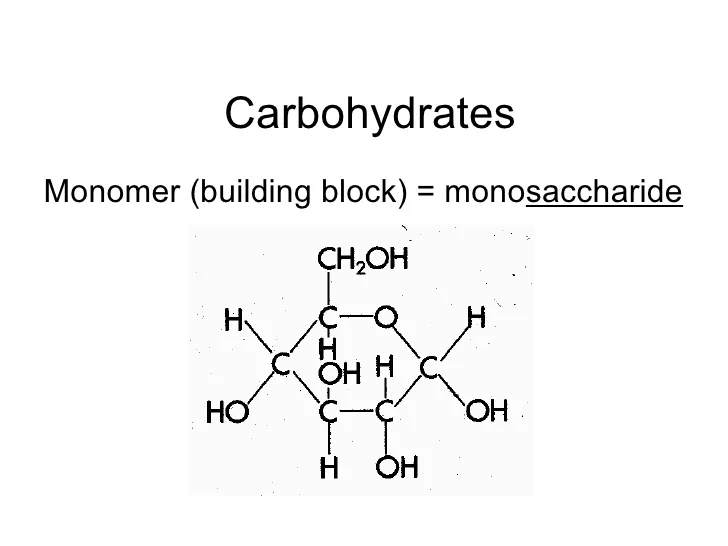
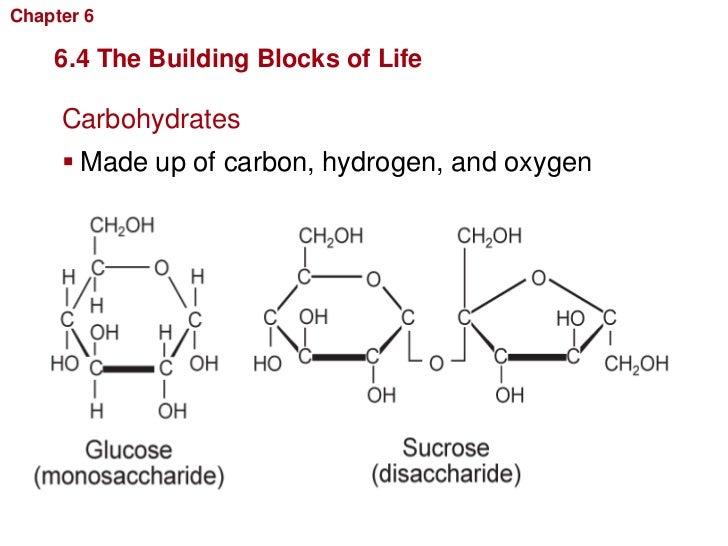
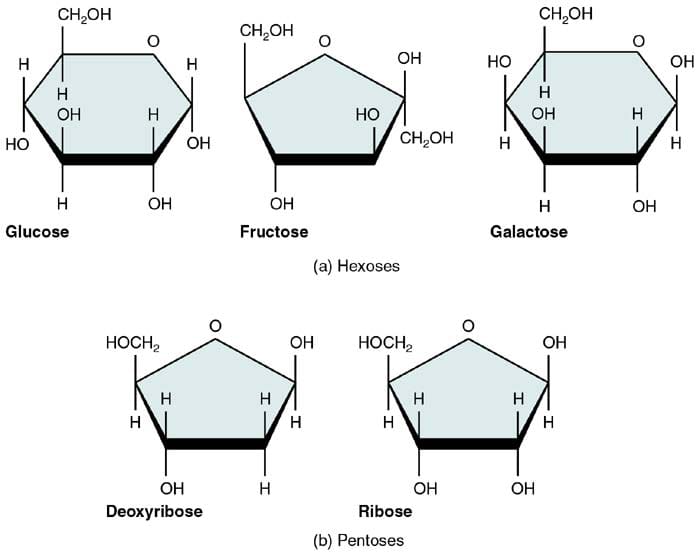
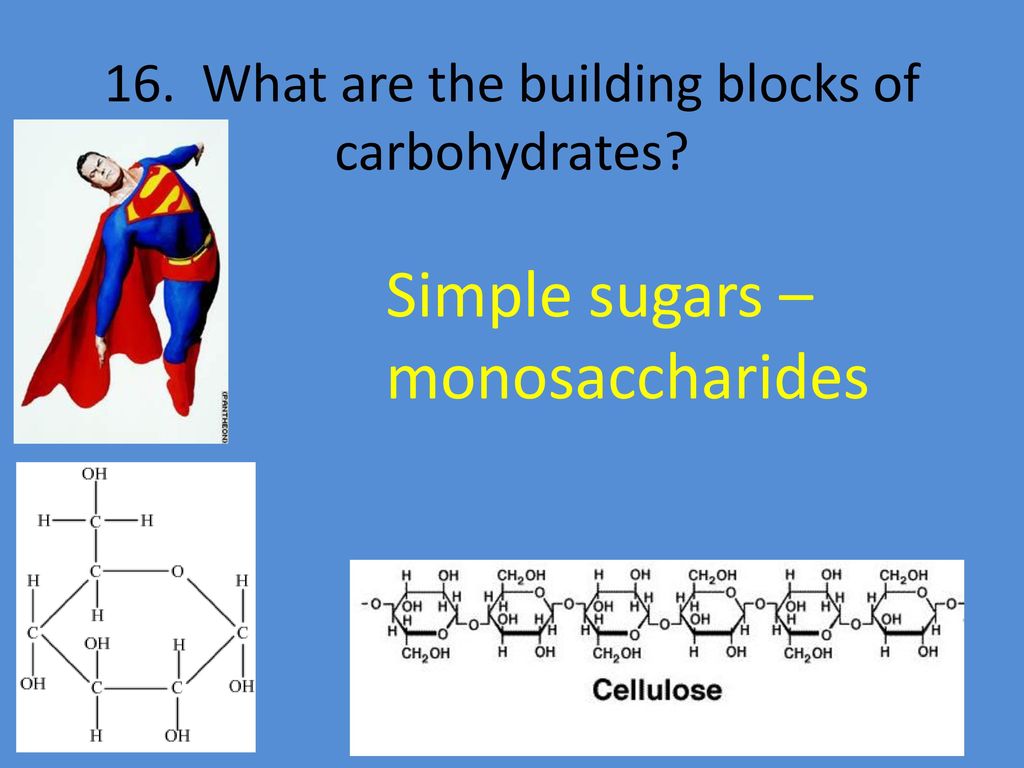
What Are Carbohydrates Building Blocks
What Are Carbohydrates Building Blocks - Monomers are the individual units that are the building blocks of the longer chain. Centers for disease control and prevention. These building blocks come together to create chains, which in turn create different types of. These cell walls provide protection and support for the cell and the whole organism. Plant and fungal cells have cell walls made from carbohydrates. The monomers of carbohydrates are monosaccharides. Polymers and carbohydrates there are four classes of organic molecules that are important to life. Glucose, fructose and galactose are examples of monosaccharides. These have the molecular formula of c 6 h 12 o 6. Monosaccharides can be found in. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use energy from sunlight to synthesize. These simple sugars include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Thus, monosaccharides are the building blocks of carbohydrates. Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrate molecules. The basic building block of carbohydrates is the monosaccharide, which consists of six carbon atoms. The building blocks of carbs are sugars, starches and fiber, inning accordance with the u.s. These building blocks come together to create chains, which in turn create different types of. Monosaccharides can be found in. The building blocks of carbohydrates are monosaccharides. This amounts less than 130 grams of carbohydrates per day, compared to a typical. Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. These cell walls provide protection and support for the cell and the whole organism. Cellulose is a large, complex carbohydrate that forms. Centers for disease control and prevention. Explore the essential roles of carbohydrates in structure, function, and metabolism within the human body. Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrate molecules. Monomers are the individual units that are the building blocks of the longer chain. Carbohydrates are the most common class of biochemical compounds. These building blocks come together to create chains, which in turn create different types of. Do you know carbohydrates building blocks? The building blocks of carbohydrates are monosaccharides. The basic building block of carbohydrates is the monosaccharide, which consists of six carbon atoms. Centers for disease control and prevention. These building blocks come together to create chains, which in turn create different types of. Do you know carbohydrates building blocks? These have the molecular formula of c 6 h 12 o 6. Carbohydrates are a fundamental component of life, providing energy. Centers for disease control and prevention. Polymers and carbohydrates there are four classes of organic molecules that are important to life. Explain what a peptidoglycan is, what role it plays in some biological systems, what bonds are used to. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use energy from sunlight to synthesize. The monomers of carbohydrates are monosaccharides. Carbohydrates are an important group of biological molecules that includes sugars and starches. These simple sugars include glucose, fructose, and galactose. These building blocks come together to create chains, which in turn create different types of. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use energy from sunlight to synthesize. Thus, monosaccharides are the building blocks of carbohydrates. This amounts less than 130 grams of carbohydrates per day, compared to a typical. Cellulose is a large, complex carbohydrate that forms. The basic building block of carbohydrates is the monosaccharide, which consists of six carbon atoms. Carbohydrates are the most common class of biochemical compounds. Explore the essential roles of carbohydrates in structure, function, and metabolism within the human body. Sugars, polysaccharides and fibers are the main answers. Polymers and carbohydrates there are four classes of organic molecules that are important to life. But how do they affect the body? Monomers are the individual units that are the building blocks of the longer chain. The basic biochemistry of living organisms can, therefore, be understood regarding the morphology and physiology of the four biological macromolecules: But how do they affect the body? The basic building block of carbohydrates is the monosaccharide, which consists of six carbon atoms. Did you know that. Thus, monosaccharides are the building blocks of carbohydrates. Monomers are the individual units that are the building blocks of the longer chain. Sugars, polysaccharides and fibers are the main answers. Glucose, fructose and galactose are examples of monosaccharides. The basic building block of carbohydrates is the monosaccharide, which consists of six carbon atoms. Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrate molecules. The building blocks of carbohydrates are monosaccharides. The basic biochemistry of living organisms can, therefore, be understood regarding the morphology and physiology of the four biological macromolecules: The basic building block of carbohydrates is the monosaccharide, which consists of six carbon atoms. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use energy from sunlight to. Sugars, polysaccharides and fibers are the main answers. The building blocks of carbohydrates are monosaccharides. The basic building block of carbohydrates is the monosaccharide, which consists of six carbon atoms. But how do they affect the body? Thus, monosaccharides are the building blocks of carbohydrates. These have the molecular formula of c 6 h 12 o 6. Monosaccharides can be found in. These simple sugars include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Carbohydrates are a fundamental component of life, providing energy. The building blocks of carbs are sugars, starches and fiber, inning accordance with the u.s. This amounts less than 130 grams of carbohydrates per day, compared to a typical. These cell walls provide protection and support for the cell and the whole organism. Plant and fungal cells have cell walls made from carbohydrates. Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrate molecules. All carbohydrates consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms and are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or are compounds that can be broken down to form such. Polymers and carbohydrates there are four classes of organic molecules that are important to life.Organic molecules
Biochemistry notes students
PPT Biochem Shmem PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5854667
PPT Orgo C licker Review PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Carbohydrates Examples Biology
2 Biological Building Blocks Carbohydrates Basicmedical Key
Building Blocks of Carbohydrates Types, Properties & Functions
1. What is the pH range of acids? ppt download
PPT Carbohydrates PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2427741
2 Biological Building Blocks Carbohydrates Basicmedical Key
These Building Blocks Come Together To Create Chains, Which In Turn Create Different Types Of.
Use Examples To Describe The Three Major Functions That Carbohydrates Perform In Cells.
Explain What A Peptidoglycan Is, What Role It Plays In Some Biological Systems, What Bonds Are Used To.
Glucose, Fructose And Galactose Are Examples Of Monosaccharides.
Related Post: