Commercial Building Improvements Depreciation Life
Commercial Building Improvements Depreciation Life - There are several types of capital assets that can be depreciated when you use them in your business. For example, a commercial building has a useful life of 39 years, while machinery often has a shorter lifespan and higher depreciation using accelerated methods like the. Calculating depreciation for commercial property involves a systematic approach that incorporates various factors and decisions. Everything in the material world has a finite lifespan—be it gadgets, vehicles, or sprawling commercial buildings. Irs regulations and guidance explain how to take advantage of the change. This guide covers the fundamentals of commercial real estate depreciation, explains how it works, and highlights strategies like cost segregation studies and bonus depreciation to help you. No you don't have the option of choosing a shorter depreciable life even when you know it won't last 39 years. But, could these be expensed under the repair regulations?. The cares act corrected an error that had made qualified improvement property ineligible for bonus depreciation; The lifespan of a roof impacts financial. Land can never be depreciated. Depreciation reduces the tax basis of a commercial property over time, allowing the owner to claim yearly tax deductions. But, could these be expensed under the repair regulations?. Residential rental property is depreciated over a lengthy 27.5 years. This rate is relatively lower compared to commercial or industrial. Understanding the depreciation life of a commercial roof is essential for businesses to manage assets effectively and optimize tax benefits. Unlike employee wages or utility bills, taxpayers do not get an immediate tax deduction for the purchase of a building. Establish a baseline value and. For example, a commercial building has a useful life of 39 years, while machinery often has a shorter lifespan and higher depreciation using accelerated methods like the. How does depreciation affect the value of a commercial property? Residential buildings residential buildings typically have a depreciation rate of around 5% per year. Establish a baseline value and. Depreciation reduces the tax basis of a commercial property over time, allowing the owner to claim yearly tax deductions. There are several types of capital assets that can be depreciated when you use them in your business. Understanding depreciation in rental. Irs regulations and guidance explain how to take advantage of the change. Depreciation reduces the tax basis of a commercial property over time, allowing the owner to claim yearly tax deductions. This guide covers the fundamentals of commercial real estate depreciation, explains how it works, and highlights strategies like cost segregation studies and bonus depreciation to help you. Understanding depreciation. Over time, factors like natural wear, technological. But, could these be expensed under the repair regulations?. Land can never be depreciated. Everything in the material world has a finite lifespan—be it gadgets, vehicles, or sprawling commercial buildings. Irs regulations and guidance explain how to take advantage of the change. Residential buildings residential buildings typically have a depreciation rate of around 5% per year. Everything in the material world has a finite lifespan—be it gadgets, vehicles, or sprawling commercial buildings. Over time, factors like natural wear, technological. So the first thing you need to do if you own commercial real estate is separate out the cost of the land from. The process begins by determining the asset’s. Irs regulations and guidance explain how to take advantage of the change. How does depreciation affect the value of a commercial property? Land can never be depreciated. No you don't have the option of choosing a shorter depreciable life even when you know it won't last 39 years. There are several types of capital assets that can be depreciated when you use them in your business. The process begins by determining the asset’s. For example, a commercial building has a useful life of 39 years, while machinery often has a shorter lifespan and higher depreciation using accelerated methods like the. The cares act corrected an error that had. “building improvements” are capital events that materially extend the useful life of a building or increase the value of a building by at least 25 percent of the original life period or. For example, a commercial building has a useful life of 39 years, while machinery often has a shorter lifespan and higher depreciation using accelerated methods like the. Commercial. This rate is relatively lower compared to commercial or industrial. Learn how to assess depreciation timelines for capital improvements, distinguishing between real and personal property, and improvements versus repairs. Establish a baseline value and. The cares act corrected an error that had made qualified improvement property ineligible for bonus depreciation; Depreciation reduces the tax basis of a commercial property over. But, could these be expensed under the repair regulations?. Irs regulations and guidance explain how to take advantage of the change. Understanding depreciation in rental property. For example, a commercial building has a useful life of 39 years, while machinery often has a shorter lifespan and higher depreciation using accelerated methods like the. Understanding the depreciation life of a commercial. Residential buildings residential buildings typically have a depreciation rate of around 5% per year. Understanding depreciation in rental property. Understanding the depreciation life of a commercial roof is essential for businesses to manage assets effectively and optimize tax benefits. [3] can i depreciate the cost of land? This rate is relatively lower compared to commercial or industrial. Irs regulations and guidance explain how to take advantage of the change. Unlike employee wages or utility bills, taxpayers do not get an immediate tax deduction for the purchase of a building. So the first thing you need to do if you own commercial real estate is separate out the cost of the land from the cost of the improvements (buildings) on the land. The lifespan of a roof impacts financial. Residential buildings residential buildings typically have a depreciation rate of around 5% per year. Over time, factors like natural wear, technological. “building improvements” are capital events that materially extend the useful life of a building or increase the value of a building by at least 25 percent of the original life period or. But, could these be expensed under the repair regulations?. Understanding depreciation in rental property. This rate is relatively lower compared to commercial or industrial. Calculating depreciation for commercial property involves a systematic approach that incorporates various factors and decisions. For example, a commercial building has a useful life of 39 years, while machinery often has a shorter lifespan and higher depreciation using accelerated methods like the. The process begins by determining the asset’s. Depreciation reduces the tax basis of a commercial property over time, allowing the owner to claim yearly tax deductions. Land can never be depreciated. Everything in the material world has a finite lifespan—be it gadgets, vehicles, or sprawling commercial buildings.Understanding the Depreciation of a Commercial Building
Depreciable Life Of Commercial Flooring Viewfloor.co
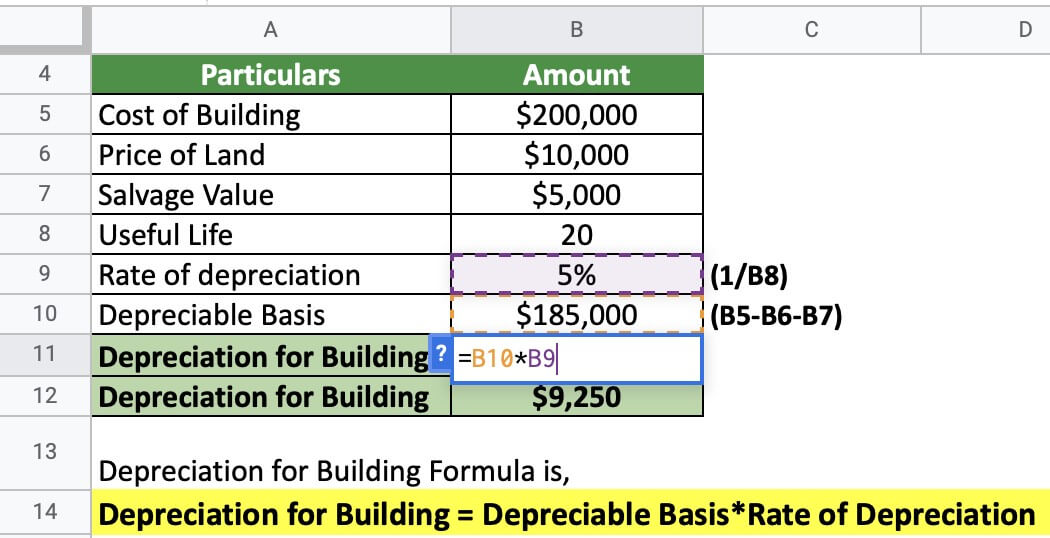
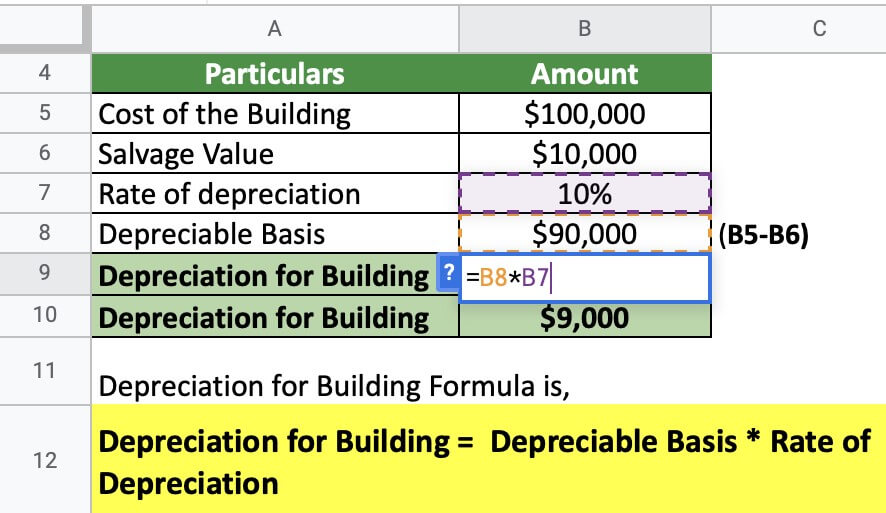
Depreciation for Building Definition, Formula, and Excel Examples
Understanding the Depreciation of a Commercial Building
Commercial Real Estate Depreciation Explained
Understanding the Depreciation of a Commercial Building
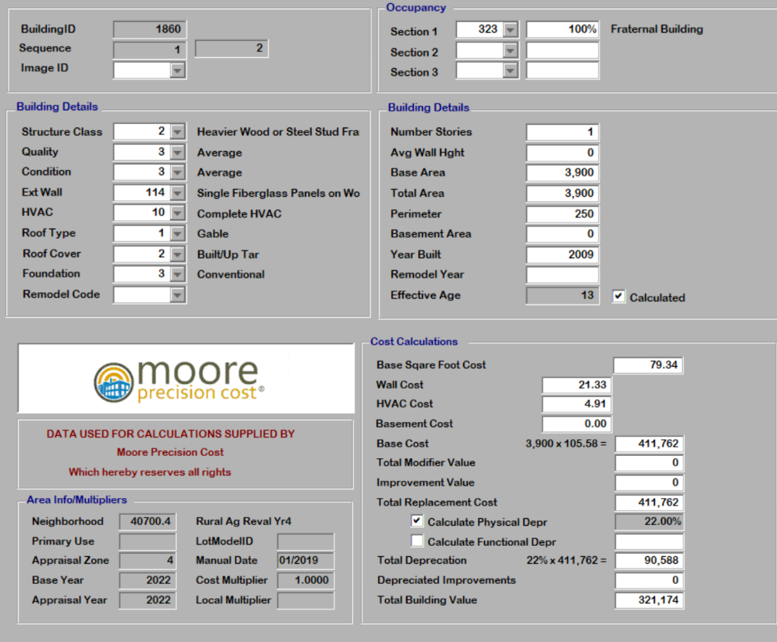
Commercial Building Depreciation Commercial Appraisal File 1
Depreciation for Building Definition, Formula, and Excel Examples
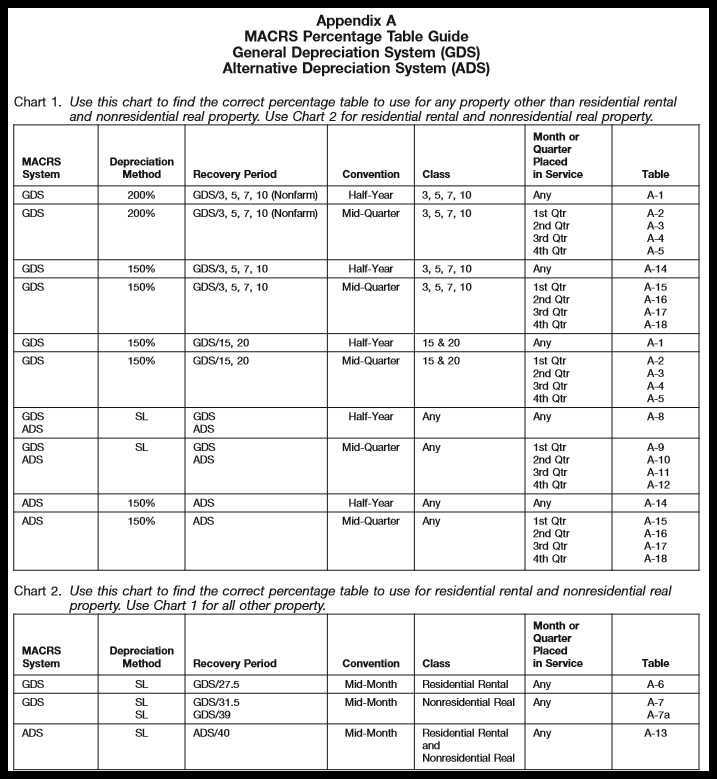
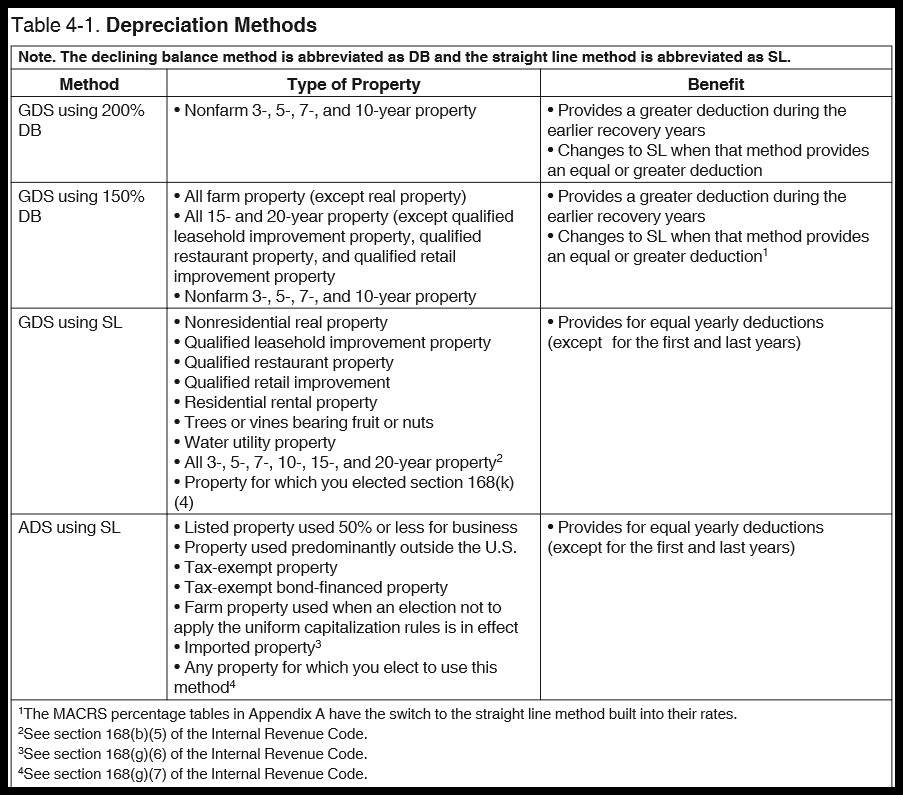
MACRS Depreciation Tables & How to Calculate
MACRS Depreciation Tables & How to Calculate
Understanding The Depreciation Life Of A Commercial Roof Is Essential For Businesses To Manage Assets Effectively And Optimize Tax Benefits.
There Are Several Types Of Capital Assets That Can Be Depreciated When You Use Them In Your Business.
Commercial Buildings And Improvements Are Depreciated Over 39 Years, But There Are Tax Breaks That Allow Deductions To Be Taken More Quickly For Certain Real Estate Investments.
How Does Depreciation Affect The Value Of A Commercial Property?
Related Post: