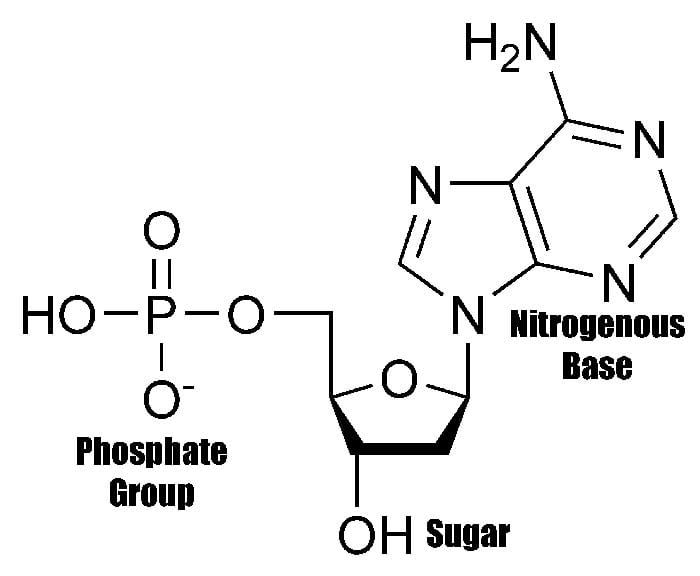
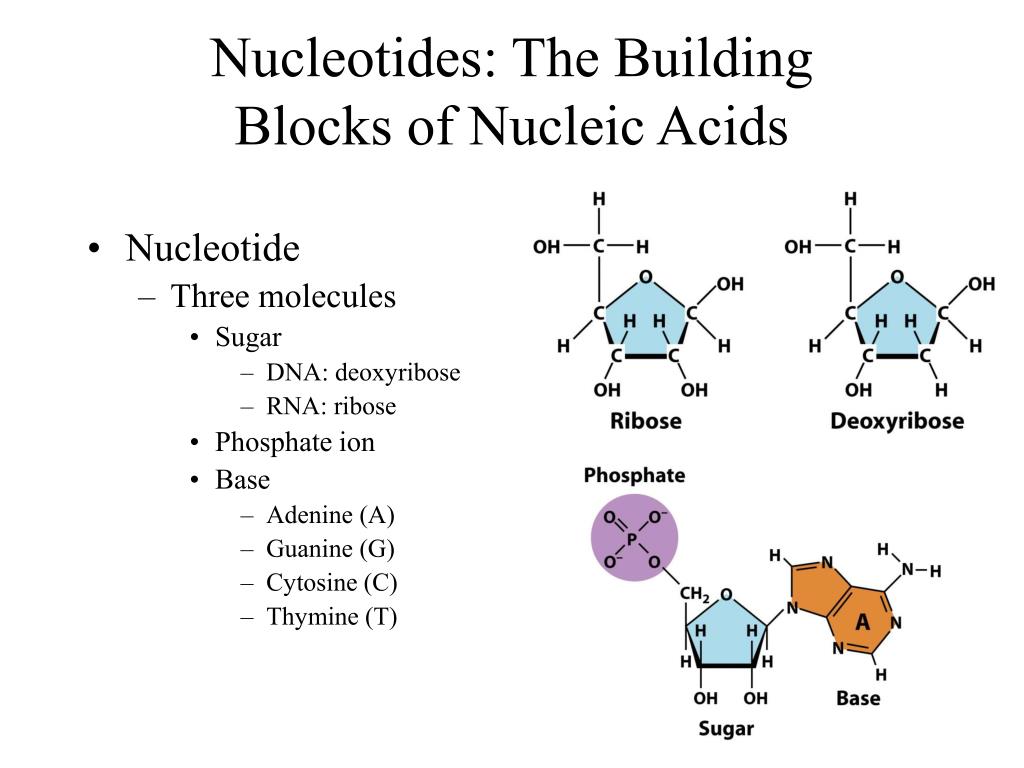
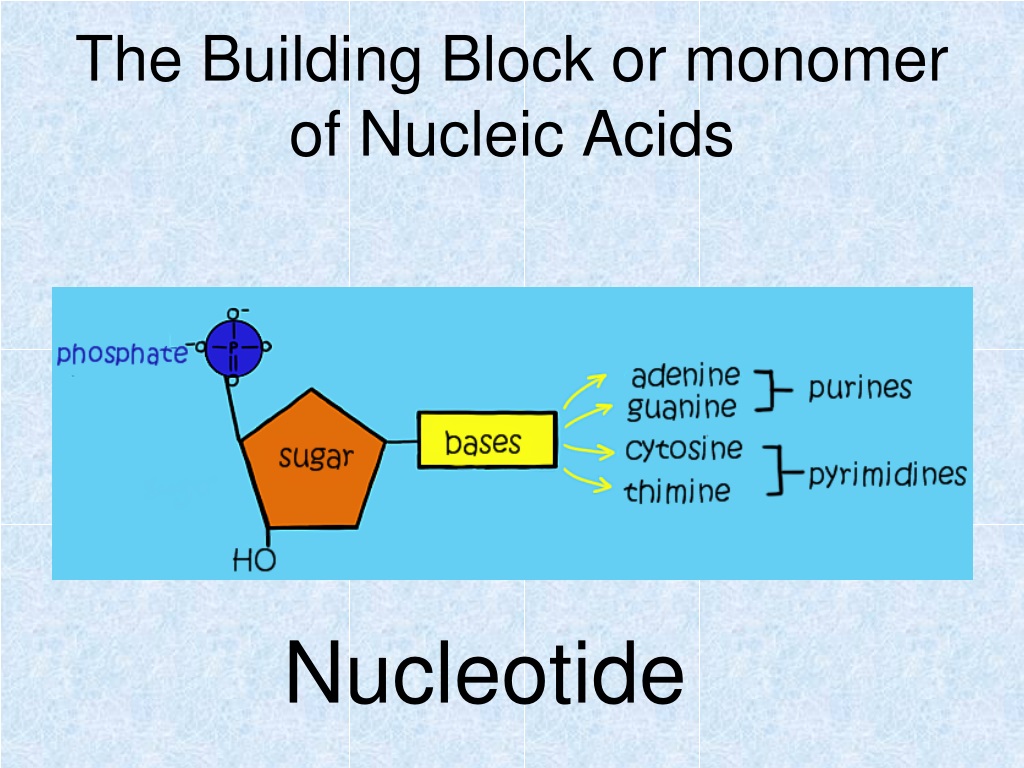
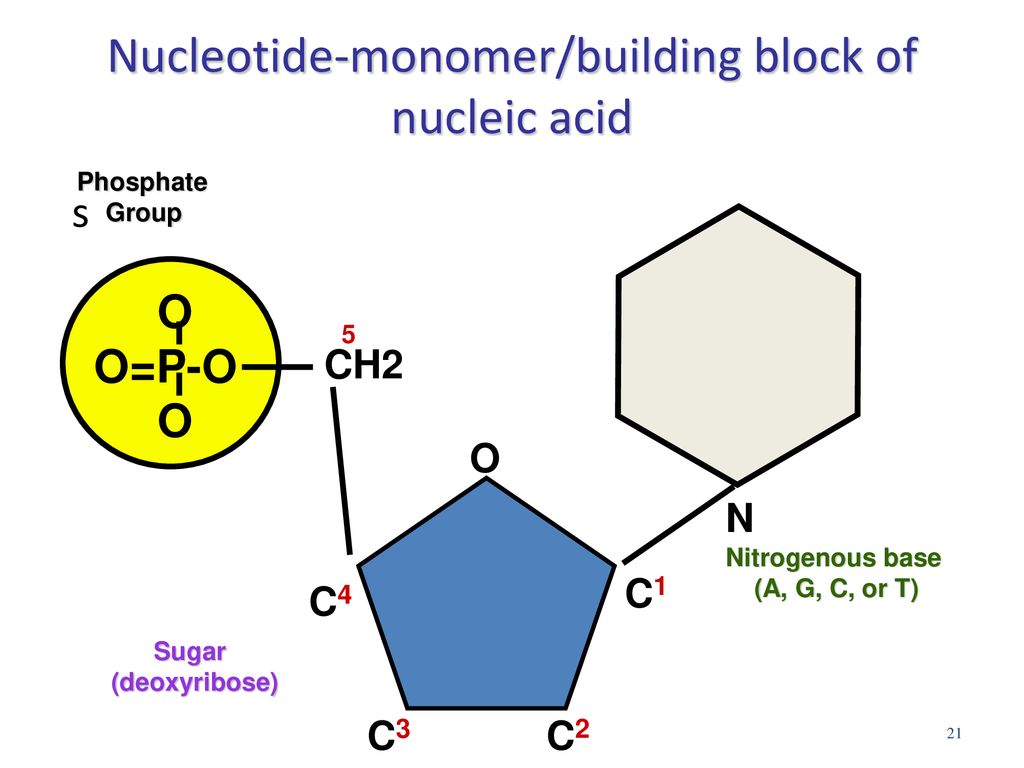
What Are The Building Blocks Monomers Of Nucleic Acids
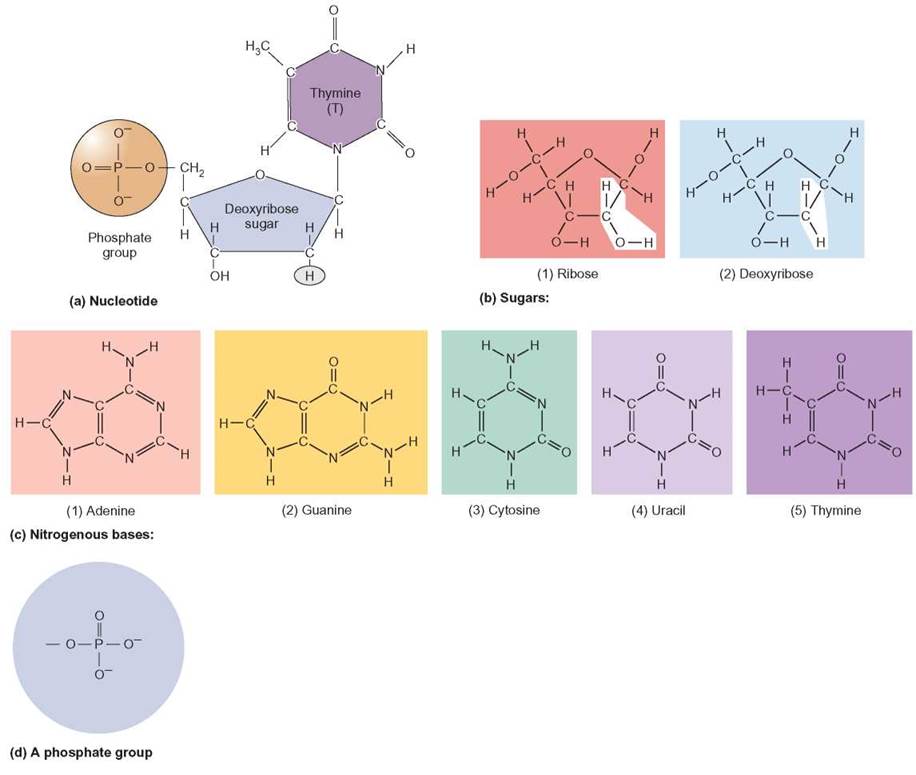
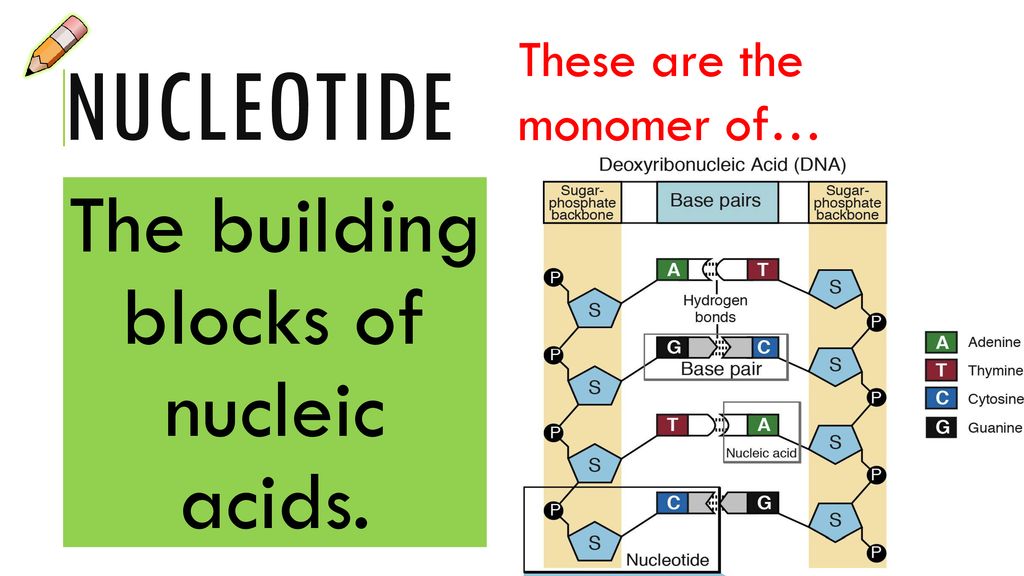
What Are The Building Blocks Monomers Of Nucleic Acids - See concept 5.5 (page 84) a nucleotide is a nucleic acid monomer consisting of a nitrogen base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. The building blocks (called monomers) of nucleic acids are nucleotides. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: Monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides: An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Both groups are made up of monomers called nucleotides. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are nucleic acids. Monomers, in the context of nucleic acids, are known as. Sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are nucleic acids. These monomers consist of a sugar molecule, a. See concept 5.5 (page 84) a nucleotide is a nucleic acid monomer consisting of a nitrogen base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Dna and rna, the nucleic acids fundamental to life, are composed of monomers that serve as the building blocks of their respective structures. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. The building blocks or monomers of nucleic acid molecules are called _____. Polymers of nucleic acids are created when monomers link together. Nucleotides are nucleosides with one or more phosphate groups attached, forming nucleotide monophosphates, diphosphates, or triphosphates. Monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides: Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. One with arms of two dna turns (fig. Nucleotides are like building blocks. To explore the impact of monomer mechanics on the growth and lattice structure, we made two 3ps variants: Sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. These monomers consist of a sugar molecule, a. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are nucleic acids. Polymers of nucleic acids are created when monomers link together. The image below shows the general structure of these nucleotides which contain a phosphate group, a pentose sugar and a base. The phosphate is attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose and the. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises. Discover the building blocks of dna, exploring its components and how they differ from rna nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Both groups are made up of monomers called nucleotides. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Nucleotides are nucleosides with one or more phosphate groups attached, forming nucleotide monophosphates, diphosphates, or triphosphates. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Nucleic acid monomers, or nucleotides, are the fundamental building blocks of the genetic material found in all living organisms. 1a, ‘short’) and a second 3ps. To explore the impact of. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. To explore the impact of monomer mechanics on the growth and lattice structure, we made two 3ps variants: The image below shows the general structure of these nucleotides which contain a phosphate group, a pentose sugar and a base. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat. The image below shows the general structure of these nucleotides which contain a phosphate group, a pentose sugar and a base. Sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base. The building blocks or monomers of nucleic acid molecules are called _____. These monomers consist of a sugar molecule, a. The phosphate is attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose and the. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are nucleosides with one or more phosphate groups attached, forming nucleotide monophosphates, diphosphates, or triphosphates. 1a, ‘short’) and a second 3ps. Polymers of nucleic acids are created when monomers link together. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides: Monomers, in the context of nucleic acids, are known as. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are nucleic acids. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Monomers, in the context of nucleic acids, are known as. Monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides: One with arms of two dna turns (fig. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. One with arms of two dna turns (fig. Sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base. Polymers of nucleic acids are created when monomers link together. Nucleic acid monomers, or nucleotides, are the fundamental building blocks of the genetic material found in all living organisms. The building blocks or monomers of nucleic acid molecules are called _____. The phosphate is attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose and the. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the functions of a nucleic acid in living organisms?, what is the building block (monomer) for a nucleic acid?,. 1a, ‘short’) and a second 3ps. Describe the secondary structure of dna and the importance of complementary base pairing. Both groups are made up of monomers called nucleotides. These monomers consist of a sugar molecule, a. The image below shows the general structure of these nucleotides which contain a phosphate group, a pentose sugar and a base. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. Nucleotides are like building blocks. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components:Structure Of Nucleic Acids Monomers
Store and transmit hereditary and information. ppt download
Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids Structures & Functions
PPT Classical and Modern PowerPoint Presentation ID143901
PPT DNA and DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Nucleic Acids Objective ppt download
Proteins. ppt download
FIGURE 3.15. The Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids
What Are the Monomer Building Blocks of Dna ElysekruwTyler
Unit 1 Section 2 vocabulary you need 3 sheets of lined paper ppt
Nucleotides Joined Together By Covalent Bonds Called Phosphodiester.
Discover The Building Blocks Of Dna, Exploring Its Components And How They Differ From Rna Nucleotides.
Dna And Rna Are Chainlike Macromolecules That Function In The Storage And Transfer Of Genetic Information.
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (Dna) And Ribonucleic Acid (Rna) Are Nucleic Acids.
Related Post:
.jpg)
.jpg)