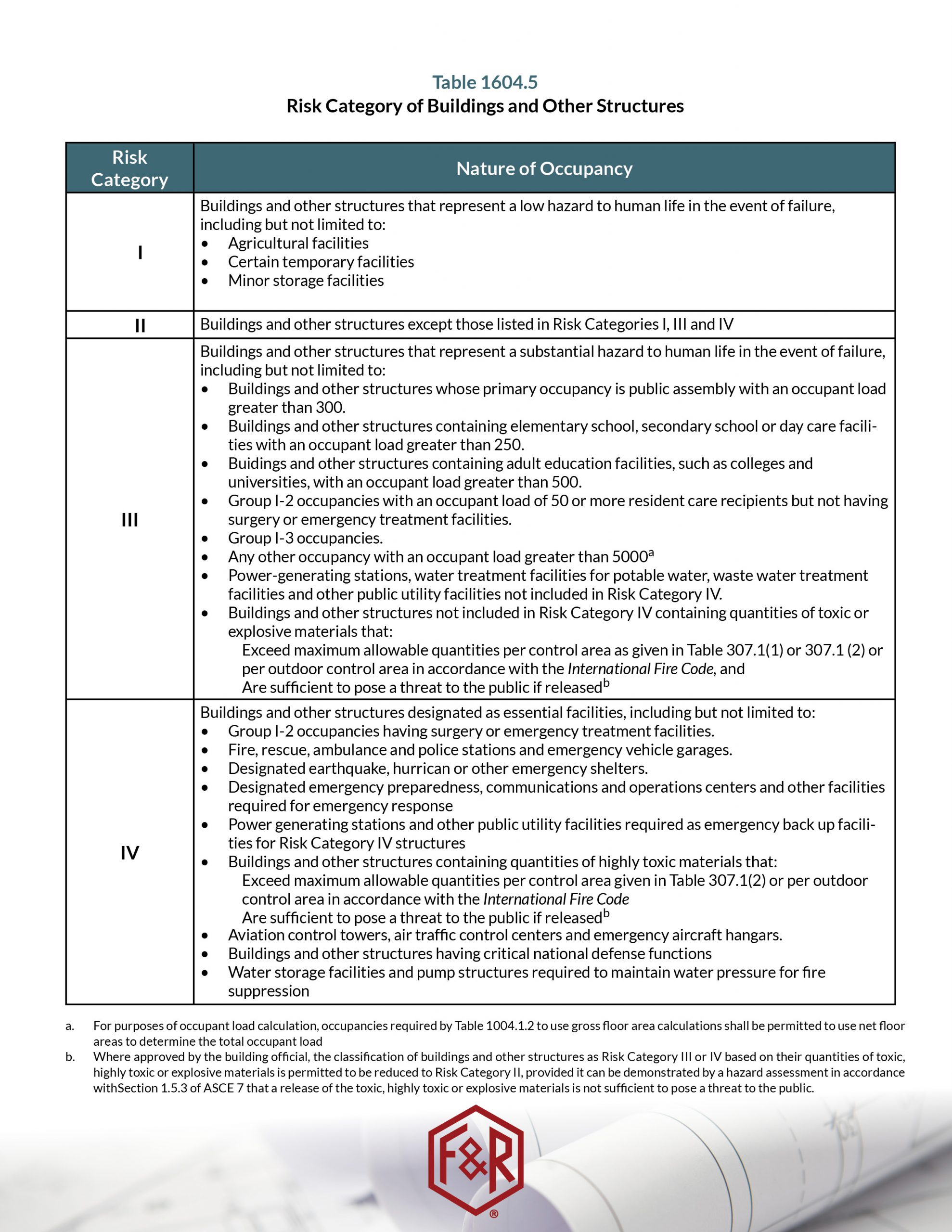
Risk Category 2 Buildings
Risk Category 2 Buildings - These buildings represent a lesser hazard to life because of fewer building occupants and smaller building size compared to those that are considered risk category iii. Risk category ii is the standard occupancy with the importance factors for earthquake, snow, and wind equal to 1.0. Each building and structure shall be assigned a structural occupancy category in accordance with table 1604.5. Where approved by the building official, the classification of buildings and other structures as risk category iii or iv based on their quantities of toxic, highly toxic or explosive materials is. The intent of this document is to provide clarity and insight regarding the risk category for a new or existing communication structure by comparing the risk categories from. Nearly all buildings and structures are considered risk category ii and are. The key differentiators that push a building up to. Where approved by the building official, the classification of buildings and other structures as risk category iii or iv based on their quantities of toxic, highly toxic or explosive materials is. In order to help define and communicate how important a given building is, engineers work together with architects and building owners to assign a risk categoryto buildings early in the design process. Buildings and other structures whose primary occupancy is public assembly. Where approved by the building official, the classification of buildings and other structures as risk category iii or iv based on their quantities of toxic, highly toxic or explosive materials is. The key differentiators that push a building up to. Where approved by the building official, the classification of buildings and other structures as risk category iii or iv based on their quantities of toxic, highly toxic or explosive materials is. Nearly all buildings and structures are considered. Risk category ii is often thought of as the “default,” since it includes any buildings that do not fall under one of the other three categories. The basic underlying principle in assigning risk category is to recognize. If structurally separated, portions of the building may be assigned. Risk category ii is the standard occupancy with the importance factors for earthquake, snow, and wind equal to 1.0. Buildings and other structures whose primary occupancy is public assembly. Also, “buildings containing hazardous materials are eligible for category ii if it can be demonstrated to the. Where approved by the building official, the classification of buildings and other structures as risk category iii or iv based on their quantities of toxic, highly toxic or explosive materials is. Risk category ii is the standard occupancy with the importance factors for earthquake, snow, and wind equal to 1.0. The intent of this document is to provide clarity and. Nonseparated occupancies exist when multiple occupancy types share a building without fire separation. Where approved by the building official, the classification of buildings and other structures as risk category iii or iv based on their quantities of toxic, highly toxic or explosive materials is. If structurally separated, portions of the building may be assigned. Where approved by the building official,. Some structures are not even occupied but were assigned an occupancy category because their failure could pose a substantial risk to the public. These buildings represent a lesser hazard to life because of fewer building occupants and smaller building size compared to those that are considered risk category iii. Where approved by the building official, the classification of buildings and. Where approved by the building official, the classification of buildings and other structures as risk category iii or iv based on their quantities of toxic, highly toxic or explosive materials is. Risk category ii is often thought of as the “default,” since it includes any buildings that do not fall under one of the other three categories. Table 1604.5 of. Nearly all buildings and structures are considered. The basic underlying principle in assigning risk category is to recognize. Where approved by the building official, the classification of buildings and other structures as risk category iii or iv based on their quantities of toxic, highly toxic or explosive materials is. Risk category ii is the standard occupancy with the importance factors. • buildings and other structures except those listed in risk categories i, iii and iv. Where approved by the building official, the classification of buildings and other structures as risk category iii or iv based on their quantities of toxic, highly toxic or explosive materials is. Most residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. The intent of this document is to provide. Some structures are not even occupied but were assigned an occupancy category because their failure could pose a substantial risk to the public. Highly toxic or explosive materials is permitted to be reduced to risk category ii, provided it can be demonstrated by a hazard assessment in accordance with section 1.5.3 of asce 7 that a. These buildings represent a. Where approved by the building official, the classification of buildings and other structures as risk category iii or iv based on their quantities of toxic, highly toxic or explosive materials is. Highly toxic or explosive materials is permitted to be reduced to risk category ii, provided it can be demonstrated by a hazard assessment in accordance with section 1.5.3 of. The key differentiators that push a building up to. Nonseparated occupancies exist when multiple occupancy types share a building without fire separation. If structurally separated, portions of the building may be assigned. Table 1604.5 of the 2012 ibc sets forth risk category descriptions for buildings and other structures. Where approved by the building official, the classification of buildings and other. Most residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. Some structures are not even occupied but were assigned an occupancy category because their failure could pose a substantial risk to the public. In order to help define and communicate how important a given building is, engineers work together with architects and building owners to assign a risk categoryto buildings early in the design. • buildings and other structures except those listed in risk categories i, iii and iv. Risk category ii is often thought of as the “default,” since it includes any buildings that do not fall under one of the other three categories. Risk category ii is the standard occupancy with the importance factors for earthquake, snow, and wind equal to 1.0. Risk category ii is the standard occupancy with the importance factors for earthquake, snow, and wind equal to 1.0. Where approved by the building official, the classification of buildings and other structures as risk category iii or iv based on their quantities of toxic, highly toxic or explosive materials is. If structurally separated, portions of the building may be assigned. Most residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. • buildings and other structures except those. Nonseparated occupancies exist when multiple occupancy types share a building without fire separation. Table 1604.5 of the 2012 ibc sets forth risk category descriptions for buildings and other structures. The key differentiators that push a building up to. Each building and structure shall be assigned a structural occupancy category in accordance with table 1604.5. The intent of this document is to provide clarity and insight regarding the risk category for a new or existing communication structure by comparing the risk categories from. Where approved by the building official, the classification of buildings and other structures as risk category iii or iv based on their quantities of toxic, highly toxic or explosive materials is. These buildings represent a lesser hazard to life because of fewer building occupants and smaller building size compared to those that are considered risk category iii. These buildings represent a lesser hazard to life because of fewer building occupants and smaller building size compared to those that are considered risk category iii.Speaking in Code IBC Risk Category Table F&R
PPT c onsulting engineers and scientists PowerPoint Presentation
Basic Design Wind Speeds, V, for Risk Category II Buildings and other
PPT April 2013 Status & Hazard Mapping PowerPoint Presentation ID
Engineering Center Designing for Earthquakes
PPT Lesson 6 ASCE 710 Basic Requirements for Structural Design
PPT 2010 Florida Building Code Wind Standard PowerPoint Presentation
Risk Category of Buildings and other Structures
The risk categories in construction projects Download Table
Ultimate Design Wind Speeds for Risk Category II Buildings and Other
Where Approved By The Building Official, The Classification Of Buildings And Other Structures As Risk Category Iii Or Iv Based On Their Quantities Of Toxic, Highly Toxic Or Explosive Materials Is.
Where Approved By The Building Official, The Classification Of Buildings And Other Structures As Risk Category Iii Or Iv Based On Their Quantities Of Toxic, Highly Toxic Or Explosive Materials Is.
Nearly All Buildings And Structures Are Considered.
In Order To Help Define And Communicate How Important A Given Building Is, Engineers Work Together With Architects And Building Owners To Assign A Risk Categoryto Buildings Early In The Design Process.
Related Post: