Depreciation Life Of A Building
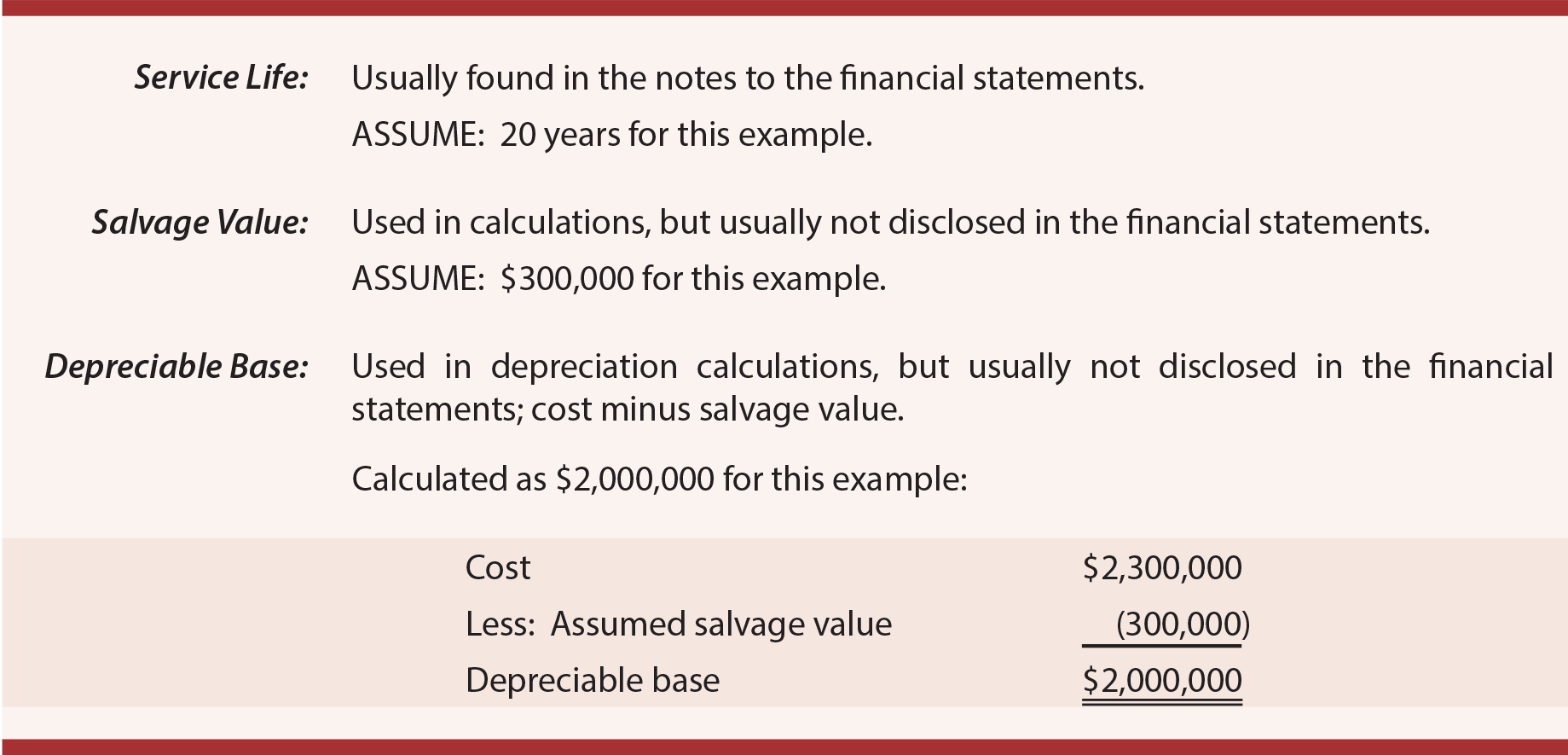
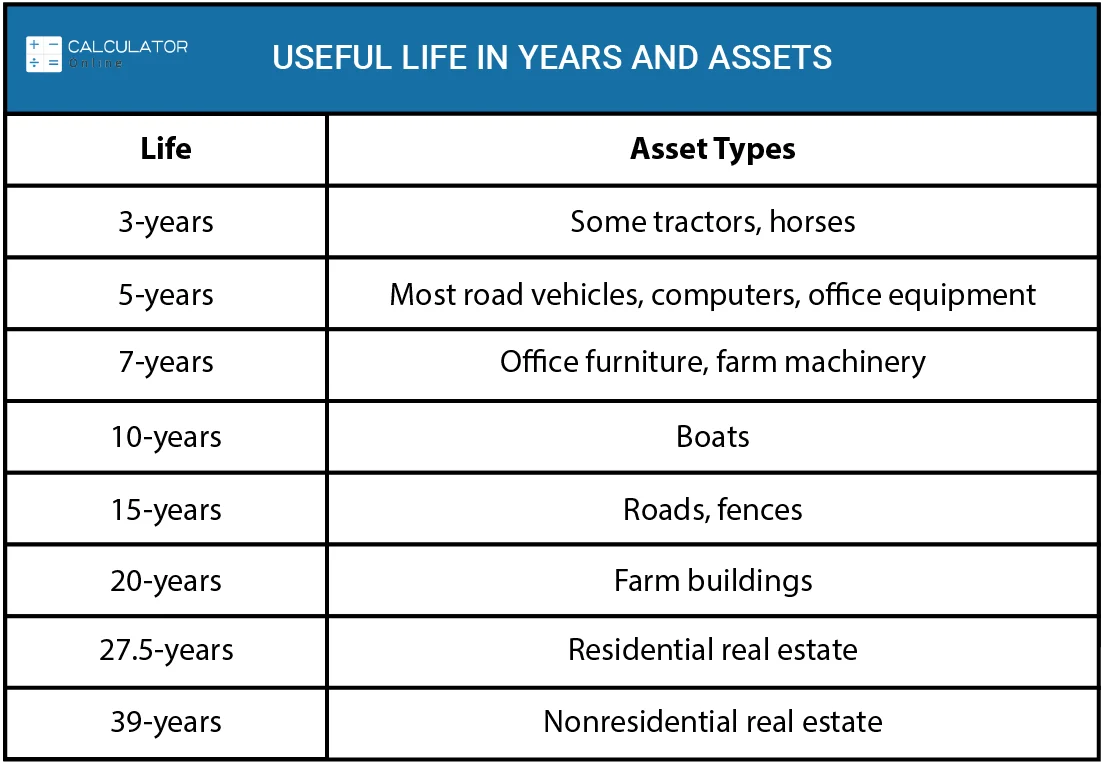
Depreciation Life Of A Building - For example, a building purchased. In most cases, when you buy a building, the. Land is never depreciable, although buildings and certain land improvements may be. Copper roofs last 70 or more years with proper care, though this type of roofing material comes at a high cost, so it is typically only used for accent pieces. Understanding the concept of building depreciation and its useful life is pivotal in the realm of real estate, accounting, and asset management. Determine the asset cost basis: Building research establishment environmental assessment method (breeam) u.s. Determine the cost of the. Depreciation accounts for the wear and tear, aging, and potential obsolescence of the asset. Because commercial real estate is considered an asset rather. Determine the cost of the. Building research establishment environmental assessment method (breeam) u.s. Whole building life cycle assessments. Depreciation is an annual tax deduction that allows small businesses to recover the cost or other basis of certain property over the time they use the property. Explore various building depreciation methods to optimize asset management and financial planning effectively. Depreciation for buildings refers to the gradual reduction in the value of a building till it reaches the final value, also known as salvage value, due to wear and tear, age, or. A building depreciation rate is the percentage at which the value of a building decreases over time due to factors like aging, wear and tear, and obsolescence. To calculate, subtract the salvage value of the property from its initial cost, then divide by the number of years it is expected to be useful. To use depreciation life effectively, follow these steps: Understanding the concept of building depreciation and its useful life is pivotal in the realm of real estate, accounting, and asset management. Determining the useful life of an asset is an important step in calculating depreciation, regardless of the depreciation method that you choose. Because commercial real estate is considered an asset rather. Determine the cost of the. Subtract the salvage value, if any, from the adjusted basis. If you know the equipment isn't going to last 39 years, do you have. Determine the cost of the. To figure your deduction, first determine the adjusted basis, salvage value, and estimated useful life of your property. It applies to commercial buildings, residential. Understanding the concept of building depreciation and its useful life is pivotal in the realm of real estate, accounting, and asset management. A building depreciation rate is the percentage at which. Subtract the salvage value, if any, from the adjusted basis. To use depreciation life effectively, follow these steps: Determine the asset cost basis: This method lets you deduct the same amount of depreciation each year over the useful life of the property. Copper roofs last 70 or more years with proper care, though this type of roofing material comes at. A building depreciation rate is the percentage at which the value of a building decreases over time due to factors like aging, wear and tear, and obsolescence. When estimating depreciation, businesses choose methods aligned with their financial strategies and the nature of the asset. To figure your deduction, first determine the adjusted basis, salvage value, and estimated useful life of. Understanding depreciation in rental property. If you know the equipment isn't going to last 39 years, do you have the option to depreciate it for a lesser amount of time? Determining the useful life of an asset is an important step in calculating depreciation, regardless of the depreciation method that you choose. Depreciation on real property, like an office building,. Ive got a client replacing the roof and hvac ducting. Include the purchase price, taxes, and other relevant costs. Commercial real estate depreciation lets investors expense the cost of income producing property over time, lower the amount of personal income tax paid, and even roll over and defer the. Whole building life cycle assessments. Depreciation on real property, like an. To use depreciation life effectively, follow these steps: A building depreciation rate is the percentage at which the value of a building decreases over time due to factors like aging, wear and tear, and obsolescence. Ive got a client replacing the roof and hvac ducting. Copper roofs last 70 or more years with proper care, though this type of roofing. To calculate, subtract the salvage value of the property from its initial cost, then divide by the number of years it is expected to be useful. To use depreciation life effectively, follow these steps: Land is never depreciable, although buildings and certain land improvements may be. Building research establishment environmental assessment method (breeam) u.s. You may depreciate property that meets. Ive got a client replacing the roof and hvac ducting. Determine the asset cost basis: A building depreciation rate is the percentage at which the value of a building decreases over time due to factors like aging, wear and tear, and obsolescence. These methods directly influence financial. Include the purchase price, taxes, and other relevant costs. Depreciation on real property, like an office building, begins in the month the building is placed in service. Commercial real estate depreciation lets investors expense the cost of income producing property over time, lower the amount of personal income tax paid, and even roll over and defer the. Because commercial real estate is considered an asset rather. To figure your. Explore various building depreciation methods to optimize asset management and financial planning effectively. Whole building life cycle assessments. When estimating depreciation, businesses choose methods aligned with their financial strategies and the nature of the asset. To calculate, subtract the salvage value of the property from its initial cost, then divide by the number of years it is expected to be useful. Depreciation on real property, like an office building, begins in the month the building is placed in service. Determining the useful life of an asset is an important step in calculating depreciation, regardless of the depreciation method that you choose. Determine the cost of the. This method lets you deduct the same amount of depreciation each year over the useful life of the property. Understanding depreciation in rental property. Depreciation for buildings refers to the gradual reduction in the value of a building till it reaches the final value, also known as salvage value, due to wear and tear, age, or. Determine the asset cost basis: If you know the equipment isn't going to last 39 years, do you have the option to depreciate it for a lesser amount of time? Depreciation of a building is the. A building depreciation rate is the percentage at which the value of a building decreases over time due to factors like aging, wear and tear, and obsolescence. To figure your deduction, first determine the adjusted basis, salvage value, and estimated useful life of your property. In most cases, when you buy a building, the.Guide to Segmented Depreciation & Depreciation Life APM
Depreciation Concepts
Methods of Depreciation Formulas, Problems, and Solutions Owlcation
Difference between Depreciation and Obsolescence Value of Building
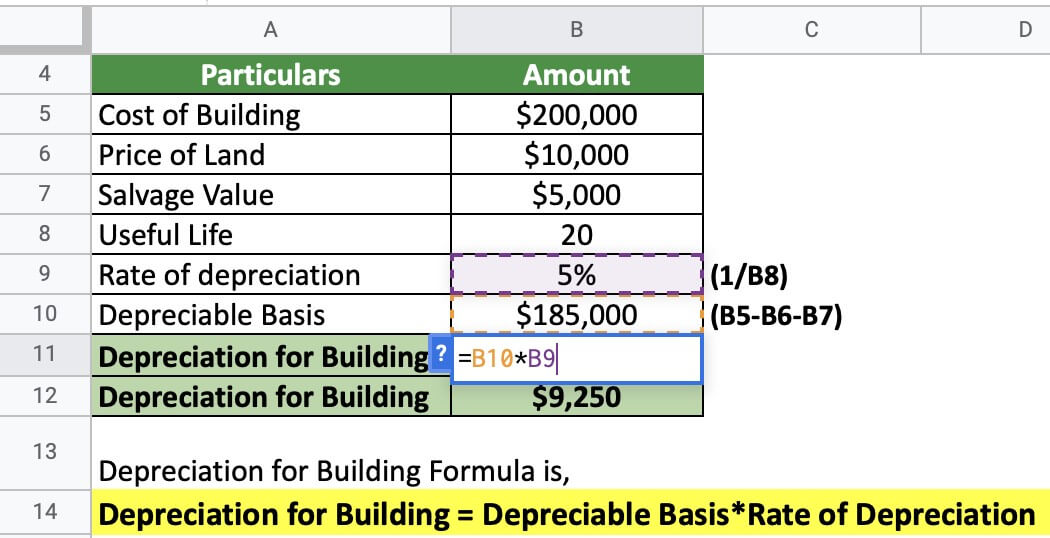
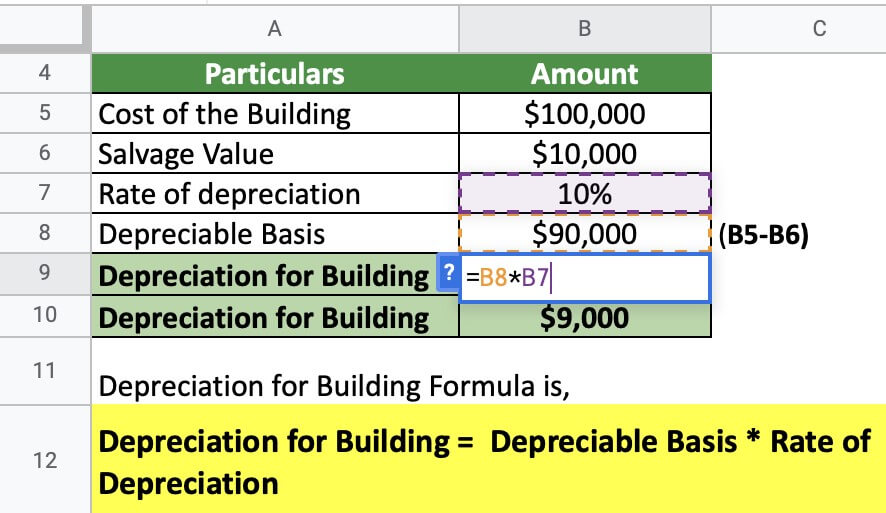
Depreciation for Building Definition, Formula, and Excel Examples
Depreciation for Building Definition, Formula, and Excel Examples
Popular Depreciation Methods To Calculate Asset Value Over The Years
PPT LongLived Assets and Depreciation PowerPoint Presentation ID
PPT Depreciation PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID249599
MACRS Depreciation Calculator
Depreciation Is A Key Accounting Concept For Managing The.
Because Commercial Real Estate Is Considered An Asset Rather.
For Example, A Building Purchased.
Subtract The Salvage Value, If Any, From The Adjusted Basis.
Related Post: