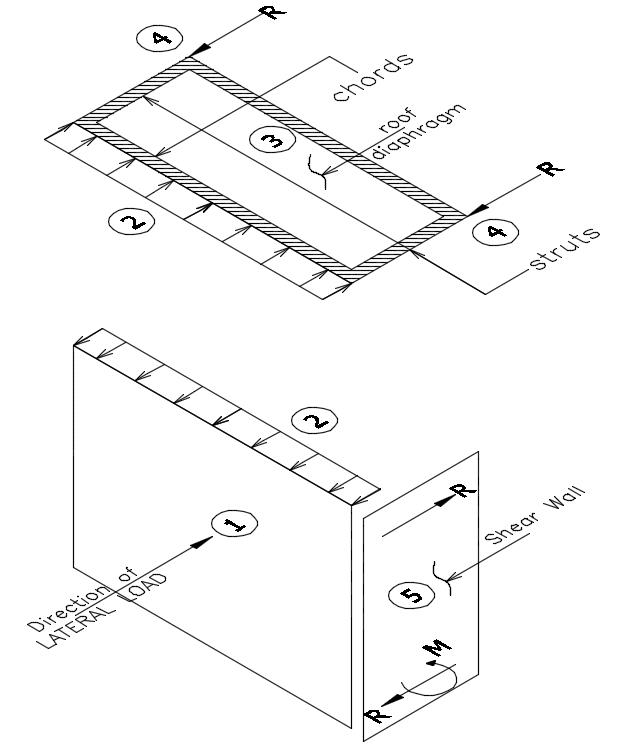
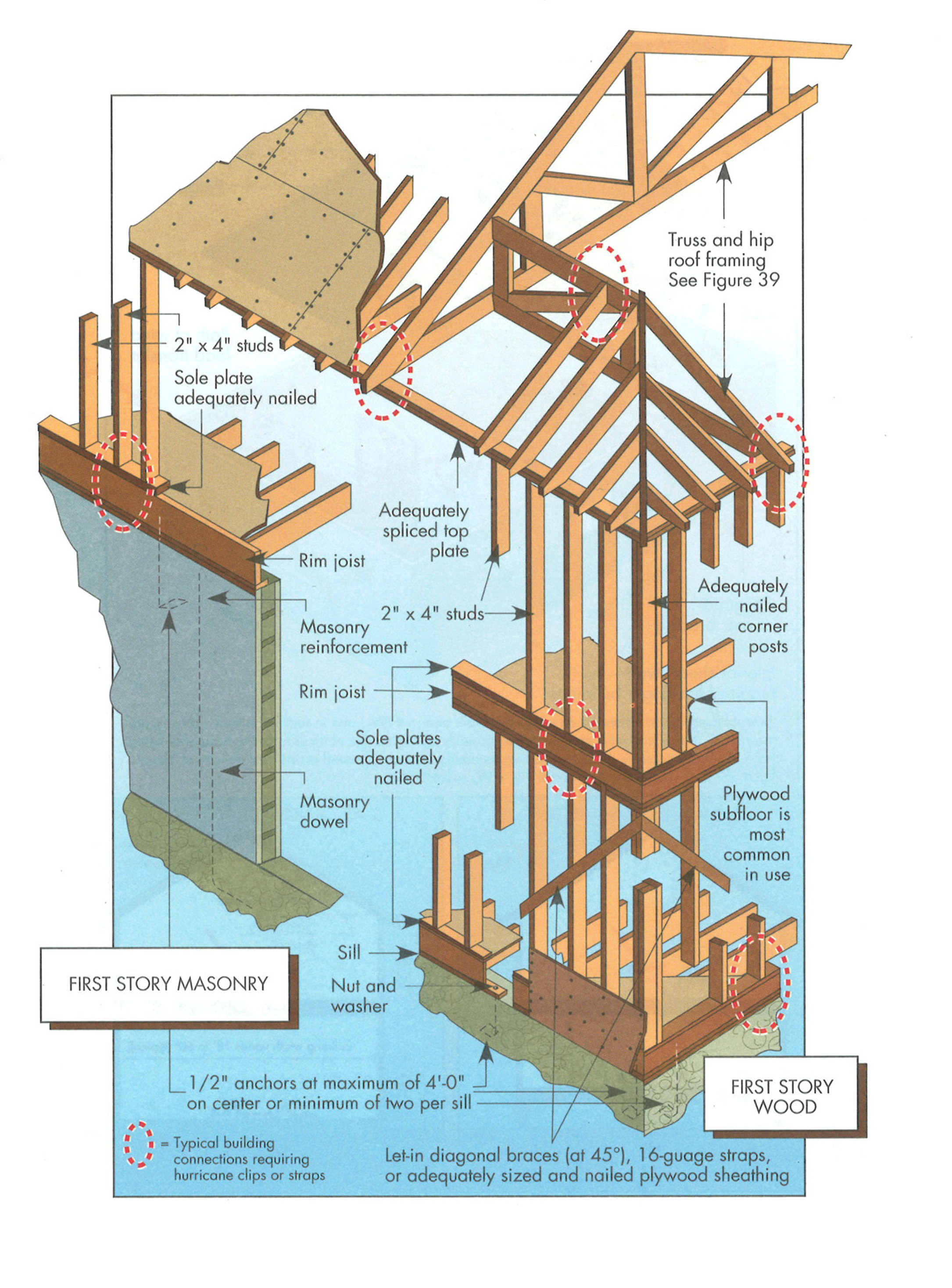
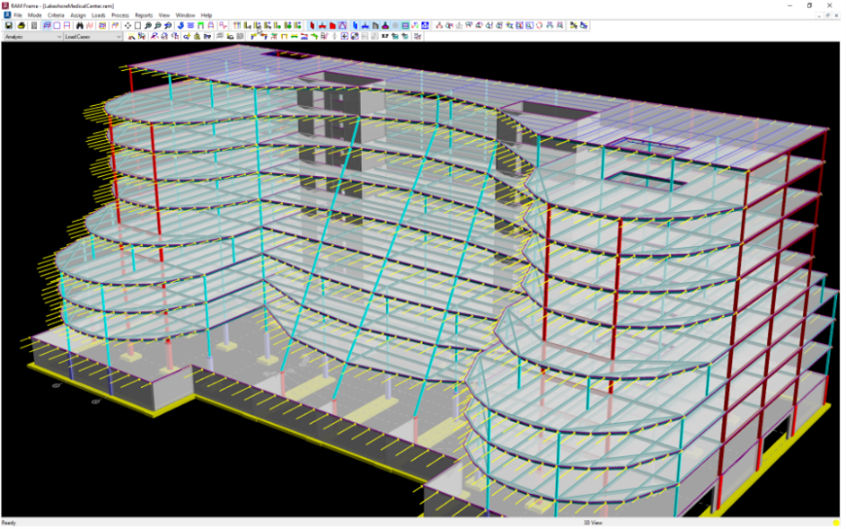
Diaphragm Building
Diaphragm Building - A shear wall, however, is a vertical,. For buildings having flexible diaphragm, the code makes an exception for type 4. Diaphragms in any building plus additional requirements for buildings assigned to seismic design category d, e, or f. In structural engineering, a diaphragm is a structural element that transmits lateral loads to the vertical resisting elements of a structure (such as shear walls or frames). Learn how to break down complex diaphragms into manageable segments. Diaphragms are horizontal elements that distribute seismic forces to vertical lateral force resisting elements. A diaphragm is a flat structural unit acting like a deep, thin beam. Learn how to analyze a diaphragm with a horizontal offset and how to transfer forces across areas of discontinuity. A diaphragm wall is a continuous, reinforced concrete wall constructed underground to support and retain soil. Explore the essential functions and various types of diaphragms in building structures, including their role in seismic design. Diaphragm wall excavation case stydy: A diaphragm in structural engineering refers to a horizontal or sloped system that helps transfer lateral loads, such as wind or seismic forces, to. Explore the essential functions and various types of diaphragms in building structures, including their role in seismic design. Diaphragm’s stiffness where the diaphragm has not been classified as rigid or flexible per section 12.3.1. Diaphragms in any building plus additional requirements for buildings assigned to seismic design category d, e, or f. Diaphragms play a crucial role in the. This course is divided into the following sections: In structural engineering, a diaphragm is a structural element that transmits lateral loads to the vertical resisting elements of a structure (such as shear walls or frames). A shear wall, however, is a vertical,. Diaphragm walls are used as retaining structures in excavation of soil. A diaphragm wall is a continuous, reinforced concrete wall constructed underground to support and retain soil. Explore the essential functions and various types of diaphragms in building structures, including their role in seismic design. A shear wall, however, is a vertical,. For buildings having flexible diaphragm, the code makes an exception for type 4. A diaphragm is a flat structural. A diaphragm wall is a continuous, reinforced concrete wall constructed underground to support and retain soil. A shear wall, however, is a vertical,. Diaphragms are horizontal elements that distribute seismic forces to vertical lateral force resisting elements. Learn how to break down complex diaphragms into manageable segments. A diaphragm is rigid for the purpose of distribution of story shear and. For buildings having flexible diaphragm, the code makes an exception for type 4. In this blog post, we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of diaphragm walls, outlining key points to remember for civil engineers considering their use. They also provide lateral support for walls and parapets. Diaphragm’s stiffness where the diaphragm has not been classified as rigid or flexible. A diaphragm wall is a continuous, reinforced concrete wall constructed underground to support and retain soil. The term “diaphragm” is usually applied to roofs and floors. A diaphragm is a flat structural unit acting like a deep, thin beam. Diaphragms are horizontal elements that distribute seismic forces to vertical lateral force resisting elements. Diaphragm walls are used as retaining structures. A diaphragm in structural engineering refers to a horizontal or sloped system that helps transfer lateral loads, such as wind or seismic forces, to. Learn how to analyze a diaphragm with a horizontal offset and how to transfer forces across areas of discontinuity. A shear wall, however, is a vertical,. In structural engineering, a diaphragm is a structural element that. Diaphragms are horizontal elements that distribute seismic forces to vertical lateral force resisting elements. For buildings having flexible diaphragm, the code makes an exception for type 4. In structural engineering, a diaphragm is a structural element that transmits lateral loads to the vertical resisting elements of a structure (such as shear walls or frames). The term “diaphragm” is usually applied. A diaphragm is a flat structural unit acting like a deep, thin beam. Learn how to analyze a diaphragm with a horizontal offset and how to transfer forces across areas of discontinuity. In this blog post, we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of diaphragm walls, outlining key points to remember for civil engineers considering their use. Diaphragms are horizontal. A diaphragm is a flat structural unit acting like a deep, thin beam. Learn how to analyze a diaphragm with a horizontal offset and how to transfer forces across areas of discontinuity. The term “diaphragm” is usually applied to roofs and floors. Diaphragm walls are used as retaining structures in excavation of soil. Diaphragms are horizontal elements that distribute seismic. Learn how to break down complex diaphragms into manageable segments. Diaphragm’s stiffness where the diaphragm has not been classified as rigid or flexible per section 12.3.1. Diaphragms in any building plus additional requirements for buildings assigned to seismic design category d, e, or f. A diaphragm wall is a continuous, reinforced concrete wall constructed underground to support and retain soil.. In structural engineering, a diaphragm is a structural element that transmits lateral loads to the vertical resisting elements of a structure (such as shear walls or frames). A shear wall, however, is a vertical,. They also provide lateral support for walls and parapets. A diaphragm is a flat structural unit acting like a deep, thin beam. This course is divided. Diaphragm’s stiffness where the diaphragm has not been classified as rigid or flexible per section 12.3.1. A diaphragm is a flat structural unit acting like a deep, thin beam. In structural engineering, a diaphragm is a structural element that transmits lateral loads to the vertical resisting elements of a structure (such as shear walls or frames). In this blog post, we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of diaphragm walls, outlining key points to remember for civil engineers considering their use. A diaphragm in structural engineering refers to a horizontal or sloped system that helps transfer lateral loads, such as wind or seismic forces, to. The term “diaphragm” is usually applied to roofs and floors. Diaphragm wall excavation case stydy: This course is divided into the following sections: Diaphragms are horizontal elements that distribute seismic forces to vertical lateral force resisting elements. A shear wall, however, is a vertical,. Diaphragms in any building plus additional requirements for buildings assigned to seismic design category d, e, or f. They also provide lateral support for walls and parapets. Learn how to break down complex diaphragms into manageable segments. A diaphragm is rigid for the purpose of distribution of story shear and torsional moment when the lateral deformation of the diaphragm is less than or equal to two times the average story drift. Diaphragm walls are used as retaining structures in excavation of soil. Diaphragms play a crucial role in the.Basics of Diaphragm Action The Structural World
Core Engineering— Introduction to Diaphragm design.
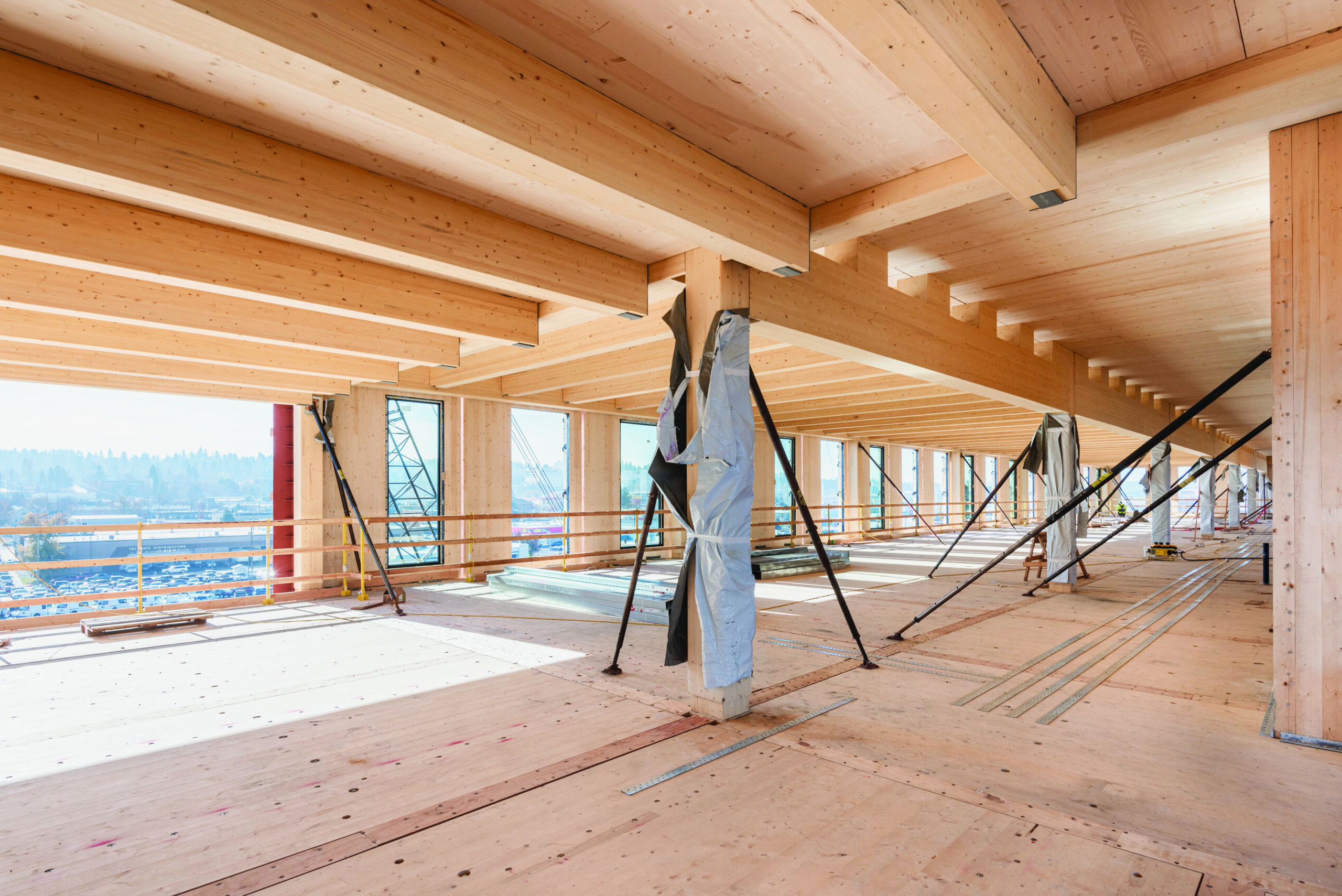
CLT Diaphragm Design Guide WoodWorks Wood Products Council
Primary wood framing systems walls, roof diaphragm, and floor
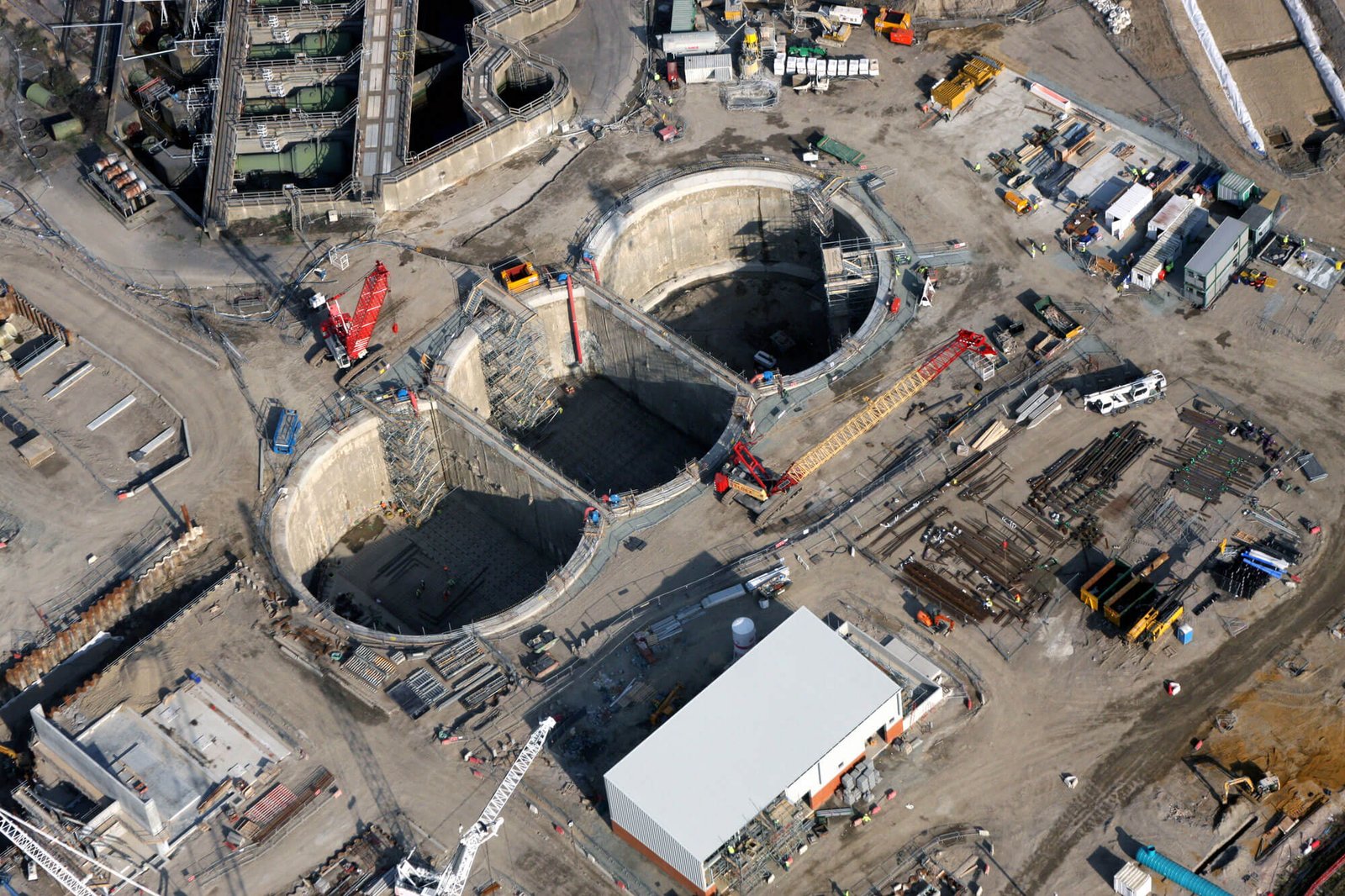
Diaphragm Retaining Walls Surveying & Architects
Diaphragms thestructuralengineer.info
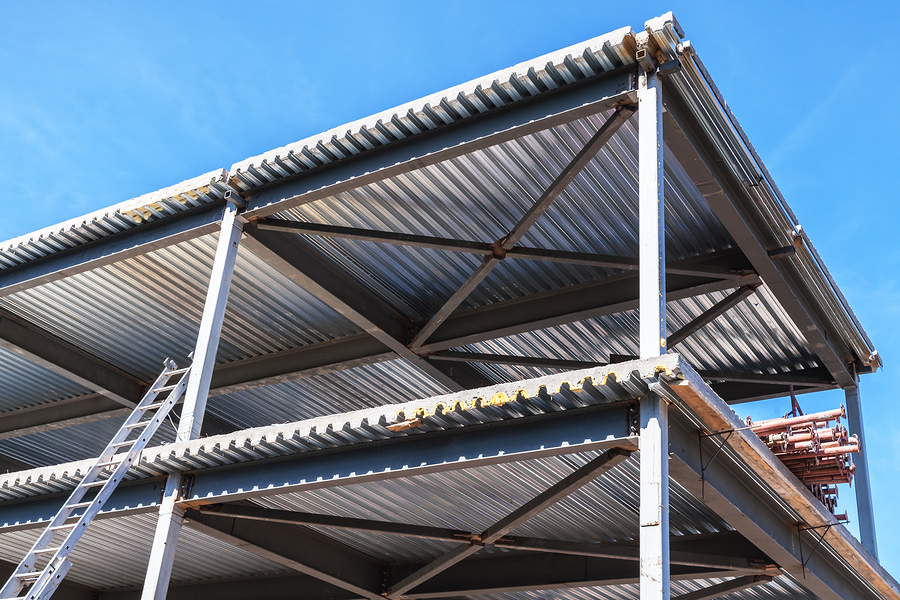
Does a fully enclosed PEMB meet the ASCE 7 definition of "Simple
Core Engineering— Introduction to Diaphragm design.
New initiative for steel diaphragm research Construction Specifier
Diaphragm Action in Steel Building YouTube
A Diaphragm Wall Is A Continuous, Reinforced Concrete Wall Constructed Underground To Support And Retain Soil.
Explore The Essential Functions And Various Types Of Diaphragms In Building Structures, Including Their Role In Seismic Design.
For Buildings Having Flexible Diaphragm, The Code Makes An Exception For Type 4.
Learn How To Analyze A Diaphragm With A Horizontal Offset And How To Transfer Forces Across Areas Of Discontinuity.
Related Post: