Fatty Acids Are The Building Blocks Of
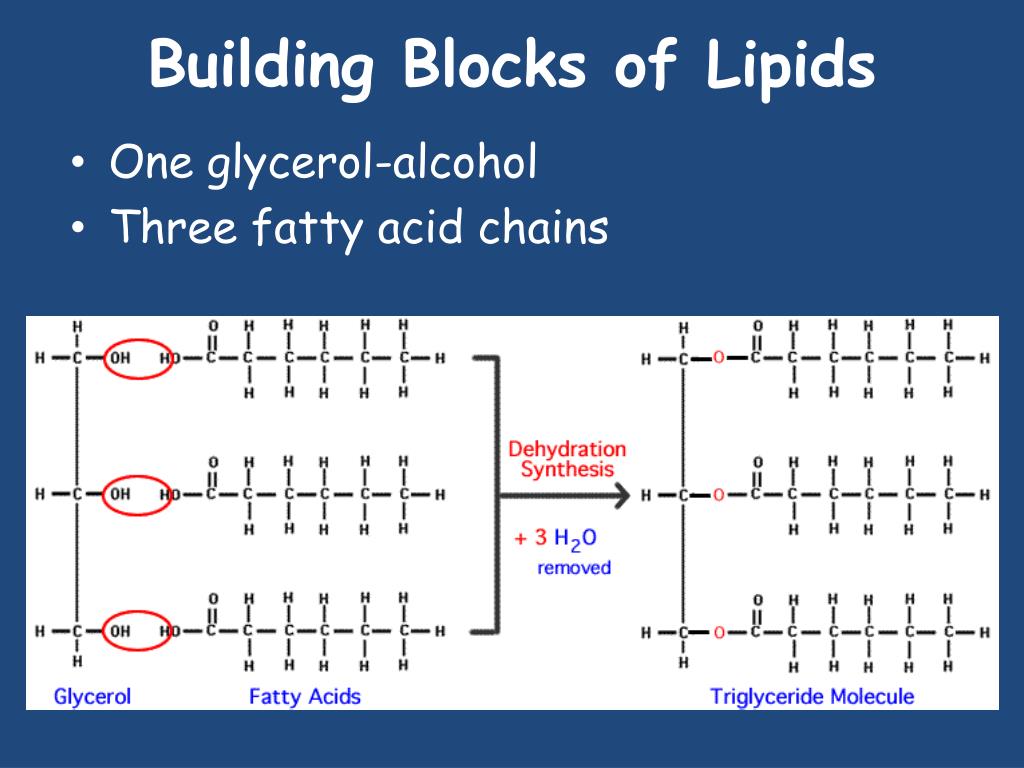
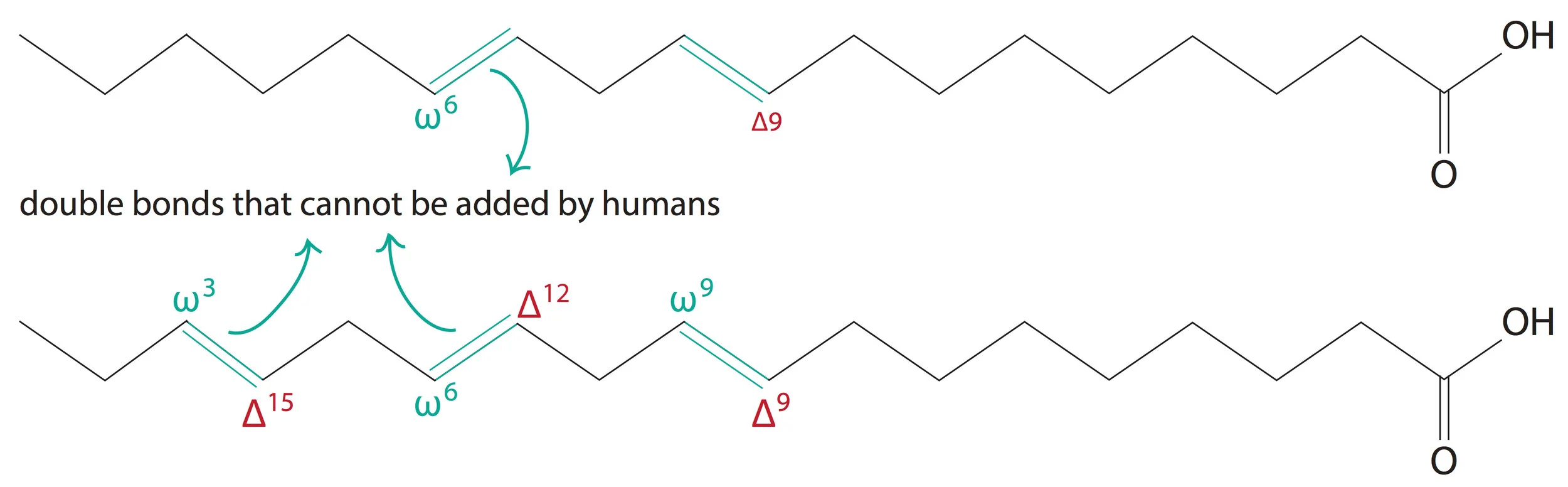
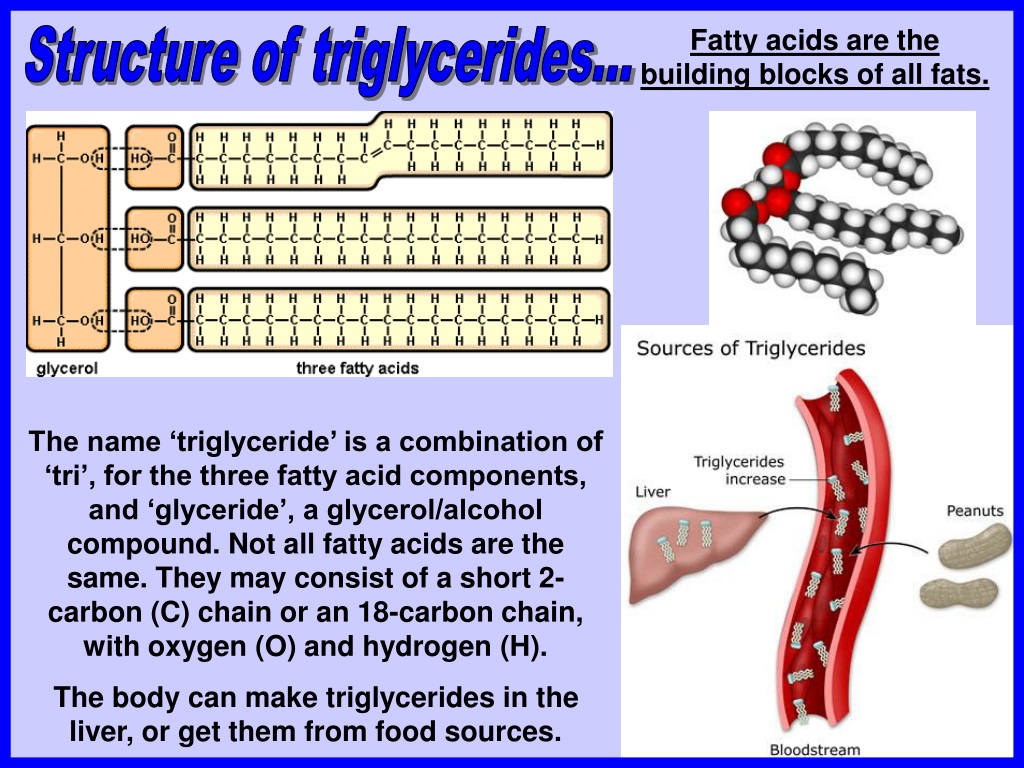
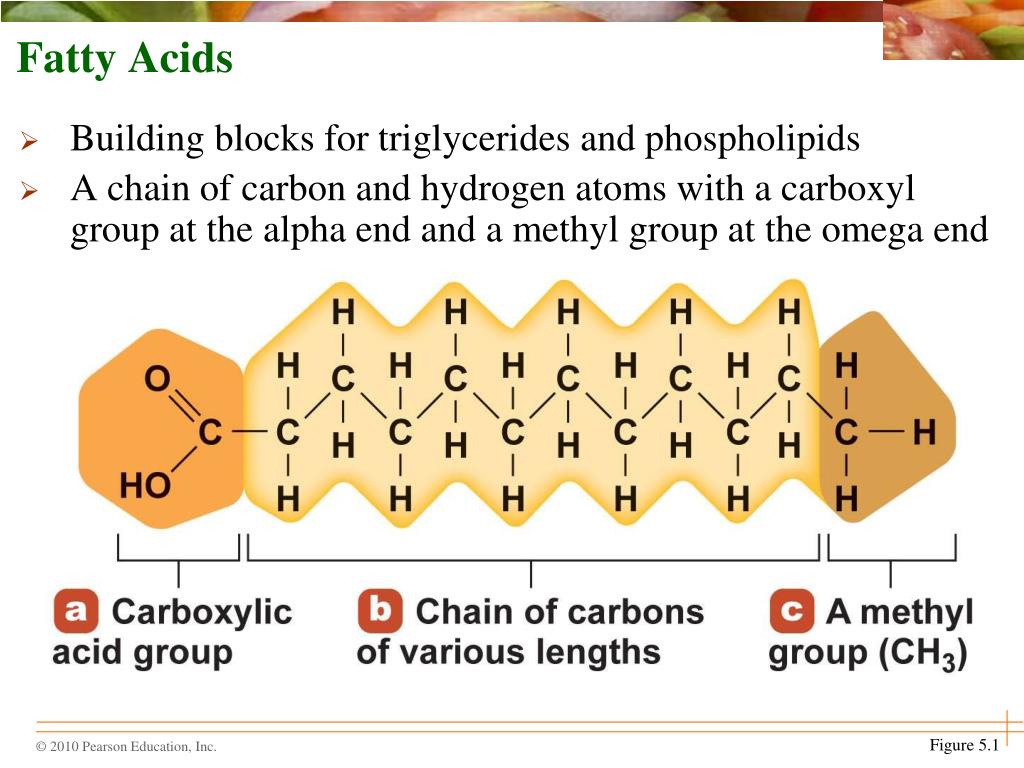
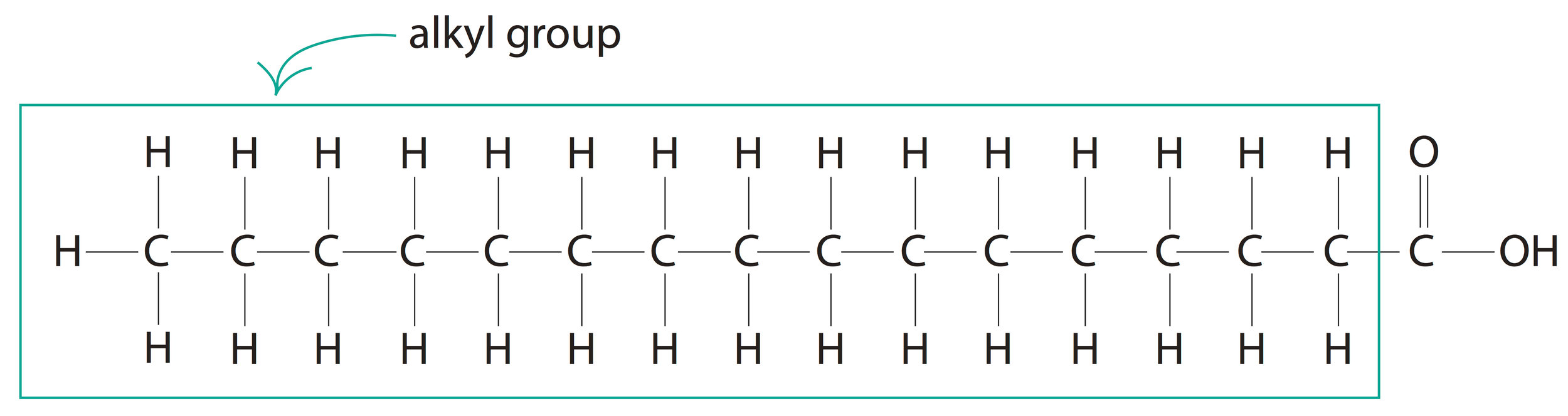
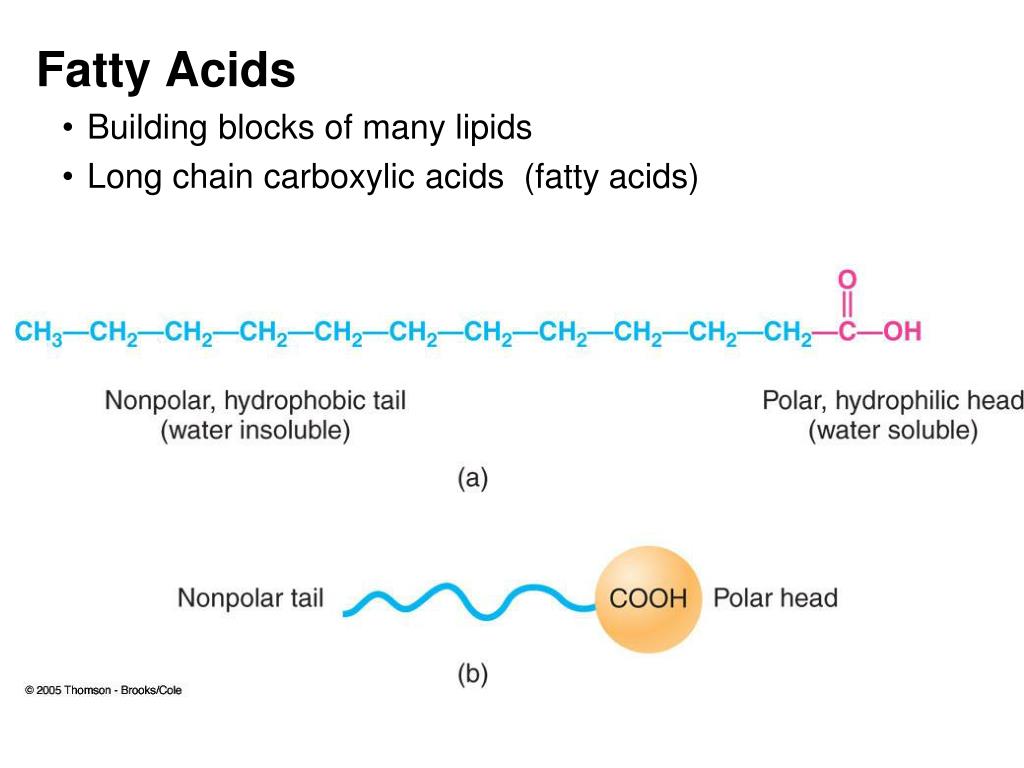
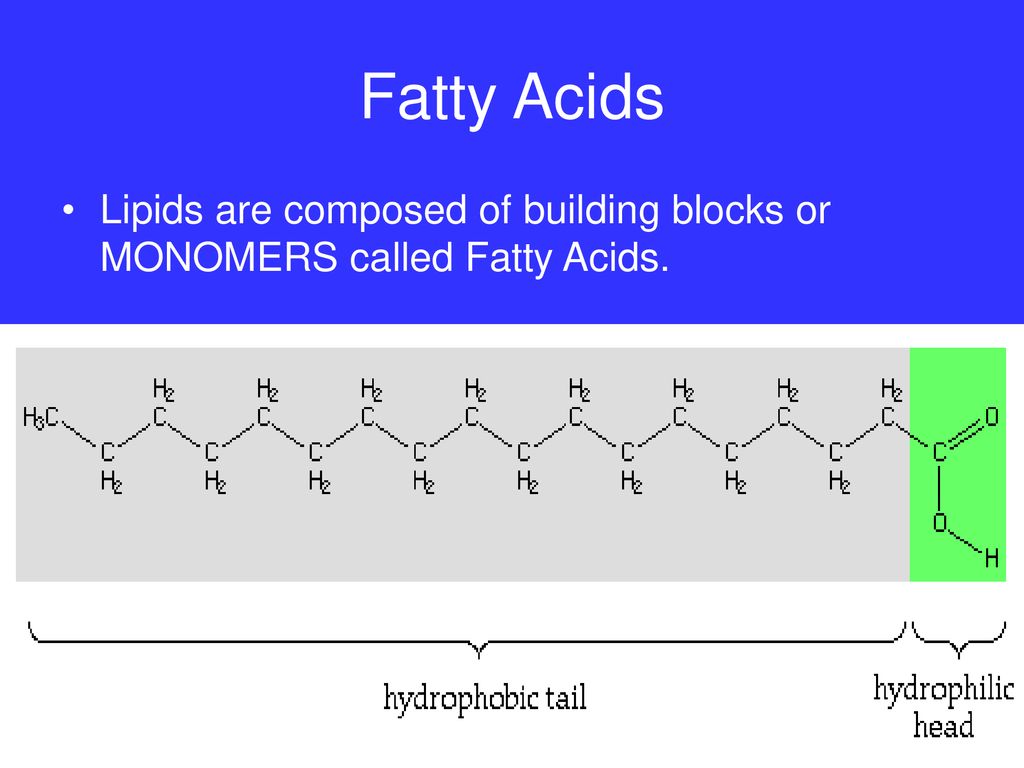
Fatty Acids Are The Building Blocks Of - Lipid molecules serve as storage. Triglycerides are the main form of lipid found in the body and in the diet. Fats are the product of the esterification of the trivalent alcohol glycerol with fatty acids of different lengths. When each carbon is bonded with two hydrogen atoms, the chain is ___ with hydrogen. Many of these molecular building blocks are similar, or homologous, in structure. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Fatty acids (fa), as part of molecules or acting individually, have diverse functions in cells that range from structural “building blocks” of cell membranes to suppliers of energy. They are used not only for energy but also for many basic structures in the human body, such as the outer membrane of every single cell. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and. Fatty acids are chains of carbon molecules with a carboxylic acid (cooh) in the first carbon and a ch3 (methyl) group at the end of the chain. It's important for bone health as it helps the body absorb the bone's