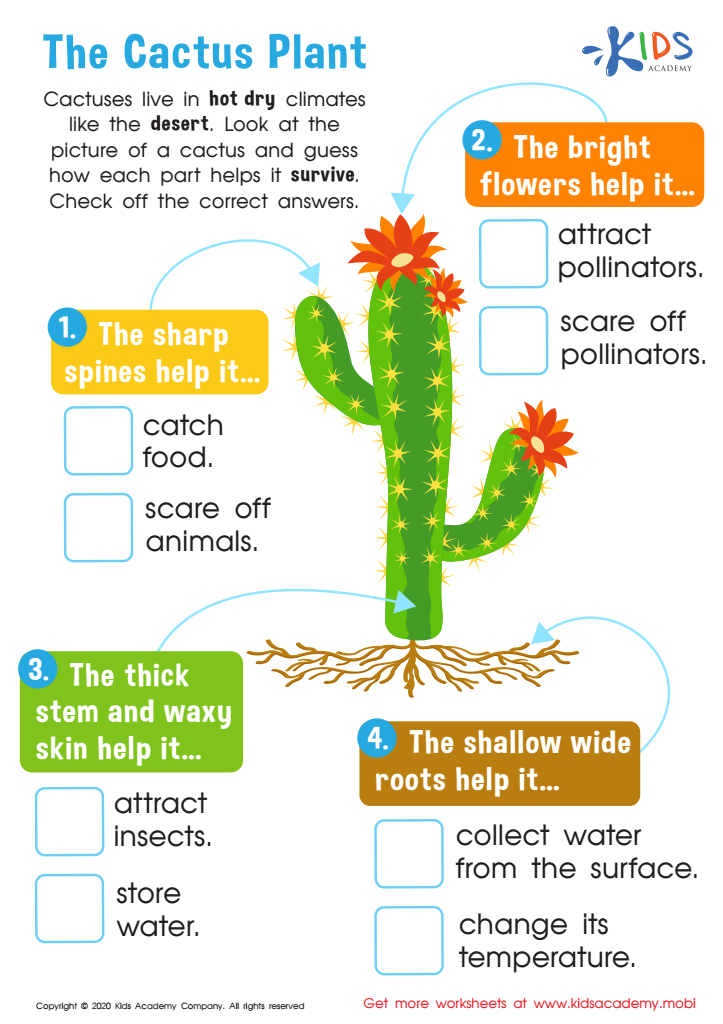
Building Vocabulary Plant Adaptations To Hot Dry Climates
Building Vocabulary Plant Adaptations To Hot Dry Climates - Plants must cope with extensive water loss. Leaves of the kukumakranka plant adapt to dry, hot conditions and continue photosynthesis by keeping their stomata open. Adaptations to reduce transpiration rate in dry environments include a thick cuticle, trichomes, and succulence. Their adaptations may help them increase water intake, decrease water loss, or store water when it. Up to 24% cash back photorespiration can drain away as much as 50% of the carbon fixed by the calvin cycle on a hot, dry day. Plant adaptations to hot, dry climates drag the terms at the left to the appropriate targets on the right to complete the sentences. Plants that are adapted to very dry environments are called xerophytes. Plants are exposed to extreme temperatures and drought conditions. Some plants have no leaves. C4 plants have evolved which of the following photosynthetic adaptations in hot, dry climates? Plants are exposed to extreme temperatures and drought conditions. This reduces water loss through transpiration. Summer deciduous plants loose their leaves when hot, dry. Not all terms will be used. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Plant adaptations to hot, dry climates part a 1. In hot and dry climates plants will have an increased rate of transpiration, the release of water through the stomata of plant cells. Plants living in dry climates, such as cacti and succulents, have several adaptations to help them survive: Plant adaptations to hot, dry climates drag the terms at the left to the appropriate targets on the right to complete the sentences. Not all terms will be used. Closing stomata on a hot, dry day is an adaptation that reduces water loss, but it also repvents co2 from entering the lead and o2 from leaving. Students will understand that plants are able to handle environmental challenges using a variety of adaptations. As a result, co2 levels get very low in the. Plant adaptations to hot, dry climates drag. Winds are often strong, and dry out plants. Not all terms will be used. Plants in hot and dry conditions experience rapid photosynthesis and respiration, leading to quick water vapor loss. This reduces water loss through transpiration. When such plants close their stomata on hot, dry days to. Plant adaptations to hot, dry climates drag the terms at the left to the appropriate targets on the right to complete the sentences. Plants “breathe” or respire through their leaves. Some plants have no leaves. As a result, co2 levels get very low in the. Up to 24% cash back photorespiration can drain away as much as 50% of the. Plants must cope with extensive water loss. Plants in hot and dry conditions experience rapid photosynthesis and respiration, leading to quick water vapor loss. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Not all terms will be used. In hot and dry climates plants will have an increased rate of transpiration, the release of water through. Plants “breathe” or respire through their leaves. Winds are often strong, and dry out plants. Not all terms will be used. Closing stomata on a hot, dry day is an adaptation that reduces water loss, but it also repvents co2 from entering the lead and o2 from leaving. Start studying lesson 14 plant adaptations. Leaves of the kukumakranka plant adapt to dry, hot conditions and continue photosynthesis by keeping their stomata open. Plants have adapted to hot, dry conditions in a variety of ways, one of which is by developing small leaves to reduce their surface area and water loss. Plant adaptations to hot, dry climates part a 1. Plants in hot and dry. Students will understand that plants are able to handle environmental challenges using a variety of adaptations. Winds are often strong, and dry out plants. Summer deciduous plants loose their leaves when hot, dry. Start studying lesson 14 plant adaptations. Plants in such conditions have special adaptations to reduce. When such plants close their stomata on hot, dry days to. Plant adaptations to hot, dry climates drag the terms at the left to the appropriate targets on the right to complete the sentences. Closing stomata on a hot, dry day is an adaptation that reduces water loss, but it also repvents co2 from entering the lead and o2 from. Leaves are covered by a. Plants “breathe” or respire through their leaves. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. This reduces water loss through transpiration. Adaptations to reduce transpiration rate in dry environments include a thick cuticle, trichomes, and succulence. Some plants have no leaves. Winds are often strong, and dry out plants. Summer deciduous plants loose their leaves when hot, dry. C4 plants have evolved which of the following photosynthetic adaptations in hot, dry climates? Plant adaptations to hot, dry climates drag the terms at the left to the appropriate targets on the right to complete the sentences. Winds are often strong, and dry out plants. Adaptations to reduce transpiration rate in dry environments include a thick cuticle, trichomes, and succulence. Plants “breathe” or respire through their leaves. In hot and dry climates plants will have an increased rate of transpiration, the release of water through the stomata of plant cells. Plant adaptations to hot, dry climates drag the terms at the left to the appropriate targets on the right to complete the sentences. Plants are exposed to extreme temperatures and drought conditions. As a result, co2 levels get very low in the. When such plants close their stomata on hot, dry days to. Plant adaptations to hot, dry climates drag the terms at the left to the appropriate targets on the right to complete the sentences. Their adaptations may help them increase water intake, decrease water loss, or store water when it. Leaves of the kukumakranka plant adapt to dry, hot conditions and continue photosynthesis by keeping their stomata open. Plants in hot and dry conditions experience rapid photosynthesis and respiration, leading to quick water vapor loss. Up to 24% cash back photorespiration can drain away as much as 50% of the carbon fixed by the calvin cycle on a hot, dry day. Plants in such conditions have special adaptations to reduce. Plants have adapted to hot, dry conditions in a variety of ways, one of which is by developing small leaves to reduce their surface area and water loss. Some plants have no leaves.Plant Adaptations Poster Teach Starter
PPT Plant Adaptations PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6899917
Plants Plant Adaptations for Grade 1
illustration of biology, Adaptation of Plant, The leaves in hot or dry
Plant adaptations
PPT How do plants adapt to their environment? PowerPoint Presentation
PPT 7CD Variation and feeding relationships PowerPoint Presentation
Chapter 10 Photosynthesis ppt download
1 Morphological adaptations by plants growing in dry and hot climates
Vocabulary Plant Adaptations printable pdf download
Not All Terms Will Be Used.
Plants Must Cope With Extensive Water Loss.
Start Studying Lesson 14 Plant Adaptations.
Summer Deciduous Plants Loose Their Leaves When Hot, Dry.
Related Post: