Commercial Building Depreciation Rate
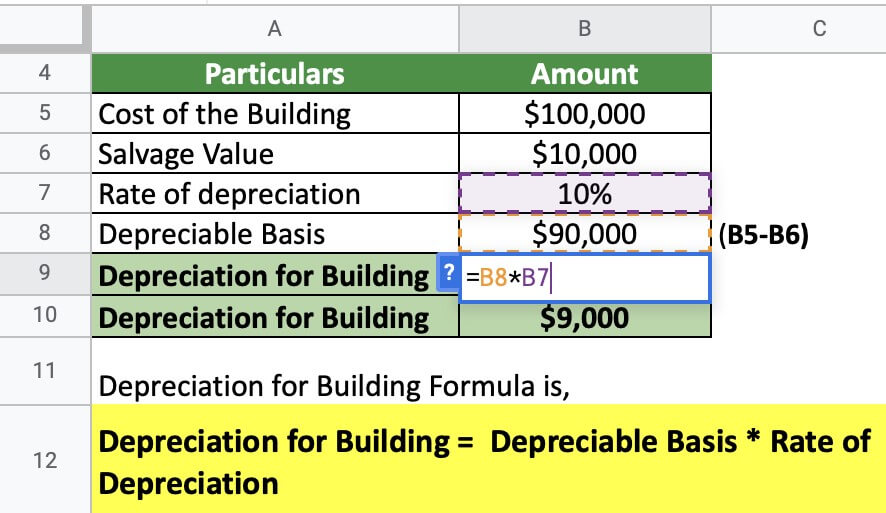
Commercial Building Depreciation Rate - To calculate the depreciable basis, we subtract the salvage value ($10,000) from the cost of building ($100,000). Depending on the type and age of your property, you could claim depreciation on the building’s structure of up to 4% a year. Assuming a 37% federal income tax rate, that would save. A building depreciation rate is the percentage at which the value of a building decreases over time due to factors like aging, wear and tear, and obsolescence. Depreciation methods for commercial property vary, each offering a different approach to expense allocation over the asset’s useful life. Depreciation reduces the tax basis of a commercial property over time, allowing the owner to claim yearly tax deductions. For example, if you use your car 60% for business use, depreciation can be claimed on 60% of the cost. Commercial and residential buildings can be depreciated over a certain number of years based on the type of property. Commercial building depreciation life commercial buildings are typically depreciated over 39 years, allowing owners to spread out the property's cost and reduce. Learn key methods and maximize your tax benefits with. These methods are crucial for. Learn key methods and maximize your tax benefits with. To calculate the depreciation, we multiply the. Understanding depreciation in rental property. How does depreciation affect the value of a commercial property? Depreciation methods for commercial property vary, each offering a different approach to expense allocation over the asset’s useful life. Commercial building depreciation life commercial buildings are typically depreciated over 39 years, allowing owners to spread out the property's cost and reduce. Depending on the type and age of your property, you could claim depreciation on the building’s structure of up to 4% a year. Understanding the depreciation life of a commercial roof is essential for businesses to manage assets effectively and optimize tax benefits. A building depreciation rate is the percentage at which the value of a building decreases over time due to factors like aging, wear and tear, and obsolescence. For tax purposes in the united states, the irs assigns a useful life of 39 years to commercial properties, meaning the building's value can be deducted in equal portions (using. These methods are crucial for. To calculate the depreciation, we multiply the. Only the business portion of the asset can be depreciated on your tax return. Depreciation reduces the tax. Depending on the type and age of your property, you could claim depreciation on the building’s structure of up to 4% a year. These methods are crucial for. Depreciation enables property owners to gradually recover the cost of assets over their useful life, thereby helping to reduce taxable income and potentially improve bottom line. Depreciation methods for commercial property vary,. Only the business portion of the asset can be depreciated on your tax return. When discussing depreciation, especially in commercial real estate investment contexts, it’s crucial to discern between two primary categories: To calculate the depreciation, we multiply the. Learn key methods and maximize your tax benefits with. Depending on the type and age of your property, you could claim. When discussing depreciation, especially in commercial real estate investment contexts, it’s crucial to discern between two primary categories: To calculate the depreciable basis, we subtract the salvage value ($10,000) from the cost of building ($100,000). Depreciation reduces the tax basis of a commercial property over time, allowing the owner to claim yearly tax deductions. Depreciation methods for commercial property vary,. Understanding the depreciation life of a commercial roof is essential for businesses to manage assets effectively and optimize tax benefits. Depreciation methods for commercial property vary, each offering a different approach to expense allocation over the asset’s useful life. Assuming a 37% federal income tax rate, that would save. How does depreciation affect the value of a commercial property? For. Learn key methods and maximize your tax benefits with. The lifespan of a roof impacts financial. Depreciation reduces the tax basis of a commercial property over time, allowing the owner to claim yearly tax deductions. To calculate the depreciation, we multiply the. When discussing depreciation, especially in commercial real estate investment contexts, it’s crucial to discern between two primary categories: For tax purposes in the united states, the irs assigns a useful life of 39 years to commercial properties, meaning the building's value can be deducted in equal portions (using. How does depreciation affect the value of a commercial property? To calculate the depreciation, we multiply the. Depreciation reduces the tax basis of a commercial property over time, allowing the. Assuming a 37% federal income tax rate, that would save. These methods are crucial for. When discussing depreciation, especially in commercial real estate investment contexts, it’s crucial to discern between two primary categories: Depending on the type and age of your property, you could claim depreciation on the building’s structure of up to 4% a year. A building depreciation rate. How does depreciation affect the value of a commercial property? Learn key methods and maximize your tax benefits with. Depending on the type and age of your property, you could claim depreciation on the building’s structure of up to 4% a year. When discussing depreciation, especially in commercial real estate investment contexts, it’s crucial to discern between two primary categories:. To calculate the depreciation, we multiply the. The lifespan of a roof impacts financial. Understanding depreciation in rental property. A building depreciation rate is the percentage at which the value of a building decreases over time due to factors like aging, wear and tear, and obsolescence. How does depreciation affect the value of a commercial property? Depreciation methods for commercial property vary, each offering a different approach to expense allocation over the asset’s useful life. Commercial building depreciation life commercial buildings are typically depreciated over 39 years, allowing owners to spread out the property's cost and reduce. Commercial and residential buildings can be depreciated over a certain number of years based on the type of property. Depreciation reduces the tax basis of a commercial property over time, allowing the owner to claim yearly tax deductions. Depending on the type and age of your property, you could claim depreciation on the building’s structure of up to 4% a year. To calculate the depreciable basis, we subtract the salvage value ($10,000) from the cost of building ($100,000). These methods are crucial for. Assuming a 37% federal income tax rate, that would save. The lifespan of a roof impacts financial. Only the business portion of the asset can be depreciated on your tax return. To calculate the depreciation, we multiply the. Understanding depreciation in rental property. Learn key methods and maximize your tax benefits with. How does depreciation affect the value of a commercial property? When discussing depreciation, especially in commercial real estate investment contexts, it’s crucial to discern between two primary categories: Understanding the depreciation life of a commercial roof is essential for businesses to manage assets effectively and optimize tax benefits.Popular Depreciation Methods To Calculate Asset Value Over The Years
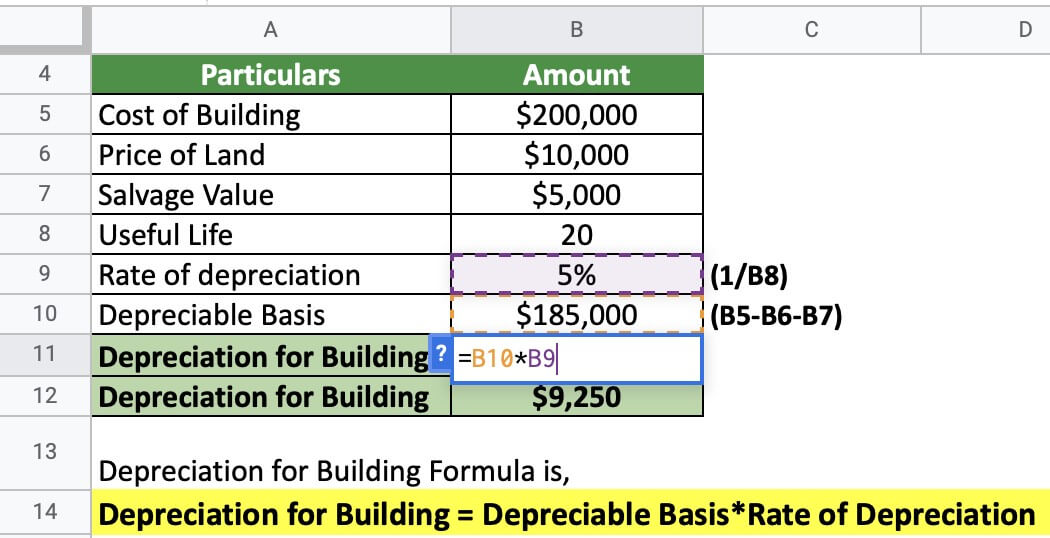
Depreciation for Building Definition, Formula, and Excel Examples
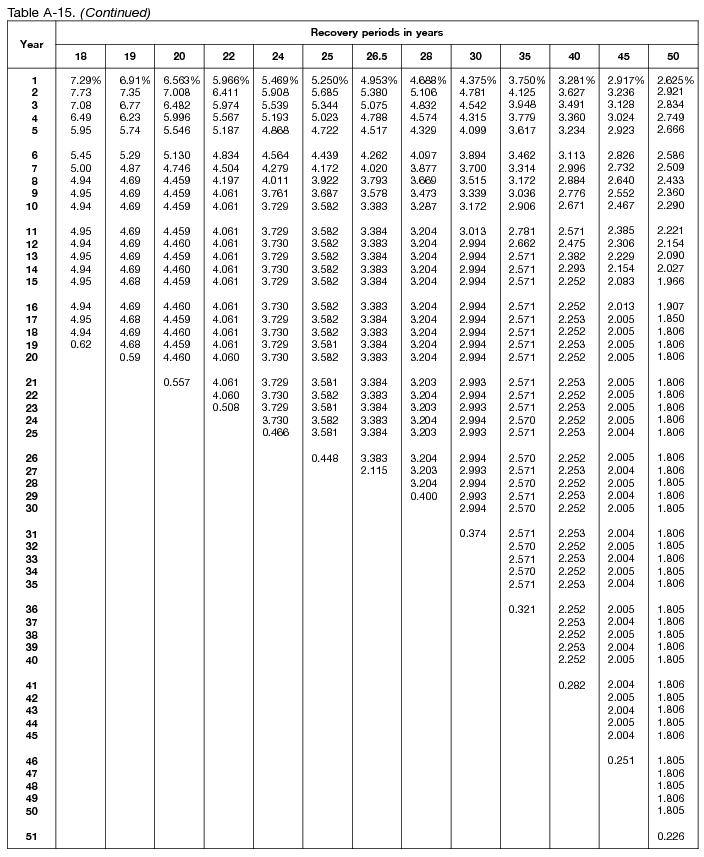
Macrs Ads Depreciation Table Elcho Table
MACRS Depreciation Table Guidance, Calculator + More
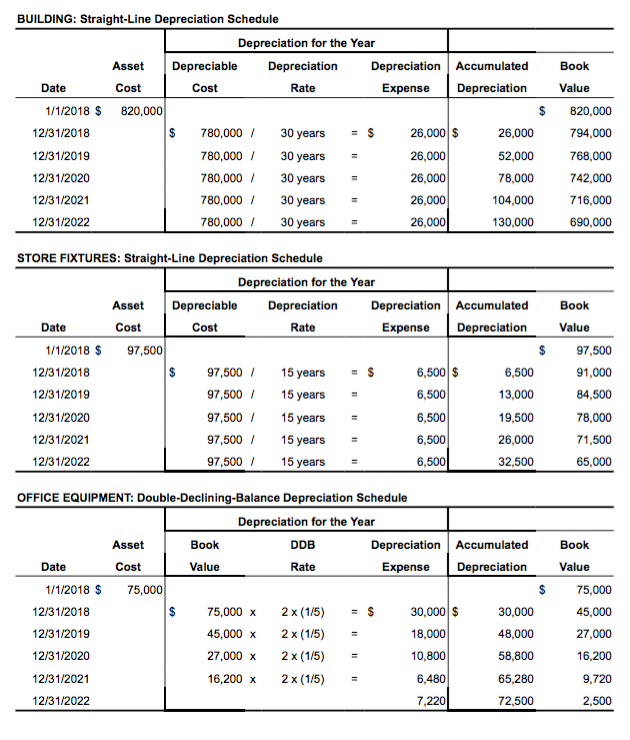
Solved BUILDING StraightLine Depreciation Schedule
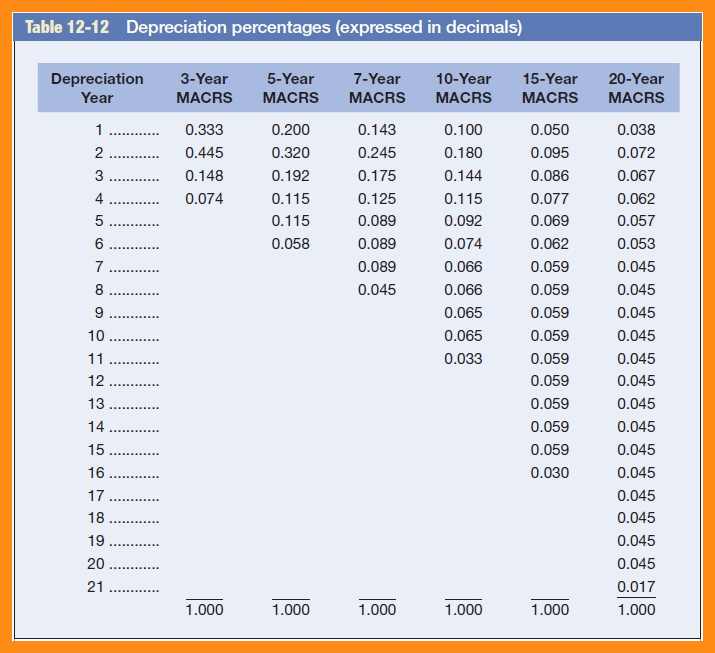
Guide to the MACRS Depreciation Method Chamber Of Commerce
MACRS Depreciation Tables & How to Calculate
Depreciation for Building Definition, Formula, and Excel Examples
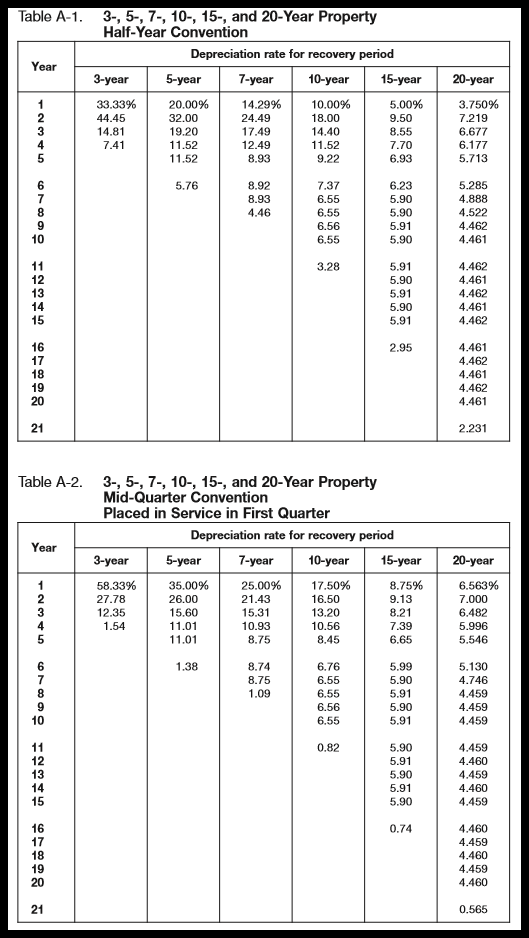
Using Percentage Tables to Calculate Depreciation Center for
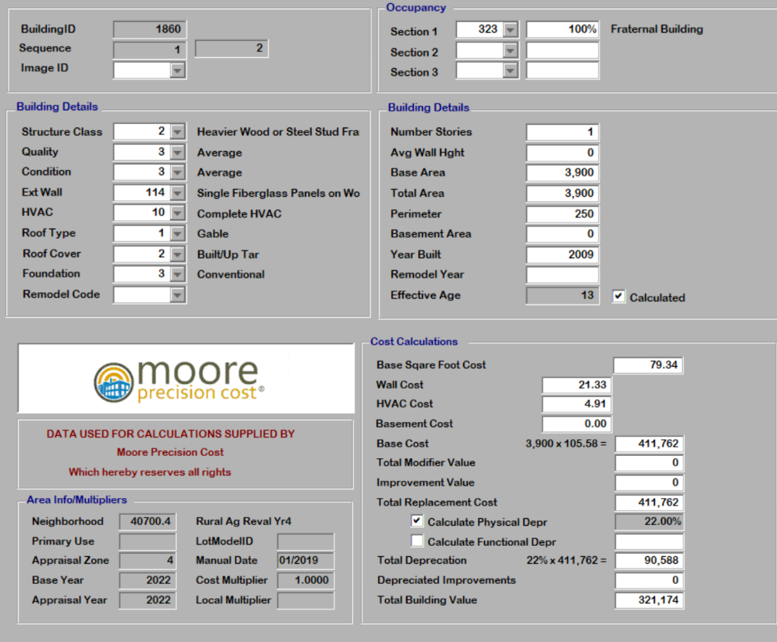
Commercial Building Depreciation Commercial Appraisal File 1
For Tax Purposes In The United States, The Irs Assigns A Useful Life Of 39 Years To Commercial Properties, Meaning The Building's Value Can Be Deducted In Equal Portions (Using.
For Example, If You Use Your Car 60% For Business Use, Depreciation Can Be Claimed On 60% Of The Cost.
Depreciation Enables Property Owners To Gradually Recover The Cost Of Assets Over Their Useful Life, Thereby Helping To Reduce Taxable Income And Potentially Improve Bottom Line.
A Building Depreciation Rate Is The Percentage At Which The Value Of A Building Decreases Over Time Due To Factors Like Aging, Wear And Tear, And Obsolescence.
Related Post: