Consistency Builds Growth Perioperative Nutrition
Consistency Builds Growth Perioperative Nutrition - We examined the effects of malnutrition and. Surgical patients may present with varying degrees of malnutrition, sarcopenia, cachexia, obesity and myosteatosis. In a multimodal concept to optimize functional results after surgery, nutritional conditioning is a key aspect to achieve optimal results. Preoperative optimization can help improve outcomes. From a metabolic and nutritional point of view, the key aspects of perioperative care include: This overview will deal with three main questions (why,. Perioperative nutrition is recognized as a substantial issue, with significant weight loss being not uncommon. Perioperative nutritional support, included within the eras (enhanced recovery after surgery) protocol, has proven to be a main element and a critical step to achieve better surgical results. Hence, personalized nutrition is recommended for each patient during the pre. Malnutrition in this setting is multifactorial, including issues with. In this narrative review, we concisely aggregate emerging data to highlight the role of nutritional optimization as a promising, practical perioperative intervention to reduce complications and. To many, “nutrition” is a vague word that conjures visions of food pyramids, healthy salads (with dressing on the side), and daily vitamins. From a metabolic and nutritional point of view, the key aspects of perioperative care include: Hence, personalized nutrition is recommended for each patient during the pre. In a multimodal concept to optimize functional results after surgery, nutritional conditioning is a key aspect to achieve optimal results. Nutrition support might be indicated for individuals with malnutrition who require a surgical intervention, or for healthy individuals undergoing major surgery with a lengthy anticipated. • integration of nutrition into the overall management of the patient. Structured, multimodal prehabilitation including nutrition counseling improves various outcomes after elective cancer and orthopedic surgeries. Perioperative nutrition is recognized as a substantial issue, with significant weight loss being not uncommon. Poor nutrition has been demonstrated to correlate with adverse surgical outcomes. Despite these challenges, it is well known that suboptimal nutritional status is a strong independent pre. Perioperative nutrition is recognized as a substantial issue, with significant weight loss being not uncommon. Nutritional status is a strong predictor of postoperative outcomes and is recognized as an important component of surgical recovery programs. Poor nutrition has been demonstrated to correlate with adverse. The key aspects of perioperative care include integration of nutrition into the overall patient management, avoiding long periods of preoperative fasting, and reinstallation of oral feeding. Perioperative nutrition is recognized as a substantial issue, with significant weight loss being not uncommon. Surgical patients may present with varying degrees of malnutrition, sarcopenia, cachexia, obesity and myosteatosis. We examined the effects of. Preoperative optimization can help improve outcomes. Perioperative nutrition is recognized as a substantial issue, with significant weight loss being not uncommon. From a metabolic and nutritional point of view, the key aspects of perioperative care include: Perioperative malnutrition has proven to be challenging to define, diagnose, and treat. The focus of this guideline is to cover both nutritional aspects of. Nutrition support might be indicated for individuals with malnutrition who require a surgical intervention, or for healthy individuals undergoing major surgery with a lengthy anticipated. Preoperative optimization can help improve outcomes. Poor nutrition has been demonstrated to correlate with adverse surgical outcomes. Despite these challenges, it is well known that suboptimal nutritional status is a strong independent pre. Surgical patients. We examined the effects of malnutrition and. Malnutrition in this setting is multifactorial, including issues with. Surgical patients may present with varying degrees of malnutrition, sarcopenia, cachexia, obesity and myosteatosis. In this narrative review, we concisely aggregate emerging data to highlight the role of nutritional optimization as a promising, practical perioperative intervention to reduce complications and. Perioperative nutrition encompasses preoperative,. Structured, multimodal prehabilitation including nutrition counseling improves various outcomes after elective cancer and orthopedic surgeries. Surgical patients may present with varying degrees of malnutrition, sarcopenia, cachexia, obesity and myosteatosis. Preoperative optimization can help improve outcomes. We examined the effects of malnutrition and. The focus of this guideline is to cover both nutritional aspects of the enhanced recovery after surgery (eras). The key aspects of perioperative care include integration of nutrition into the overall patient management, avoiding long periods of preoperative fasting, and reinstallation of oral feeding. Structured, multimodal prehabilitation including nutrition counseling improves various outcomes after elective cancer and orthopedic surgeries. In a multimodal concept to optimize functional results after surgery, nutritional conditioning is a key aspect to achieve optimal. In this narrative review, we concisely aggregate emerging data to highlight the role of nutritional optimization as a promising, practical perioperative intervention to reduce complications and. Despite these challenges, it is well known that suboptimal nutritional status is a strong independent pre. Malnutrition in this setting is multifactorial, including issues with. Perioperative nutritional support, included within the eras (enhanced recovery. Perioperative nutrition encompasses preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care. Preoperative optimization can help improve outcomes. The key aspects of perioperative care include integration of nutrition into the overall patient management, avoiding long periods of preoperative fasting, and reinstallation of oral feeding. Poor nutrition has been demonstrated to correlate with adverse surgical outcomes. Structured, multimodal prehabilitation including nutrition counseling improves various outcomes. Despite these challenges, it is well known that suboptimal nutritional status is a strong independent pre. Preoperative optimization can help improve outcomes. Perioperative nutrition encompasses preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care. Perioperative nutritional support, included within the eras (enhanced recovery after surgery) protocol, has proven to be a main element and a critical step to achieve better surgical results. The focus. This overview will deal with three main questions (why,. Perioperative malnutrition has proven to be challenging to define, diagnose, and treat. Preoperative optimization can help improve outcomes. Surgical patients may present with varying degrees of malnutrition, sarcopenia, cachexia, obesity and myosteatosis. Poor nutrition has been demonstrated to correlate with adverse surgical outcomes. • integration of nutrition into the overall management of the patient. Despite these challenges, it is well known that suboptimal nutritional status is a strong independent pre. We examined the effects of malnutrition and. Hence, personalized nutrition is recommended for each patient during the pre. Perioperative nutritional support, included within the eras (enhanced recovery after surgery) protocol, has proven to be a main element and a critical step to achieve better surgical results. The key aspects of perioperative care include integration of nutrition into the overall patient management, avoiding long periods of preoperative fasting, and reinstallation of oral feeding. Nutritional status is a strong predictor of postoperative outcomes and is recognized as an important component of surgical recovery programs. In a multimodal concept to optimize functional results after surgery, nutritional conditioning is a key aspect to achieve optimal results. The focus of this guideline is to cover both nutritional aspects of the enhanced recovery after surgery (eras) concept and the special nutritional needs of patients. Perioperative nutrition encompasses preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care. From a metabolic and nutritional point of view, the key aspects of perioperative care include:Unresolved issues in perioperative nutrition A narrative review
Strategies for perioperative nutrition support in obese, diabetic and
Unresolved issues in perioperative nutrition A narrative review
PPT Nutrition care plan for surgical patients PowerPoint Presentation
Perioperative Nutrition Screen (PONS). This algorithmic approach is
Summary of key for perioperative nutrition care. POQI
Perioperative Nutrition Screen (PONS). This algorithmic approach is
Perioperative Nutrition Screen (PONS). This algorithmic approach is
Unresolved issues in perioperative nutrition A narrative review
ABCs of Perioperative Care Nutrition Surgical Interest Group of
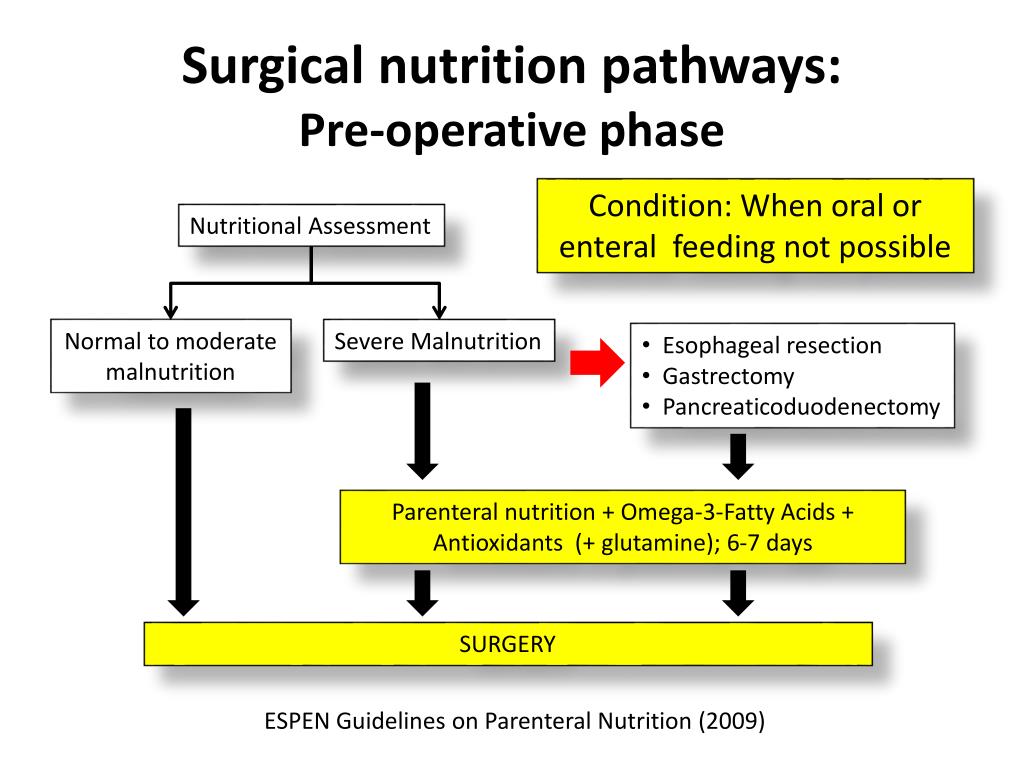
Malnutrition In This Setting Is Multifactorial, Including Issues With.
Several Barriers Lead To Insufficient Postoperative Nutrition Intake, Like The Lack Of Knowledge Regarding Nutrition Management, And Unnecessary Postoperative Fasting Periods.
Structured, Multimodal Prehabilitation Including Nutrition Counseling Improves Various Outcomes After Elective Cancer And Orthopedic Surgeries.
To Many, “Nutrition” Is A Vague Word That Conjures Visions Of Food Pyramids, Healthy Salads (With Dressing On The Side), And Daily Vitamins.
Related Post: