Dehydration Synthesis Builds Molecules By Removing A
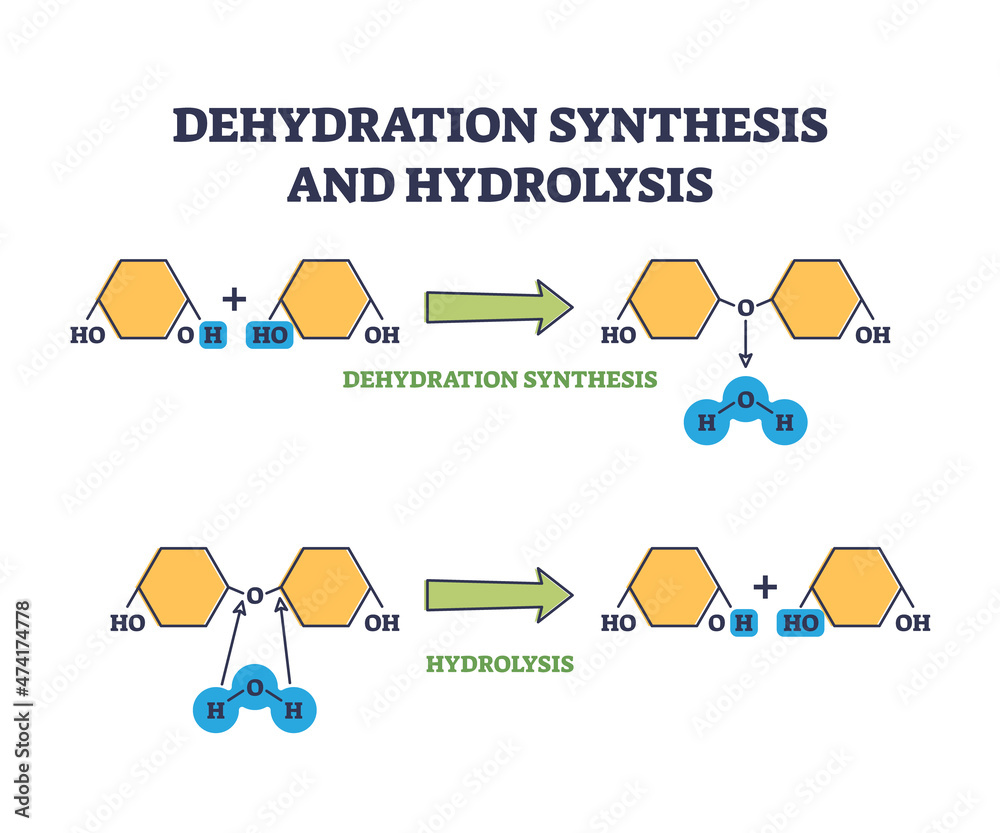
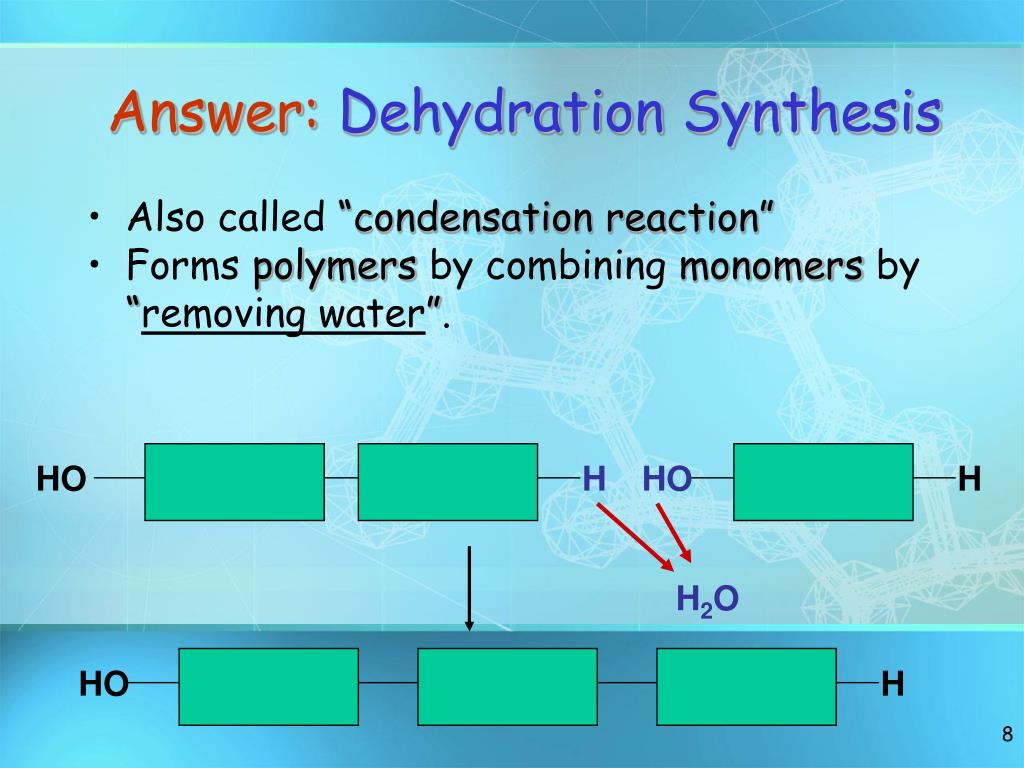
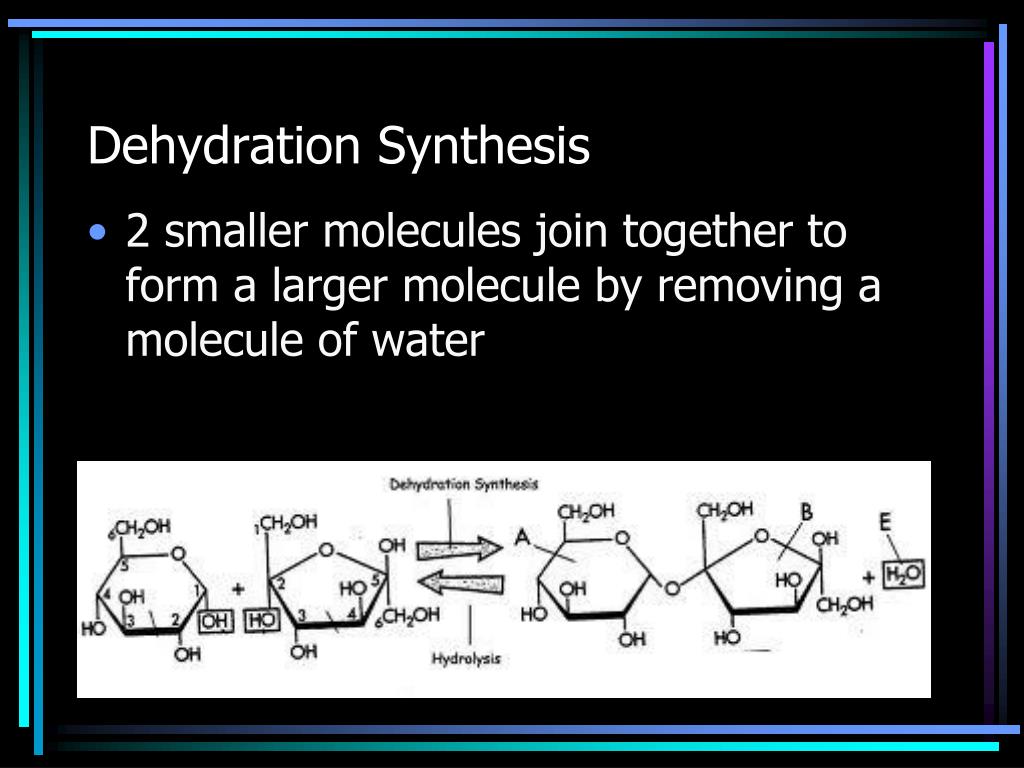
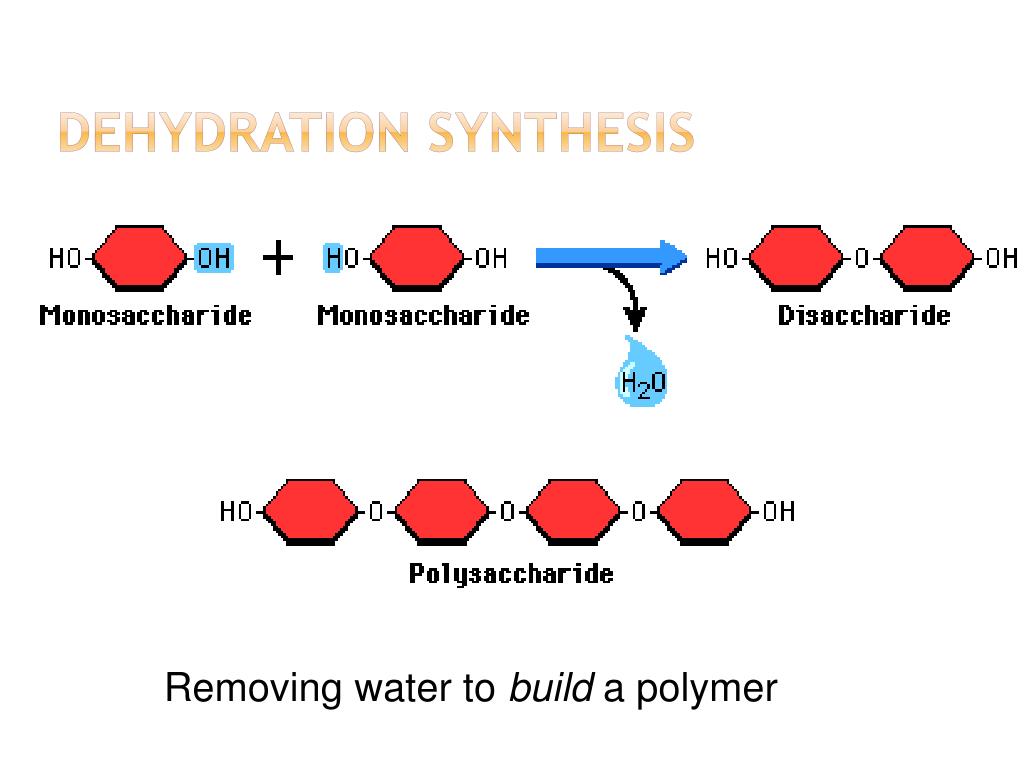
Dehydration Synthesis Builds Molecules By Removing A - This reaction is essential for the formation of macromolecules,. In the process of dehydration synthesis, two smaller molecules are joined chemically while removing elements from both the reactant molecules and forming a new. Also known as a condensation reaction or a dehydration reaction, dehydration synthesis occurs when two molecules are joined by removing water. This process is crucial in forming larger biological macromolecules. Many reactions involving dehydration synthesis are associated with the formation of biological polymers where the addition of each monomer is accompanied by the elimination. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. On the basis of the structure of hydrocarbons, organic. This process is crucial in forming larger organic molecules, such. In dehydration synthesis, a water molecule is removed as two monomers join to form a polymer. Dehydration synthesis refers to the formation of larger molecules from smaller reactants, accompanied by the loss of a water molecule. While dehydration synthesis builds complex molecules by removing water, hydrolysis breaks them down by adding water. Dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis are complementary reactions in biological systems. Many reactions involving dehydration synthesis are associated with the formation of biological polymers where the addition of each monomer is accompanied by the elimination. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. In the process of dehydration synthesis, two smaller molecules are joined chemically while removing elements from both the reactant molecules and forming a new. Dehydration synthesis refers to the formation of larger molecules from smaller reactants, accompanied by the loss of a water molecule. Also known as a condensation reaction or a dehydration reaction, dehydration synthesis occurs when two molecules are joined by removing water. This process is crucial in forming larger organic molecules, such. Dehydration synthesis builds larger molecules by removing water and forming bonds, while. Dehydration synthesis is the reverse process of hydrolysis, where a water molecule is added to break apart larger molecules. In the process of dehydration synthesis, two smaller molecules are joined chemically while removing elements from both the reactant molecules and forming a new. This process is crucial for the formation of glycosidic bonds in carbohydrates and peptide. While dehydration synthesis builds complex molecules by removing water, hydrolysis breaks them down by adding water. This process is crucial in forming. On the basis of the structure of hydrocarbons, organic. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. In dehydration synthesis, a water molecule is removed as two monomers join to form a polymer. In the process of dehydration synthesis, two smaller molecules are joined chemically while removing elements from both the reactant molecules and forming a new. This process. This process is crucial for the formation of glycosidic bonds in carbohydrates and peptide. While dehydration synthesis builds complex molecules by removing water, hydrolysis breaks them down by adding water. Many reactions involving dehydration synthesis are associated with the formation of biological polymers where the addition of each monomer is accompanied by the elimination. On the basis of the structure. Dehydration synthesis is the reverse process of hydrolysis, where a water molecule is added to break apart larger molecules. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as. This process is crucial in forming larger organic molecules, such. Dehydration synthesis is a chemical reaction in which two molecules are joined together by the removal of a water molecule. When p/p 0. This process is crucial for the formation of glycosidic bonds in carbohydrates and peptide. The monomers combine with each other via covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. Dehydration synthesis builds larger molecules by removing water, while hydrolysis breaks down compounds into smaller parts using water, with examples like combining glucose and fructose. Dehydration synthesis is a reaction. This process is crucial for the formation of glycosidic bonds in carbohydrates and peptide. While dehydration synthesis builds complex molecules by removing water, hydrolysis breaks them down by adding water. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as byproducts. The monomers combine with each other via covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as polymers. Dehydration synthesis, also known as. This process is crucial in forming larger organic molecules, such. Dehydration synthesis builds larger molecules by removing water and forming bonds, while. Dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis are two fundamental chemical. At low relative pressure, h 2 o molecules predominantly adsorb near the organic ligands, mainly near the o atoms of the terephthalic acid ligands. When p/p 0 = 0.625, the. This reaction is essential for the formation of macromolecules,. Dehydration synthesis, also known as a condensation reaction, facilitates the formation of covalent bonds between monomers, resulting in polymers. In the process of dehydration synthesis, two smaller molecules are joined chemically while removing elements from both the reactant molecules and forming a new. When p/p 0 = 0.625, the. Dehydration synthesis. This process is crucial in forming larger biological macromolecules. This type of reaction is dehydration synthesis, which means “to put together while losing water.” figure 1. On the basis of the structure of hydrocarbons, organic. Also known as a condensation reaction or a dehydration reaction, dehydration synthesis occurs when two molecules are joined by removing water. While dehydration synthesis builds. Dehydration synthesis refers to the formation of larger molecules from smaller reactants, accompanied by the loss of a water molecule. Dehydration synthesis builds larger molecules by removing water and forming bonds, while. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as. Dehydration synthesis builds larger molecules by removing water, while hydrolysis breaks down compounds into smaller parts using water, with examples. Dehydration synthesis, also known as a condensation reaction, facilitates the formation of covalent bonds between monomers, resulting in polymers. At low relative pressure, h 2 o molecules predominantly adsorb near the organic ligands, mainly near the o atoms of the terephthalic acid ligands. This reaction is essential for the formation of macromolecules,. Dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis are two fundamental chemical. Dehydration synthesis refers to the formation of larger molecules from smaller reactants, accompanied by the loss of a water molecule. Also known as a condensation reaction or a dehydration reaction, dehydration synthesis occurs when two molecules are joined by removing water. Dehydration synthesis is a chemical reaction in which two molecules are joined together by the removal of a water molecule. This process is crucial for the formation of glycosidic bonds in carbohydrates and peptide. Dehydration synthesis builds larger molecules by removing water and forming bonds, while. Dehydration synthesis is a chemical reaction that involves the joining of two molecules by removing a water molecule. On the basis of the structure of hydrocarbons, organic. Dehydration synthesis is a reaction where two smaller molecules are joined chemically by removing elements from each of these molecules. In doing so, monomers release water molecules as. When p/p 0 = 0.625, the. Here is the science behind how water facilitates the building and breaking down of biomolecules in processes called dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis. This process is crucial in forming larger organic molecules, such.Diagram The Process Of Dehydration Synthesis And Hydrolysis
Stockvektorbilden Dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis chemical process
Dehydration Synthesis & Hydrolysis Making and Breaking Biomolecules
PPT Chapter 5 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1460955
PPT Levels of Organization PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Organic Chemistry. ppt download
PPT Biochemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9134641
Chapter 5 Biological molecules Chemistry for Biology 1190 Students
PPT Chapter 23 the PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5808961
Topic Dehydration Synthesis & Hydrolysis (pg ppt download
Dehydration Synthesis And Hydrolysis Are Complementary Reactions In Biological Systems.
While Dehydration Synthesis Builds Complex Molecules By Removing Water, Hydrolysis Breaks Them Down By Adding Water.
This Type Of Reaction Is Dehydration Synthesis, Which Means “To Put Together While Losing Water.” Figure 1.
Many Reactions Involving Dehydration Synthesis Are Associated With The Formation Of Biological Polymers Where The Addition Of Each Monomer Is Accompanied By The Elimination.
Related Post:





.jpg)