building blocks: Learn how fatty acids are the simplest forms of lipids and how they are esters of glycerol. Many of these molecular building blocks are similar, or homologous, in structure. Learn about the different types of fatty acids, their functions in the body and cell membranes, and their importance for health and longevity. Fats play a vital role in the body, supporting energy production, tissue development, and overall cellular function. They have a long chain of hydrocarbons to which a carboxyl (carboxylic acid) group is attached, hence the name “fatty. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. To promote fat digestion, the gallbladder releases ___ into the small intestine. During digestion, the body converts fats into fatty acids, which are then absorbed into the bloodstream. Fatty acids are chains of carbon molecules with a carboxylic acid (cooh) in the first carbon and a ch3 (methyl) group at the end of the chain. Fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks of triglycerides. Lipid molecules serve as storage. They have a long chain of hydrocarbons to which a carboxyl (carboxylic acid) group is attached, hence the name “fatty. Understand the properties and types of fatty acids and how they are used to make. Fatty acids are chains of carbon molecules with a carboxylic. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and. Lipids are also the building blocks of many hormones and are an important constituent of all cellular membranes. When each carbon is bonded with two hydrogen atoms, the chain is ___ with hydrogen. Fats are the product of the esterification of the trivalent alcohol glycerol with fatty acids of different lengths. Lipids are. The homologies allow lipids to be classified into a few major groups: Lipid molecules serve as storage. Fatty acids (fa), as part of molecules or acting individually, have diverse functions in cells that range from structural “building blocks” of cell membranes to suppliers of energy. Lipids are also the building blocks of many hormones and are an important constituent of. Fatty acids are chains of carbon molecules with a carboxylic acid (cooh) in the first carbon and a ch3 (methyl) group at the end of the chain. Fatty acids are the building blocks of fats. Fatty acids are the building blocks of the fat in our bodies and in the food we eat. Glycerol and fatty acids are the basic. Understand the properties and types of fatty acids and how they are used to make. Learn how fatty acids are the simplest forms of lipids and how they are esters of glycerol. Fats play a vital role in the body, supporting energy production, tissue development, and overall cellular function. The homologies allow lipids to be classified into a few major. Fatty acids are the building blocks of fat in our bodies and the food we consume. Fats play a vital role in the body, supporting energy production, tissue development, and overall cellular function. Triglycerides are the main form of lipid found in the body and in the diet. Fatty acids are the building blocks of fats. Lipids are also the. Glycerol and fatty acids are the basic building blocks of fats (lipids). Fatty acids (fa), as part of molecules or acting individually, have diverse functions in cells that range from structural “building blocks” of cell membranes to suppliers of energy. Fatty acids are the building blocks of the fat in our bodies and in the food we eat. Many of. The homologies allow lipids to be classified into a few major groups: During digestion, the body breaks down fats into fatty acids, which can then be absorbed into the blood. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. It's important for bone health as it helps the body absorb the bone's building blocks: Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and. The homologies allow lipids to be classified into a few major groups: Fatty acids (fa), as part of molecules or acting individually, have diverse functions in cells that range from structural “building blocks” of cell membranes to suppliers of energy. Many of these molecular building blocks are similar, or homologous, in structure. Understand the properties and types of fatty acids. Learn how fatty acids are the simplest forms of lipids and how they are esters of glycerol. During digestion, the body breaks down fats into fatty acids, which can then be absorbed into the blood. Glycerol and fatty acids are the basic building blocks of fats (lipids). Fatty acids (fa), as part of molecules or acting individually, have diverse functions. Glycerol is a thick, smooth, syrupy compound that is. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. During digestion, the body breaks down fats into fatty acids, which can then be absorbed into the blood. Fatty acids (fa), as part of molecules or acting individually, have diverse functions in cells that range from structural “building blocks” of cell membranes to suppliers of energy. Lipid molecules serve as storage. When each carbon is bonded with two hydrogen atoms, the chain is ___ with hydrogen. Learn about the different types of fatty acids, their functions in the body and cell membranes, and their importance for health and longevity. Fatty acids are chains of carbon molecules with a carboxylic acid (cooh) in the first carbon and a ch3 (methyl) group at the end of the chain. Triglycerides are the main form of lipid found in the body and in the diet. Fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks of triglycerides. They have a long chain of hydrocarbons to which a carboxyl (carboxylic acid) group is attached, hence the name “fatty. Fatty acids are the building blocks of fat in our bodies and the food we consume. Many of these molecular building blocks are similar, or homologous, in structure. Learn how fatty acids are the simplest forms of lipids and how they are esters of glycerol. Fatty acids are building blocks in several other types of lipids. They are used not only for energy but also for many basic structures in the human body, such as the outer membrane of every single cell.PPT Lipids & Nucleic Acids PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Fatty Acids The building blocks of lipids — Firstclass
Fatty acids are the Building Blocks of Fats and Oils (Basics)
PPT FATS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9300520
PPT Chapter 5 Fats, Oils, and Other Lipids PowerPoint Presentation
Fatty Acids The building blocks of lipids — Firstclass
PPT Chapter 21 Lipids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1446650
Fatty Acids The Building Blocks of Fats Fab & Nutritious
nukilan rasa from the beginner lipids,gallstones
Lipids. ppt download
Lipids Are Also The Building Blocks Of Many Hormones And Are An Important Constituent Of All Cellular Membranes.
Lipids Include Fats, Oils, Waxes, Phospholipids, And.
Fatty Acids Are The Building Blocks Of The Fat In Our Bodies And In The Food We Eat.
To Promote Fat Digestion, The Gallbladder Releases ___ Into The Small Intestine.
Related Post: