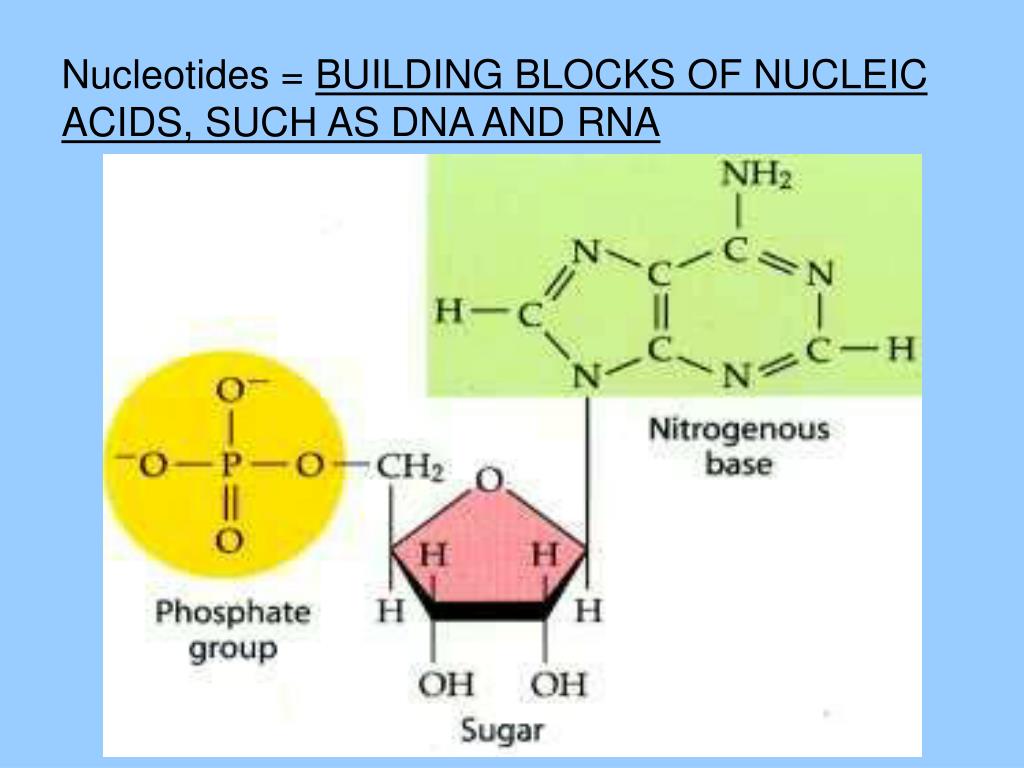
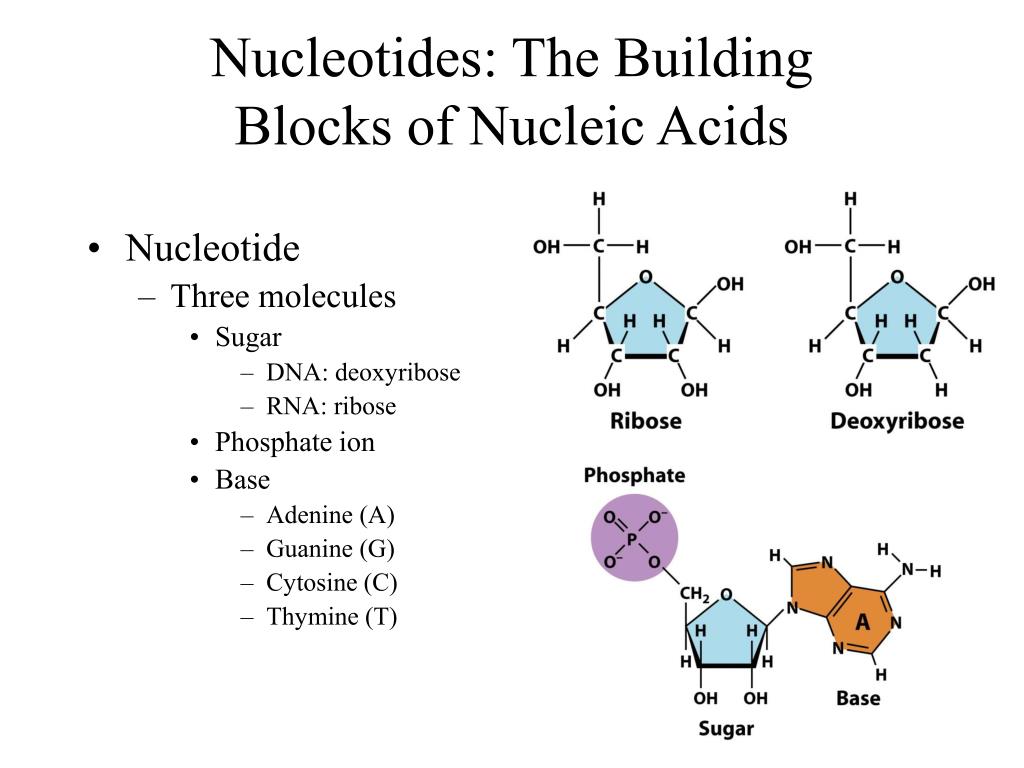
What Are The Building Blocks For Nucleic Acids
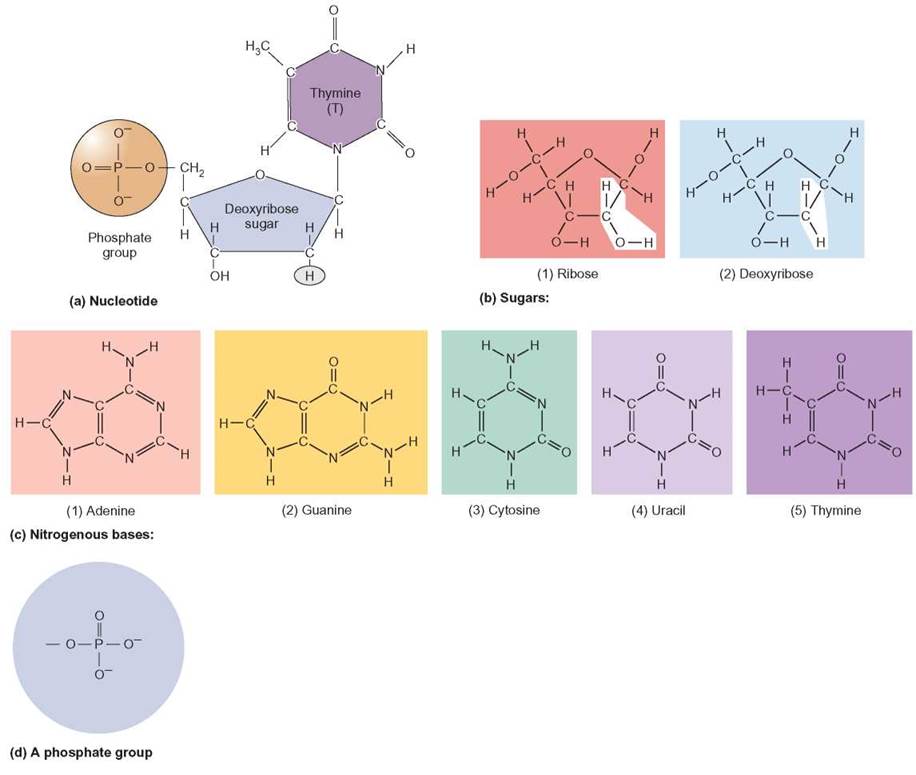
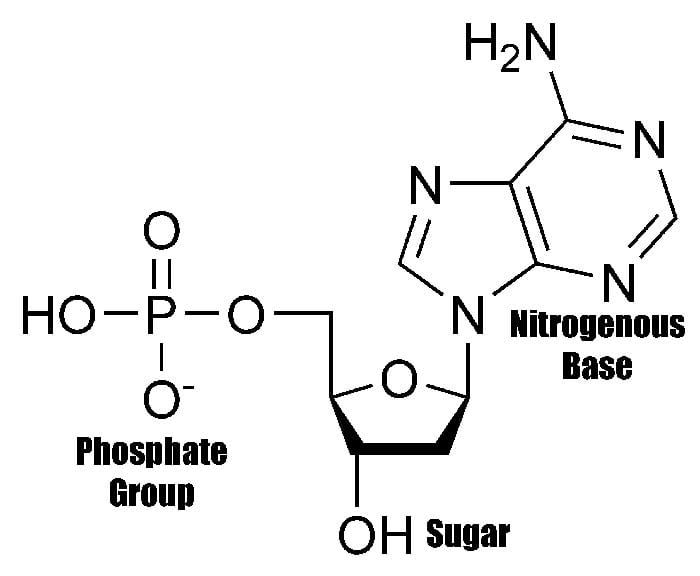
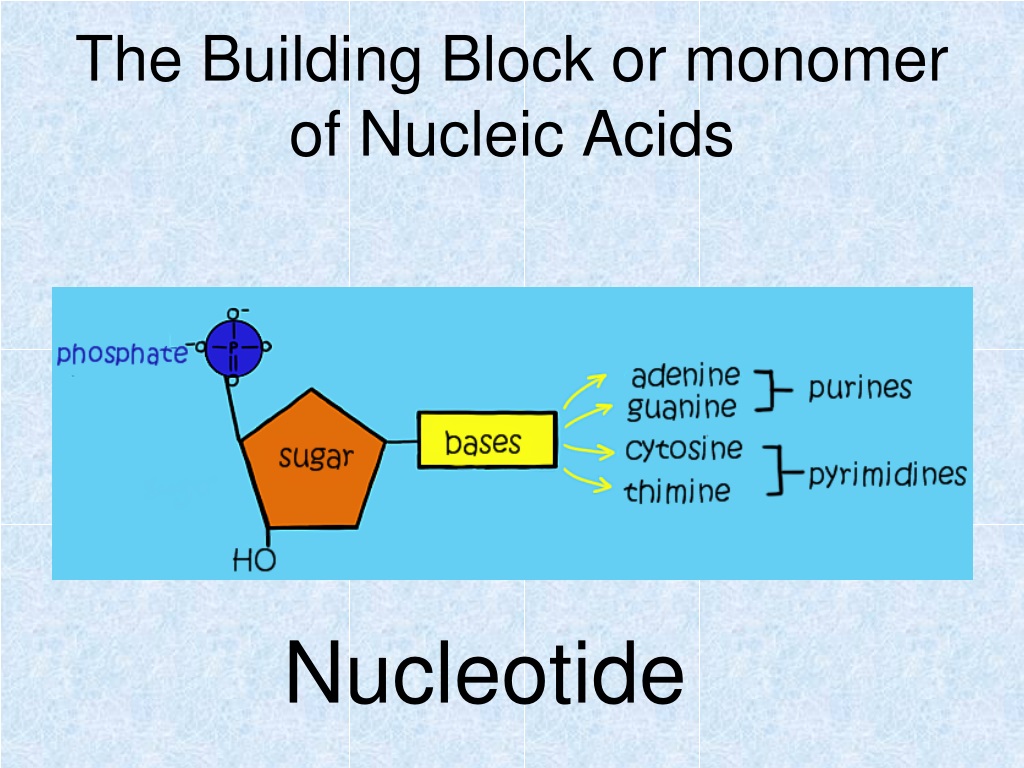
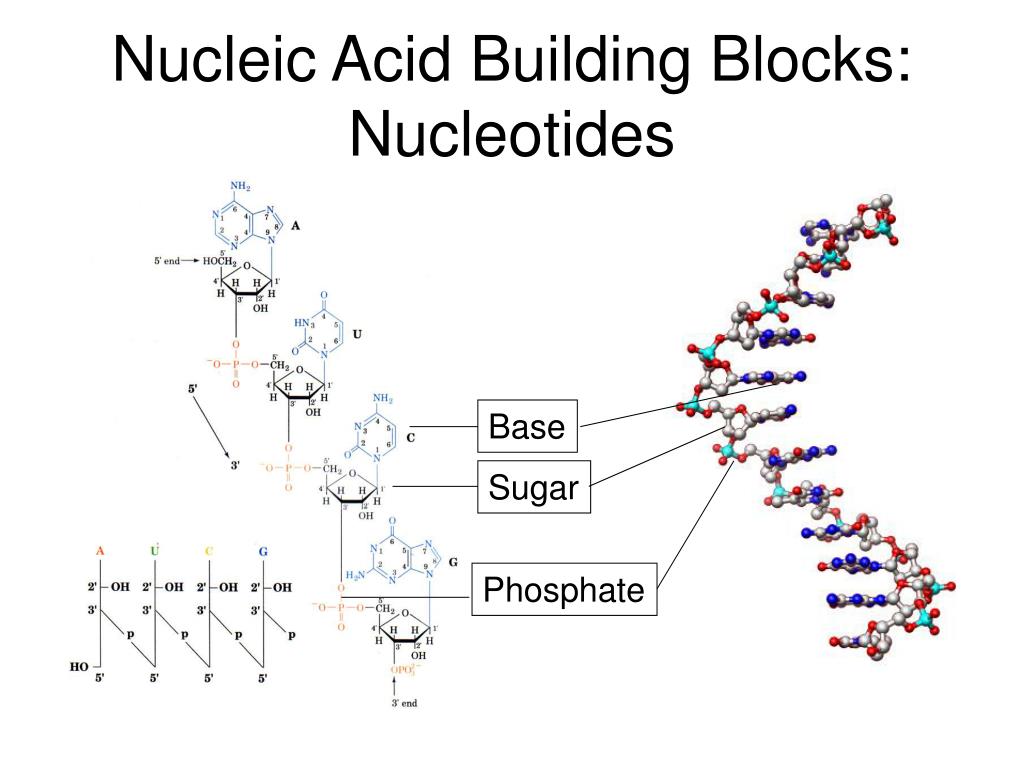
What Are The Building Blocks For Nucleic Acids - Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. This replacement affects the stability and functionality of the nucleic acids. A key aspect of this structure involves nitrogen bases—molecules that form the building blocks of rna strands. Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the mysteries. To truly understand nucleic acids, we must delve into the realm of their building blocks. Nucleotides contain three primary structural components. Each nucleotide is a composite organic molecule made up of a nitrogen base, five carbon sugars and at least one phosphate. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Describe how nucleotides are linked together to form nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are the molecules within a cell that are responsible for these amazing capabilities. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. A nucleotide is made up of. Nucleotides are the basic units that assemble to form these intricate molecules. Nucleotides contain three primary structural components. Describe how nucleotides are linked together to form nucleic acids. To truly understand nucleic acids, we must delve into the realm of their building blocks. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. This replacement affects the stability and functionality of the nucleic acids. The first isolation of nucleic acid. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. This replacement affects the stability and functionality of the nucleic acids. Dna and rna are two types. To truly understand nucleic acids, we must delve into the realm of their building blocks. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Understand the function of nucleic acids. They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. A key aspect of this structure involves nitrogen bases—molecules that form the building blocks of rna strands. They are major components of. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. Dna and rna are two types. Identify the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the mysteries. Understand the function of nucleic acids. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. Understand the function of nucleic acids. Dna and rna are two types. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. The nitrogenous bases found in nucleic. The first isolation of nucleic acid we now refer to as dna was accomplished by swiss. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are key macromolecules in the continuity of life. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. Nucleic acids are key macromolecules in the continuity of life. Understand the function of nucleic acids. Each nucleotide is a composite organic molecule made up of a nitrogen base, five carbon sugars and at least one phosphate. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Nucleotides contain three primary structural components. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. The nitrogenous bases found in nucleic. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Dna and rna are two types. To truly understand nucleic acids, we must delve into the realm of their building blocks. The nitrogenous bases found in nucleic. Monomers, in the context of nucleic acids, are known as. Describe how nucleotides are linked together to form nucleic acids. The phosphate is attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose and the. Nucleic acids are the molecules within a cell that are responsible for these amazing capabilities. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. Nucleotides contain three primary structural components. Describe how nucleotides are linked together to form nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are the molecules within a cell that are responsible for these amazing capabilities. Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the mysteries. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. Nucleic acids are key macromolecules in the continuity of life. Dna and rna are two types. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Nucleotides are the basic units that assemble to form these intricate molecules. Nucleotides contain three primary structural components. This replacement affects the stability and functionality of the nucleic acids. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. The nitrogenous bases found in nucleic. Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the mysteries. Identify the two types of nucleic acids and the function of each type. Understand the function of nucleic acids. Monomers, in the context of nucleic acids, are known as. A key aspect of this structure involves nitrogen bases—molecules that form the building blocks of rna strands. Each nucleotide is a composite organic molecule made up of a nitrogen base, five carbon sugars and at least one phosphate.FIGURE 3.15. The Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids
Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids Structures & Functions
PPT DNA and DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Proteins and nucleic acids notes
What are the building blocks of nucleic acids Everdaily Review
PPT Exploring Nucleic Acid Structures PowerPoint Presentation, free
building blocks of nucleic acids building blocks
PPT DNA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5754268
PPT Classical and Modern PowerPoint Presentation ID143901
PPT Nucleic Acids The Ultimate Building Blocks PowerPoint
Nucleotides Are The Building Blocks, I.e., The Repeat Units Or Monomers Of Nucleic Acids.
Describe The Secondary Structure Of Dna.
These Molecules, Known As Nucleosides And Nucleotides, Are The Building Blocks Of Nucleic Acids Like Dna And Rna.
Nucleotides Are The Building Blocks Of Nucleic Acids.
Related Post: