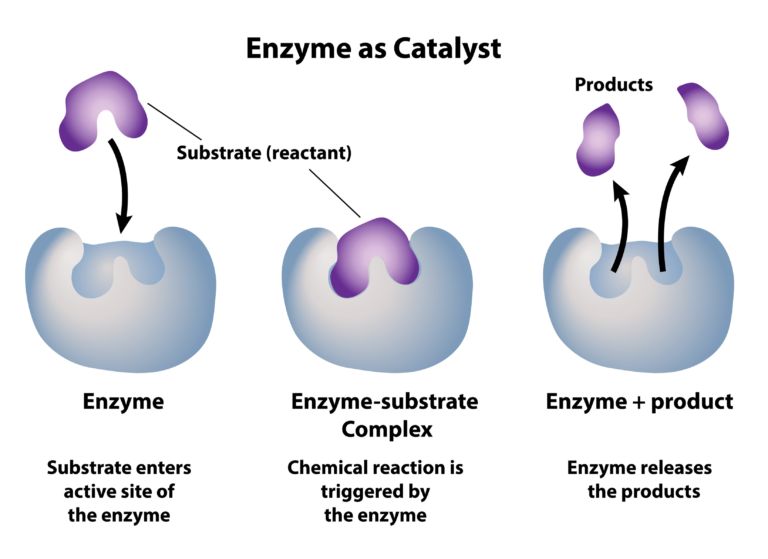
Enzymes Can Both Build Up Or Break Down A Substrate
Enzymes Can Both Build Up Or Break Down A Substrate - Enzymes can be catabolic and anabolic. Enzymes can both build up or break down a substrate. In some reactions, a single reactant substrate is broken down into multiple products. The substrates bind to a region on the enzyme called the active site. With a catabolic reaction , the activation energy is low. Each enzyme typically binds only one substrate. Enzymes bind with chemical reactants called substrates. A protein which can either build up (catabolize) or break down (metabolize) a substrate, while the enzyme itself remains unchanged. The substrates bind to a region on the. Enzymes are not consumed during a reaction; With a catabolic reaction , the activation energy is low. There are two theories explaining the. In others, two substrates may come together to create one larger molecule. Enzymes speed up and direct chemical reactions. The substrates bind to a region on the. Once the substrate attaches to the enzymes for which it fits in the. Bringing substrates together in an optimal orientation, compromising the bond structures of substrates so that. An enzyme is a biological catalyst that works on one substrate, which is substrate specific. When a substrate approaches an enzyme, it can interact with the active site. The molecules that an enzyme works with are called substrates. Enzymes are biological catalysts that lower activation energy, allowing chemical reactions to proceed more easily. A protein which can either build up (catabolize) or break down (metabolize) a substrate, while the enzyme itself remains unchanged. A chemical which speeds up the rate of a reaction. In some reactions, a single reactant substrate is broken down into multiple products. The molecules. Enzymes are proteins that speed up reactions by reducing the activation energy. In some reactions, a single reactant substrate is broken down into multiple products. Bringing substrates together in an optimal orientation, compromising the bond structures of substrates so that. There may be one or more substrates for each type of enzyme, depending on the particular chemical reaction. Enzymes bind. The molecules that an enzyme works with are called substrates. True, enzymes can both build up and break down a substrate. Enzymes can both build up or break down a substrate. Enzymes are biological catalysts that lower activation energy, allowing chemical reactions to proceed more easily. In others, two substrates may come together to create one larger molecule. The substrates bind to a region on the enzyme called the active site. Enzymes bind to substrates and catalyze reactions in four different ways: The items that bind to the active sites of enzymes are called? Enzymes can both build up or break down a substrate. A chemical which speeds up the rate of a reaction. Enzymes are not consumed during a reaction; Global plastic production is increasing yearly, with packaging materials and disposable plastics accounting for a sizable portion of the total. Once the substrate attaches to the enzymes for which it fits in the. A protein which can either build up (catabolize) or break down (metabolize) a substrate Enzymes bind to substrates and catalyze. The molecules that an enzyme works with are called substrates. Enzymes bind with chemical reactants called substrates, which may be one or more. The substrates bind to a region on the. Enzymes are called catalysts because they speed up chemical reactions without being permanently changed by the reaction. There may be one or more substrates for each type of enzyme,. Enzymes can both build up or break down a substrate. Enzymes speed up and direct chemical reactions. An enzyme is a biological catalyst that works on one substrate, which is substrate specific. With a catabolic reaction , the activation energy is low. Global plastic production is increasing yearly, with packaging materials and disposable plastics accounting for a sizable portion of. Enzymes break down the bonds in substrates by lowering the activation energy required for a reaction. There may be one or more substrates for each type of enzyme, depending on the particular chemical reaction. Enzymes bind with chemical reactants called substrates. An enzyme will only fit a substrate for which for which it is responsible for catalyzing the reaction of.. With a catabolic reaction , the activation energy is low. They can both break down and build molecules, are recyclable, and are. True, enzymes can both build up and break down a substrate. There are two theories explaining the. Enzymes that break down substrates are referred to as catabolic enzymes, while those that synthesize more. Enzymes can be catabolic and anabolic. Enzymes are called catalysts because they speed up chemical reactions without being permanently changed by the reaction. In some reactions, a single reactant substrate is broken down into multiple products. A protein which can either build up (catabolize) or break down (metabolize) a substrate Enzymes bind with chemical reactants called substrates. A protein which can either build up (catabolize) or break down (metabolize) a substrate, while the enzyme itself remains unchanged. Enzymes bind with chemical reactants called substrates. Enzymes are not consumed during a reaction; Enzymes that break down substrates are referred to as catabolic enzymes, while those that synthesize more. Global plastic production is increasing yearly, with packaging materials and disposable plastics accounting for a sizable portion of the total. Once the substrate attaches to the enzymes for which it fits in the. These complexes break down or build up the substrate,. They can both break down and build molecules, are recyclable, and are. A protein which can either build up (catabolize) or break down (metabolize) a substrate The molecules that an enzyme works with are called substrates. Enzymes bind to substrates and catalyze reactions in four different ways: A chemical which speeds up the rate of a reaction. Each enzyme typically binds only one substrate. An enzyme is a biological catalyst that works on one substrate, which is substrate specific. The substrates bind to a region on the. Enzymes can be catabolic and anabolic.Draw A Schematic Model Of An Enzyme Enzyme Function Substrat
The combination formed by an enzyme and its substrates is called the
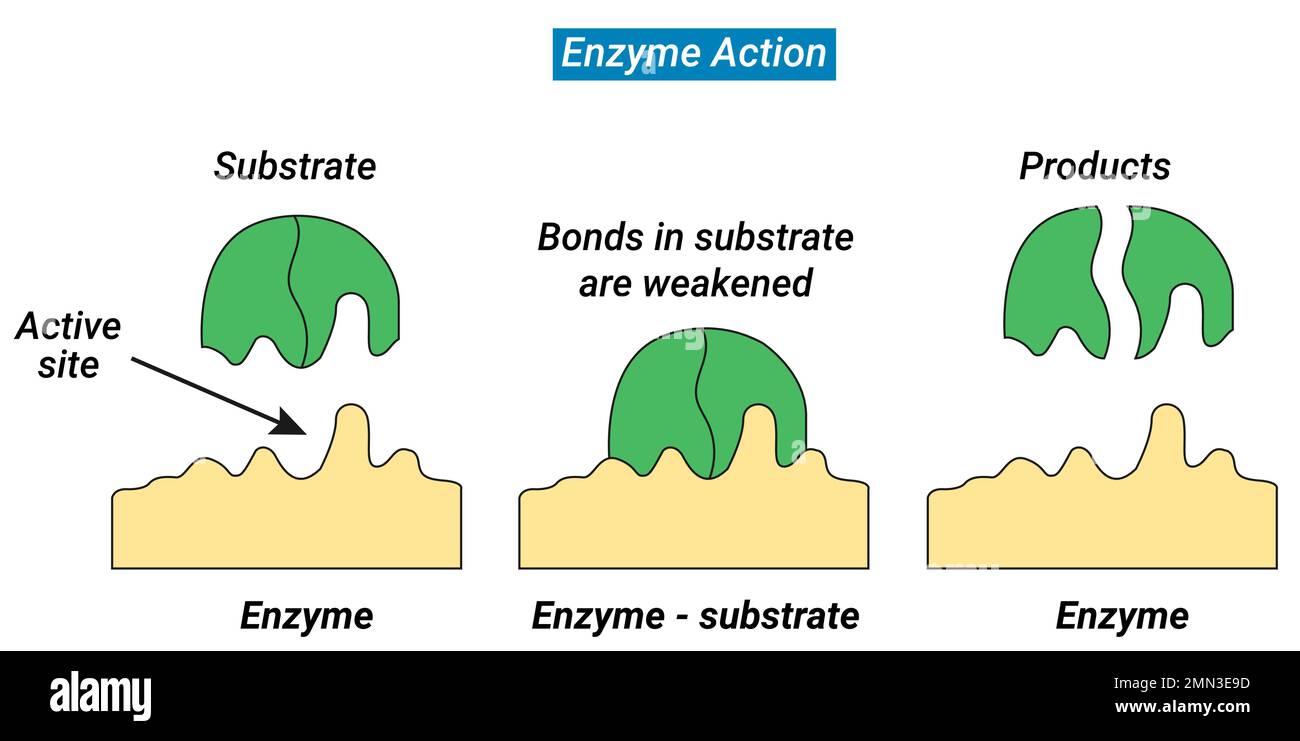
Diagram Of Enzyme And Substrate Label The Diagram Of The Enz
Enzyme & Their Substrates Mode of Action Plantlet
Diagram Of Enzyme And Substrate Label The Diagram Of The Enz
5.1. Enzymes Biology Notes for IGCSE 2014 & 2024
Enzymes. A Cell's Catalysts Presentation Biology
How enzymes work Talking Pools Podcast News
Module 3, lesson 2 enzymes3
Draw A Schematic Model Of An Enzyme Enzyme Function Substrat
Enzymes Are Biological Catalysts That Lower Activation Energy, Allowing Chemical Reactions To Proceed More Easily.
With A Catabolic Reaction , The Activation Energy Is Low.
There May Be One Or More Substrates For Each Type Of Enzyme, Depending On The Particular Chemical Reaction.
Enzymes Are Called Catalysts Because They Speed Up Chemical Reactions Without Being Permanently Changed By The Reaction.
Related Post:



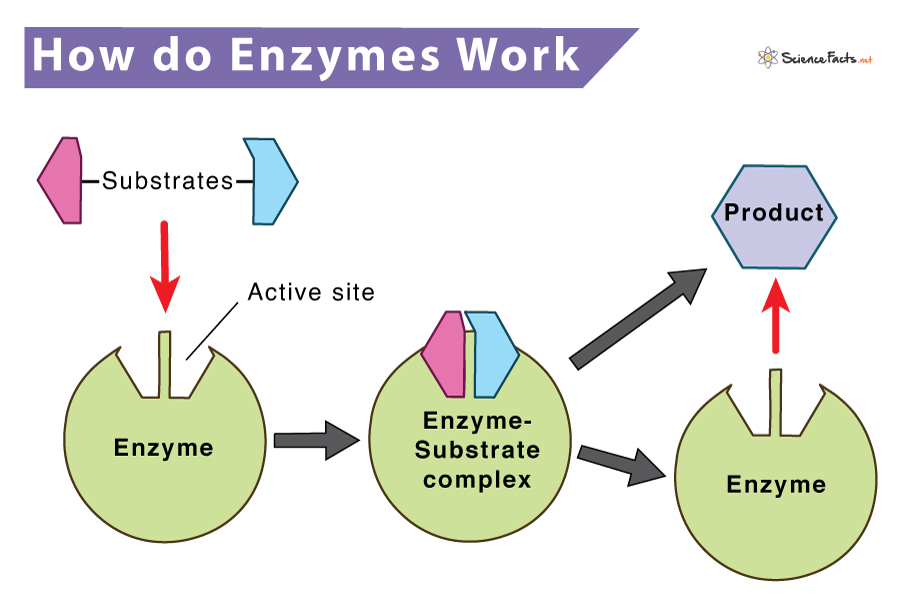

.PNG)