Useful Life Of A Building
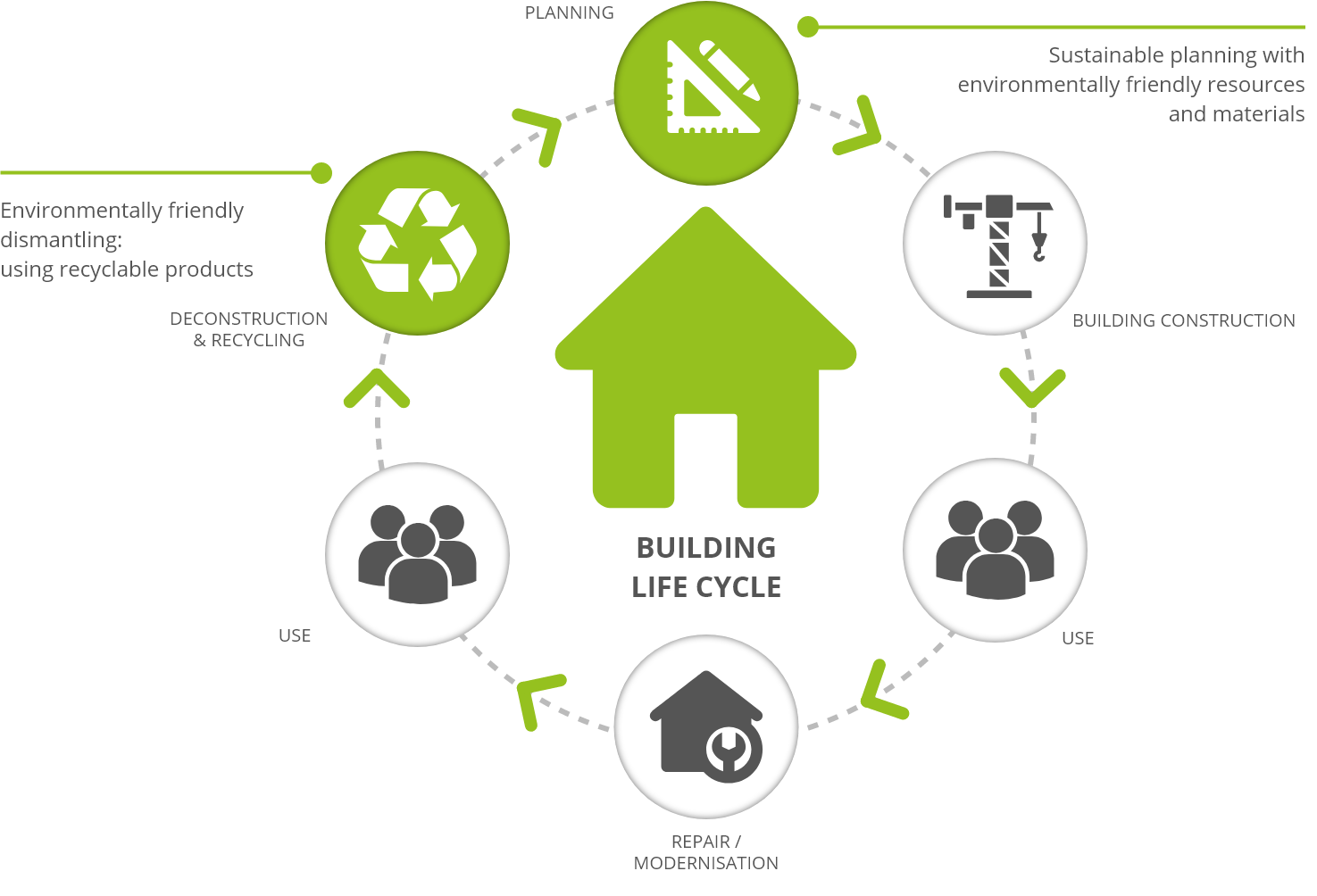
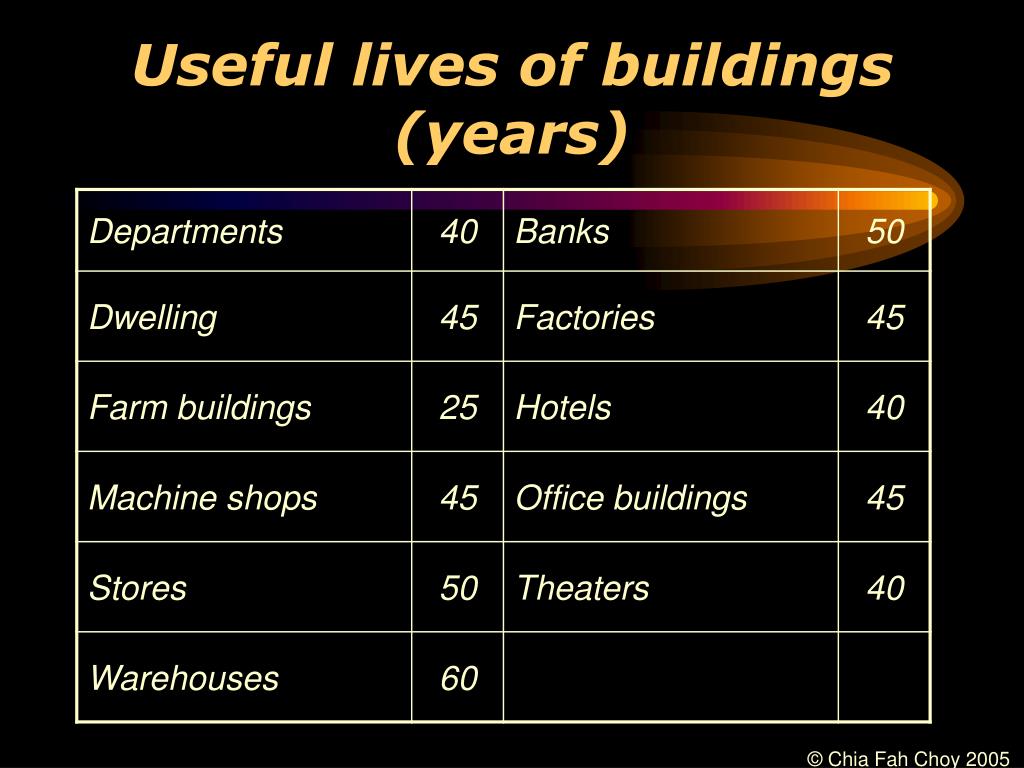
Useful Life Of A Building - For our playground structure, let’s say the cost was $21,500. Gaap doesn't require you to peer into the future and know how long you'll use a particular asset. For example, firm a buys a building. Typically, nonresidential buildings have a useful life of 39 years, and residential rental properties are depreciated over 27.5 years under gaap. The useful life of an asset is dependent on a number of entity. Each phase of a building’s life cycle — design, construction, operations — often operates in isolation, with little to no communication or data sharing between the teams. The building is estimated to have a useful life of 20 years, and at the end of the 20 years, the building is expected to have a salvage value of $10,000. In 2023, the former cinema was to become a wetherspoons but. Determine the annual depreciation of. The period over which an asset is expected to contribute directly or indirectly to future cash flows. Typically, nonresidential buildings have a useful life of 39 years, and residential rental properties are depreciated over 27.5 years under gaap. Land is not depreciable because it does not wear out. The building is estimated to have a useful life of 20 years, and at the end of the 20 years, the building is expected to have a salvage value of $10,000. Determining the useful life of an asset involves factors that vary across industries and asset types. What is the useful life of an asset? Depreciation is a key accounting concept for managing the. It also includes profitability and upkeep costs. Copper roofs last 70 or more years with proper care, though this type of roofing material comes at a high cost, so it is typically only used for accent pieces. Determine the annual depreciation of. The period over which an asset is expected to contribute directly or indirectly to future cash flows. The period over which an asset is expected to contribute directly or indirectly to future cash flows. Here are some methods commonly used to estimate the useful life of buildings: This is the simplest method, where the cost of the building is. To calculate depreciation, we must first identify the acquisition cost, salvage value, and useful life. The useful life. A nonresidential building has a useful life of 39 years. Figuring out an asset’s useful life is more than just its lifespan. This is the simplest method, where the cost of the building is. Gaap doesn't require you to peer into the future and know how long you'll use a particular asset. Land is not depreciable because it does not. A nonresidential building has a useful life of 39 years. Determining the useful life of an asset involves factors that vary across industries and asset types. Land is not depreciable because it does not wear out. This is the simplest method, where the cost of the building is. Typically, nonresidential buildings have a useful life of 39 years, and residential. For our playground structure, let’s say the cost was $21,500. A nonresidential building has a useful life of 39 years. Here are some methods commonly used to estimate the useful life of buildings: Copper roofs last 70 or more years with proper care, though this type of roofing material comes at a high cost, so it is typically only used. Determine the annual depreciation of. A residential rental building has a useful life of 27.5 years, according to the irs. We’ll use a salvage value of 0. Copper roofs last 70 or more years with proper care, though this type of roofing material comes at a high cost, so it is typically only used for accent pieces. For our playground. Determine the annual depreciation of. The building is estimated to have a useful life of 20 years, and at the end of the 20 years, the building is expected to have a salvage value of $10,000. The useful life of an asset is dependent on a number of entity. A nonresidential building has a useful life of 39 years. Gaap. Here are some methods commonly used to estimate the useful life of buildings: A nonresidential building has a useful life of 39 years. Land is not depreciable because it does not wear out. For example, firm a buys a building. Figuring out an asset’s useful life is more than just its lifespan. A nonresidential building has a useful life of 39 years. Determining the useful life of an asset involves factors that vary across industries and asset types. Depreciation is a key accounting concept for managing the. This is the simplest method, where the cost of the building is. The period over which an asset is expected to contribute directly or indirectly. Gaap doesn't require you to peer into the future and know how long you'll use a particular asset. Each phase of a building’s life cycle — design, construction, operations — often operates in isolation, with little to no communication or data sharing between the teams. The period over which an asset is expected to contribute directly or indirectly to future. This helps businesses make smart choices about fixing or. The useful life of an asset is dependent on a number of entity. Each phase of a building’s life cycle — design, construction, operations — often operates in isolation, with little to no communication or data sharing between the teams. It also includes profitability and upkeep costs. A nonresidential building has. Figuring out an asset’s useful life is more than just its lifespan. Management should carefully evaluate situations where the useful life of a building is considered to be longer than the useful life of the structure of the building, such as the walls. For example, firm a buys a building. Land is not depreciable because it does not wear out. This is the simplest method, where the cost of the building is. It also includes profitability and upkeep costs. The building is estimated to have a useful life of 20 years, and at the end of the 20 years, the building is expected to have a salvage value of $10,000. This helps businesses make smart choices about fixing or. The period over which an asset is expected to contribute directly or indirectly to future cash flows. The useful life of a commercial property refers to the estimated period over which the property is expected to provide economic benefits to the owner. Determine the annual depreciation of. A residential rental building has a useful life of 27.5 years, according to the irs. Determining the useful life of an asset involves factors that vary across industries and asset types. Depreciation is a key accounting concept for managing the. Examining these factors helps companies make informed decisions about. Typically, nonresidential buildings have a useful life of 39 years, and residential rental properties are depreciated over 27.5 years under gaap.Solved a. The buildings have an estimated useful life of
Design life of buildings by category. Download Table
Estimated Useful Lives of Building Components in Life cycle Cost
Sustainable Building Construction For a healthy Environment
Understanding Whole Building Life Cycle Assessment for a Better
Life of a Building Informatics CHPC New York
PPT Topic 4 Life Cycle Costing PowerPoint Presentation, free
What Happens Over the Life of a Building..? YouTube
LIFE OF BUILDING
Estimated Useful Lives of Building Components in Life cycle Cost
The Useful Life Of An Asset, Also Known As Economic Life Or Service Life, Is An Estimate Of How Long You Can Reasonably Expect To Use An Asset For The.
The Useful Life Of An Asset Is Dependent On A Number Of Entity.
Instead, You Can Base Depreciation On A Useful Life Of Assets Table.
We’ll Use A Salvage Value Of 0.
Related Post: