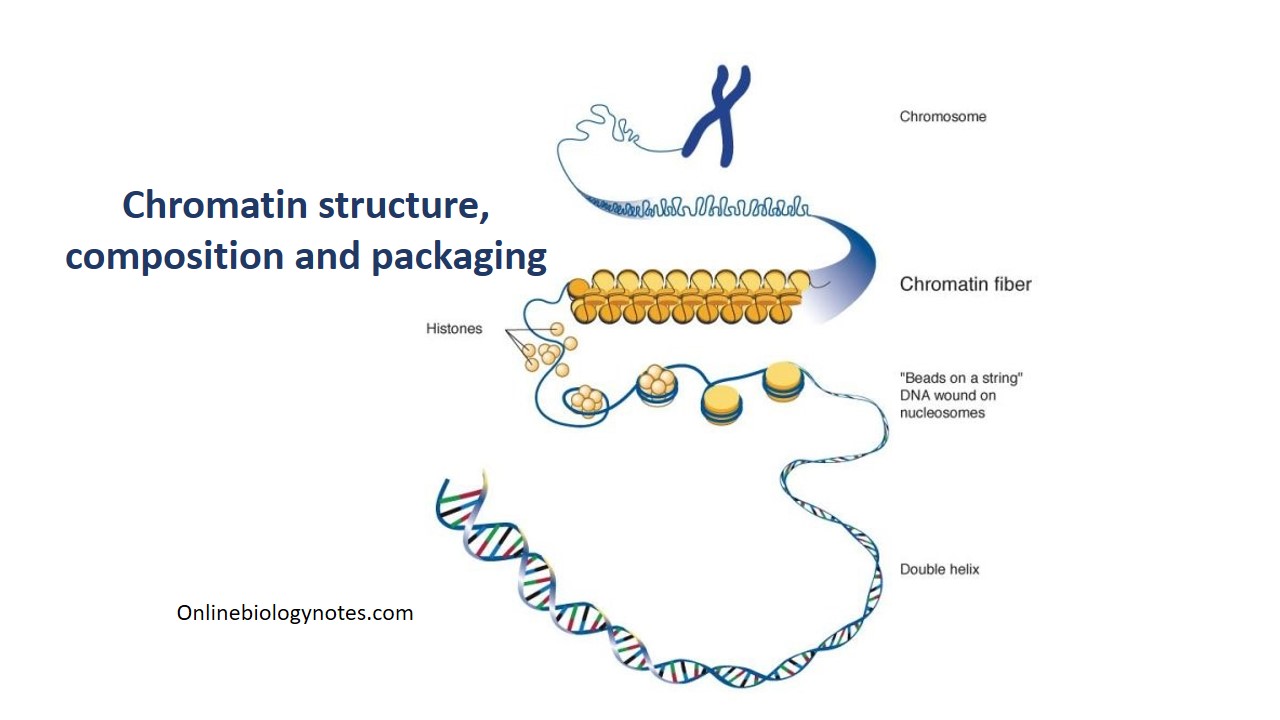
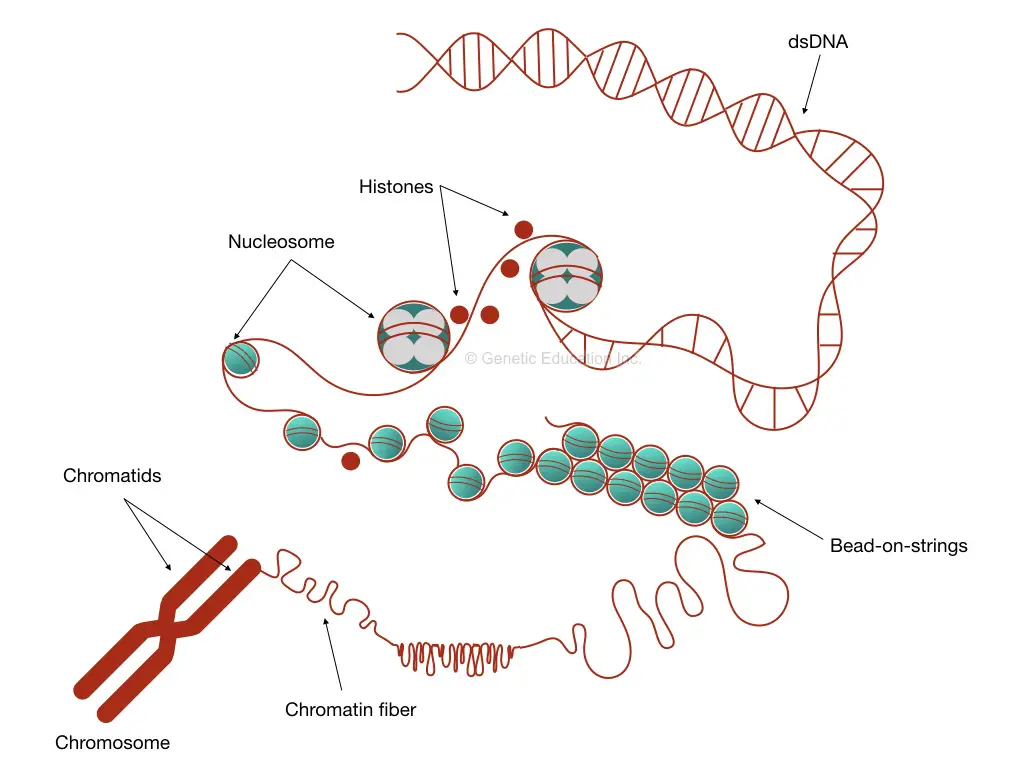
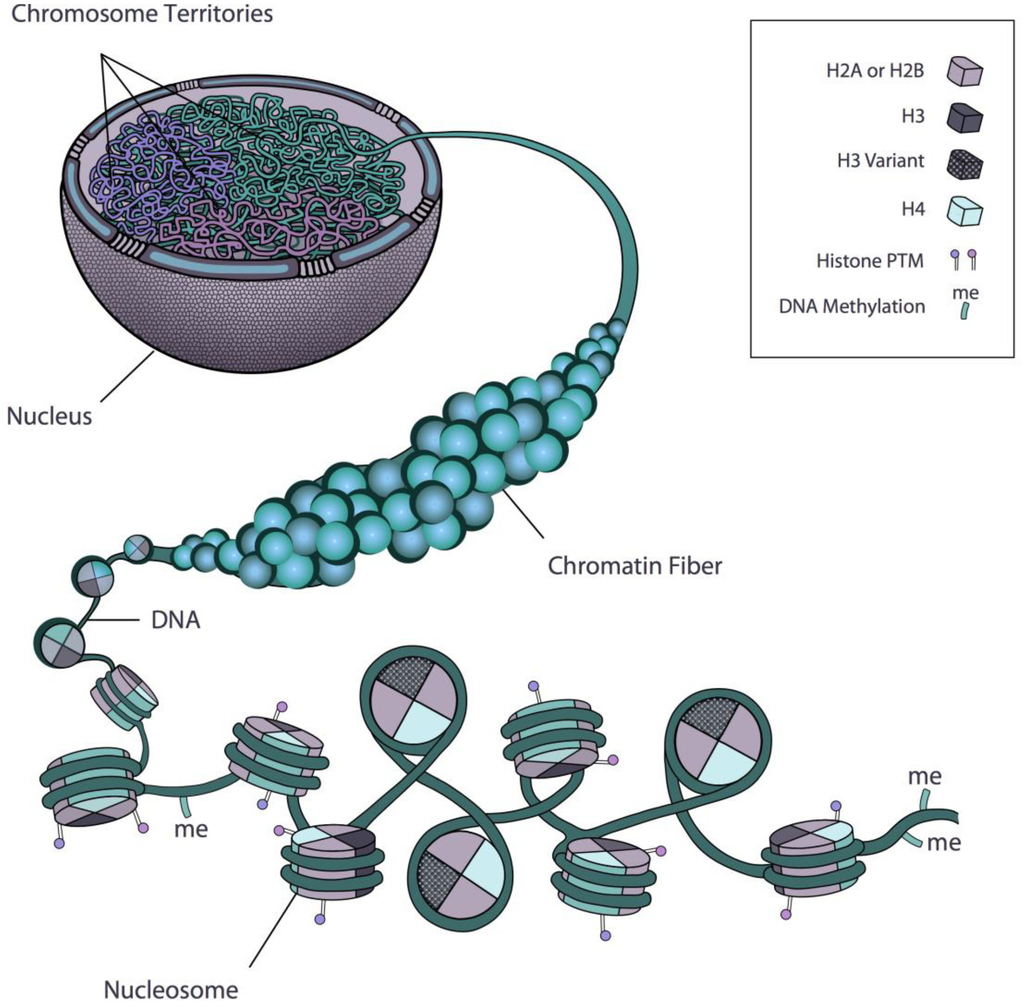
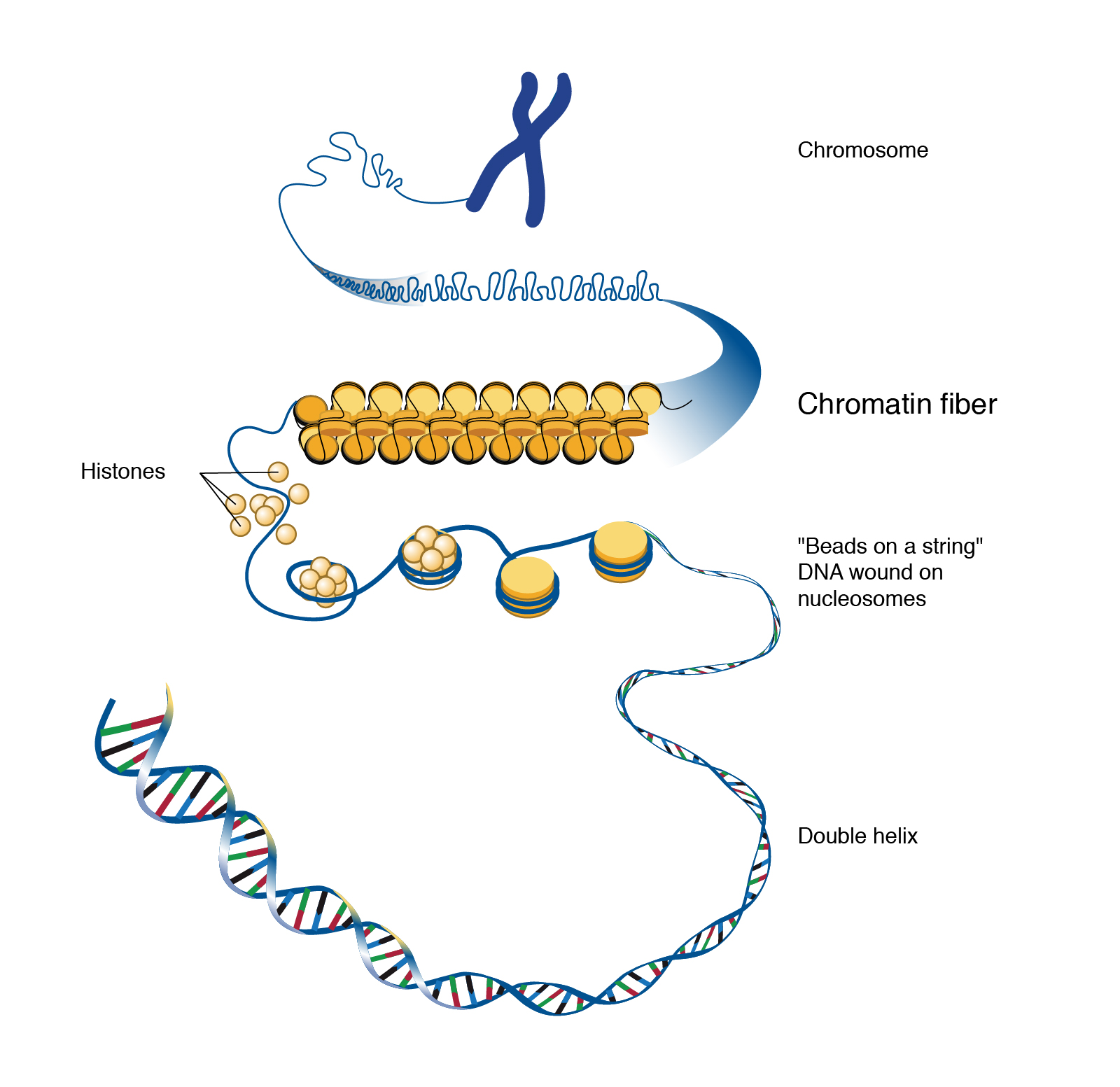
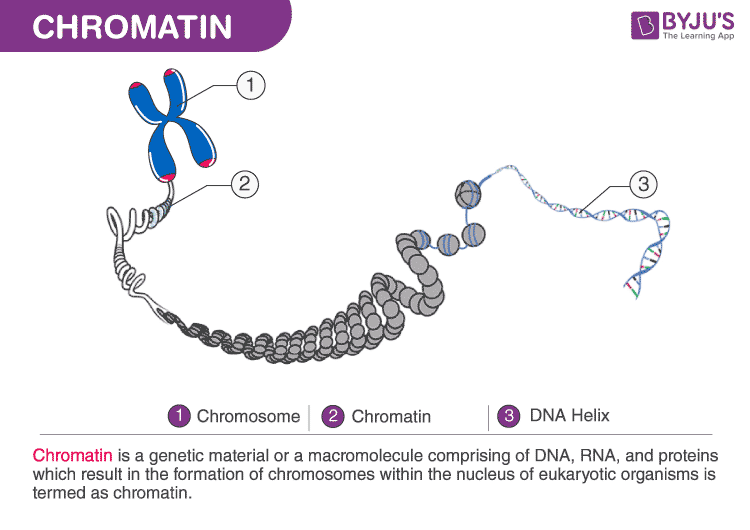
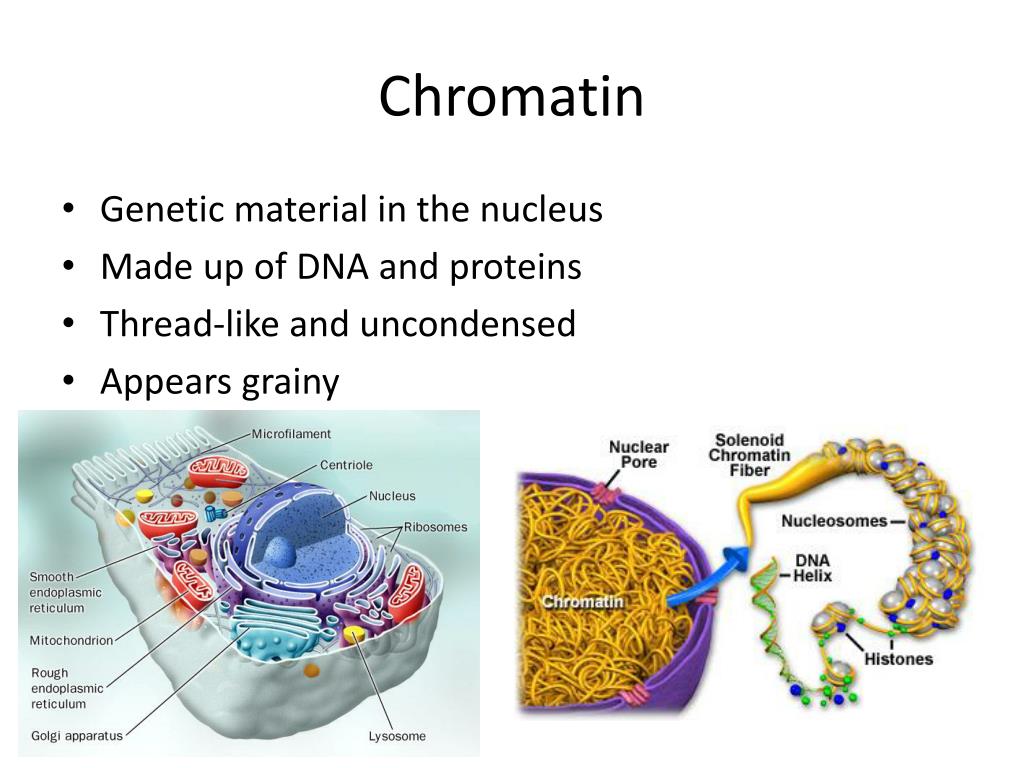
Chromatin Is The Building Material Of
Chromatin Is The Building Material Of - Understanding the mechanisms driving this. Its primary function is to package dna to fit into the cell, to strengthen the dna. Explore the intricate architecture of dna, from its nucleotide building blocks to the complex organization of chromatin. Dna is the genetic material that carries genetic information, and proteins help package and regulate the structure of dna. Dna, histone proteins, chromatin remodelers and transcription factors. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is the molecular blueprint. A systematic effort is needed to create a robust catalogue of human gene functions to mitigate this biased understanding of human genes. Inside the cell nucleus, dna and proteins form a complex called chromatin, which has several levels of organization, allowing cells to cram 2 meters of dna into a nucleus that. The chromatin fiber also supports gene expression and replication of. It is a dynamic and highly organized structure that enables the. Chromatin is a complex of dna and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. To package dna into a smaller. Thus, materials with heavy atoms. It is a dynamic and highly organized structure that enables the. During wintering, red tilapia may develop variable black spots on their bodies, significantly reducing their market value. Chromatin domains in yeast can be generated in vitro from four defined components: Inside the cell nucleus, dna and proteins form a complex called chromatin, which has several levels of organization, allowing cells to cram 2 meters of dna into a nucleus that. Chromatin is the combination of dna and proteins that make up the contents of the nucleus of a cell. The primary functions of chromatin are: Its primary function is to package dna to fit into the cell, to strengthen the dna. Chromatin is a complex of dna and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Inside the cell nucleus, chromatin fiber interacts with itself to condense into a chromosome. Dna is the genetic material that carries genetic information, and proteins help package and regulate the structure of dna. It is a dynamic and highly organized structure that enables. To package dna into a smaller. The primary functions of chromatin are: Its primary function is to package dna to fit into the cell, to strengthen the dna. Thus, materials with heavy atoms. Chromatin is the combination of dna and proteins that make up the contents of the nucleus of a cell. The higher the atomic number, the brighter the material appears in the image. Thus, materials with heavy atoms. Inside the cell nucleus, dna and proteins form a complex called chromatin, which has several levels of organization, allowing cells to cram 2 meters of dna into a nucleus that. Inside the cell nucleus, chromatin fiber interacts with itself to condense into. Inside the cell nucleus, dna and proteins form a complex called chromatin, which has several levels of organization, allowing cells to cram 2 meters of dna into a nucleus that. Explore the intricate architecture of dna, from its nucleotide building blocks to the complex organization of chromatin. Inside the cell nucleus, chromatin fiber interacts with itself to condense into a. To package dna into a smaller. Chromatin domains in yeast can be generated in vitro from four defined components: Dna, histone proteins, chromatin remodelers and transcription factors. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is the molecular blueprint. The primary function is to package long dna molecules into more compact, denser structures. Its primary function is to package dna to fit into the cell, to strengthen the dna. Chromatin, the complex of dna and proteins within the nucleus of a cell, plays a crucial role in the storage, organization, and regulation of genetic information. Dna, histone proteins, chromatin remodelers and transcription factors. Such reference data would annotate the. It is a dynamic. Chromatin is a complex of dna and protein that forms the major component of eukaryotic chromosomes. Understanding the mechanisms driving this. Explore the intricate architecture of dna, from its nucleotide building blocks to the complex organization of chromatin. Inside the cell nucleus, dna and proteins form a complex called chromatin, which has several levels of organization, allowing cells to cram. Together, the entire complex of dna and proteins that is the building material of chromosomes is referred to as chromatin. To package dna into a smaller. Understanding the mechanisms driving this. The primary function is to package long dna molecules into more compact, denser structures. Chromatin is a complex of dna and protein found in eukaryotic cells. Thus, materials with heavy atoms. The chromatin fiber also supports gene expression and replication of. Together, the entire complex of dna and proteins that is the building material of chromosomes is referred to as chromatin. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is the molecular blueprint. Chromatin is made up of dna and proteins. Dna is the genetic material that carries genetic information, and proteins help package and regulate the structure of dna. Inside the cell nucleus, dna and proteins form a complex called chromatin, which has several levels of organization, allowing cells to cram 2 meters of dna into a nucleus that. Chromatin is a complex of dna and protein that forms the. Chromatin, the complex of dna and proteins within the nucleus of a cell, plays a crucial role in the storage, organization, and regulation of genetic information. Inside the cell nucleus, chromatin fiber interacts with itself to condense into a chromosome. Together, the entire complex of dna and proteins that is the building material of chromosomes is referred to as chromatin. Chromatin is composed of dna, histone, and nonhistone proteins as well as. Inside the cell nucleus, dna and proteins form a complex called chromatin, which has several levels of organization, allowing cells to cram 2 meters of dna into a nucleus that. These genetic memories can degrade over. Nuclear dna does not appear in free linear strands; The bse detector reveals differences in atomic number; Explore the intricate architecture of dna, from its nucleotide building blocks to the complex organization of chromatin. Thus, materials with heavy atoms. A systematic effort is needed to create a robust catalogue of human gene functions to mitigate this biased understanding of human genes. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in reinforcing the dna during cell division, preventing dna damage, and regulating gene expression and dna replication. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or dna, is the molecular blueprint. Chromatin is made up of dna and proteins. Its primary function is to package dna to fit into the cell, to strengthen the dna. Dna is the genetic material that carries genetic information, and proteins help package and regulate the structure of dna.Chromatin structure, composition and packaging Online Biology Notes
What are chromatin? Definition, Types and Importance biology AESL
Inside Chromatin Definition, Structure, and Function Education
Biology Free FullText Insights into Chromatin Structure and
Chromatin
Chromatin Structure, Functions and Chromatin Analysis
PPT Structure of Chromatin PowerPoint Presentation, free download
PPT Structure of Material PowerPoint Presentation, free
Histone Description, Chromatin, Structure, Functions, & Facts
What are chromatin? Definition, Types and Importance biology AESL
To Package Dna Into A Smaller.
Chromatin Is A Complex Of Dna And Proteins That Forms Chromosomes Within The Nucleus Of Eukaryotic Cells.
Such Reference Data Would Annotate The.
The Findings Show That Cells Use Transcriptional Memories To Establish Predictable, Stable Behaviors Within Tissues, Backman Said.
Related Post: