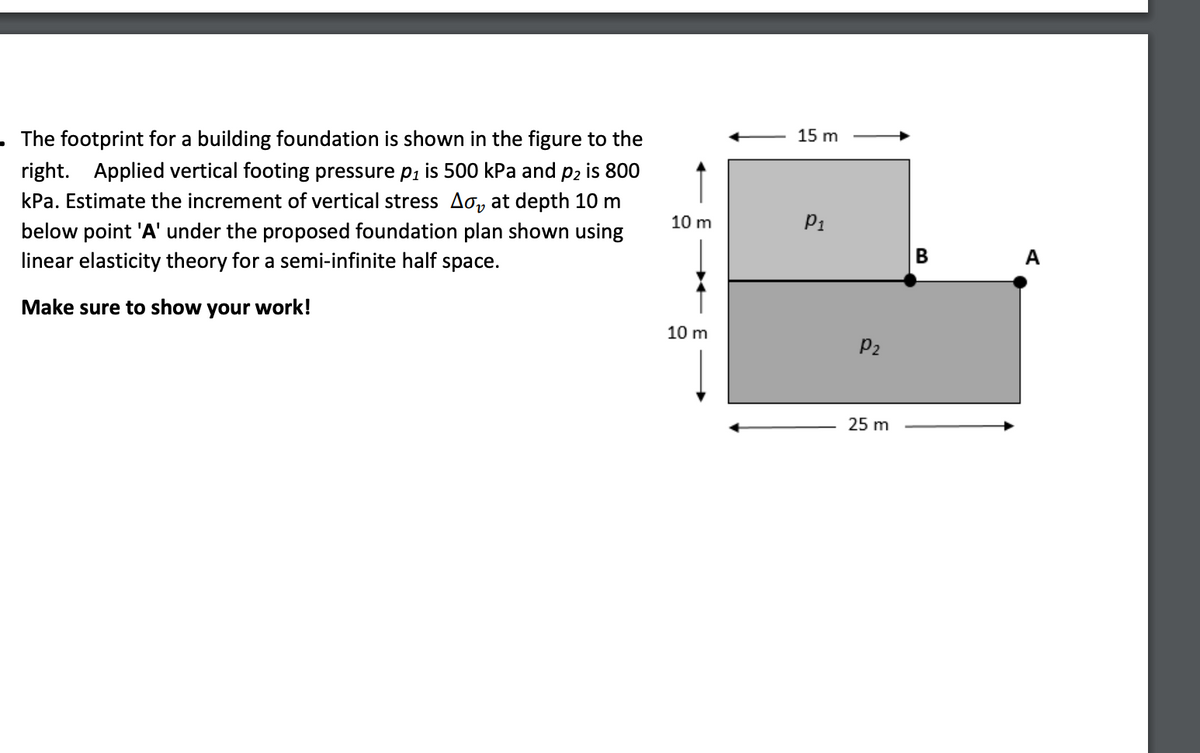
Answered The footprint for a building foundation… bartleby
Building Footprints Essential Data for Accurate Geospatial Analysis
ONEGEO Blog
Basic building footprint calculations • foot
What is a building footprint, and how do I work with it?
Building Footprints Are Polygons Representing The Extent Of Individual Building Structures In The Physical World.
In Gis, A Building Footprint Refers To A Polygon Or Set Of Polygons That Represent A Specific Building In The Physical World.
What Is A Building Footprint?
Building Footprint — Literally The Footprint Of A Building On The Ground, The Area Of The Surface That The Building Occupies.
Related Post: