How Does Nitrogen Connect To The Building Of Certain Macromolecules
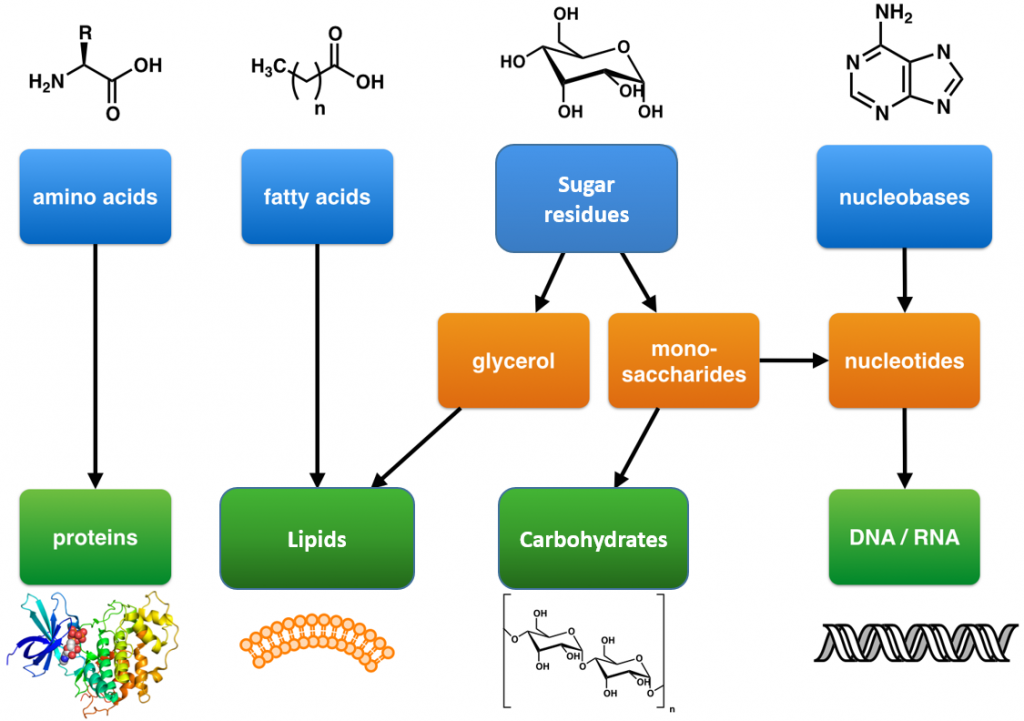
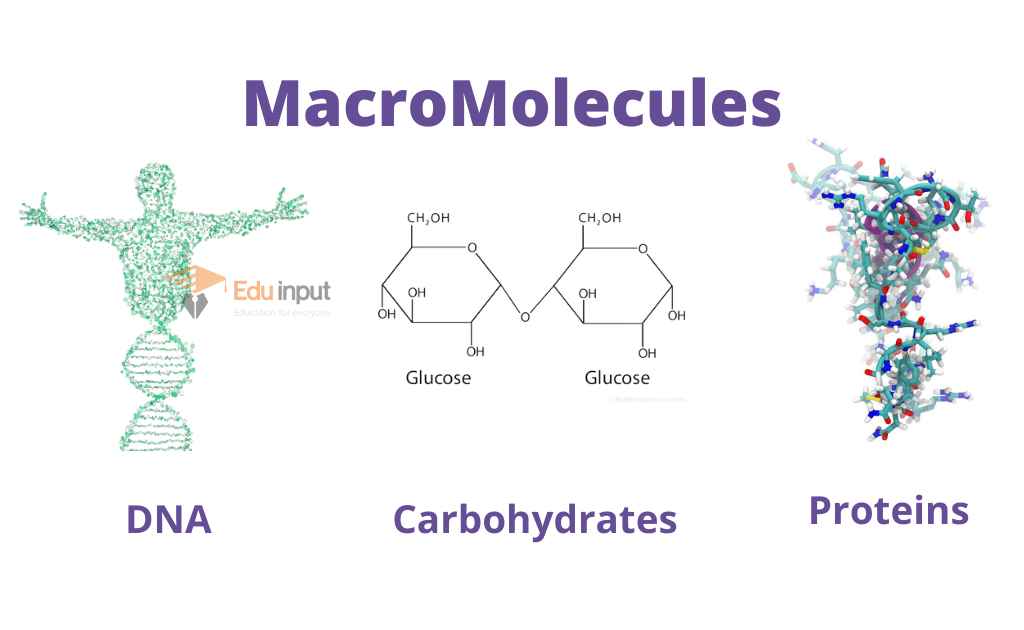
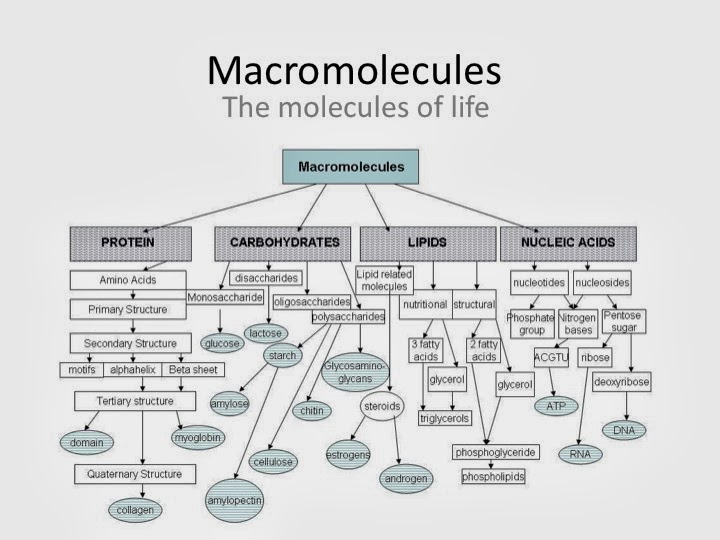
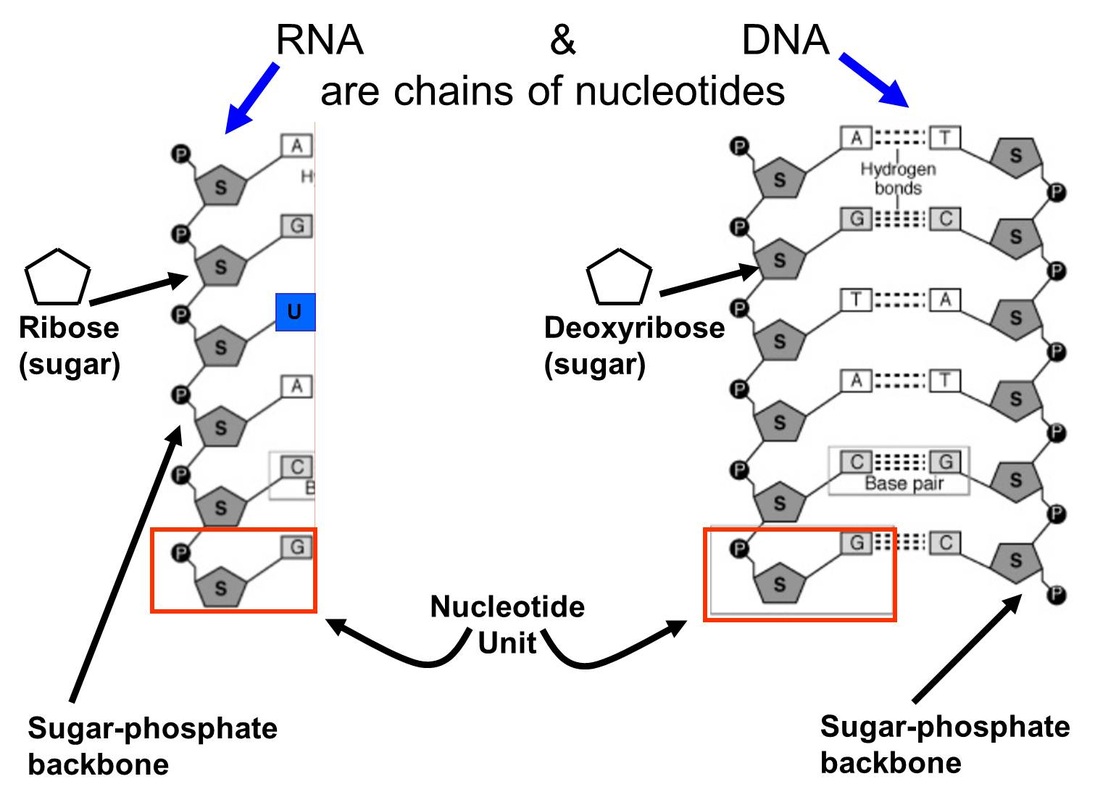
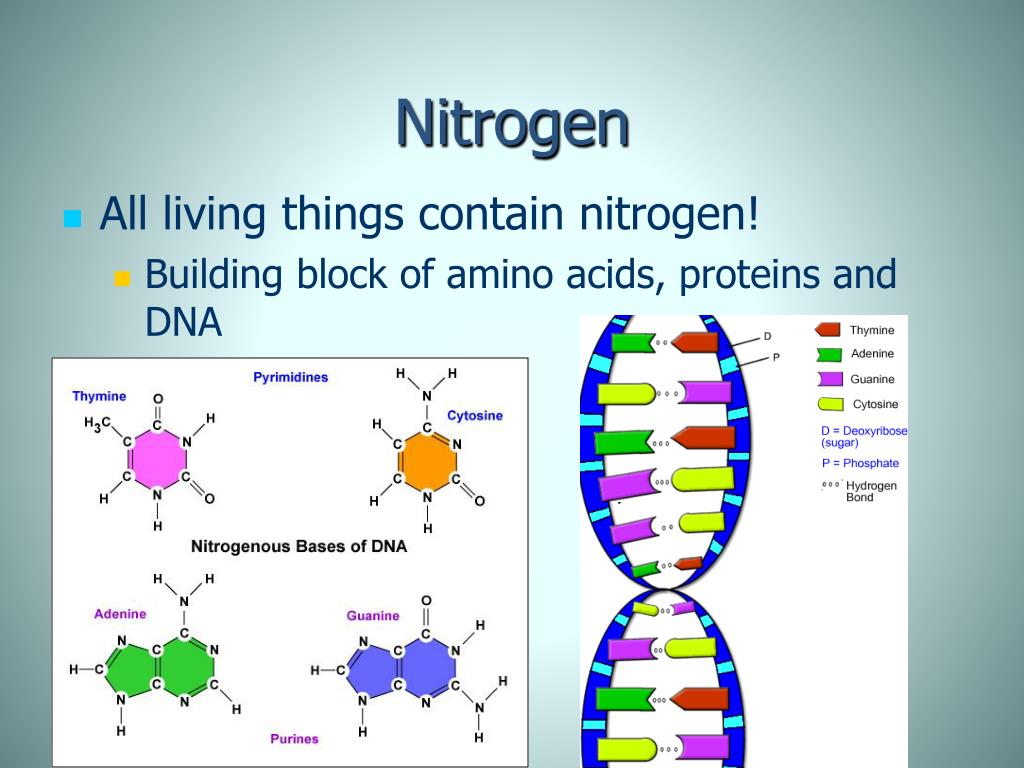
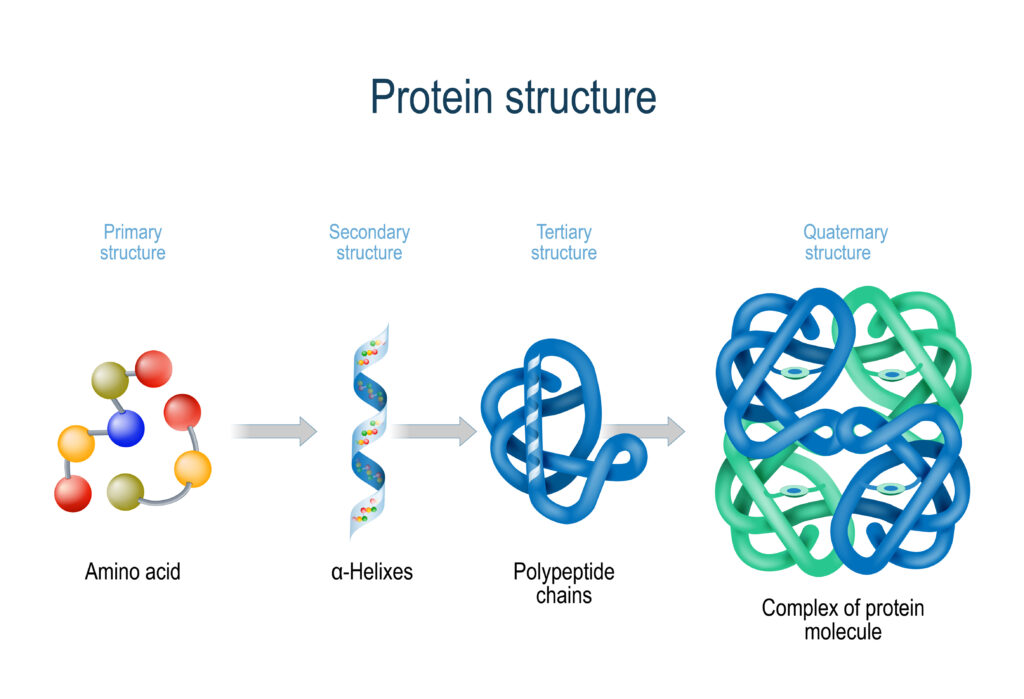
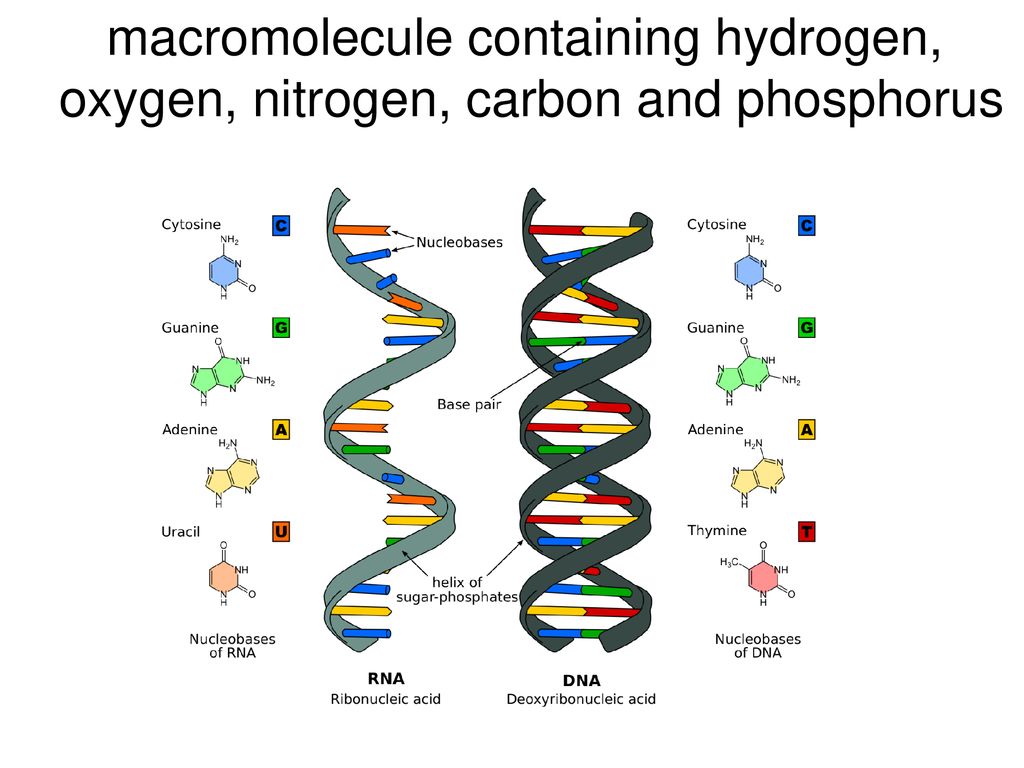
How Does Nitrogen Connect To The Building Of Certain Macromolecules - Nitrogen is crucial for the structure and. How does nitrogen connect to the building of certain macromolecules? It is a fundamental building block of many biological molecules, including proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. Describe the biological significance of nitrogenase in converting atmospheric n₂ into ammonia (nh₃) and its essential. The reactions shown are oxidative and reductive. The reduced form of nitrogen is particularly vital, as it constitutes the primary element found within three crucial biological macromolecules: Certain bacteria in the soil and water can convert this atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia (nh₃) through a process called nitrogen fixation. It is reused through plant and animal. Nitrogen is also involved in pivotal biological processes such as the. The nitrogen cycle and building macromolecules are connected because the nitrogen cycle ensures that nitrogen is available for the building of macromolecules in both plants and animals. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what processes do the kelp perform to make their food molecules and break them down for energy?, what process do the. Where does nitrogen come from and how is it reused/recycled? Lack of cytoplasmic glutamate dehydrogenase leads to a dependency of amino acids consumption as the source of organic nitrogen, i.e., the organism in a certain sense actually. The nitrogen cycle and building macromolecules are connected because the nitrogen cycle ensures that nitrogen is available for the building of macromolecules in both plants and animals. How does the nitrogen cycle connect to building macromolecules ? The presence of nitrogen is a key factor that differentiates proteins from other macromolecules such as carbohydrates and lipids. Composed of building blocks called amino acids, which contain an amino group that. Nitrogen is crucial for the structure and. This ammonia can then be used by. Nitrogen is also involved in pivotal biological processes such as the. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what processes do the kelp perform to make their food molecules and break them down for energy?, what process do the. How does the nitrogen cycle connect to building macromolecules ? These macromolecules store and transfer genetic information critical for cell function and heredity. Nitrogen is also involved in pivotal biological. Composed of building blocks called amino acids, which contain an amino group that. Where does nitrogen come from and how is it reused/recycled? How does nitrogen connect to the building of certain macromolecules? These macromolecules store and transfer genetic information critical for cell function and heredity. Nitrogen is a crucial element for all life on earth. This ammonia can then be used by. How does the nitrogen cycle connect to building macromolecules ? Describe the biological significance of nitrogenase in converting atmospheric n₂ into ammonia (nh₃) and its essential. Nucleic acids use nitrogen for nitrogen bases such as adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. Lack of cytoplasmic glutamate dehydrogenase leads to a dependency of amino acids consumption. Nitrogen is also involved in pivotal biological processes such as the. Understanding the role of nitrogenase in nitrogen metabolism. Proteins contain amino acids with nitrogen in the form of an amino group, while nucleic acids contain nitrogenous bases for genetic information storage. How does nitrogen connect to the building of certain macromolecules? Nitrogen (found in proteins) is digested in food,. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what processes do the kelp perform to make their food molecules and break them down for energy?, what process do the. Composed of building blocks called amino acids, which contain an amino group that. The reduced form of nitrogen is particularly vital, as it constitutes the primary element found within three. Describe the biological significance of nitrogenase in converting atmospheric n₂ into ammonia (nh₃) and its essential. These macromolecules store and transfer genetic information critical for cell function and heredity. Nitrogen comes from bacteria in plant roots and soil, lightning, and the atmosphere. It is reused through plant and animal. Nitrogen is also involved in pivotal biological processes such as the. Describe the biological significance of nitrogenase in converting atmospheric n₂ into ammonia (nh₃) and its essential. The reactions shown are oxidative and reductive. Lack of cytoplasmic glutamate dehydrogenase leads to a dependency of amino acids consumption as the source of organic nitrogen, i.e., the organism in a certain sense actually. How does the nitrogen cycle connect to building macromolecules ?. Proteins use nitrogen as part of amino group, which is nh2. Certain bacteria in the soil and water can convert this atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia (nh₃) through a process called nitrogen fixation. The presence of nitrogen is a key factor that differentiates proteins from other macromolecules such as carbohydrates and lipids. How does nitrogen connect to the building of certain. The nitrogen cycle and building macromolecules are connected because the nitrogen cycle ensures that nitrogen is available for the building of macromolecules in both plants and animals. How does the nitrogen cycle connect to building macromolecules ? Composed of building blocks called amino acids, which contain an amino group that. Nitrogen comes from bacteria in plant roots and soil, lightning,. How does nitrogen connect to the building of certain macromolecules? The reactions shown are oxidative and reductive. This ammonia can then be used by. The nitrogen cycle and building macromolecules are connected because the nitrogen cycle ensures that nitrogen is available for the building of macromolecules in both plants and animals. Proteins contain amino acids with nitrogen in the form. Biological fixation of n takes place mainly through enzymatic reactions and occurs only in certain organisms which include prokaryotes, cyanobacteria and some symbiotic plants such as. It is a fundamental building block of many biological molecules, including proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. Proteins contain amino acids with nitrogen in the form of an amino group, while nucleic acids contain nitrogenous bases for genetic information storage. The reduced form of nitrogen is particularly vital, as it constitutes the primary element found within three crucial biological macromolecules: This ammonia can then be used by. How does nitrogen connect to the building of certain macromolecules? Nitrogen (found in proteins) is digested in food, and then chemical reactions take place in the body where bonds. Nitrogen is also involved in pivotal biological processes such as the. Nitrogen is crucial for the structure and. Understanding the role of nitrogenase in nitrogen metabolism. Proteins/polypeptides, dna and rna, and polymers. These macromolecules store and transfer genetic information critical for cell function and heredity. Where does nitrogen come from and how is it reused/recycled? Both of these macromolecules contain nitrogen as an essential component: Describe the biological significance of nitrogenase in converting atmospheric n₂ into ammonia (nh₃) and its essential. Nitrogen is a crucial element for all life on earth.Macromolecules & Enzymes ppt download
CH103 Chapter 8 The Major Macromolecules Chemistry
What are Macromolecules?Definition and Examples
Mr. Maxey's Biology Blog The Building Blocks of Life Macromolecules
PPT Nitrogen Cycle! PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9153503
simple diagram of macromolecules, proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and
Nucleic Acids Macromolecule Mania
PPT Nitrogen Cycle PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1992023
Plant Nutrition The Macro Nutrients Nitrogen Arktivate Organic
BIOLOGY Vocabulary Chapter 12 & ppt download
The Reactions Shown Are Oxidative And Reductive.
The Nitrogen Cycle And Building Macromolecules Are Connected Because The Nitrogen Cycle Ensures That Nitrogen Is Available For The Building Of Macromolecules In Both Plants And Animals.
Proteins Use Nitrogen As Part Of Amino Group, Which Is Nh2.
Certain Bacteria In The Soil And Water Can Convert This Atmospheric Nitrogen Into Ammonia (Nh₃) Through A Process Called Nitrogen Fixation.
Related Post: