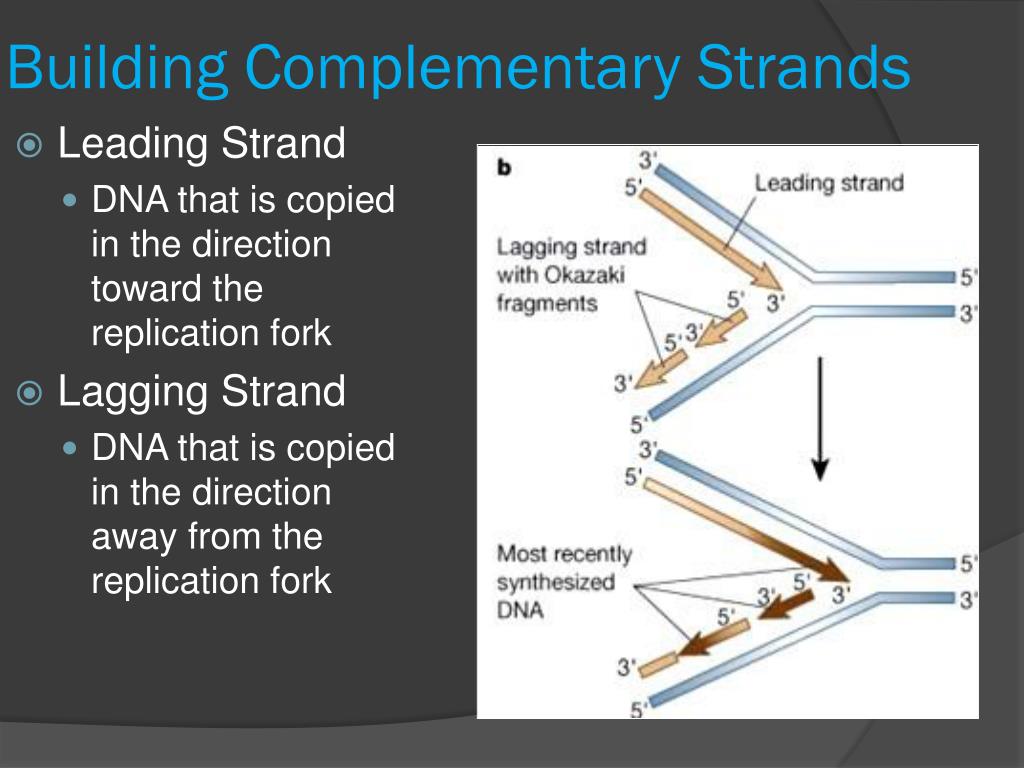
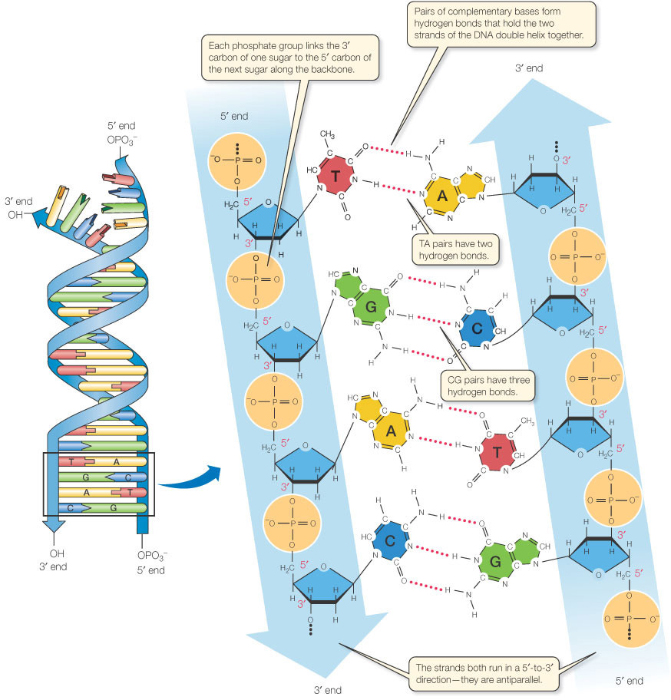
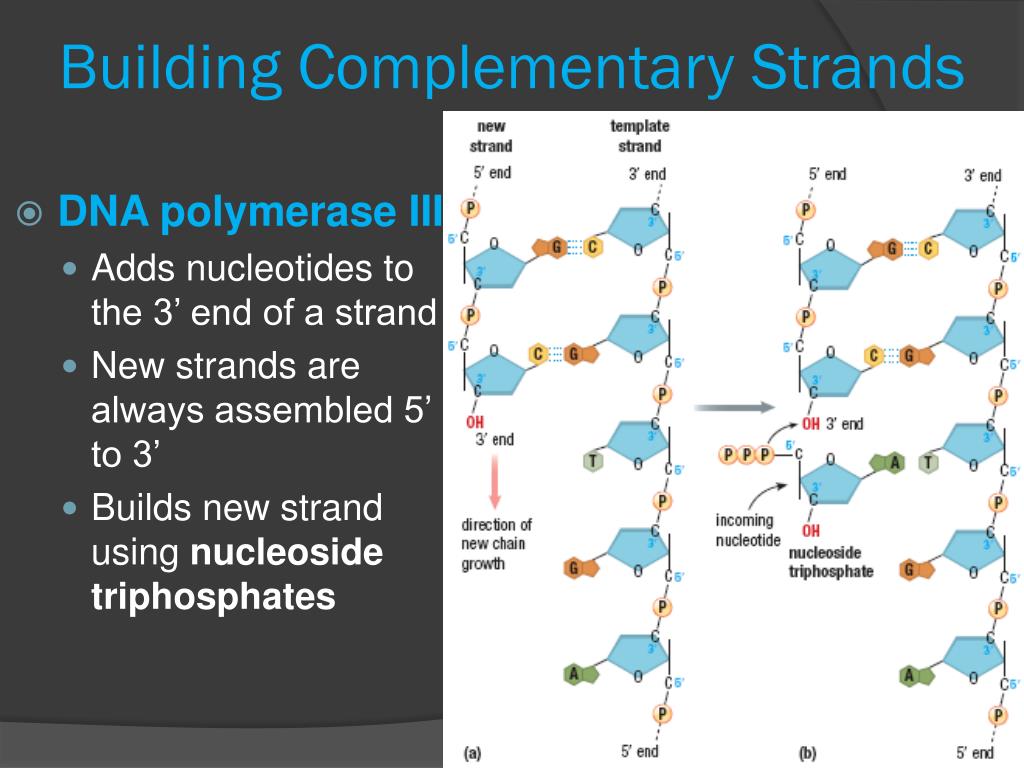
Builds A New Dna Strand By Adding Complementary Bases
Builds A New Dna Strand By Adding Complementary Bases - A new primer is added as the replication fork is further opened and the dna polymerase delta builds the new dna strand away from the replication fork, creating okazaki. As discussed in chapter 3, dna replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. One new strand is made continuously, while the other strand is made in pieces. See how replication forks, origins of replication,. The enzyme then catalyzes the formation of an ester. The other strand, complementary to the 5’ to 3’ parental dna, grows away from the replication fork, so the polymerase must move back toward the replication fork to begin adding bases to a. Explore the history, enzymes, and proofreading of dna replication, and the role of telomeres in protecting. Primers are removed, new dna. Once it hits part of the. Dna polymerase, an enzyme, recognizes each base in a template strand and matches it to the complementary base in a free nucleotide. Learn how dna replicates by adding complementary bases to form new strands. Explore the history, enzymes, and proofreading of dna replication, and the role of telomeres in protecting. Learn how dna polymerases catalyze the formation of a new complementary strand by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of a growing chain. Explore the structure and function of nucleotides and dna replication in this interactive activity. Builds a new dna strand by adding complementary bases 6. The enzyme then catalyzes the. New bases are added to the complementary parental strands. Stabilizes the dna molecule during replication by easing torsion upstream an downstream. Dna polymerase controls the addition of dna nucleotides to the new strand of dna. Dna polymerase, an enzyme, recognizes each base in a template strand and matches it to the complementary base in a free nucleotide. In this process, a dna polymerase attaches to the single stranded dna and builds the complementary strand while moving away from the replication fork. Explore the history, enzymes, and proofreading of dna replication, and the role of telomeres in protecting. Primers are removed, new dna. Dna polymerase, an enzyme, recognizes each base in a template strand and matches it to. A new primer is added as the replication fork is further opened and the dna polymerase delta builds the new dna strand away from the replication fork, creating okazaki. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like enzyme that undwinds dna, fragments of copied dna created on the lagging strand, strand that is copied in a continuous. Learn how. Dna polymerase controls the addition of dna nucleotides to the new strand of dna. Builds a new dna strand by adding complementary bases 6. See how replication forks, origins of replication,. Learn how dna polymerases catalyze the formation of a new complementary strand by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of a growing chain. Dna polymerase, an enzyme, recognizes each. Dna polymerase controls the addition of dna nucleotides to the new strand of dna. Learn how dna replicates by adding complementary bases to form new strands. One new strand is made continuously, while the other strand is made in pieces. Primers are removed, new dna. See how replication forks, origins of replication,. One new strand is made continuously, while the other strand is made in pieces. See how replication forks, origins of replication,. Primers are removed, new dna. Dna polymerase controls the addition of dna nucleotides to the new strand of dna. The other strand, complementary to the 5’ to 3’ parental dna, grows away from the replication fork, so the polymerase. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like enzyme that undwinds dna, fragments of copied dna created on the lagging strand, strand that is copied in a continuous. Dna polymerase can only synthesize dna in. One new strand is made continuously, while the other strand is made in pieces. Learn how dna replicates by adding complementary bases to form. Dna polymerase synthesizes new strands of dna along each template strand by adding complementary nucleotides to the chain. Dna polymerase, an enzyme, recognizes each base in a template strand and matches it to the complementary base in a free nucleotide. An enzyme called ‘dna polymerase’ drives the process of building a new strand of dna. As discussed in chapter 3,. Learn how dna polymerases catalyze the formation of a new complementary strand by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of a growing chain. Once it hits part of the. Builds a new dna strand by adding complementary bases 6. Stabilizes the dna molecule during replication by easing torsion upstream an downstream. Dna polymerase synthesizes new strands of dna along each. See how replication forks, origins of replication,. Learn how dna polymerases catalyze the formation of a new complementary strand by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of a growing chain. As discussed in chapter 3, dna replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. Explore. Stabilizes the dna molecule during replication by easing torsion upstream an downstream. Explore the structure and function of nucleotides and dna replication in this interactive activity. Dna polymerase, an enzyme, recognizes each base in a template strand and matches it to the complementary base in a free nucleotide. New bases are added to the complementary parental strands. An enzyme called. One new strand is made continuously, while the other strand is made in pieces. Explore the structure and function of nucleotides and dna replication in this interactive activity. See how replication forks, origins of replication,. As discussed in chapter 3, dna replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. Stabilizes the dna molecule during replication by easing torsion upstream an downstream. Dna polymerase, an enzyme, recognizes each base in a template strand and matches it to the complementary base in a free nucleotide. Primers are removed, new dna. New bases are added to the complementary parental strands. The enzyme then catalyzes the formation of an ester. Learn how dna polymerases catalyze the formation of a new complementary strand by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of a growing chain. Explore the history, enzymes, and proofreading of dna replication, and the role of telomeres in protecting. Dna polymerase controls the addition of dna nucleotides to the new strand of dna. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like enzyme that undwinds dna, fragments of copied dna created on the lagging strand, strand that is copied in a continuous. The enzyme then catalyzes the. Builds a new dna strand by adding complementary bases 6. Topoisomerases (red) reduce torsional strain caused by the unwinding of the dna double helix;PPT DNA Hereditary Molecules of Life PowerPoint Presentation, free
Solved Unzipped Complementary Single Strand Strand Build the
Question Video Determining the Complementary Sequence of a DNA Strand
DNA Replication · Concepts of Biology
Original Template Dna Strand
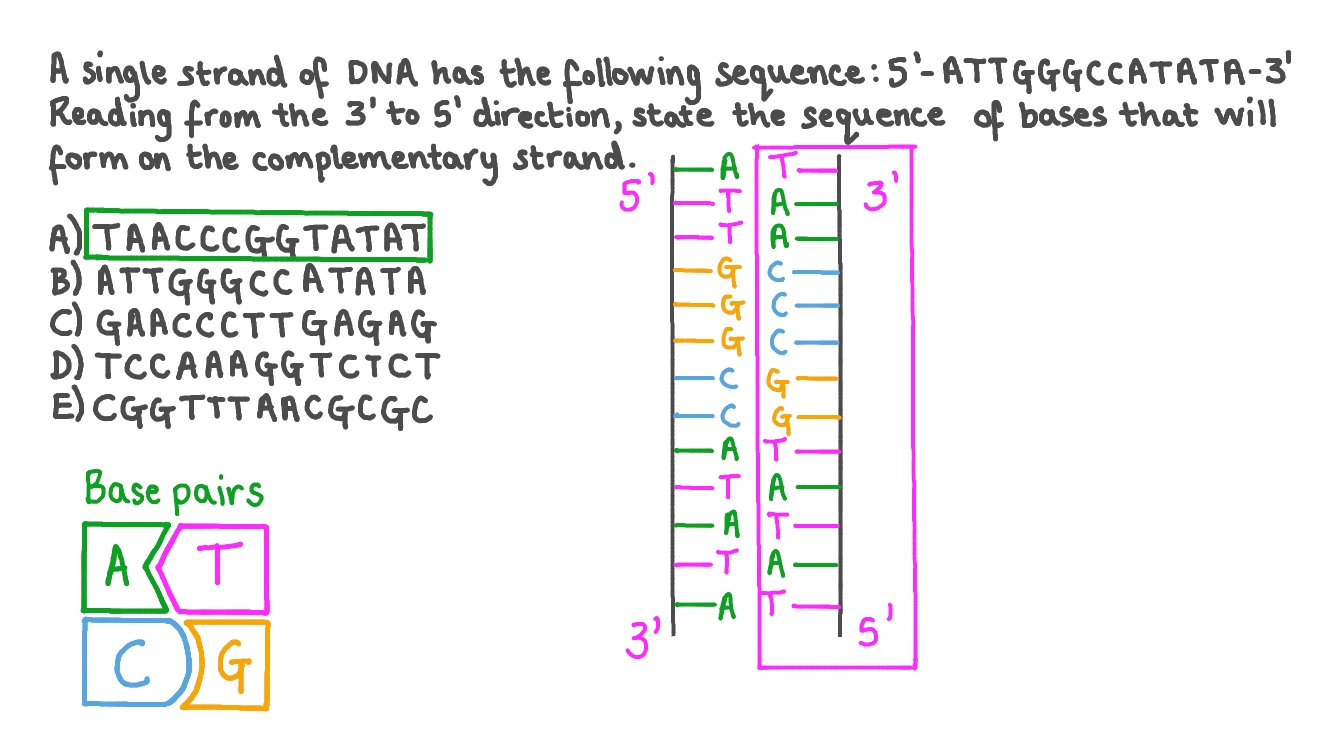
Question Video Determining the Complementary Sequence of Bases to a
DNA. Structure and Replication Presentation Biology
PPT DNA Hereditary Molecules of Life PowerPoint Presentation, free
What is Complementary Bases in DNA
PPT DNA Hereditary Molecules of Life PowerPoint Presentation, free
Learn How Dna Replicates By Adding Complementary Bases To Form New Strands.
An Enzyme Called ‘Dna Polymerase’ Drives The Process Of Building A New Strand Of Dna.
Dna Polymerase Can Only Synthesize Dna In.
Dna Polymerase Synthesizes New Strands Of Dna Along Each Template Strand By Adding Complementary Nucleotides To The Chain.
Related Post:
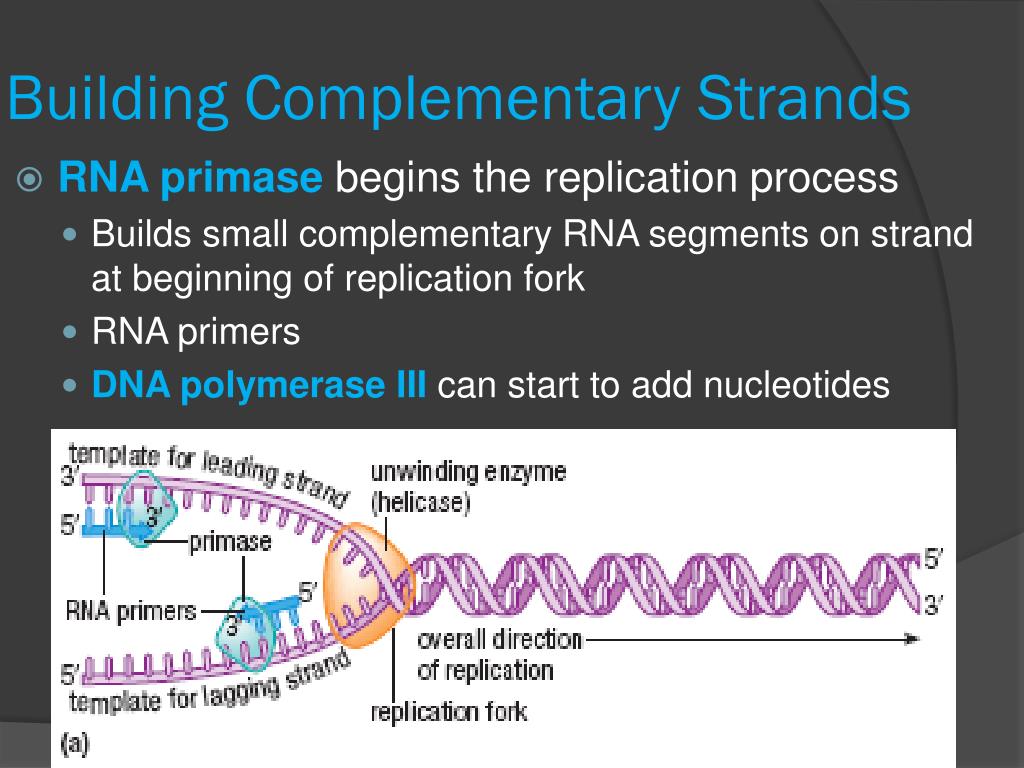



.PNG)