Macromolecule Building
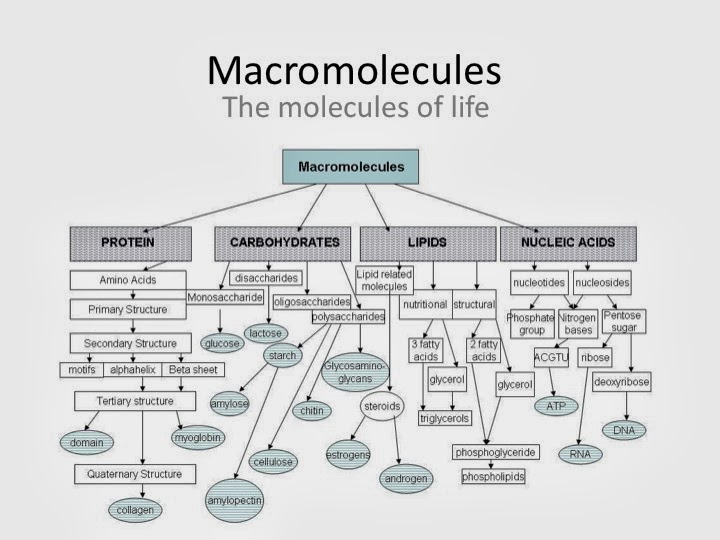
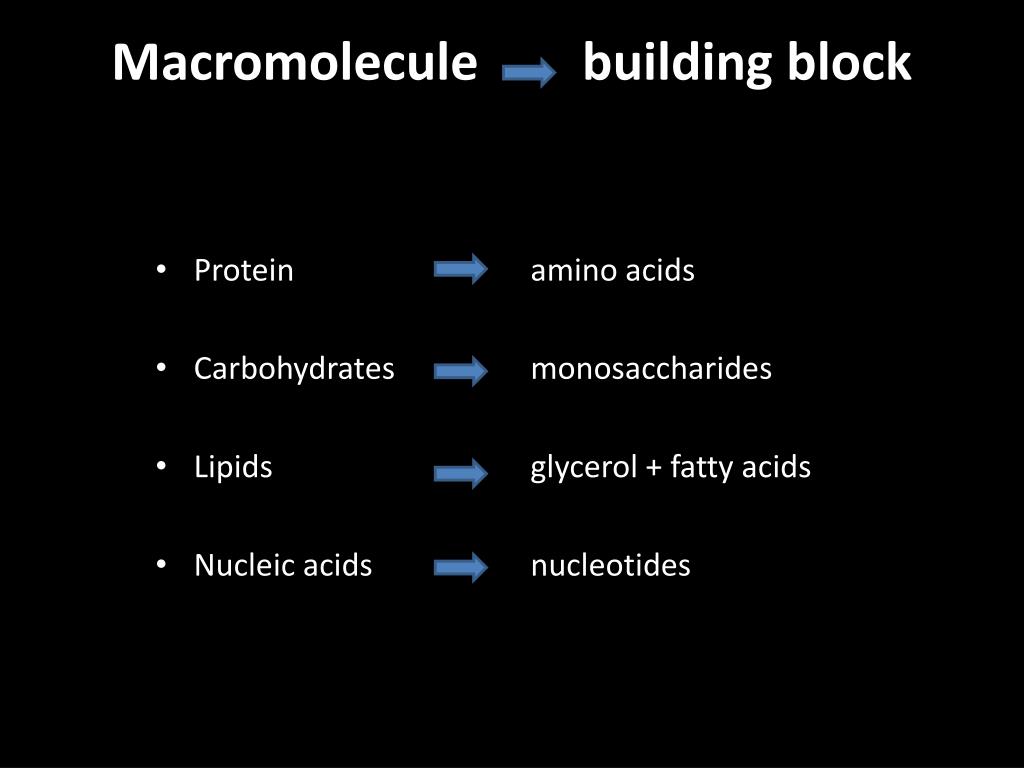
Macromolecule Building - The basic chemistry of life is based mostly on carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. In this chapter, we’ll first consider how macromolecules are built. They are composed of amino acids as their building blocks. They are involved in a wide range of biological processes, such as dna. Characterization of macromolecules using various biophysical instruments (mass photometry (mp), surface. The first three groups of. The majority of the equipment. Up to 24% cash back building macromolecules our bodies are amazing machines capable of breaking down and building up complex molecules required for life. The biophysics core offers three main categories of research and services: The building will house engineers investigating phenomena on a scale from the very large — bridge and highway components — to the exceedingly small, such as nanoscale. Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic. Then we’ll examine the structure and function of all four classes of large biological molecules: Start your lesson off with this exploratory. They are involved in a wide range of biological processes, such as dna. In human nutrition, macromolecules are indispensable for providing energy, building materials, and regulatory molecules necessary for health and development. The majority of the equipment. A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar. Up to 24% cash back macromolecules •large organic molecules. Polysaccharides, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are the 3 building blocks of all living things that we will focus on this unit. Characterization of macromolecules using various biophysical instruments (mass photometry (mp), surface. Polysaccharides, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic. In this chapter, we’ll first consider how macromolecules are built. They are involved in a wide range of biological. In this chapter, we’ll first consider how macromolecules are built. Characterization of macromolecules using various biophysical instruments (mass photometry (mp), surface. They are composed of amino acids as their building blocks. Up to 24% cash back building macromolecules our bodies are amazing machines capable of breaking down and building up complex molecules required for life. From absolute properties to kinetic. The majority of the equipment. The biophysics core offers three main categories of research and services: They are involved in a wide range of biological processes, such as dna. In human nutrition, macromolecules are indispensable for providing energy, building materials, and regulatory molecules necessary for health and development. Up to 24% cash back building macromolecules our bodies are amazing machines. The majority of the equipment. Characterization of macromolecules using various biophysical instruments (mass photometry (mp), surface. In this chapter, we’ll first consider how macromolecules are built. A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar. •made up of smaller “building blocks” called monomers. The first three groups of. Macromolecules form the building blocks of life and have immense potential in biotechnology. Proteins, enzymes, antibodies, and hemoglobin are all macromolecules that share a common feature: •made up of smaller “building blocks” called monomers. Polysaccharides, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Polysaccharides, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. The building will house engineers investigating phenomena on a scale from the very large — bridge and highway components — to the exceedingly small, such as nanoscale. Macromolecules form the building blocks of life and have immense potential in biotechnology. The majority of the equipment. Start your lesson off with this exploratory. Up to 24% cash back macromolecules •large organic molecules. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are the 3 building blocks of all living things that we will focus on this unit. In human nutrition, macromolecules are indispensable for providing energy, building materials, and regulatory molecules necessary for health and development. The biophysics core offers three main categories of research and services: The. Up to 24% cash back macromolecules •large organic molecules. Macromolecules form the building blocks of life and have immense potential in biotechnology. In this chapter, we’ll first consider how macromolecules are built. •made up of smaller “building blocks” called monomers. The first three groups of. The biophysics core offers three main categories of research and services: They are composed of amino acids as their building blocks. Up to 24% cash back macromolecules •large organic molecules. Characterization of macromolecules using various biophysical instruments (mass photometry (mp), surface. Up to 24% cash back building macromolecules our bodies are amazing machines capable of breaking down and building up. The biophysics core offers three main categories of research and services: Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are the 3 building blocks of all living things that we will focus on this unit. They are composed of amino acids as their building blocks. The majority of the equipment. Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large. The biophysics core offers three main categories of research and services: Investigate the major types of macromolecules, macromolecule bonds, and how our body uses them every day! The building will house engineers investigating phenomena on a scale from the very large — bridge and highway components — to the exceedingly small, such as nanoscale. They are composed of amino acids as their building blocks. Up to 24% cash back building macromolecules our bodies are amazing machines capable of breaking down and building up complex molecules required for life. Characterization of macromolecules using various biophysical instruments (mass photometry (mp), surface. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are the 3 building blocks of all living things that we will focus on this unit. Macromolecules form the building blocks of life and have immense potential in biotechnology. From absolute properties to kinetic studies, we provide the tools, training, and assistance for quantitative analysis of macromolecules and their interactions. In human nutrition, macromolecules are indispensable for providing energy, building materials, and regulatory molecules necessary for health and development. The majority of the equipment. They are involved in a wide range of biological processes, such as dna. The first three groups of. •made up of smaller “building blocks” called monomers. Then we’ll examine the structure and function of all four classes of large biological molecules: Polysaccharides, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.CH103 Chapter 8 The Major Macromolecules Chemistry
Mr. Maxey's Biology Blog The Building Blocks of Life Macromolecules
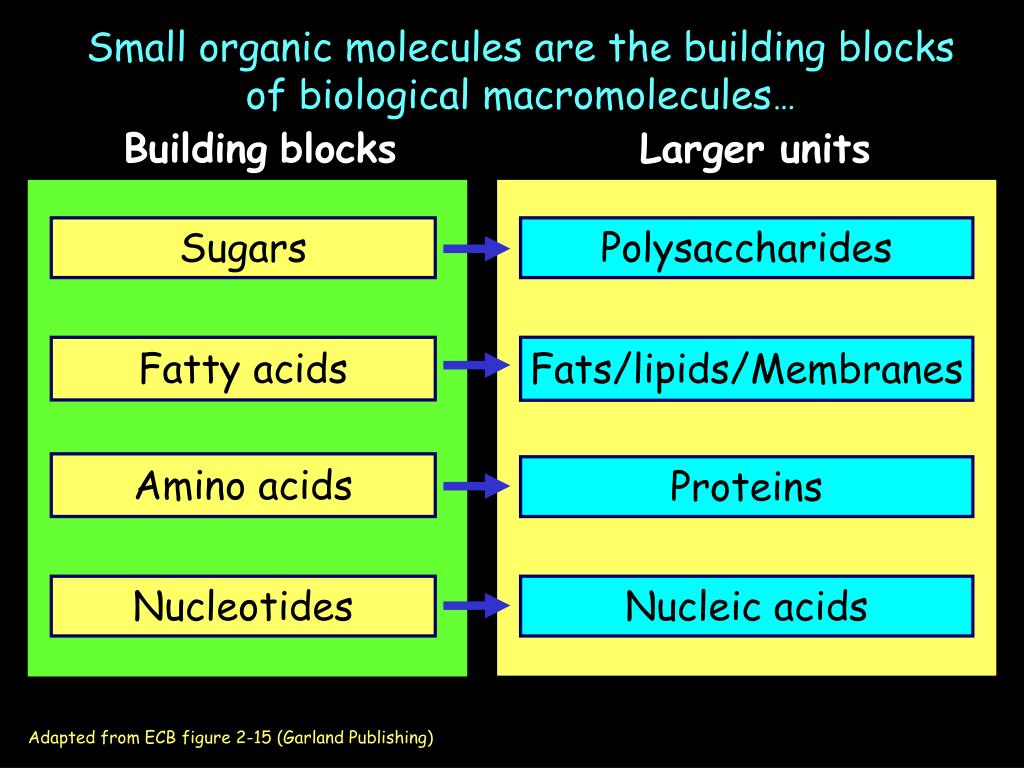
PPT Small organic molecules are the building blocks of biological
Exploring Macromolecules Building Blocks and Diverse Structures
PPT Macromolecules Building blocks of life PowerPoint Presentation
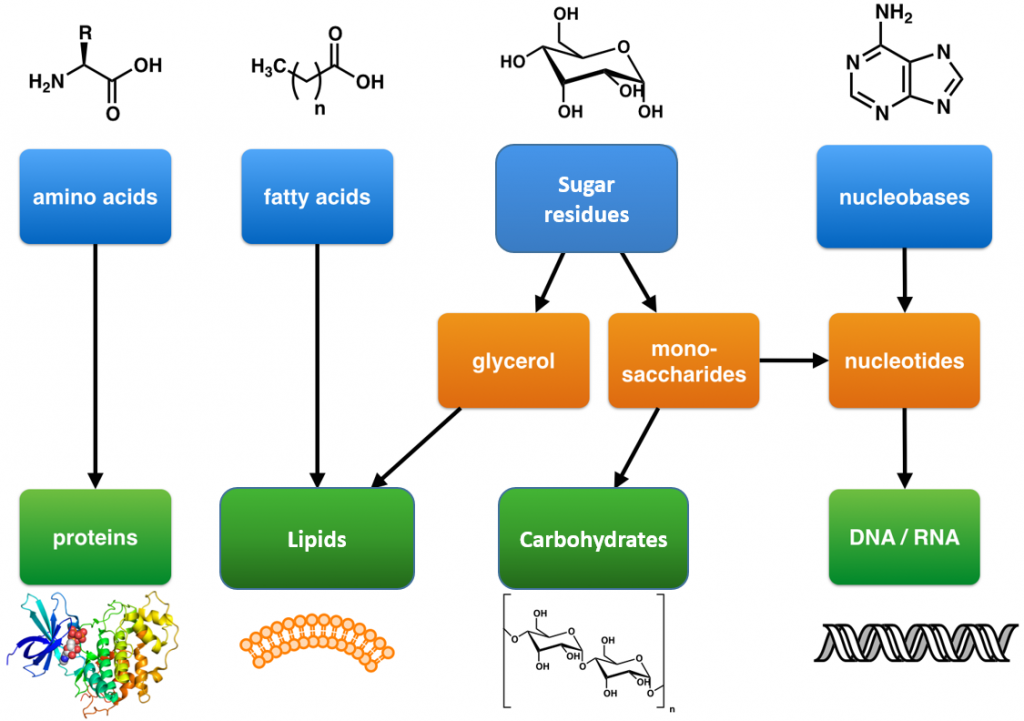
Some examples of "building blocks" (BBs) in biological macromolecules
Building Blocks of Life 28 Macromolecules Activities Teaching Expertise
Build MACROmolecules Mrs Gs Classroom
PPT Macromolecules For Identification PowerPoint Presentation, free
Teaching Macromolecules in Biology ⋆ The Trendy Science Teacher
Start Your Lesson Off With This Exploratory.
Proteins, Enzymes, Antibodies, And Hemoglobin Are All Macromolecules That Share A Common Feature:
These Are Called Macromolecules Because They Are Large Molecules.
Up To 24% Cash Back Macromolecules •Large Organic Molecules.
Related Post: