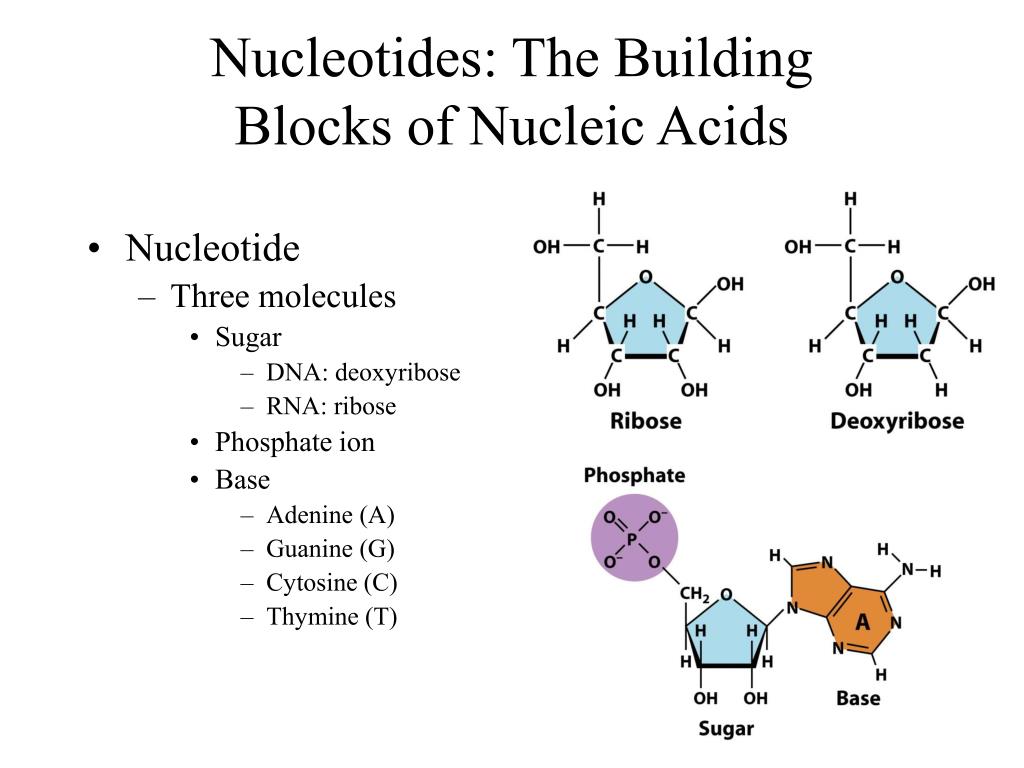
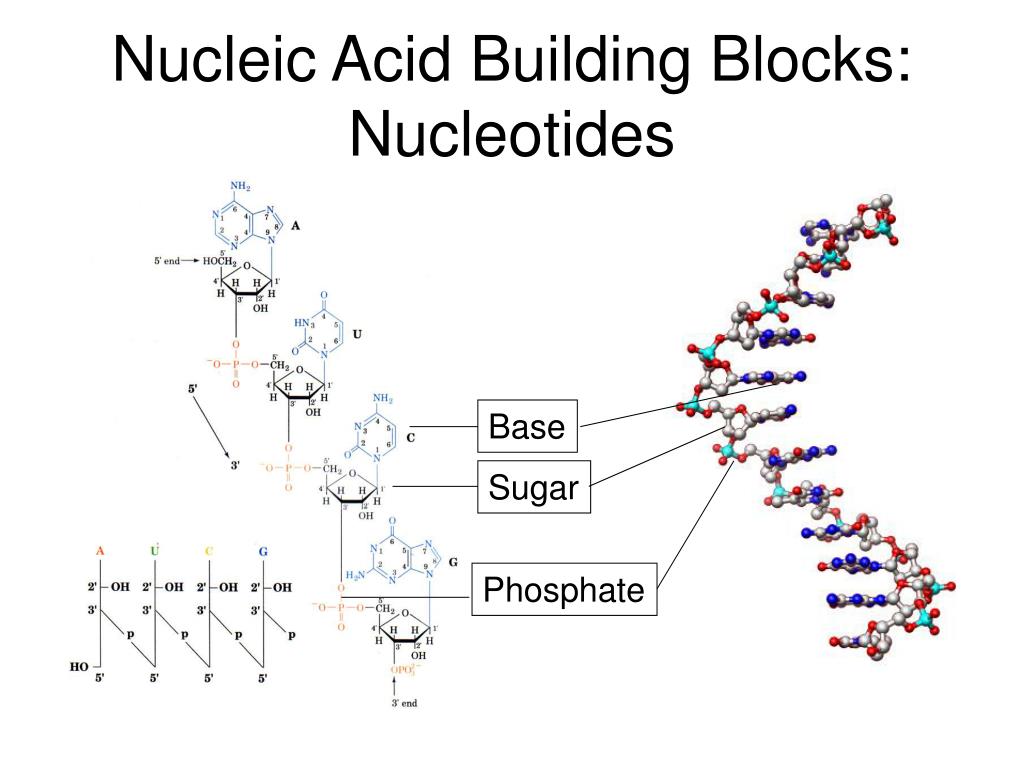
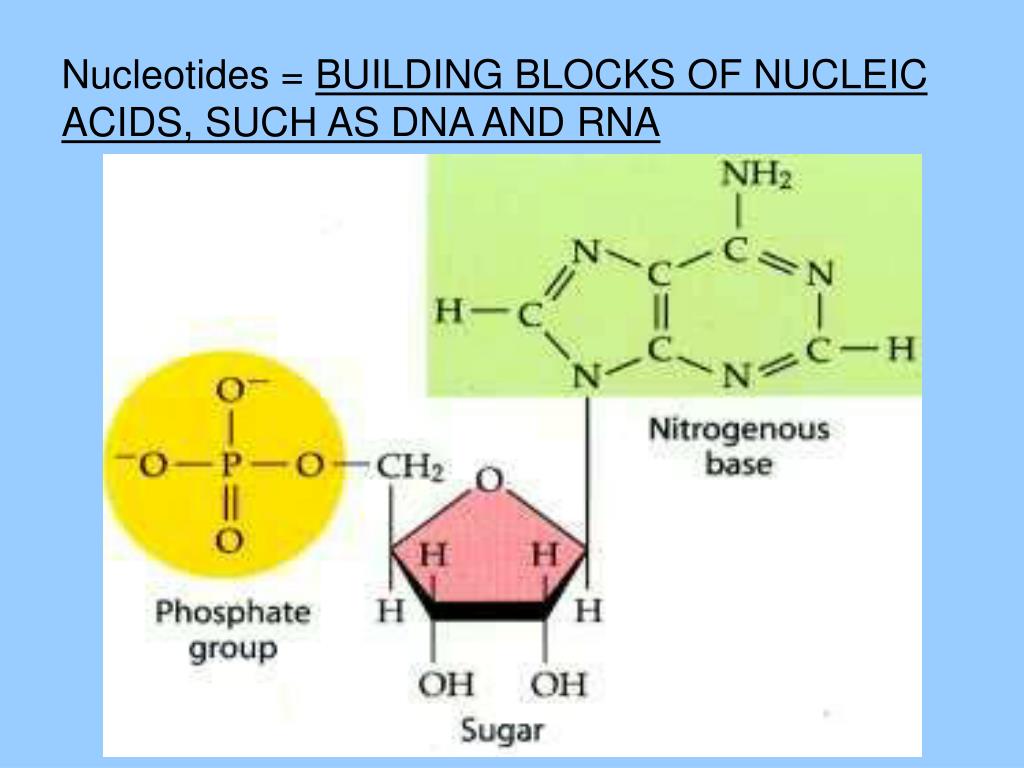
What Are Nucleic Acid Building Blocks
What Are Nucleic Acid Building Blocks - At the heart of these remarkable molecules lie their. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Vadim backman, phd, the sachs family professor of biomedical engineering and medicine, was senior author of the study. In order to discuss this important. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. The term nucleotide refers to the building blocks of both dna (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, dntps) and rna (ribonucleoside triphosphates, ntps). Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Northwestern medicine scientists have discovered. Rna, or ribonucleic acid, plays a crucial role in translating genetic information from dna into proteins. Vadim backman, phd, the sachs family professor of biomedical engineering and medicine, was senior author of the study. At the heart of these remarkable molecules lie their. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. In order to discuss this important. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. They consist of numerous nucleotides chained together. Nucleotides are organic molecules that serve as the basic structural (monomer) units for dna and rna, which, as we know, are the building blocks responsible for all life on earth. Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. Identify the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the mysteries. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Dna and rna are two types. These molecular building blocks are fundamental to dna, encoding the information necessary for growth, development, and reproduction in living organisms. Identify the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Northwestern medicine scientists have discovered. What are the building blocks of nucleic acids? Each nucleotide is a composite organic molecule made up of a nitrogen base, five carbon sugars and at least one phosphate. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. These molecular building blocks are fundamental to dna, encoding the information necessary. Pentose sugar, the phosphate group, and the nitrogenous base. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. Vadim backman, phd, the sachs family professor of biomedical engineering and medicine, was senior author of the study. Each nucleotide is a composite organic molecule made up of a nitrogen base, five carbon. In order to discuss this important. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. The structure of nucleic acids (i.e., dna) can be likened to a ladder that is made up of alternating steps that are symbolizing its three significant parts: An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Describe how nucleotides. Describe how nucleotides are linked together to form nucleic acids. Each nucleotide is a composite organic molecule made up of a nitrogen base, five carbon sugars and at least one phosphate. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Nucleotides are organic molecules that serve as the basic structural (monomer) units for dna. These molecular building blocks are fundamental to dna, encoding the information necessary for growth, development, and reproduction in living organisms. In order to discuss this important. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are organic molecules that serve as the basic structural (monomer) units for dna and rna, which, as we know,. Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. The term nucleotide refers to the building blocks of both dna (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, dntps) and rna (ribonucleoside triphosphates, ntps). Describe how nucleotides are linked together to form nucleic acids. These molecular building blocks are fundamental. The structure of nucleic acids (i.e., dna) can be likened to a ladder that is made up of alternating steps that are symbolizing its three significant parts: Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. Identify the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. What are the building blocks of nucleic acids? They. Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the mysteries. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. Nucleic acids are the cornerstone of life, playing a pivotal role in the storage and transmission of genetic information. Identify the two types of nucleic acids and the. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. Pentose sugar, the phosphate group, and the nitrogenous base. The term nucleotide refers to the building blocks of both dna (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, dntps) and rna (ribonucleoside triphosphates, ntps). Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are the cornerstone of life, playing a pivotal role. Describe the secondary structure of dna. The structure of nucleic acids (i.e., dna) can be likened to a ladder that is made up of alternating steps that are symbolizing its three significant parts: Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. Dna and rna are two types. Vadim backman, phd, the sachs family professor of biomedical engineering and medicine, was senior author of the study. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the mysteries. Identify the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Northwestern medicine scientists have discovered. Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. Northwestern medicine scientists have discovered new details about how the human genome produces instructions for creating proteins and cells, the building blocks of life,. They consist of numerous nucleotides chained together. Rna, or ribonucleic acid, plays a crucial role in translating genetic information from dna into proteins. Linear polymers of nucleotides that function in the storage & expression of genetic information, and its transfer from one generation to the next.PPT DNA and DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download
PPT Nucleic Acids The Ultimate Building Blocks PowerPoint
Nucleic Acid Building Blocks AAT Bioquest
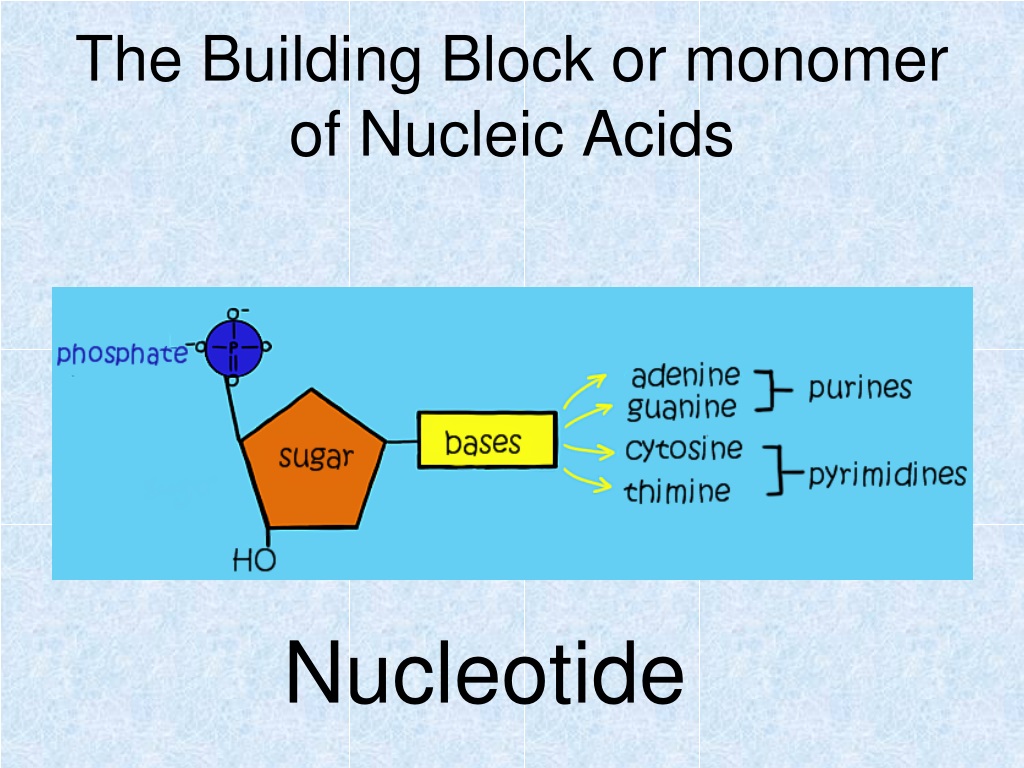
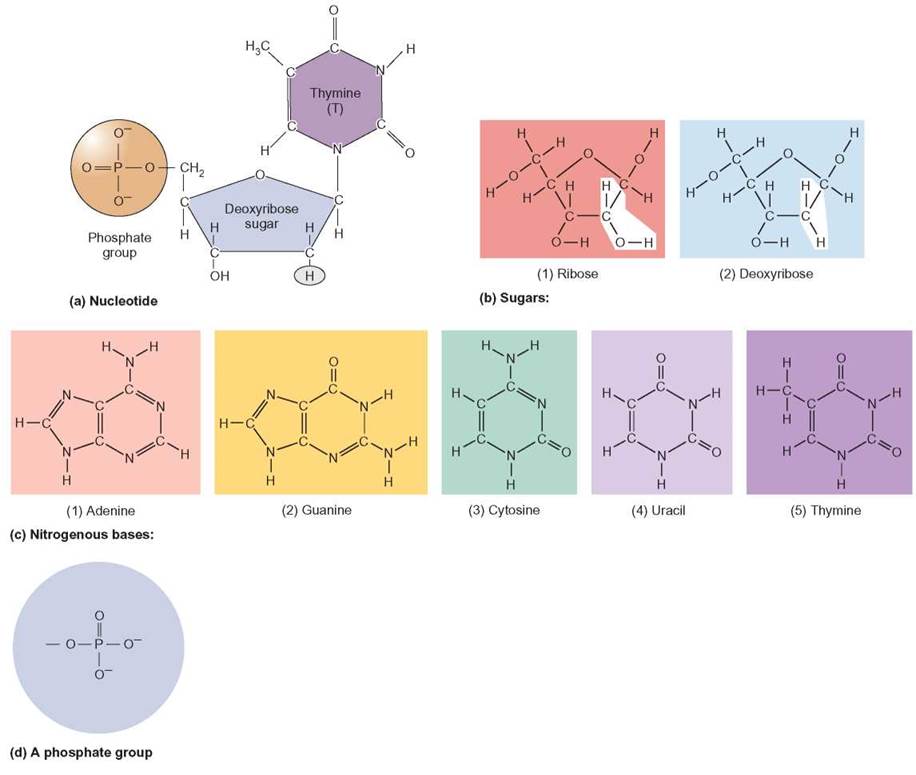
FIGURE 3.15. The Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids
Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids Structures & Functions
Properties of nucleic acids. a) The structures of deoxyribonucleotides
building blocks of nucleic acids building blocks
PPT Classical and Modern PowerPoint Presentation ID143901
PPT Exploring Nucleic Acid Structures PowerPoint Presentation, free
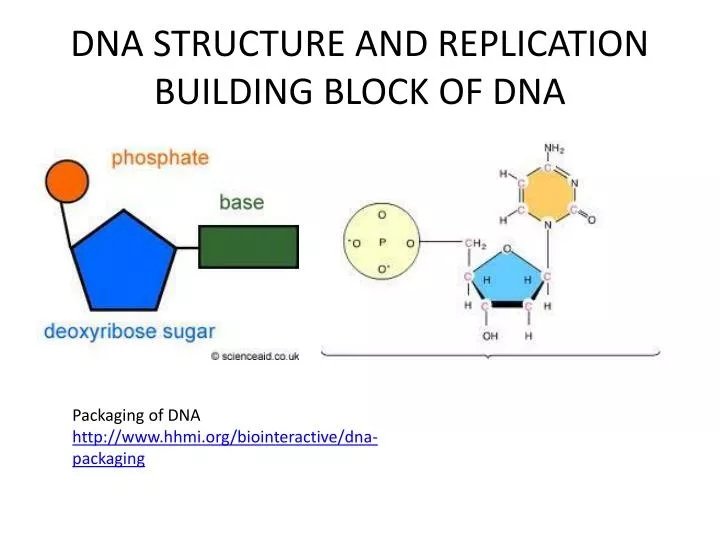
PPT DNA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5754268
Describe How Nucleotides Are Linked Together To Form Nucleic Acids.
An Anion Of Phosphoric Acid, I.e.,.
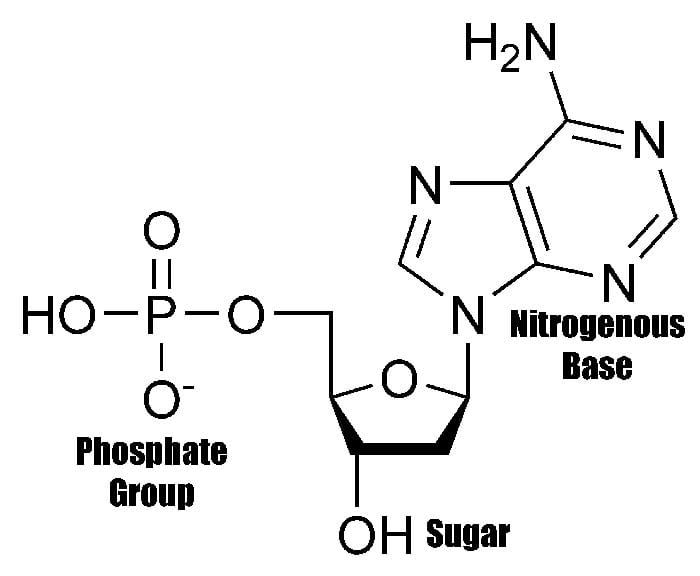
Nucleotides Are Organic Molecules That Serve As The Basic Structural (Monomer) Units For Dna And Rna, Which, As We Know, Are The Building Blocks Responsible For All Life On Earth.
Nucleic Acids Are The Cornerstone Of Life, Playing A Pivotal Role In The Storage And Transmission Of Genetic Information.
Related Post: