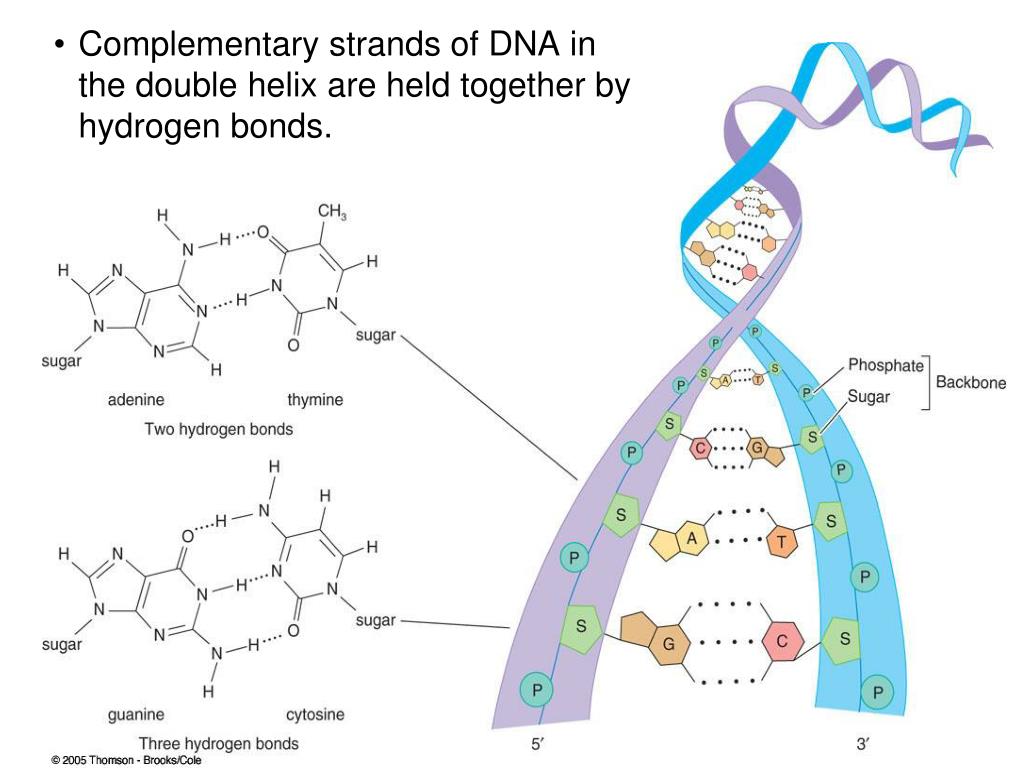
This Is The Enzyme That Builds Complementary Dna Strands
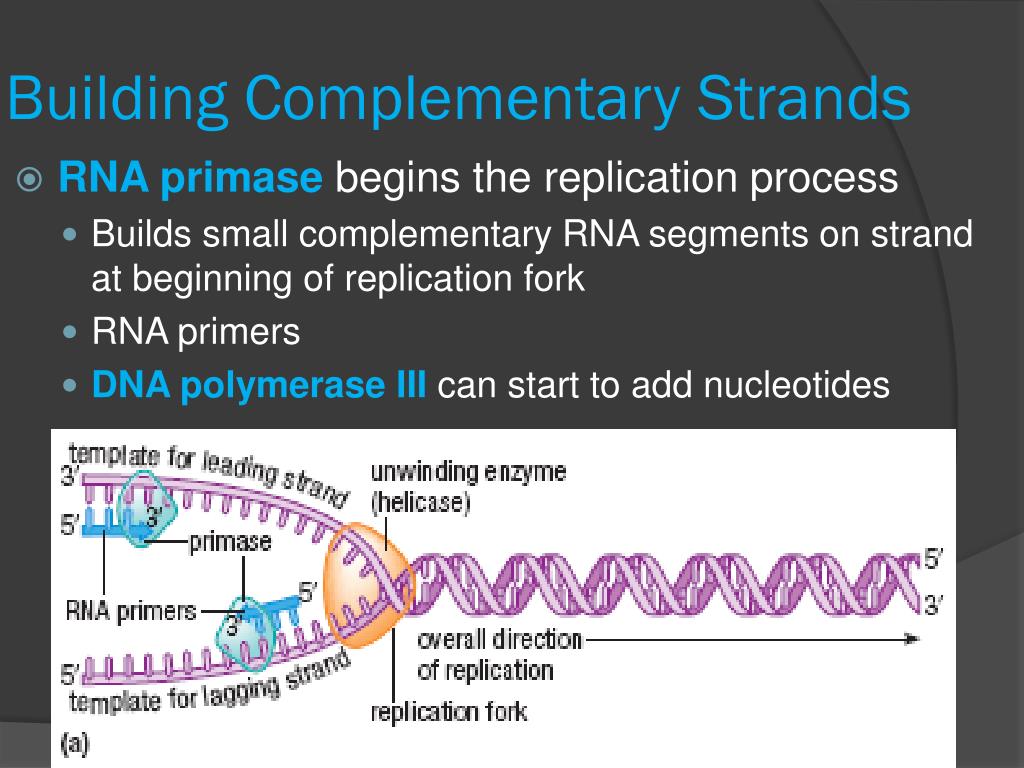
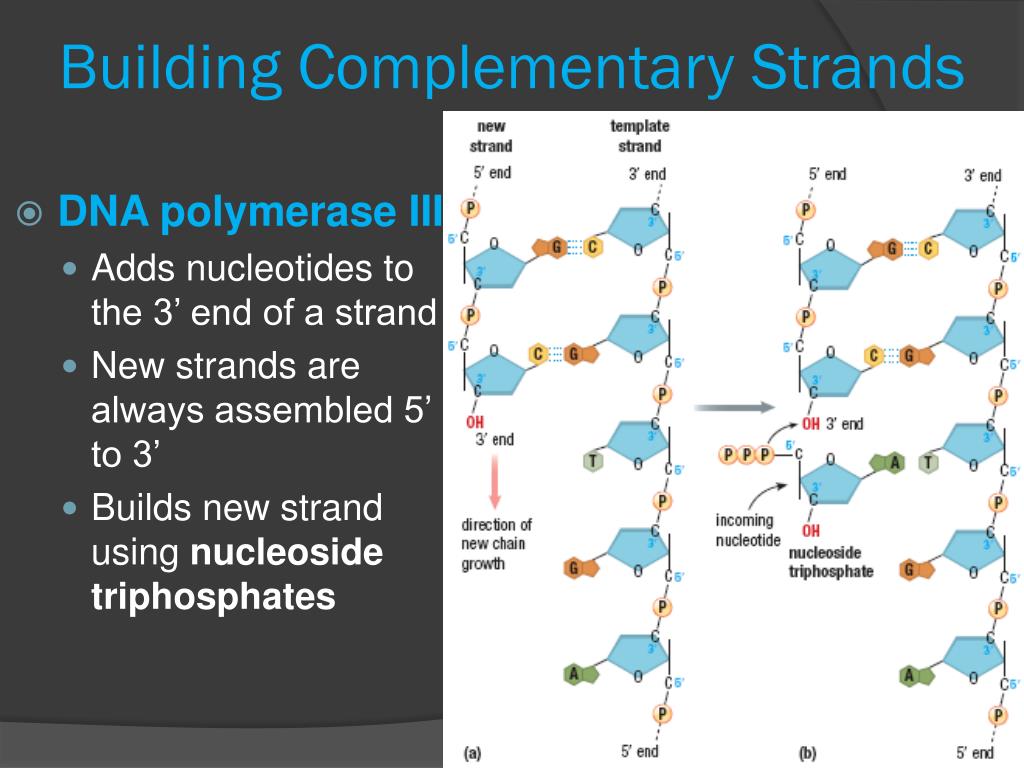
This Is The Enzyme That Builds Complementary Dna Strands - Dna polymerase is an enzyme responsible for synthesizing a complementary strand of dna during dna replication, repair, and recombination. The precision of transcription is enhanced by the enzyme’s ability to. It does this by adding dna nucleotides one at a time. The complementary nature of the four bases provides the information. The enzyme responsible for building a new dna strand by laying complementary bases during dna replication is called dna polymerase. The enzyme responsible for gluing nucleotides to form a new strand of dna is dna polymerase, specifically dna polymerase iii in prokaryotes. This enzyme has the ability. Enzyme that creates a complementary rna fragment next to dna about to be replicated During dna replication, the lagging strand is synthesized by forming okazaki fragments. This enzyme plays a crucial role in the replication. During dna replication, the lagging strand is synthesized by forming okazaki fragments. This problem is solved by topoisomerases, enzymes that catalyze the reversible breakage and rejoining of dna strands. The enzyme that joins okazaki fragments together is. Dna polymerase iii (dna pol iii): Because dna polymerase can only add new nucleotides at the end of a backbone, a primer sequence, which provides this starting point, is. There are two types of these enzymes: During replication, the two dna strands separate at multiple points along the length of the chromosome. Dna polymerase is an enzyme responsible for synthesizing a complementary strand of dna during dna replication, repair, and recombination. It does this by adding dna nucleotides one at a time. Dna polymerase binds to a dna strands and adds new material to it in order to build a complementary strand. Which statement best describes strand characteristics as it relates. It adds nucleotides in the 5'. Dna polymerase is the enzyme that adds new nucleotides to the growing dna strand, following the base pairing rules: The enzyme responsible for gluing nucleotides to form a new strand of dna is dna polymerase, specifically dna polymerase iii in prokaryotes. Enzyme that creates a. So an enzyme that attaches many pieces of dna). Because dna polymerase can only add new nucleotides at the end of a backbone, a primer sequence, which provides this starting point, is. During dna replication, the lagging strand is synthesized by forming okazaki fragments. It adds nucleotides in the 5'. Nucleotides pair with complementary bases on the dna template strand,. Dna polymerase binds to a dna strands and adds new material to it in order to build a complementary strand. This enzyme has the ability. The model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is. During dna replication, the. Dna polymerase is the enzyme that adds new nucleotides to the growing dna strand, following the base pairing rules: This enzyme plays a crucial role in the replication. During elongation, an enzyme called dna polymerase adds dna nucleotides to the 3′ end of the template. This problem is solved by topoisomerases, enzymes that catalyze the reversible breakage and rejoining of. It adds nucleotides in the 5'. The enzyme responsible for gluing nucleotides to form a new strand of dna is dna polymerase, specifically dna polymerase iii in prokaryotes. Because dna polymerase can only add new nucleotides at the end of a backbone, a primer sequence, which provides this starting point, is. Dna polymerase iii (dna pol iii): Study with quizlet. Dna polymerases are indispensable enzymes in the dna replication process, responsible for synthesizing new dna strands by adding nucleotides to a growing chain. It does this by adding dna nucleotides one at a time. This is the main dna synthesizing enzyme. The complementary nature of the four bases provides the information. The model for dna replication suggests that the two. Dna polymerase binds to a dna strands and adds new material to it in order to build a complementary strand. It adds nucleotides in the 5'. During elongation, an enzyme called dna polymerase adds dna nucleotides to the 3′ end of the template. Dna polymerase iii (dna pol iii): Enzyme that creates a complementary rna fragment next to dna about. It does this by adding dna nucleotides one at a time. The precision of transcription is enhanced by the enzyme’s ability to. It adds nucleotides in the 5'. So an enzyme that attaches many pieces of dna). Dna polymerase is an enzyme responsible for synthesizing a complementary strand of dna during dna replication, repair, and recombination. Dna polymerase is an enzyme responsible for synthesizing a complementary strand of dna during dna replication, repair, and recombination. Dna polymerase is an enzyme that builds new strands of dna. The precision of transcription is enhanced by the enzyme’s ability to. The enzyme that joins okazaki fragments together is. This problem is solved by topoisomerases, enzymes that catalyze the reversible. The enzyme responsible for building a new dna strand by laying complementary bases during dna replication is called dna polymerase. The enzyme dna polymerase reads the dna code on the parental strands and builds new partner strands that are complementary to the original strands. Enzyme that creates a complementary rna fragment next to dna about to be replicated The model. This problem is solved by topoisomerases, enzymes that catalyze the reversible breakage and rejoining of dna strands. The enzyme responsible for gluing nucleotides to form a new strand of dna is dna polymerase, specifically dna polymerase iii in prokaryotes. This is the main dna synthesizing enzyme. The model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is. Nucleotides pair with complementary bases on the dna template strand, substituting uracil for thymine. The enzyme that joins okazaki fragments together is. Dna polymerase iii (dna pol iii): Dna polymerase is an enzyme that builds new strands of dna. The enzyme responsible for building a new dna strand by laying complementary bases during dna replication is called dna polymerase. Which statement best describes strand characteristics as it relates. During elongation, an enzyme called dna polymerase adds dna nucleotides to the 3′ end of the template. The two dna polymerase iii enzymes that are following the opening replication forks are synthesizing new complementary dna strands and attaching new nucleotides at the 3′ end. Dna polymerase is the enzyme that adds new nucleotides to the growing dna strand, following the base pairing rules: Because dna polymerase can only add new nucleotides at the end of a backbone, a primer sequence, which provides this starting point, is. This enzyme has the ability. So an enzyme that attaches many pieces of dna).Solved After DNA Polymerase III builds complementary strands, another
PPT DNA Hereditary Molecules of Life PowerPoint Presentation, free
The model represents DNA replication. What does enzyme 2 do? A. It
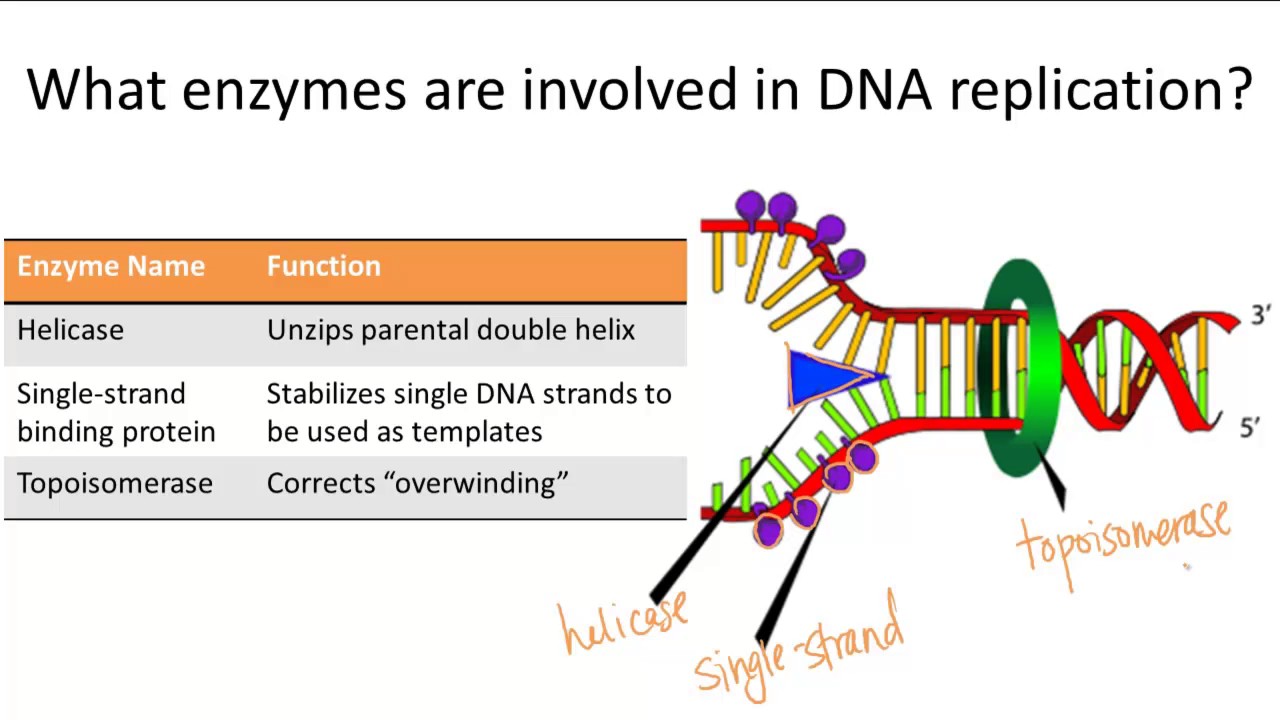
Enzymes Involved in DNA Replication YouTube
14.5 DNA Replication in Prokaryotes Biology LibreTexts
PPT DNA Hereditary Molecules of Life PowerPoint Presentation, free
Question Video Determining the Complementary Sequence of a DNA Strand
DNA is Composed of Complementary Strands
DNA. Structure and Replication Presentation Biology
PPT Chapter 26 DNA; RNA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
It Adds Nucleotides In The 5'.
There Are Two Types Of These Enzymes:
Dna Polymerase Binds To A Dna Strands And Adds New Material To It In Order To Build A Complementary Strand.
Dna Polymerase Is An Enzyme Responsible For Synthesizing A Complementary Strand Of Dna During Dna Replication, Repair, And Recombination.
Related Post:


.PNG)