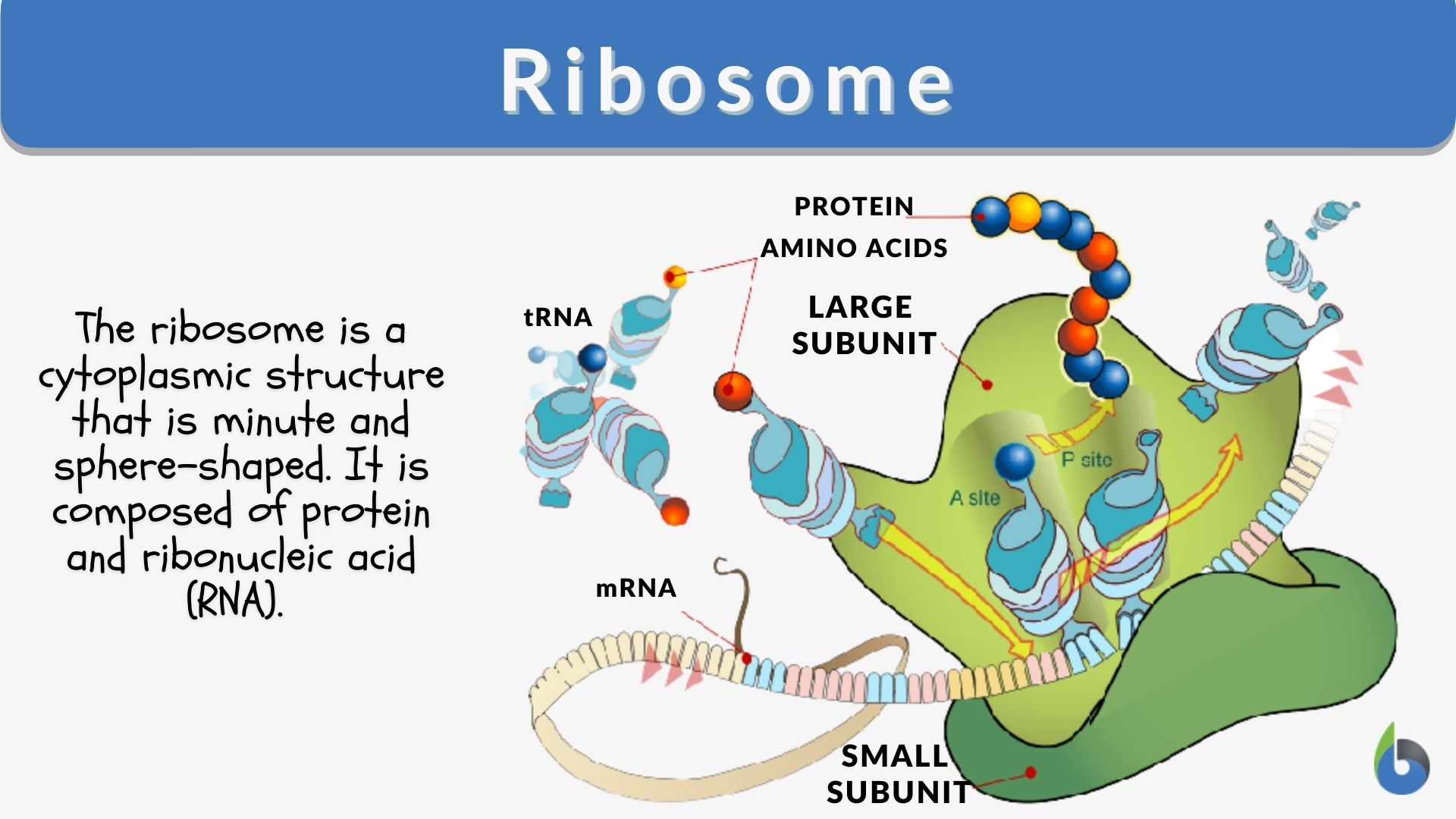
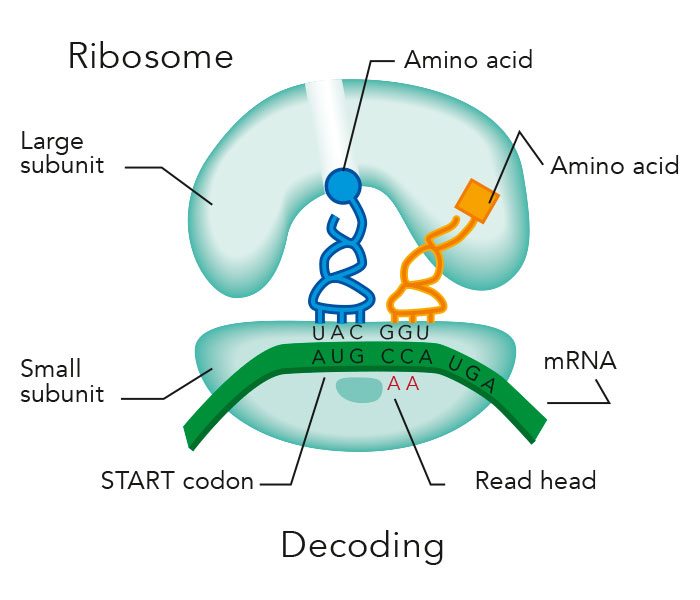
How Does The Ribosome Build A Protein
How Does The Ribosome Build A Protein - Ribosomes are biological machines that consist of rna and proteins. Coli, this complex involves the small 30s ribosome, the mrna template, three initiation factors (ifs; Reading the mrna from 5′ to 3′ and synthesizing the polypeptide from the. In prokaryotes, there is no nucleus in the cell so the ribosomes catalyze the formation of proteins by working on the mrna in the cytoplasm with the help of trna. The ribosome provides a substrate for translation, bringing together and aligning the mrna molecule with the molecular “translators” that must decipher its code. Each mrna molecule is simultaneously translated by many ribosomes, all synthesizing protein in the same direction: The synthesis of proteins consumes more of a cell’s energy than any other metabolic process. Rrna (ribosome) builds the polypeptide we've already learned. Ribosome, particle that is present in large numbers in all living cells and serves as the site of protein synthesis. Protein synthesis begins with the formation of an initiation complex. Reading the mrna from 5′ to 3′ and synthesizing the polypeptide from the. Ribosomes are key molecular machines in cell biology that are needed for making proteins. Protein synthesis begins with the formation of an initiation complex. In turn, proteins account for more mass than any other component of living organisms (other than. Mrna carries the instructions 2. In eukaryotes, there is a. Coli, this complex involves the small 30s ribosome, the mrna template, three initiation factors (ifs; Rrna (ribosome) builds the polypeptide we've already learned. Within the ribosome, the rrna molecules direct the catalytic steps of protein synthesis — the stitching together of amino acids to make a protein molecule. Each mrna molecule is simultaneously translated by many ribosomes, all synthesizing protein in the same direction: Mrna carries the instructions 2. The translation of information and the linking of. Ribosomes are biological machines that consist of rna and proteins. Each mrna molecule is simultaneously translated by many ribosomes, all synthesizing protein in the same direction: Each mrna molecule is simultaneously translated by many ribosomes, all synthesizing protein in the same direction: Mrna carries the instructions 2. Within the ribosome, the rrna molecules direct the catalytic steps of protein synthesis — the stitching together of amino acids to make a protein molecule. The translation of information and the linking of. The ribosome provides a substrate for translation, bringing together and aligning the mrna molecule with the molecular “translators” that must decipher its. Coli, this complex involves the small 30s ribosome, the mrna template, three initiation factors (ifs; Understanding protein synthesis reveals insights into how cells operate and respond to various stimuli. Each mrna molecule is simultaneously translated by many ribosomes, all synthesizing protein in the same direction: Reading the mrna from 5′ to 3′ and synthesizing the polypeptide from the. Within the. Within the ribosome, the rrna molecules direct the catalytic steps of protein synthesis — the stitching together of amino acids to make a protein molecule. Ribosomes are biological machines that consist of rna and proteins. Protein synthesis begins with the formation of an initiation complex. The ribosome provides a substrate for translation, bringing together and aligning the mrna molecule with. The synthesis of proteins consumes more of a cell’s energy than any other metabolic process. Ribosomes occur both as free particles in prokaryotic and. Ribosomes play a crucial role in the process of translation, where genetic information from mrna is used to synthesize proteins. Ribosomes are key molecular machines in cell biology that are needed for making proteins. Each mrna. In eukaryotes, there is a. Ribosomes are composed of special proteins and nucleic acids. Reading the mrna from 5' to 3' and synthesizing. Ribosomes synthesize proteins by translating messenger rna into amino acid sequences, essential for cellular functions. Protein synthesis begins with the formation of an initiation complex. Ribosome, particle that is present in large numbers in all living cells and serves as the site of protein synthesis. In turn, proteins account for more mass than any other component of living organisms (other than. Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis, translating genetic information into functional proteins. Ribosomes synthesize proteins by translating messenger rna into amino acid sequences, essential. Protein synthesis begins with the formation of an initiation complex. Reading the mrna from 5' to 3' and synthesizing. Ribosome, particle that is present in large numbers in all living cells and serves as the site of protein synthesis. Understanding protein synthesis reveals insights into how cells operate and respond to various stimuli. They are made of ribosomal rna (rrna). In eukaryotes, there is a. Coli, this complex involves the small 30s ribosome, the mrna template, three initiation factors (ifs; Reading the mrna from 5' to 3' and synthesizing. Reading the mrna from 5′ to 3′ and synthesizing the polypeptide from the. Ribosomes are key molecular machines in cell biology that are needed for making proteins. Within the ribosome, the rrna molecules direct the catalytic steps of protein synthesis — the stitching together of amino acids to make a protein molecule. Each mrna molecule is simultaneously translated by many ribosomes, all synthesizing protein in the same direction: In eukaryotes, there is a. Ribosomes play a crucial role in the process of translation, where genetic information from. In eukaryotes, there is a. Each mrna molecule is simultaneously translated by many ribosomes, all synthesizing protein in the same direction: Ribosomes play a crucial role in the process of translation, where genetic information from mrna is used to synthesize proteins. Rrna (ribosome) builds the polypeptide we've already learned. Mrna carries the instructions 2. Each mrna molecule is simultaneously translated by many ribosomes, all synthesizing protein in the same direction: In prokaryotes, there is no nucleus in the cell so the ribosomes catalyze the formation of proteins by working on the mrna in the cytoplasm with the help of trna. The ribosome provides a substrate for translation, bringing together and aligning the mrna molecule with the molecular “translators” that must decipher its code. Trna provides the building materials (amino acids) 3. Ribosomes synthesize proteins by translating messenger rna into amino acid sequences, essential for cellular functions. Ribosome, particle that is present in large numbers in all living cells and serves as the site of protein synthesis. Reading the mrna from 5′ to 3′ and synthesizing the polypeptide from the. In turn, proteins account for more mass than any other component of living organisms (other than. Ribosomes are composed of special proteins and nucleic acids. Coli, this complex involves the small 30s ribosome, the mrna template, three initiation factors (ifs; Coli, this complex involves the small 30s ribosome, the mrna template, three initiation factors (ifs;Ribosomes and Protein Assembly
Ribosomes The protein factory of the cell
Ribosomes and Protein Assembly
Ribosome protein factory definition, function, structure and biology
Ribosome protein factory definition, function, structure and biology
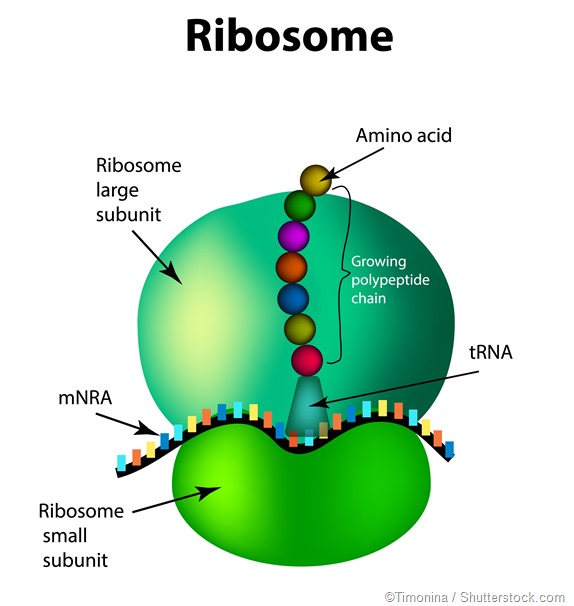
Ribosome Structure
Ribosomes and Protein Assembly
Ribosome Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Choreographed movement unlocking the inner workings of the ribosome
The structure of the ribosome Infographics on Vector Image
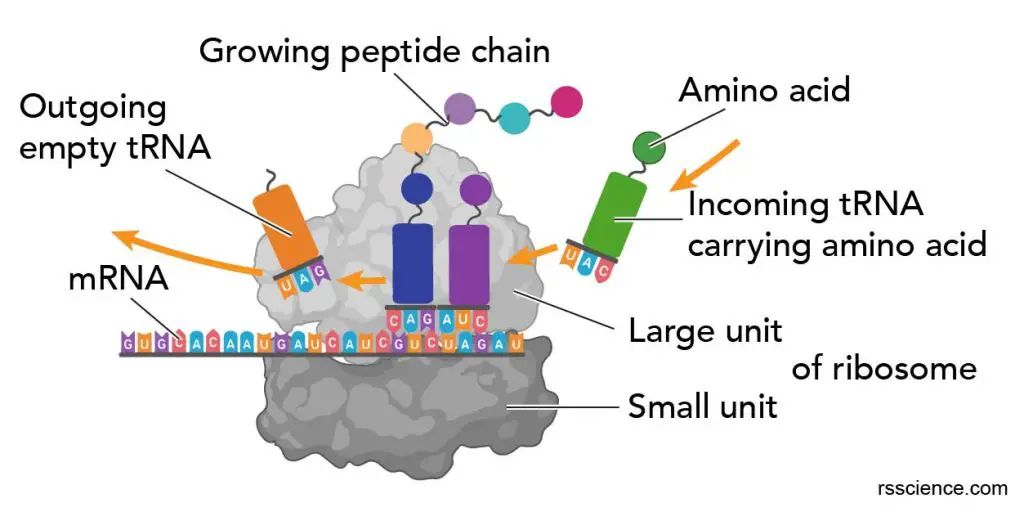
Ribosomes Are Key Molecular Machines In Cell Biology That Are Needed For Making Proteins.
Protein Synthesis Begins With The Formation Of An Initiation Complex.
Ribosomes Are Biological Machines That Consist Of Rna And Proteins.
They Are Made Of Ribosomal Rna (Rrna) And Proteins And Serve To Translate Messenger Rna.
Related Post:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rough_ER-4e539384788e43c498d45acaf500e5bf.jpg)
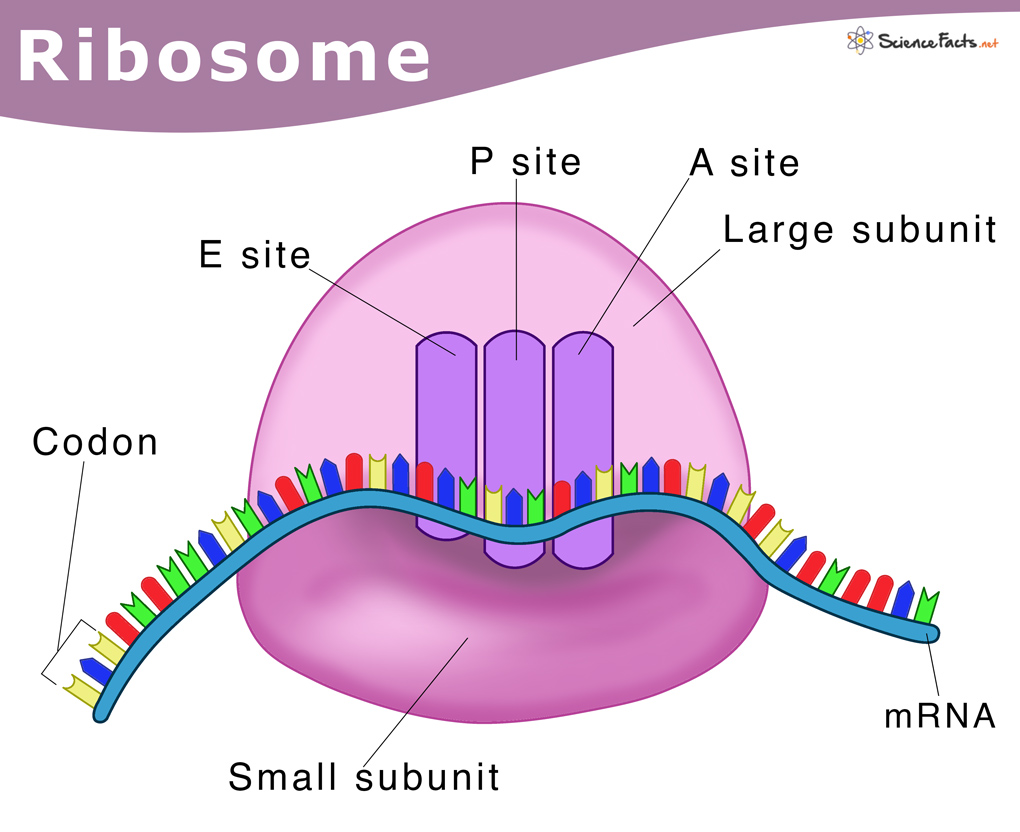
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/protein_synthesis-6c2ebf130fd141f3944ff88dbe4481c8.jpg)
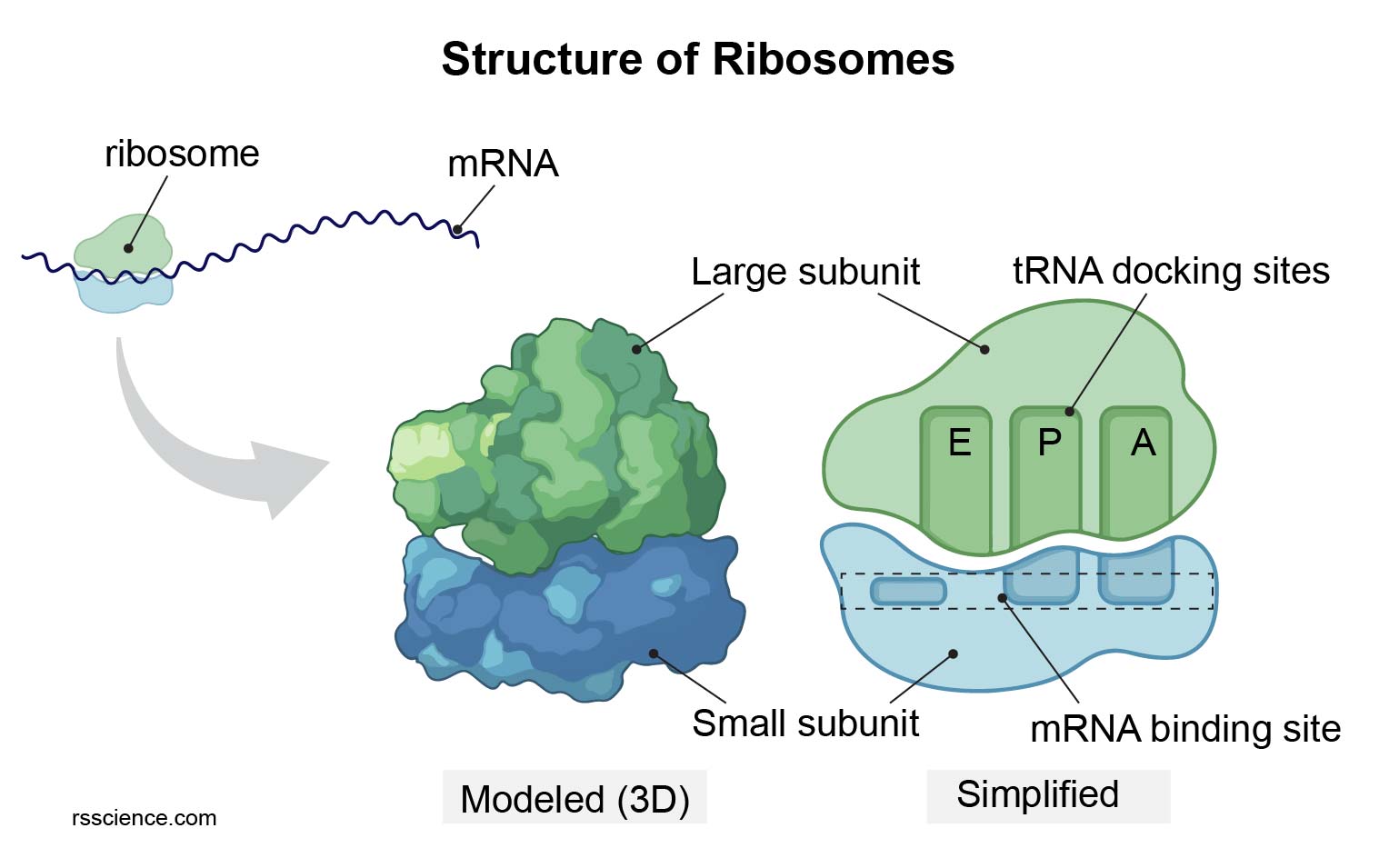
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ribosome_lrg_sm_subunits-23b46a3be6354c4eacb550b25fa3c69d.jpg)