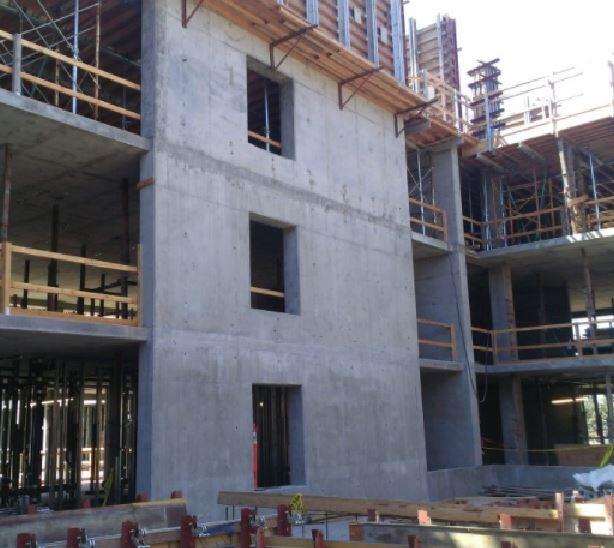
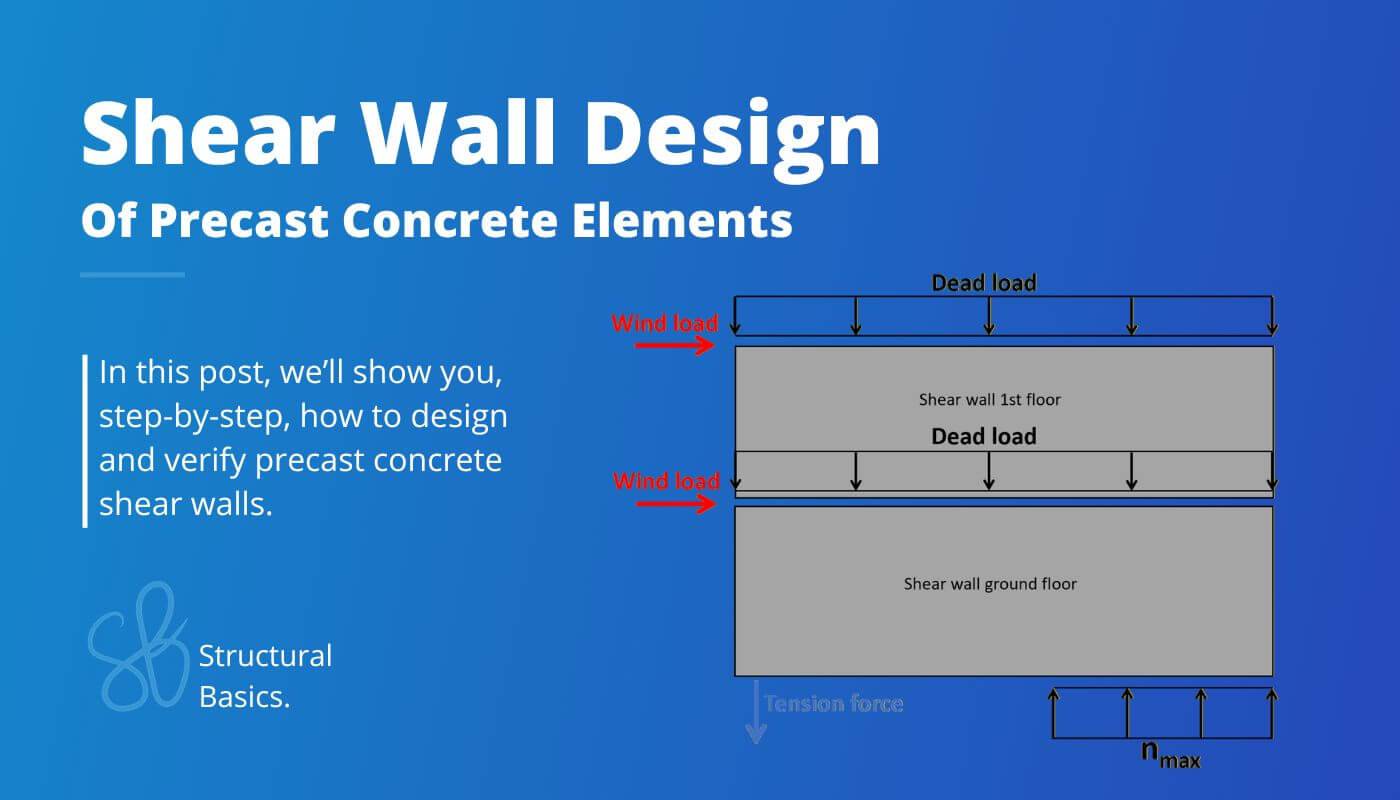
Shear Wall Building Example
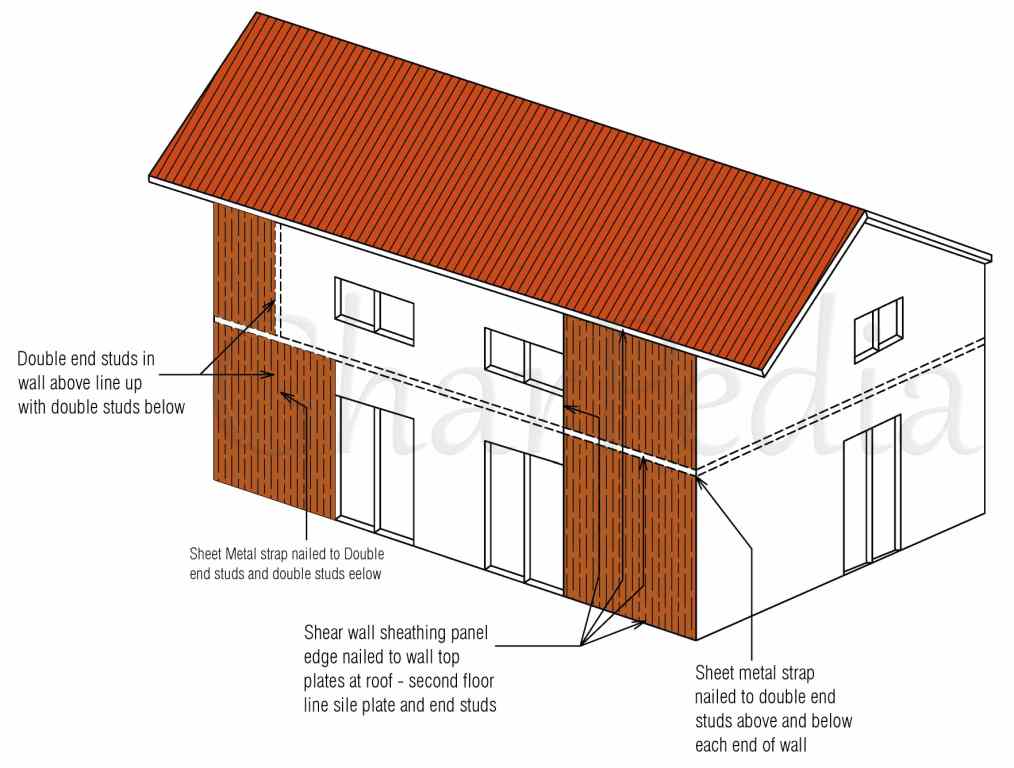
Shear Wall Building Example - Think of a wooden square with four edges, it has two columns and two beams. Shear walls stabilize a building. This example references the aghayere structural wood design: Shear walls are walls made of concrete blocks that are spaced at a height to allow for beams placed on top of the blocks to span the entire wall. They resist horizontal loads such as wind and seismic loads and transfer these loads down to the foundation. 1) the wall is 4.16m long, 250mm thick and subjected to. This frame can support the. There are two blast load cases, one applied to the long side of the building, and the other applied to the short side. The shear wall has “flanges” which provide additional stability and protection against weathering or crushing damage. In this how it works article, senior editor rob yagid explains how overwhelming natural. These shear walls, by their shearing resistance and resistance to. They resist horizontal loads such as wind and seismic loads and transfer these loads down to the foundation. Lateral forces of wind and earthquake are usually resisted by shear walls which are parallel to the direction of the lateral load. Shear walls stabilize a building. In this worked example, we’ll go through the design process of a shear wall for a two story building. In this how it works article, senior editor rob yagid explains how overwhelming natural. Shear walls play a crucial role in modern construction, providing essential lateral stability to buildings. A shear wall is also known as a braced frame structure in some areas. This frame can support the. 1) the wall is 4.16m long, 250mm thick and subjected to. Think of a wooden square with four edges, it has two columns and two beams. A shear wall is also known as a braced frame structure in some areas. This example references the aghayere structural wood design: There are two blast load cases, one applied to the long side of the building, and the other applied to the short side.. Shear walls play a crucial role in modern construction, providing essential lateral stability to buildings. Shear walls are typically identified on blueprints by a solid line with a thinner line indicating the sheathing that will cover it (and which is usually then specified in a separate sheathing schedule). The shear wall has “flanges” which provide additional stability and protection against. A shear wall is also known as a braced frame structure in some areas. In this worked example, we’ll go through the design process of a shear wall for a two story building. Shear walls are one of many building components that are shown on architectural plans. Think of a wooden square with four edges, it has two columns and. Assumed effective width only results in a small shift of neutral axis. They resist horizontal loads such as wind and seismic loads and transfer these loads down to the foundation. Lateral forces of wind and earthquake are usually resisted by shear walls which are parallel to the direction of the lateral load. Shear walls stabilize a building. These shear walls,. This frame can support the. Shear walls are one of many building components that are shown on architectural plans. It uses a graphical interface that enables. Shear walls are typically identified on blueprints by a solid line with a thinner line indicating the sheathing that will cover it (and which is usually then specified in a separate sheathing schedule). Shear. A shear wall is also known as a braced frame structure in some areas. It uses a graphical interface that enables. Shear walls are walls made of concrete blocks that are spaced at a height to allow for beams placed on top of the blocks to span the entire wall. This example references the aghayere structural wood design: 1) the. This example references the aghayere structural wood design: There are two blast load cases, one applied to the long side of the building, and the other applied to the short side. These structural elements are designed to resist forces such as wind and. They resist horizontal loads such as wind and seismic loads and transfer these loads down to the. 1) the wall is 4.16m long, 250mm thick and subjected to. This frame can support the. Think of a wooden square with four edges, it has two columns and two beams. The shear wall has “flanges” which provide additional stability and protection against weathering or crushing damage. These structural elements are designed to resist forces such as wind and. 1) the wall is 4.16m long, 250mm thick and subjected to. Shear walls are walls made of concrete blocks that are spaced at a height to allow for beams placed on top of the blocks to span the entire wall. These shear walls, by their shearing resistance and resistance to. In this worked example, we’ll go through the design process. These shear walls, by their shearing resistance and resistance to. It uses a graphical interface that enables. This frame can support the. 1) the wall is 4.16m long, 250mm thick and subjected to. These structural elements are designed to resist forces such as wind and. These structural elements are designed to resist forces such as wind and. There are two blast load cases, one applied to the long side of the building, and the other applied to the short side. Lateral forces of wind and earthquake are usually resisted by shear walls which are parallel to the direction of the lateral load. The shear wall has “flanges” which provide additional stability and protection against weathering or crushing damage. These shear walls, by their shearing resistance and resistance to. Think of a wooden square with four edges, it has two columns and two beams. In this how it works article, senior editor rob yagid explains how overwhelming natural. This frame can support the. Shear walls are typically identified on blueprints by a solid line with a thinner line indicating the sheathing that will cover it (and which is usually then specified in a separate sheathing schedule). Shear walls stabilize a building. Shear walls play a crucial role in modern construction, providing essential lateral stability to buildings. In this worked example, we’ll go through the design process of a shear wall for a two story building. Assumed effective width only results in a small shift of neutral axis. Shear walls are walls made of concrete blocks that are spaced at a height to allow for beams placed on top of the blocks to span the entire wall. 1) the wall is 4.16m long, 250mm thick and subjected to. This example references the aghayere structural wood design:Shear Walls What are they? Lynn Engineering
What Is Shear Wall Its Types And Location In Buildings
What is Shear Wall?
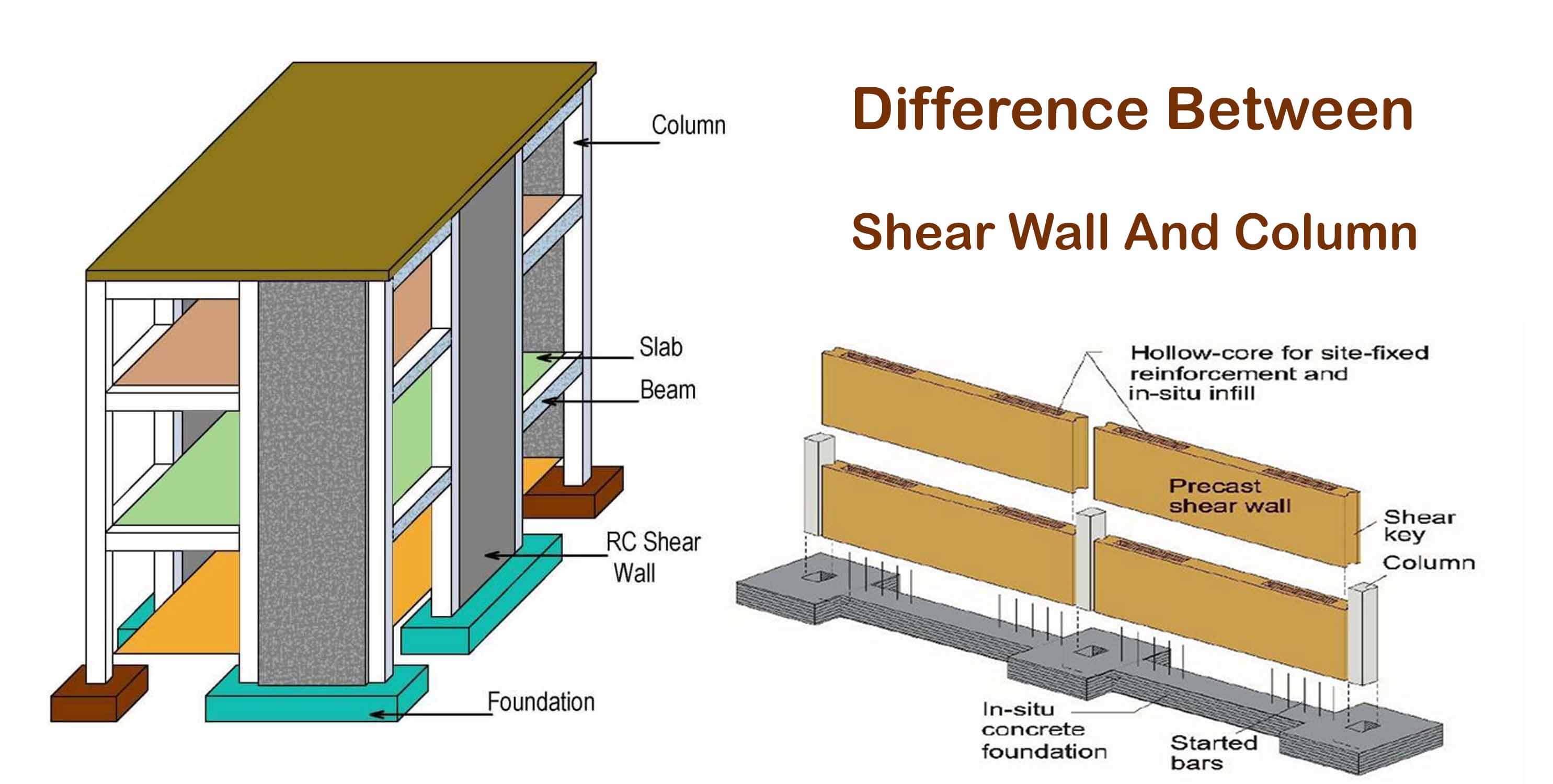
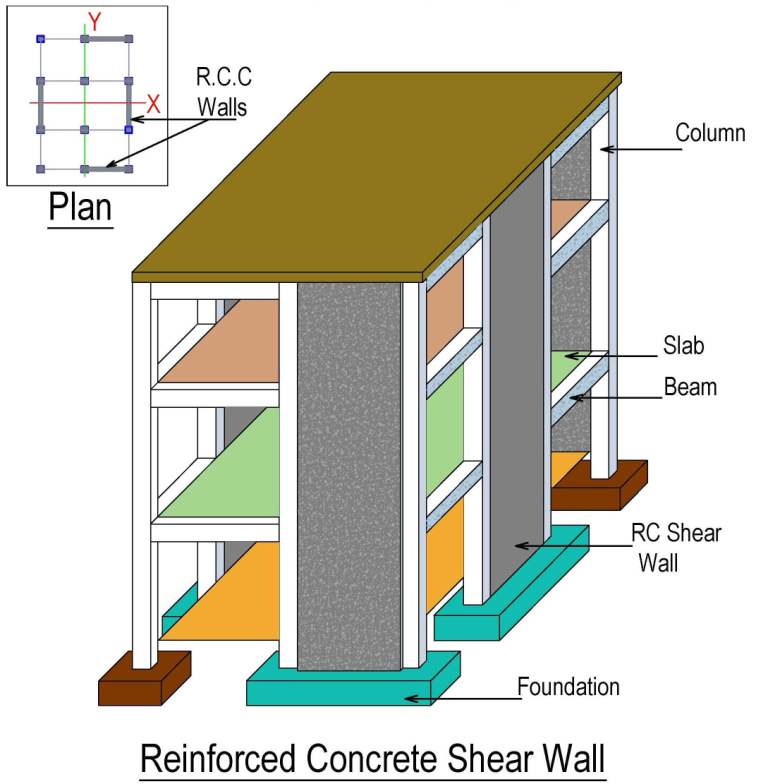
Difference Between Shear Wall And Column Engineering Discoveries
What is a Frame with Shear Wall Structural System?
Design of Shear Walls Structville
Shear Wall Design StepByStep Guide Shear Wall Design Example
Shear Wall Design
Shear Wall Design in ETABS The Structural World
All About Shear Wall [Design Considerations] Structural Guide
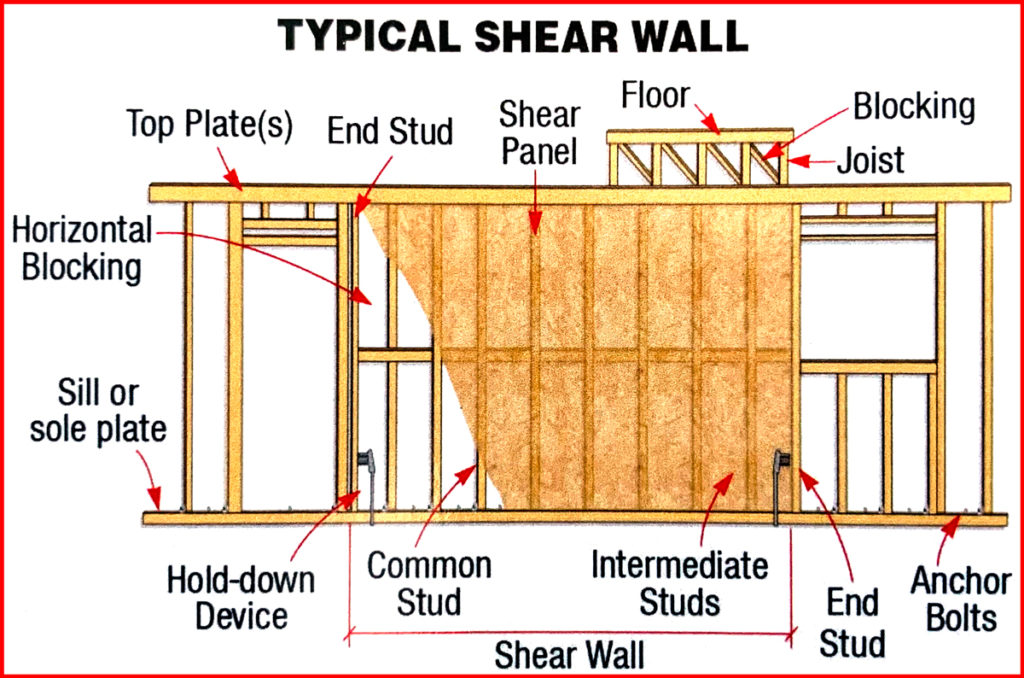
Shear Walls Are One Of Many Building Components That Are Shown On Architectural Plans.
It Uses A Graphical Interface That Enables.
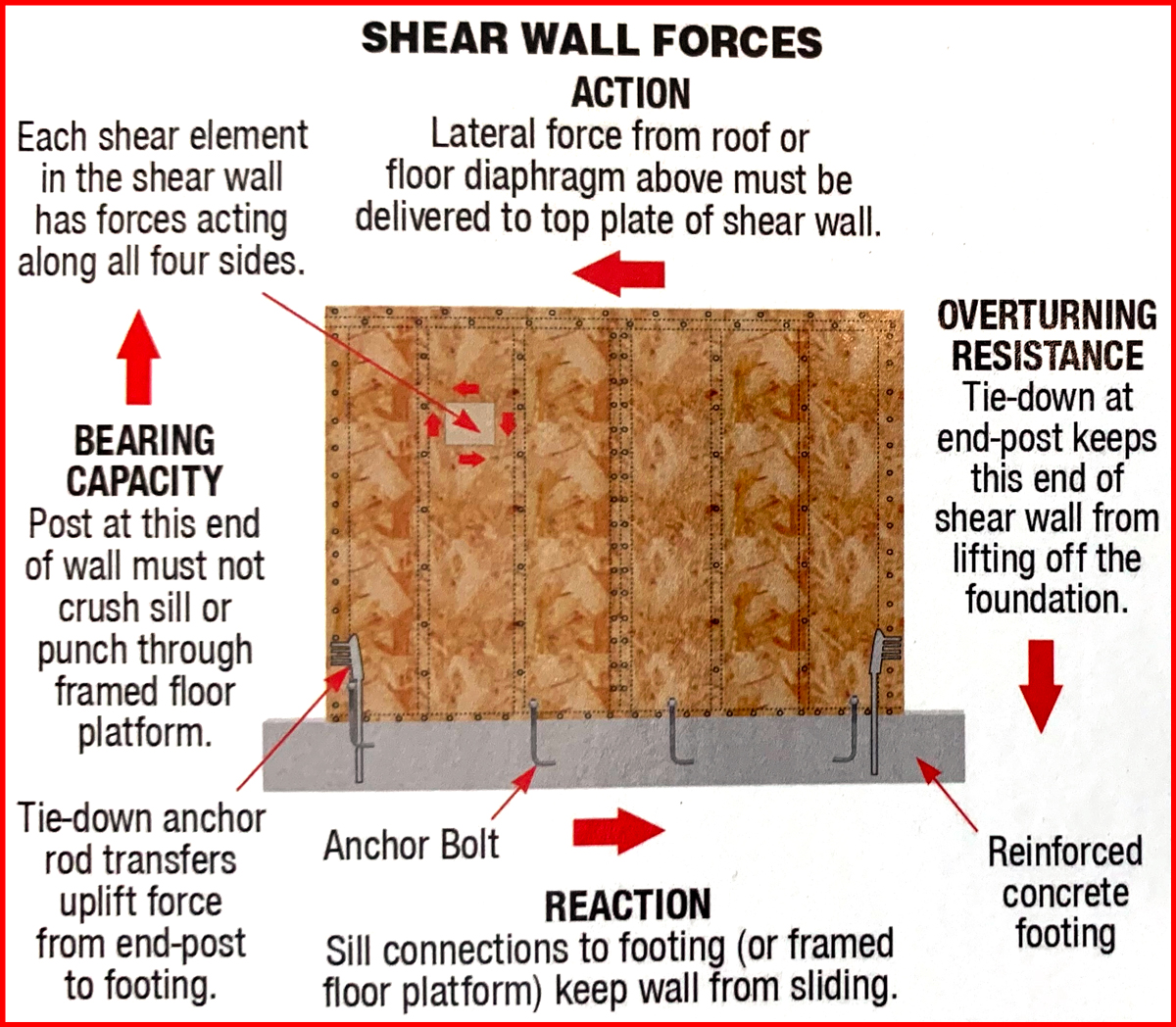
They Resist Horizontal Loads Such As Wind And Seismic Loads And Transfer These Loads Down To The Foundation.
A Shear Wall Is Also Known As A Braced Frame Structure In Some Areas.
Related Post:



![All About Shear Wall [Design Considerations] Structural Guide](https://www.structuralguide.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Shear-wall.jpg)