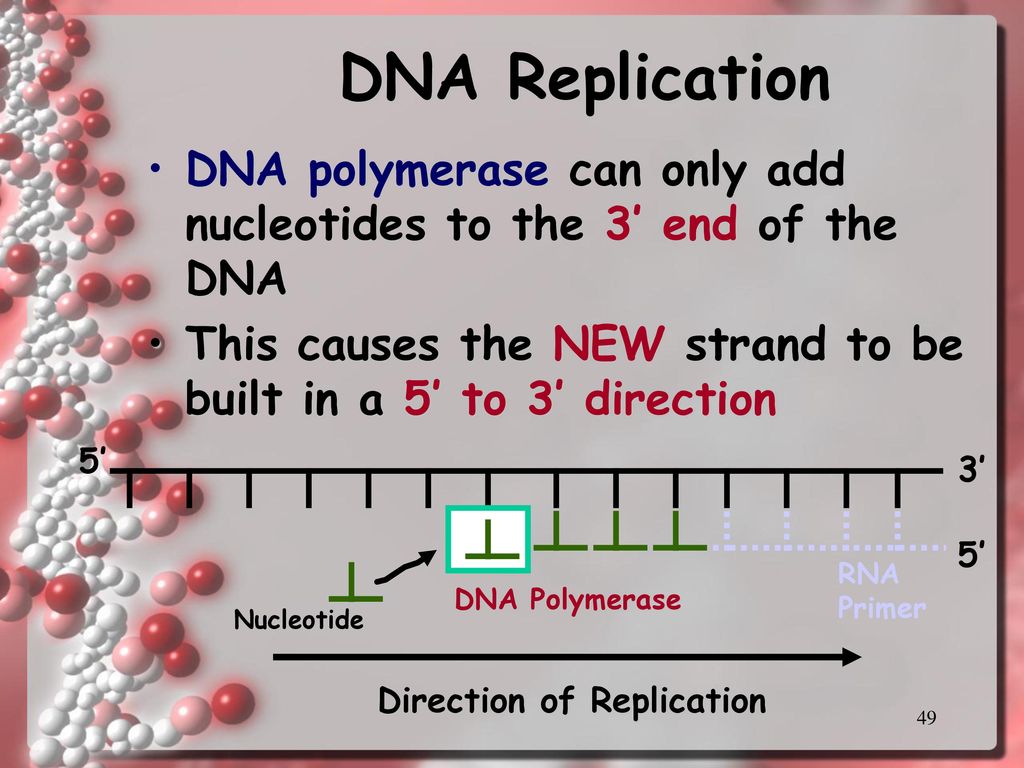
Dna Polymerase Can Only Build In What Direction
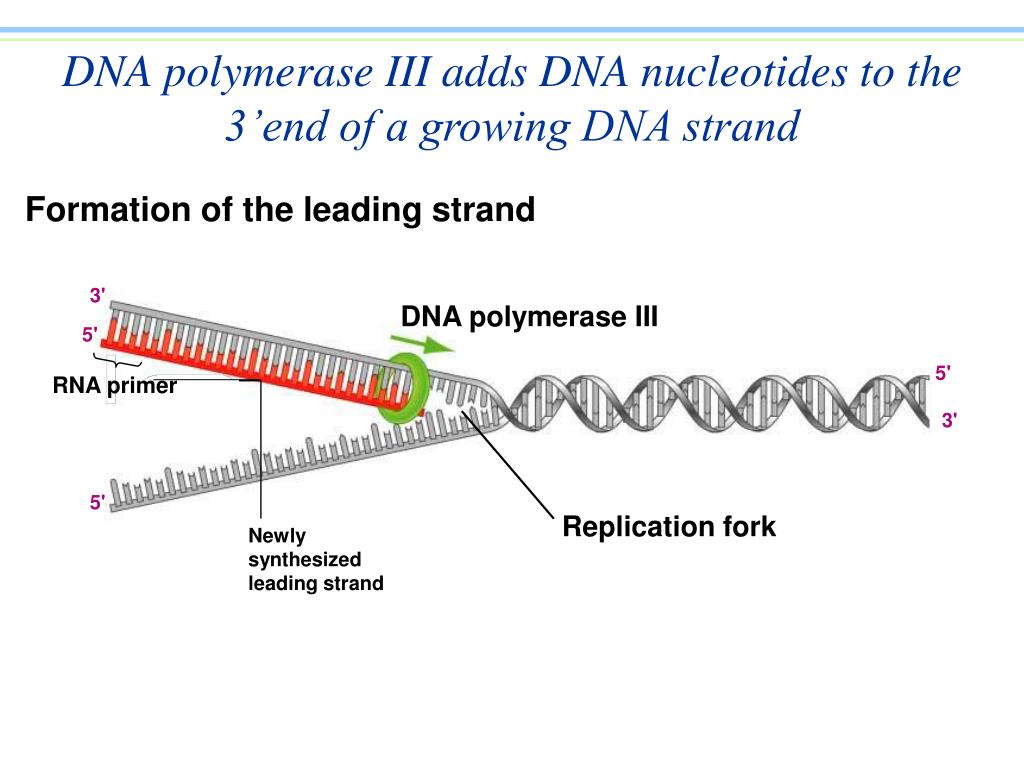
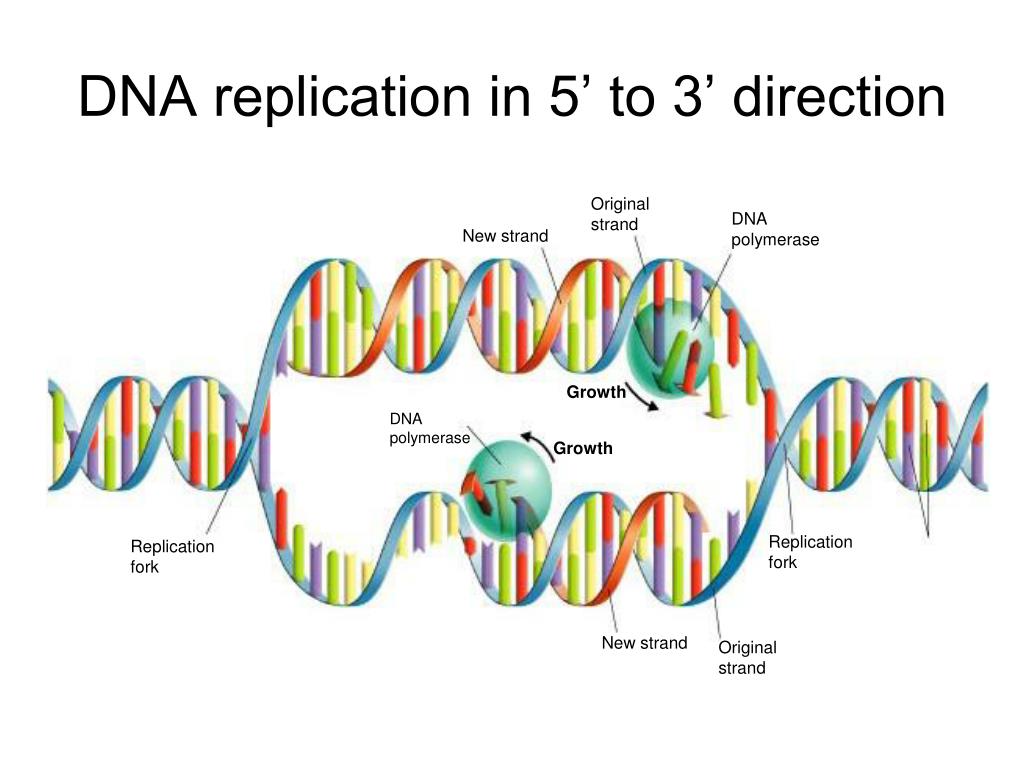
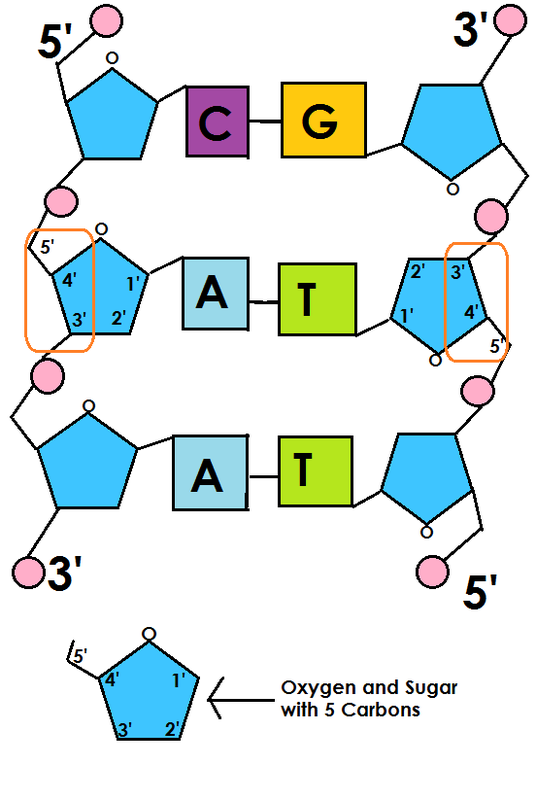
Dna Polymerase Can Only Build In What Direction - At a replication fork, the dna of both new daughter strands is synthesized by a multienzyme complex that contains the dna polymerase. However, dna pol iii is able to add nucleotides only in the 5’ to 3’. Thus, this “lagging” strand is synthesized in short segments known as okazaki fragments. During dna replication, the leading strand is. Two replication forks moving in opposite. The 5' to 3' growth of both new strands means that one of the strands is made in pieces. This means that it adds nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing dna strand, utilizing the 5' end of the incoming. Dna polymerases can only extend a strand in the 5' to 3' direction. Dna polymerases can only extend a strand in the 5' to 3' direction. The lagging strand is therefore synthesised in fragments. At a replication fork, the dna of both new daughter strands is synthesized by a multienzyme complex that contains the dna polymerase. Dna polymerase can only synthesize new dna strands in the 5' to 3' direction. Dna polymerases can only extend a strand in the 5' to 3' direction. Here we review the physical, chemical and. Here's a breakdown of how it works: Dna polymerase only moves in one direction after a primer is synthesized on a strand of dna and the dna strands unwind, synthesis and elongation can proceed in only one direction. Dna polymerase cannot build a strand in the 3' → 5' direction. This here concludes our brief introduction to dna polymerases, and we'll continue to talk more about dna polymerases and. Two replication forks moving in opposite. Because dna polymerase can only synthesize in one direction, one strand is built in a direction which is. Dna polymerase cannot build a strand in the 3' → 5' direction. However, dna pol iii is able to add nucleotides only in the 5’ to 3’. This means that it adds nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing dna strand, utilizing the 5' end of the incoming. During dna replication, the leading strand is. This here concludes our. During dna replication, the leading strand is. However, dna pol iii is able to add nucleotides only in the 5’ to 3’. Dna polymerases can only extend a strand in the 5' to 3' direction. The 5' to 3' extension of both new strands at a single replication fork means that one of the strands is. The 5' to 3'. How do dna polymerases work? Two replication forks moving in opposite. This means that it adds nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing dna strand, utilizing the 5' end of the incoming. It has a specific direction in which it can add nucleotides to a growing dna strand. The 5' to 3' growth of both new strands means that. The 5' to 3' extension of both new strands at a single replication fork means that one of the strands is. This here concludes our brief introduction to dna polymerases, and we'll continue to talk more about dna polymerases and. The 5' to 3' growth of both new strands means that one of the strands is made in pieces. At. Dna polymerases can only extend a strand in the 5' to 3' direction. The lagging strand is therefore synthesised in fragments. Thus, this “lagging” strand is synthesized in short segments known as okazaki fragments. The 5' to 3' extension of both new strands at a single replication fork means that one of the strands is. Here we review the physical,. It has a specific direction in which it can add nucleotides to a growing dna strand. This means that it adds nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing dna strand, utilizing the 5' end of the incoming. It is called the lagging strand because since it can only build in the 5' to 3' direction, the other stand is.. It has a specific direction in which it can add nucleotides to a growing dna strand. The 5' to 3' extension of both new strands at a single replication fork means that one of the strands is. Dna polymerases can only extend a strand in the 5' to 3' direction. During dna replication, the leading strand is. At a replication. How do dna polymerases work? The new dna strands can only be built in this direction, from 5' to 3'. Nucleotides cannot be added to the phosphate (5’) end because dna polymerase can only add dna nucleotides in a 5’ to 3’ direction. Dna polymerases can only extend a strand in the 5' to 3' direction. Dna polymerases can only. Nucleotides cannot be added to the phosphate (5’) end because dna polymerase can only add dna nucleotides in a 5’ to 3’ direction. Thus, this “lagging” strand is synthesized in short segments known as okazaki fragments. It has a specific direction in which it can add nucleotides to a growing dna strand. Two replication forks moving in opposite. It is. Because dna polymerase can only synthesize in one direction, one strand is built in a direction which is. Here we review the physical, chemical and. Dna polymerases can only extend a strand in the 5' to 3' direction. Two replication forks moving in opposite. However, dna pol iii is able to add nucleotides only in the 5’ to 3’. How do dna polymerases work? However, dna pol iii is able to add nucleotides only in the 5’ to 3’. Dna polymerases can only extend a strand in the 5' to 3' direction. The 5' to 3' extension of both new strands at a single replication fork means that one of the strands is. The 5' to 3' growth of both new strands means that one of the strands is made in pieces. This here concludes our brief introduction to dna polymerases, and we'll continue to talk more about dna polymerases and. Here's a breakdown of how it works: Dna polymerase only moves in one direction after a primer is synthesized on a strand of dna and the dna strands unwind, synthesis and elongation can proceed in only one direction. Thus, this “lagging” strand is synthesized in short segments known as okazaki fragments. Dna polymerase can only build in the 5' to 3' direction, which is the leading strand. It has a specific direction in which it can add nucleotides to a growing dna strand. The 5' to 3' extension of both new strands at a single replication fork means that one of the strands is. Dna polymerases can only extend a strand in the 5' to 3' direction. Dna polymerase is an enzyme involved in the synthesis of dna. Here we review the physical, chemical and. This means that it adds nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing dna strand, utilizing the 5' end of the incoming.DNA and Replication. ppt download
DNA Polymerase Definition & Function Video & Lesson Transcript
Dna Polymerase Structure Diagram Biochem Nucleic Acids Struc
PPT DNA Synthesis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID162332
How DNA Polymerase Works YouTube
PPT DNA History, Structure and Replication PowerPoint Presentation
Mrs. Stewart Biology I Honors ppt download
Direction of DNA DNA Replication
DNA Replication The Details. ppt download
DNA. Structure and Replication Presentation Biology
Dna Polymerases Can Only Extend A Strand In The 5' To 3' Direction.
Dna Polymerase Can Only Synthesize New Dna Strands In The 5' To 3' Direction.
The New Dna Strands Can Only Be Built In This Direction, From 5' To 3'.
It Is Called The Lagging Strand Because Since It Can Only Build In The 5' To 3' Direction, The Other Stand Is.
Related Post:





.PNG)