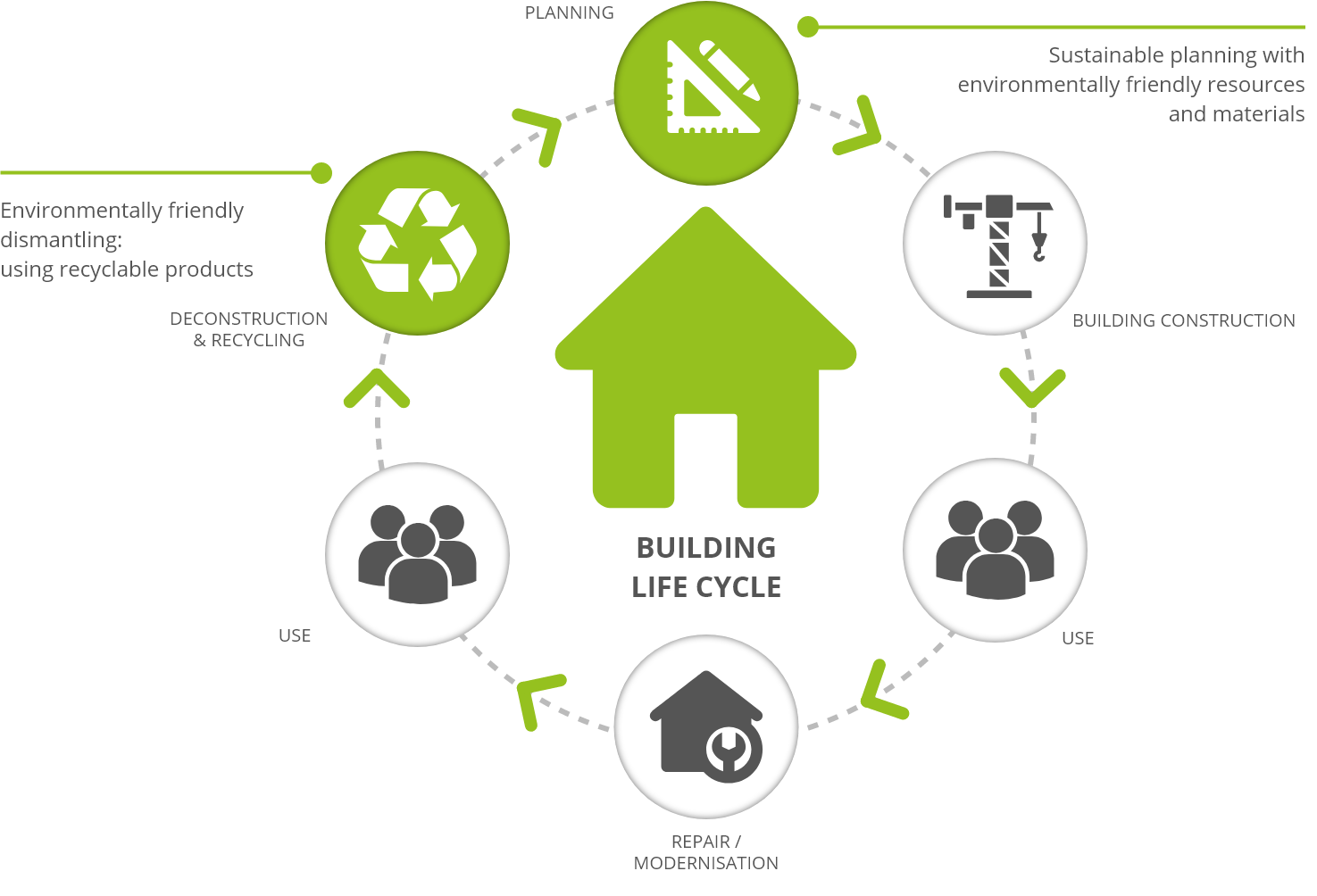
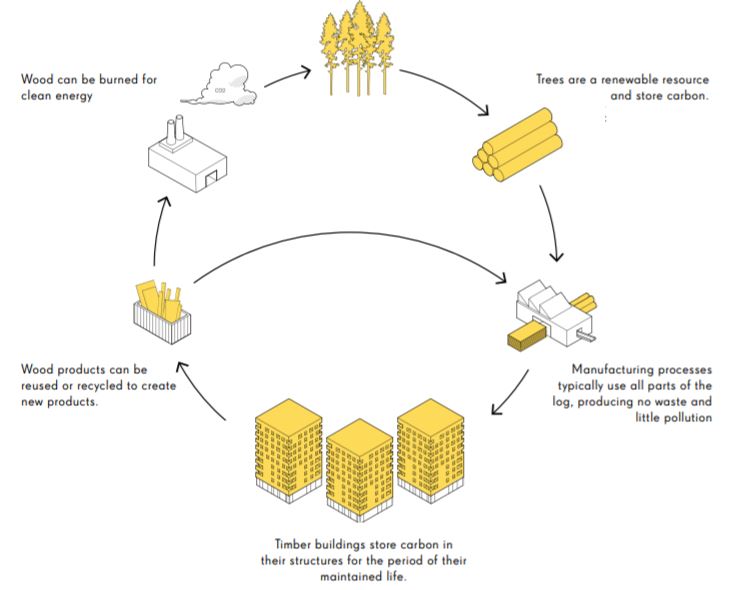
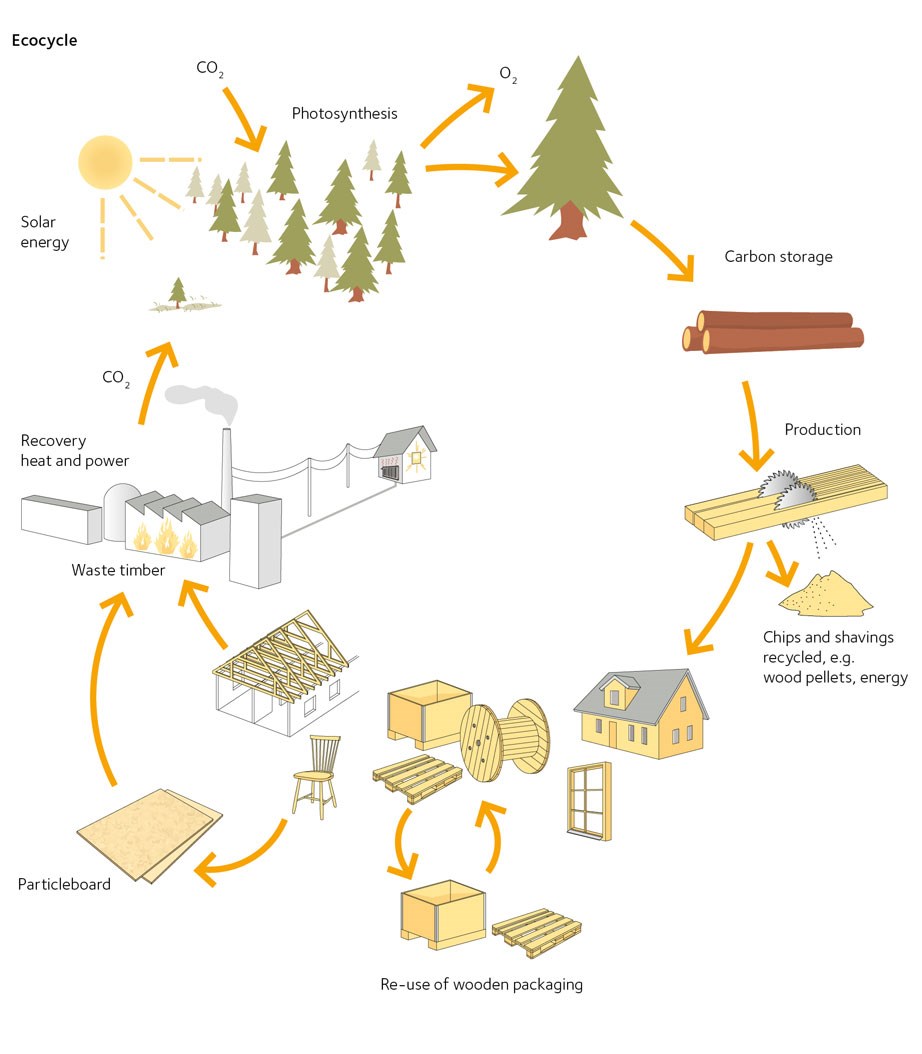
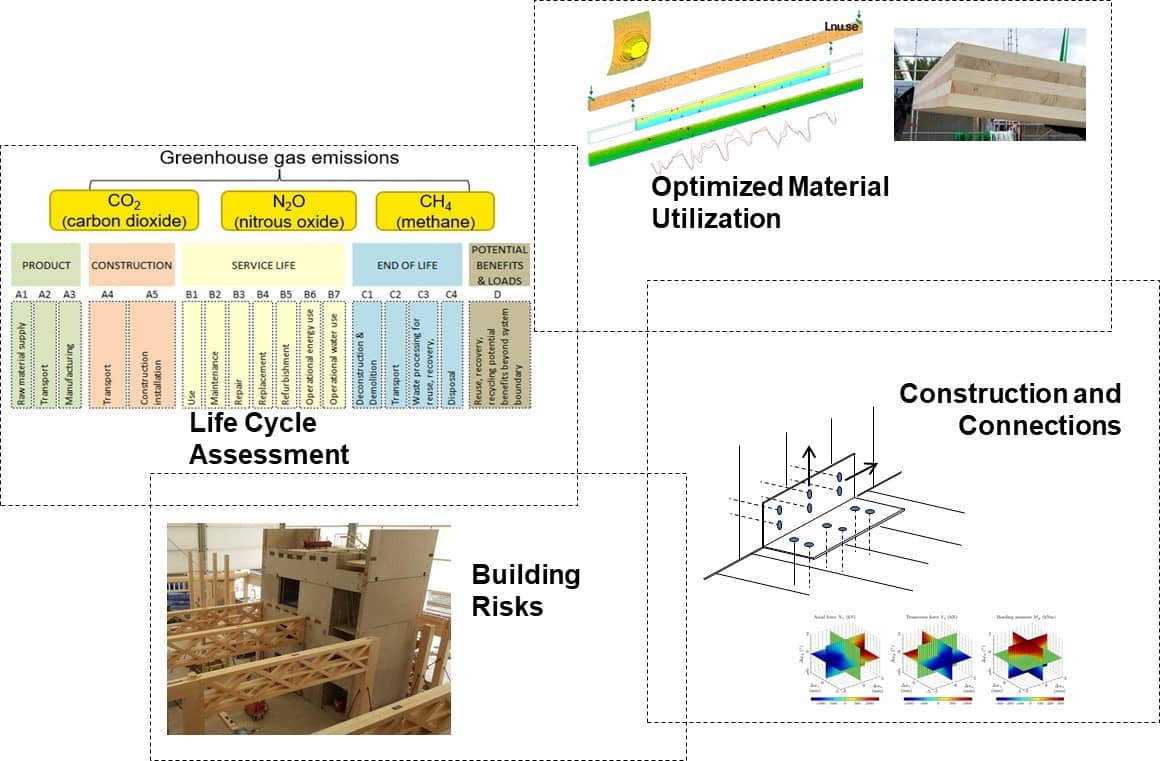
Life Cycle Clt Building Benefits Diagram
Life Cycle Clt Building Benefits Diagram - Numerous studies have investigated the environmental benefits of cross laminated timber (clt) construction in comparison to conventional construction, typically using a life cycle. #9 “intro to life cycle assessment” provides a diagram and. In this wblca, it is assumed that 14.5% of wood and clt is recycled, 22% is incinerated with energy recovery, and 63.5% is landfilled. Clt is a type of engineered. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the comparative analysis of clt and traditional materials, focusing on cost, performance, and sustainability. Presents several current knowledge gaps and recommendations about wood, carbon, clt, and life cycle assessments (lcas). The business case for green building. Whole building life cycle assessments. Using athena impact estimator for buildings (ie4b), this paper. This study uses life cycle assessment to assess the potential environmental impacts across the entire life cycle which includes resource extraction, building material fabrication, building. In this wblca, it is assumed that 14.5% of wood and clt is recycled, 22% is incinerated with energy recovery, and 63.5% is landfilled. Clt is a sustainable and versatile building material. This study quantifies the life cycle ghg emissions and life cycle cost for two type of construction (rc and clt) for midrise residential buildings, in the three cities (melbourne,. The research on life cycle carbon footprint explores and identifies strategies to optimise the climate impact of clt buildings, focusing on the synergies between the structural. Numerous studies have investigated the environmental benefits of cross laminated timber (clt) construction in comparison to conventional construction, typically using a life cycle. Clt is a type of engineered. Using athena impact estimator for buildings (ie4b), this paper. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the comparative analysis of clt and traditional materials, focusing on cost, performance, and sustainability. Presents several current knowledge gaps and recommendations about wood, carbon, clt, and life cycle assessments (lcas). #9 “intro to life cycle assessment” provides a diagram and. Clt is a type of engineered. In this wblca, it is assumed that 14.5% of wood and clt is recycled, 22% is incinerated with energy recovery, and 63.5% is landfilled. The business case for green building. Leed’s evolution is deeply tied to market dynamics, and leed v5 reflects an alignment between sustainability goals and economic. Environmental management — life cycle. The research on life cycle carbon footprint explores and identifies strategies to optimise the climate impact of clt buildings, focusing on the synergies between the structural. Quantifying the impact of building materials can be critical to developing an effective greenhouse gas mitigation strategy. This study uses life cycle assessment to assess the potential environmental impacts across the entire life cycle. In this wblca, it is assumed that 14.5% of wood and clt is recycled, 22% is incinerated with energy recovery, and 63.5% is landfilled. This study quantifies the life cycle ghg emissions and life cycle cost for two type of construction (rc and clt) for midrise residential buildings, in the three cities (melbourne,. Using athena impact estimator for buildings (ie4b),. Clt is a type of engineered. #9 “intro to life cycle assessment” provides a diagram and. Quantifying the impact of building materials can be critical to developing an effective greenhouse gas mitigation strategy. Numerous studies have investigated the environmental benefits of cross laminated timber (clt) construction in comparison to conventional construction, typically using a life cycle. This study quantifies the. Whole building life cycle assessments. The authors performed a brief review. The business case for green building. Presents several current knowledge gaps and recommendations about wood, carbon, clt, and life cycle assessments (lcas). This study uses life cycle assessment to assess the potential environmental impacts across the entire life cycle which includes resource extraction, building material fabrication, building. Presents several current knowledge gaps and recommendations about wood, carbon, clt, and life cycle assessments (lcas). Whole building life cycle assessments. #9 “intro to life cycle assessment” provides a diagram and. Environmental management — life cycle assessment — principles and framework. Leed’s evolution is deeply tied to market dynamics, and leed v5 reflects an alignment between sustainability goals and economic. In this wblca, it is assumed that 14.5% of wood and clt is recycled, 22% is incinerated with energy recovery, and 63.5% is landfilled. Clt is a type of engineered. Presents several current knowledge gaps and recommendations about wood, carbon, clt, and life cycle assessments (lcas). This study uses life cycle assessment to assess the potential environmental impacts across the. This study uses life cycle assessment to assess the potential environmental impacts across the entire life cycle which includes resource extraction, building material fabrication, building. #9 “intro to life cycle assessment” provides a diagram and. The authors performed a brief review. Leed’s evolution is deeply tied to market dynamics, and leed v5 reflects an alignment between sustainability goals and economic.. Presents several current knowledge gaps and recommendations about wood, carbon, clt, and life cycle assessments (lcas). The business case for green building. This study uses life cycle assessment to assess the potential environmental impacts across the entire life cycle which includes resource extraction, building material fabrication, building. Using athena impact estimator for buildings (ie4b), this paper. The authors performed a. This study uses life cycle assessment to assess the potential environmental impacts across the entire life cycle which includes resource extraction, building material fabrication, building. This study quantifies the life cycle ghg emissions and life cycle cost for two type of construction (rc and clt) for midrise residential buildings, in the three cities (melbourne,. Quantifying the impact of building materials. This study uses life cycle assessment to assess the potential environmental impacts across the entire life cycle which includes resource extraction, building material fabrication, building. Quantifying the impact of building materials can be critical to developing an effective greenhouse gas mitigation strategy. Numerous studies have investigated the environmental benefits of cross laminated timber (clt) construction in comparison to conventional construction, typically using a life cycle. #9 “intro to life cycle assessment” provides a diagram and. Presents several current knowledge gaps and recommendations about wood, carbon, clt, and life cycle assessments (lcas). The research on life cycle carbon footprint explores and identifies strategies to optimise the climate impact of clt buildings, focusing on the synergies between the structural. Using athena impact estimator for buildings (ie4b), this paper. Leed’s evolution is deeply tied to market dynamics, and leed v5 reflects an alignment between sustainability goals and economic. Environmental management — life cycle assessment — principles and framework. The business case for green building. Whole building life cycle assessments. The authors performed a brief review. This study quantifies the life cycle ghg emissions and life cycle cost for two type of construction (rc and clt) for midrise residential buildings, in the three cities (melbourne,.Why Is Architecture and Building So Different in Europe?
UK CLT
Sustainable Building Construction For a healthy Environment
3 Emerging Trends in Sustainable Architecture and Construction
How CLT Can Save The World Waugh Thistleton Architects
Life cycle thinking buildings Download Scientific Diagram
Sustainability Free FullText Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of Cross
Climatepositive products that build the future Swedish Wood
LifeCycle Assessment of a Building Epsten Group
Structural Engineering and Carbon Footprints of CLT Buildings
Clt Is A Sustainable And Versatile Building Material.
In This Wblca, It Is Assumed That 14.5% Of Wood And Clt Is Recycled, 22% Is Incinerated With Energy Recovery, And 63.5% Is Landfilled.
Clt Is A Type Of Engineered.
In This Comprehensive Guide, We Will Delve Into The Comparative Analysis Of Clt And Traditional Materials, Focusing On Cost, Performance, And Sustainability.
Related Post:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/__opt__aboutcom__coeus__resources__content_migration__treehugger__images__2018__12__CLT-save-world-f63176965e4148bc97fa8c0e0b2ae8c9.jpg)