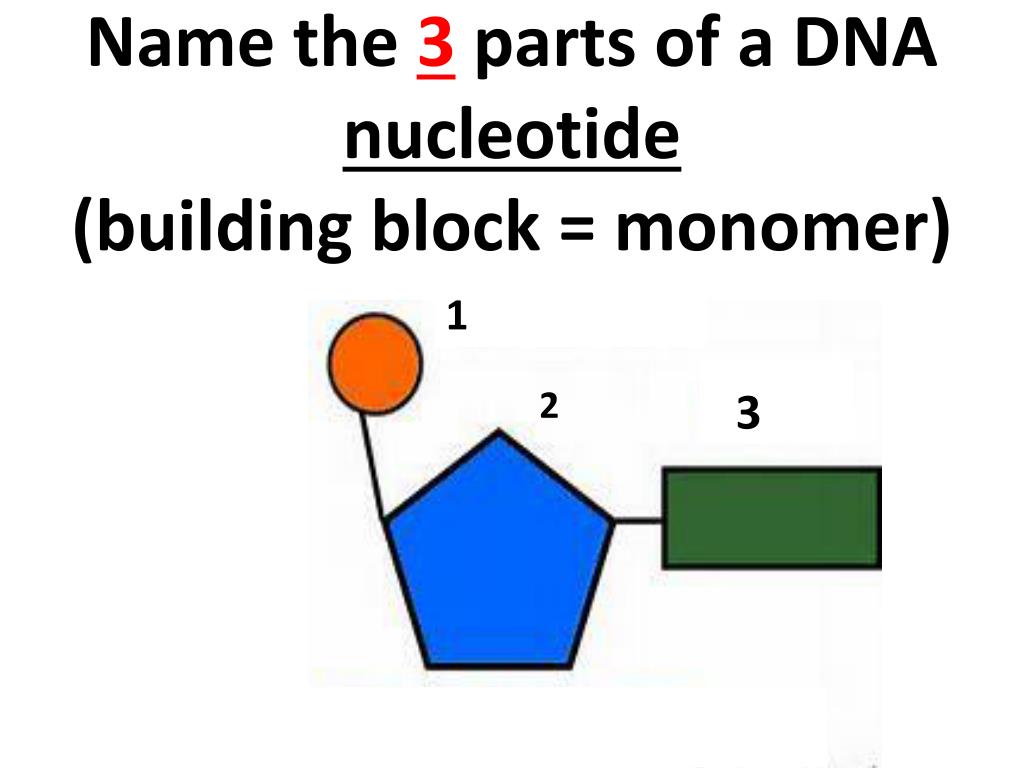
The Primary Building Block Monomer Of Proteins Is
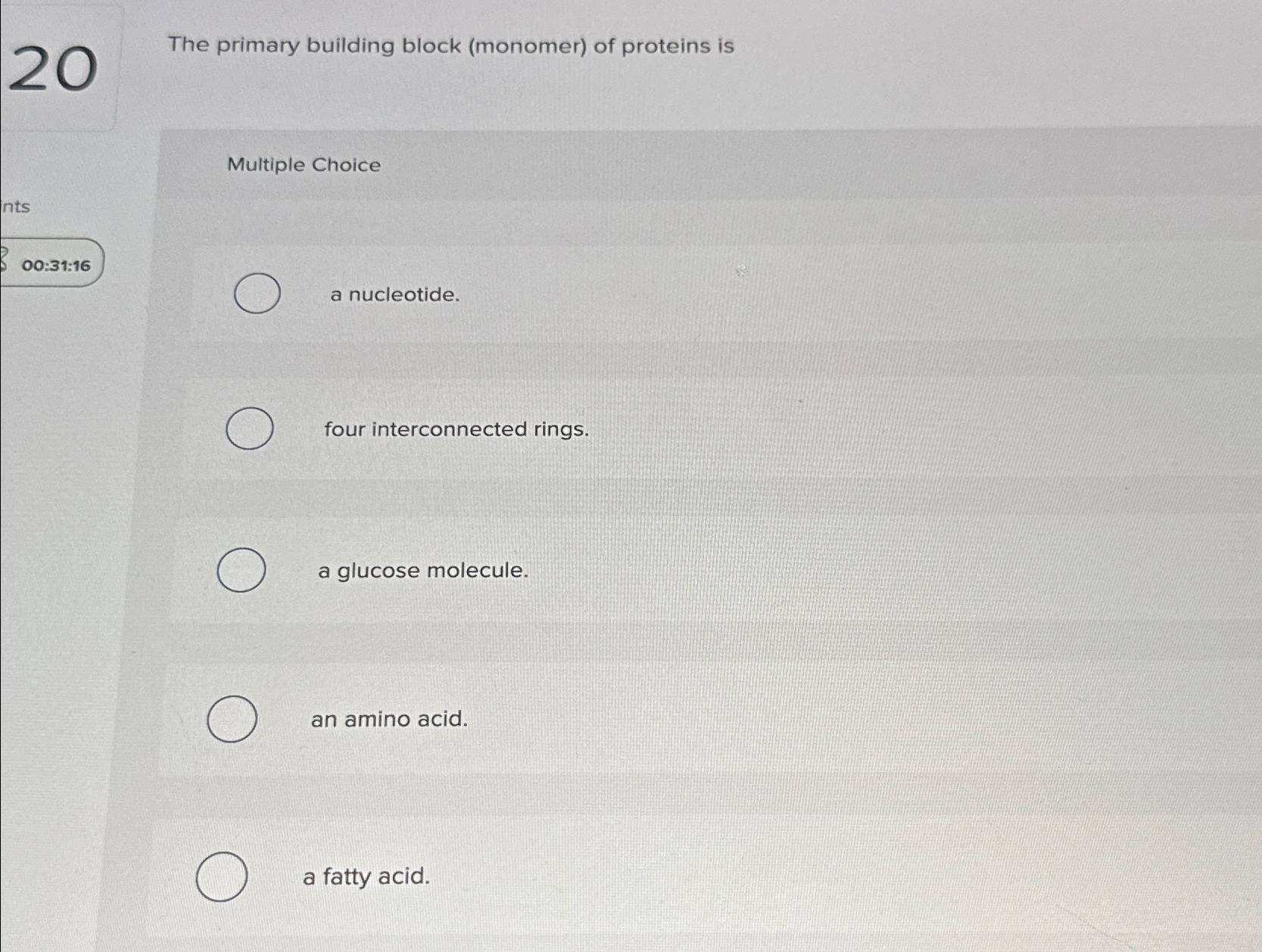
The Primary Building Block Monomer Of Proteins Is - Proteins & amino acids 5 many of the most important macromolecules in living systems are polymers. As their name implies they contain a carboxylic acid functional group and an amine functional group. These polymers are composed of small building blocks that are linked together in. The major building block of proteins are called alpha (α) amino acids. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha ( α ). Monomers are molecules that can bind into long chains—these long chains are called “polymers.” in other words, a polymer (“poly” = many) are made of. A protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. In other words, if you replaced the r groups in the last diagram by real groups. Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. The primary building blocks (monomers) of proteins are: The major building block of proteins are called alpha (α) amino acids. As their name implies they contain a carboxylic acid functional group and an amine functional group. At its simplest, the term is used to describe the order of the amino acids joined together to make the protein. This question falls under the topic of biochemistry, specifically focusing on the basic building blo. A protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. These polymers are composed of small building blocks that are linked together in. Proteins & amino acids 5 many of the most important macromolecules in living systems are polymers. Not the question you’re looking for? There are 3 steps to solve this one. Monomers are molecules that can bind into long chains—these long chains are called “polymers.” in other words, a polymer (“poly” = many) are made of. There are 3 steps to solve this one. The primary building blocks (monomers) of proteins are: Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha ( α ). Proteins & amino acids 5 many of the most important macromolecules in. The major building block of proteins are called alpha (α) amino acids. A protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. There are 3 steps to solve this one. Proteins & amino acids 5 many of the most important macromolecules in living systems are polymers. We will then use this. A protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. As their name implies they contain a carboxylic acid functional group and an amine functional group. The primary building blocks (monomers) of proteins are: Not the question you’re looking for? There are 3 steps to solve this one. Every protein at least contains a primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. These polymers are composed of small building blocks that are linked together in. At its simplest, the term is used to describe the order of the amino acids joined together to make the protein. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure, which consists of a central carbon atom,. A protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha ( α ). Only some proteins have a. These polymers are composed of small building blocks that are linked together in. The major building block of proteins are. We will then use this. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha ( α ). Monomers are molecules that can bind into long chains—these long chains are called “polymers.” in other words, a polymer (“poly” = many) are made of. In other words, if you replaced the. Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. These polymers are composed of small building blocks that are linked together in. We will then use this. This question falls under the topic of biochemistry, specifically focusing on the basic building blo. Only some proteins have a. Only some proteins have a. We will then use this. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha ( α ). At its simplest, the term is used to describe the order of the amino acids joined together to make the protein. A protein can be identified based. A protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. This question falls under the topic of biochemistry, specifically focusing on the basic building blo. As their name implies they contain a carboxylic acid functional group and an amine functional group. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha ( α ). Monomers are molecules that can bind into long chains—these long chains are called “polymers.” in other words, a polymer (“poly” = many) are made of. There are 3 steps to solve this one. Proteins & amino acids. These polymers are composed of small building blocks that are linked together in. Proteins & amino acids 5 many of the most important macromolecules in living systems are polymers. This question falls under the topic of biochemistry, specifically focusing on the basic building blo. In other words, if you replaced the r groups in the last diagram by real groups. Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. There are 3 steps to solve this one. A protein can be identified based on each level of its structure. The primary building blocks (monomers) of proteins are: Only some proteins have a. Not the question you’re looking for? At its simplest, the term is used to describe the order of the amino acids joined together to make the protein. As their name implies they contain a carboxylic acid functional group and an amine functional group. The major building block of proteins are called alpha (α) amino acids.Solved The primary building block (monomer) of proteins
Monomers Definition, Types, Structure, Examples
PPT Polymer Monomer (basic building block *) Protein 20 amino acids
Building Blocks of Proteins Structure, Properties & Functions
The fundamental building block of protein is(a)Nitrogen (b){ NH
PPT DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Solved The primary building block (monomer) of proteins
PPT Polymer Monomer (basic building block *) Protein 20 amino acids
Proteins and Amino Acids DNATRO
PPT Polymer Properties and Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free
We Will Then Use This.
Every Protein At Least Contains A Primary, Secondary, And Tertiary Structure.
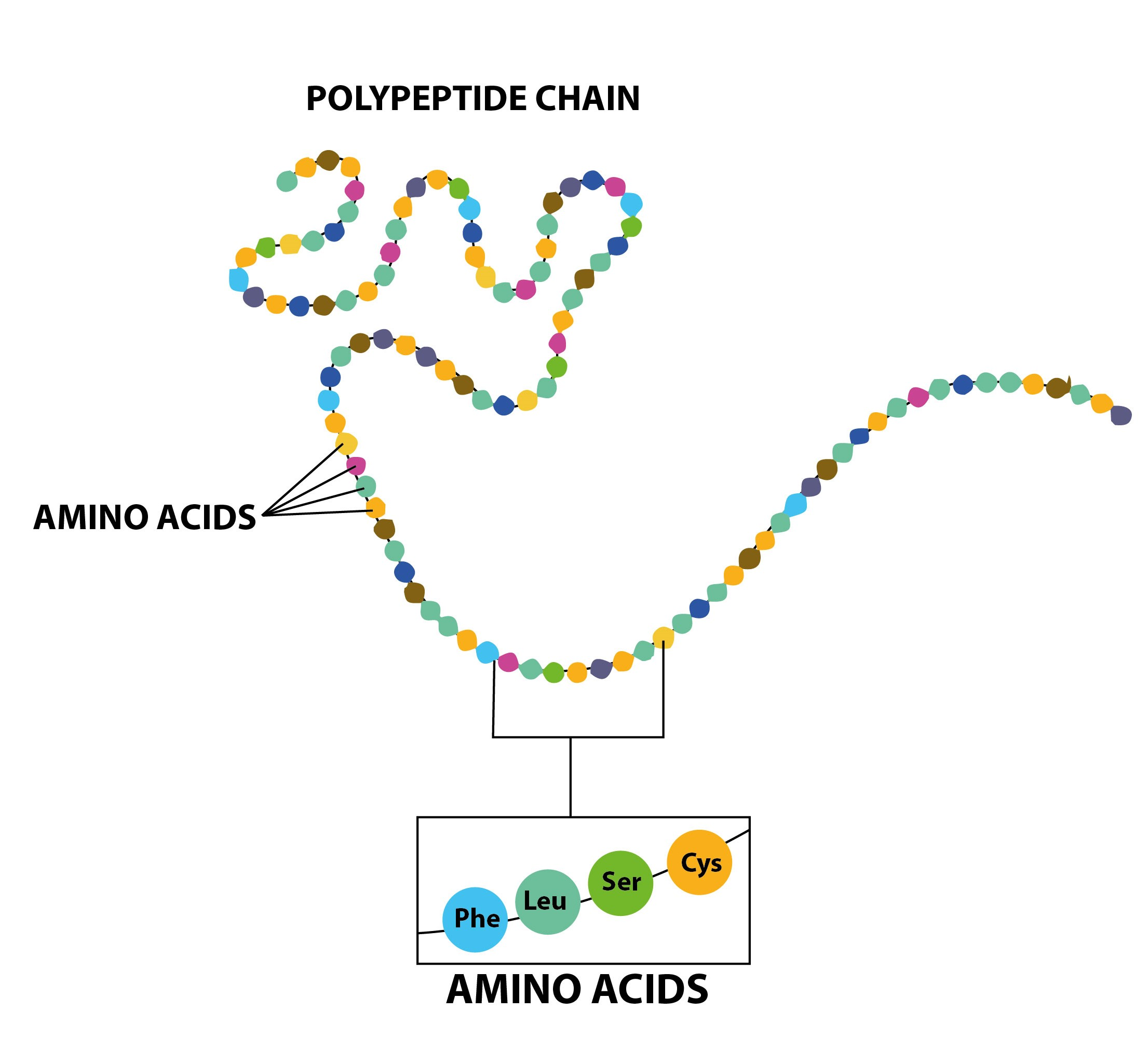
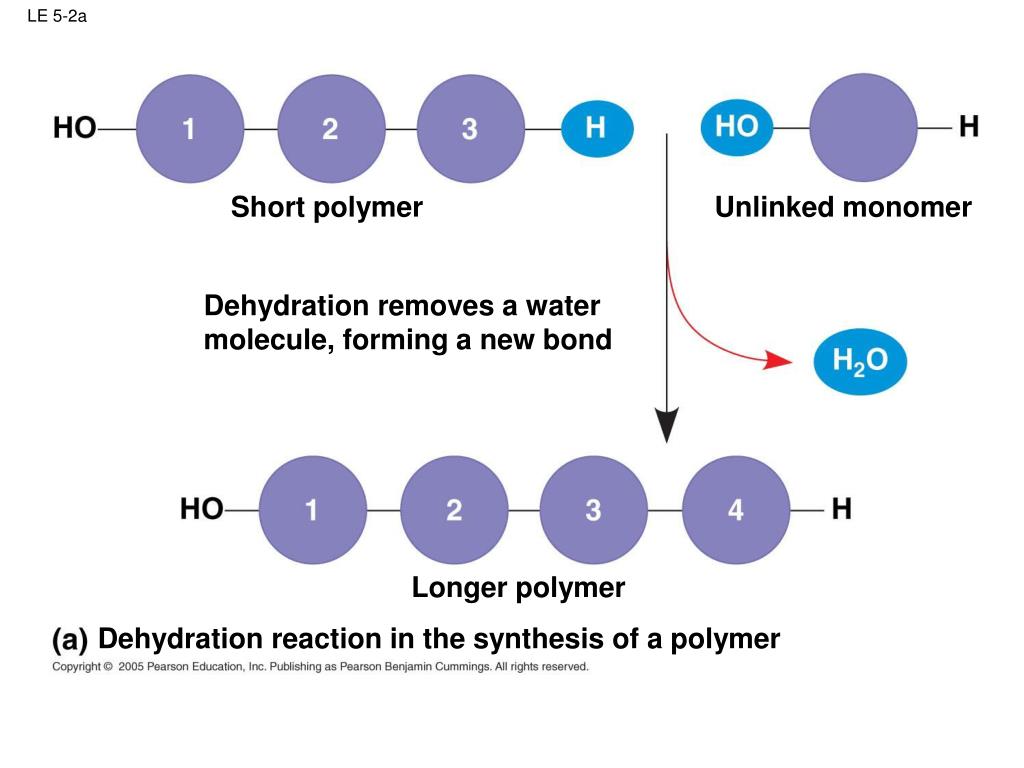
Monomers Are Molecules That Can Bind Into Long Chains—These Long Chains Are Called “Polymers.” In Other Words, A Polymer (“Poly” = Many) Are Made Of.
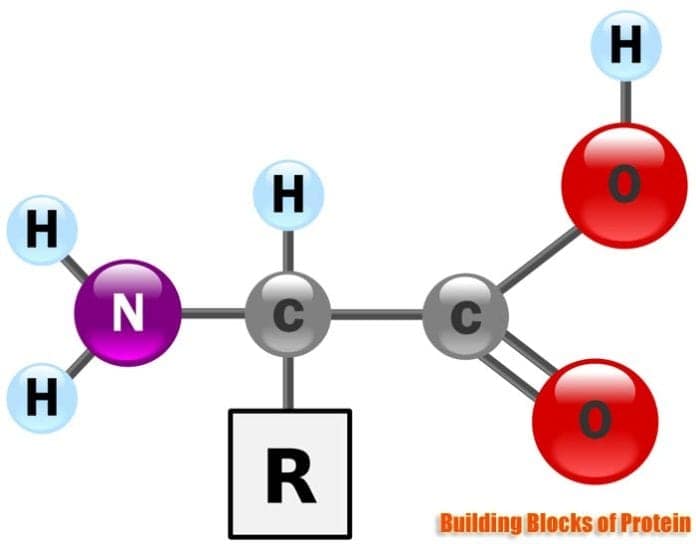
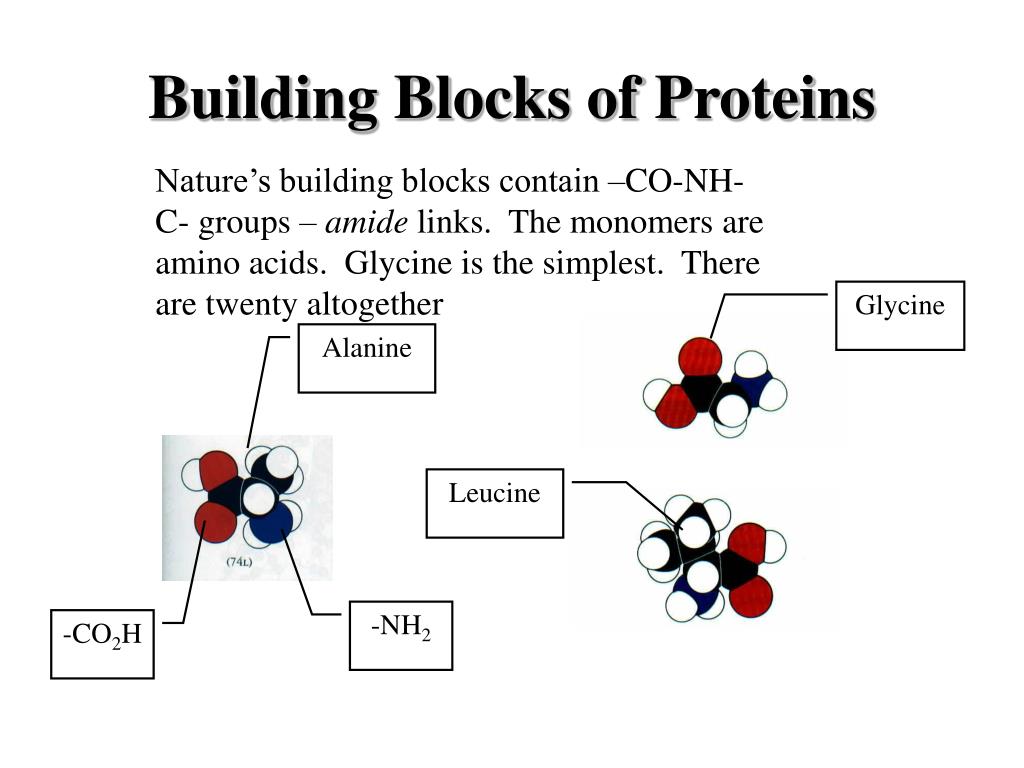
Each Amino Acid Has The Same Fundamental Structure, Which Consists Of A Central Carbon Atom, Also Known As The Alpha ( Α ).
Related Post: