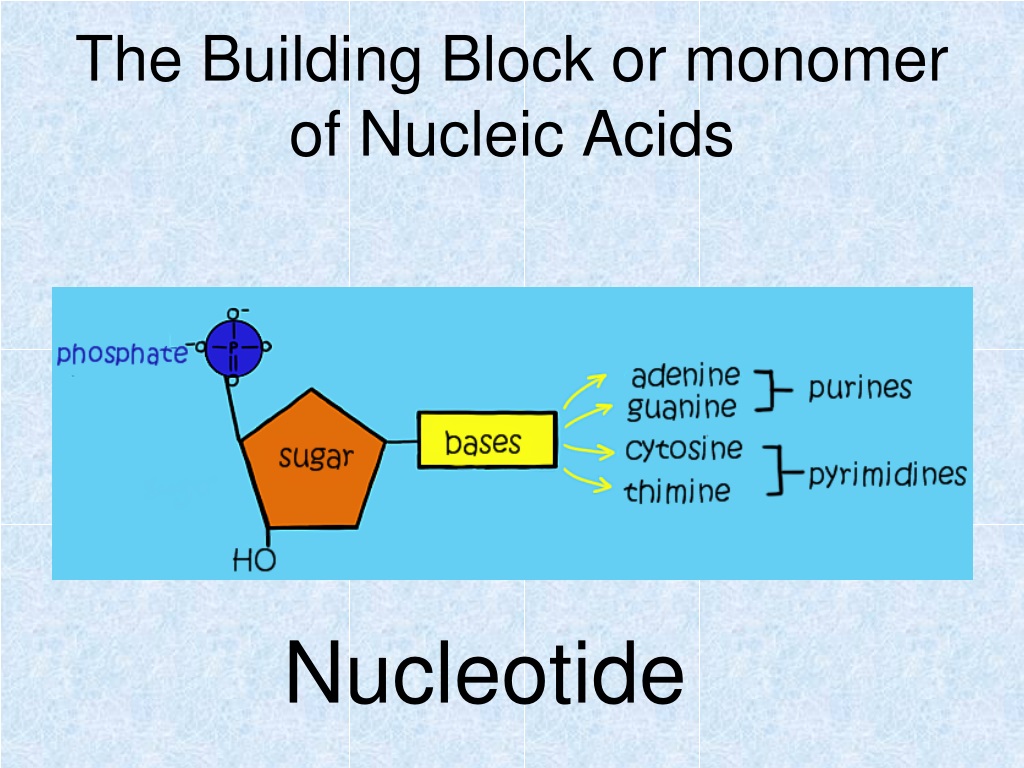
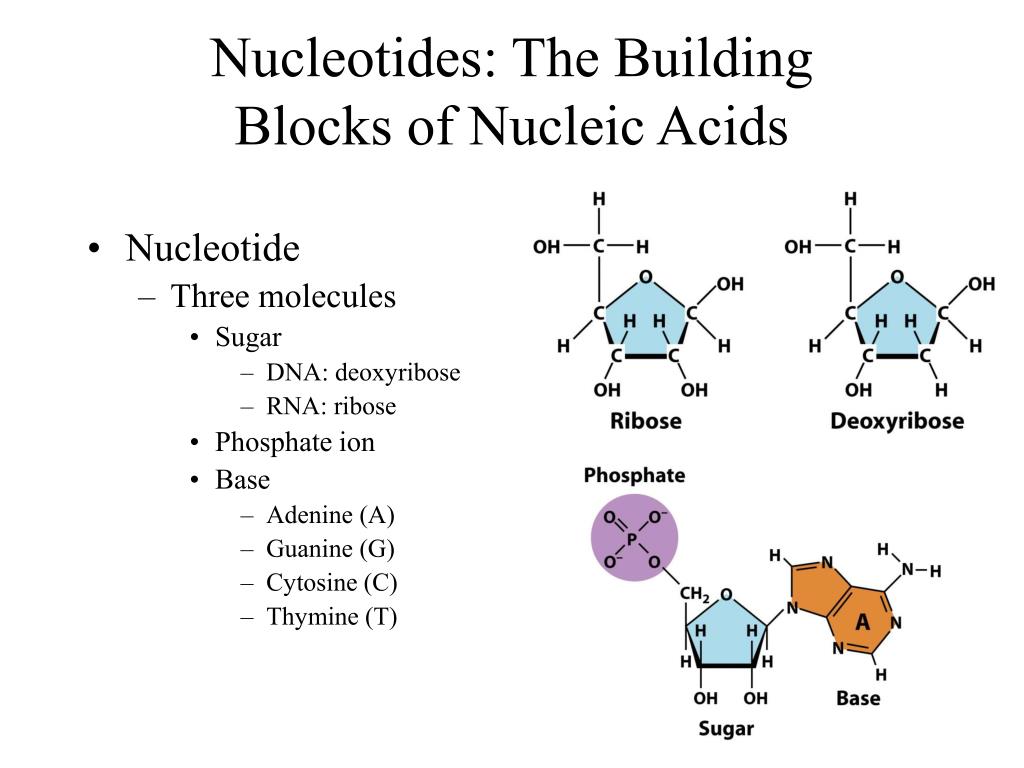
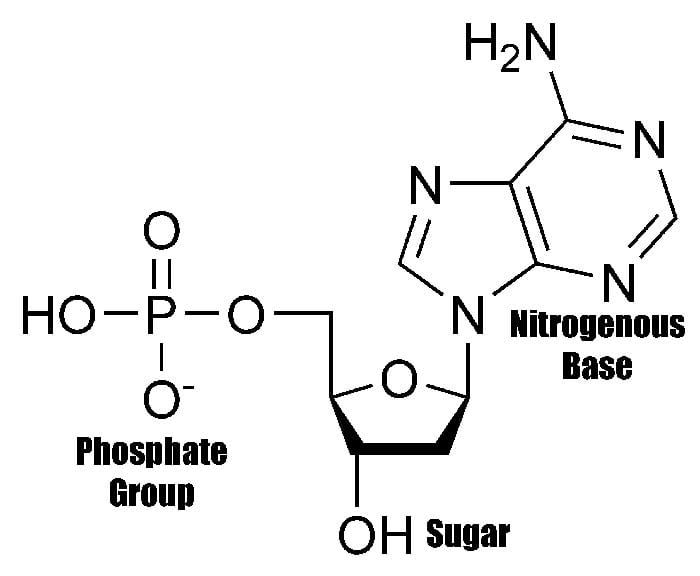
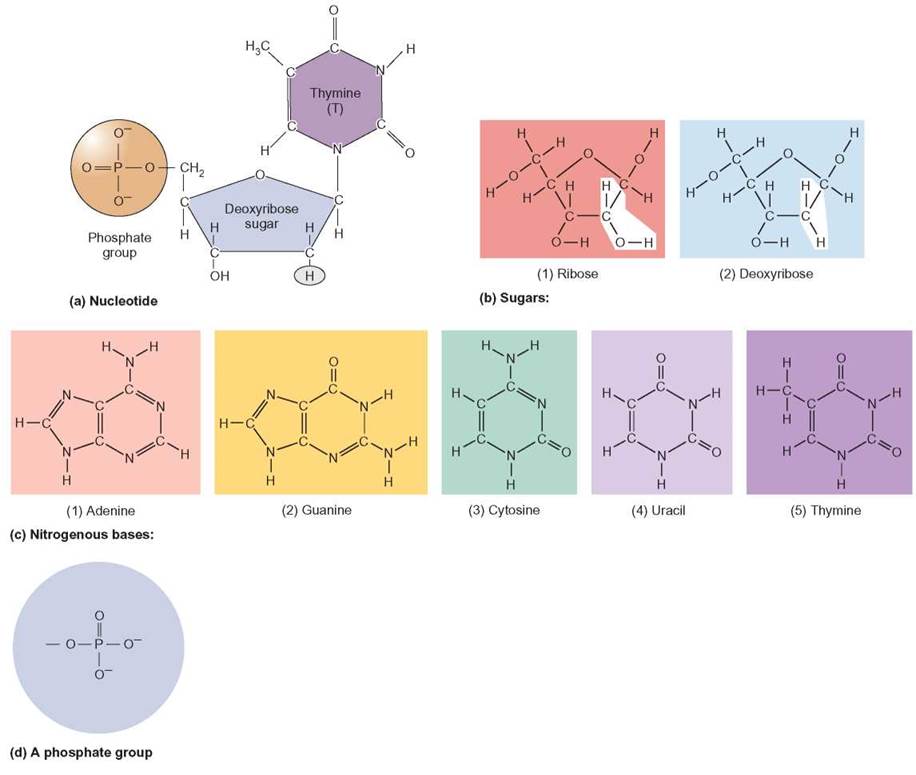
What Are The Building Blocks Of A Nucleic Acid
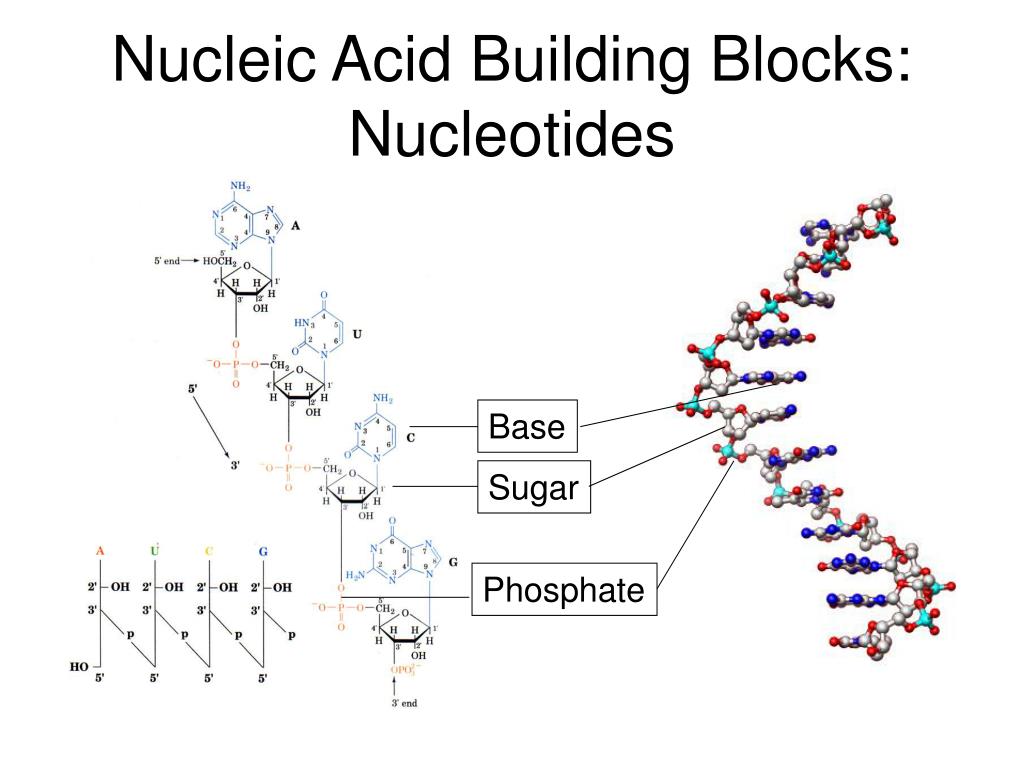
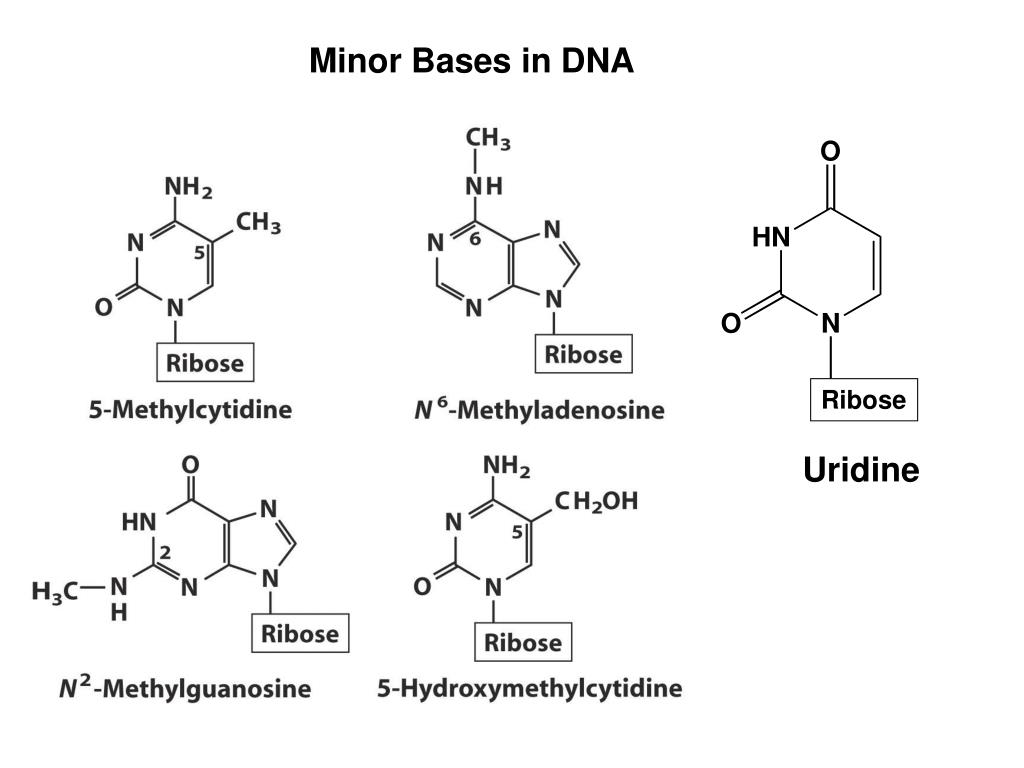
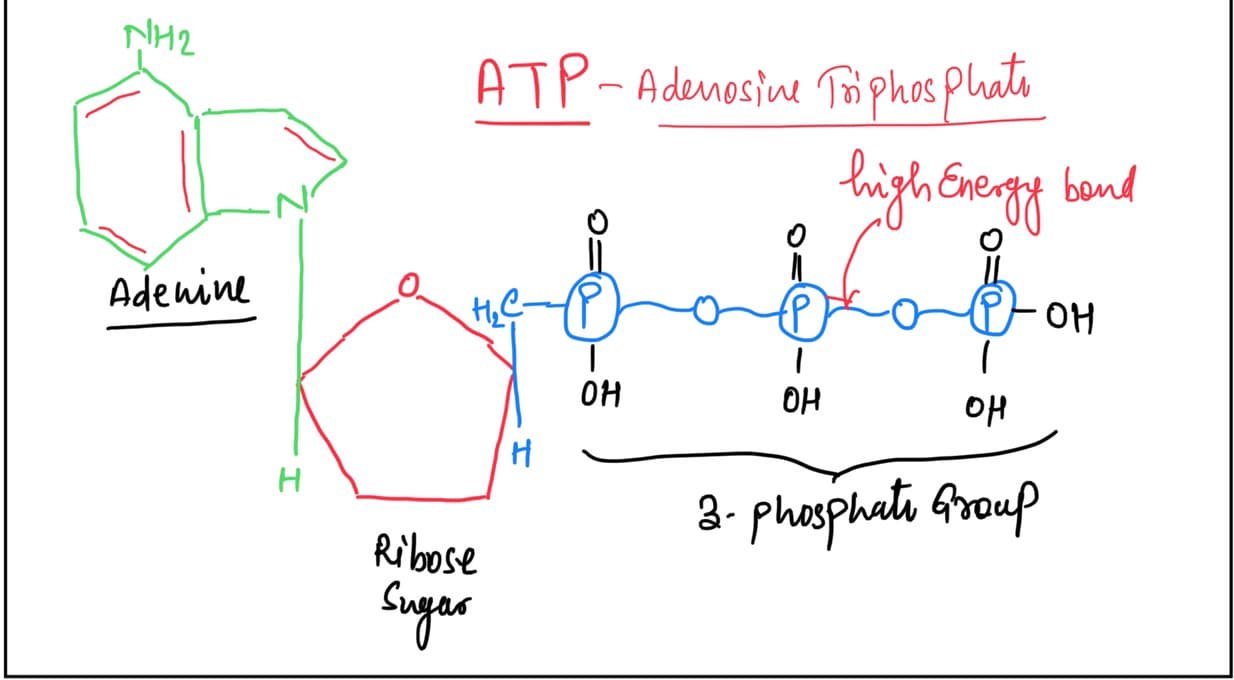
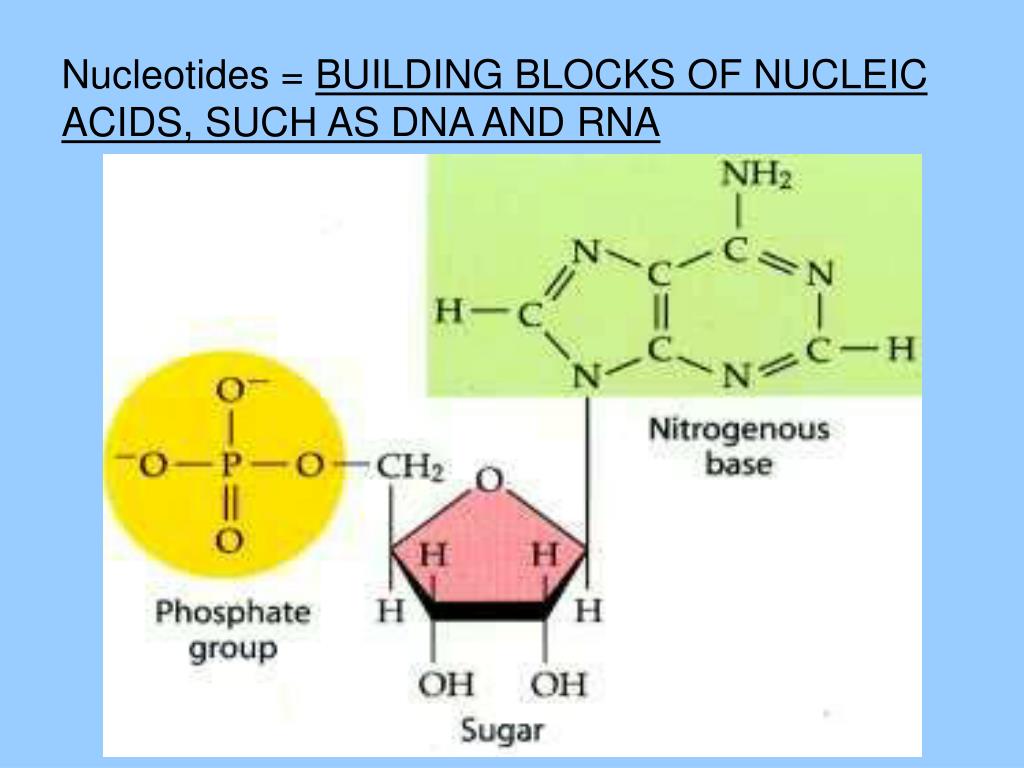
What Are The Building Blocks Of A Nucleic Acid - Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Dna and rna are two types. The structure of nucleic acids (i.e., dna) can be likened to a ladder that is made up of alternating steps that are symbolizing its three significant parts: Pentose sugar, the phosphate group, and the nitrogenous base. Describe the secondary structure of dna. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. To truly understand nucleic acids, we must delve into the realm of their building blocks. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in rna or deoxyribose in dna) attached. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Describe the secondary structure of dna. Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. Phosphocreatin is a storage form of energy in muscles. Define the basic building blocks of nucleic acids, including nucleotides, nitrogenous bases, the pentose sugar, and the phosphate group. Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the mysteries. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. The term nucleotide refers to the building blocks of both dna (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, dntps) and rna (ribonucleoside triphosphates, ntps). An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Rna translates dna instructions into proteins. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. The phosphate is attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose and the. Rna, or ribonucleic acid, plays a crucial role in translating genetic information from dna into proteins. Dna carries the genetic code for traits. Here are some key roles of nucleic acids: Here are some key roles of nucleic acids: Rna translates dna instructions into proteins. Define the basic building blocks of nucleic acids, including nucleotides, nitrogenous bases, the pentose sugar, and the phosphate group. Nucleotides are the basic units that assemble to form these intricate molecules. Dna and rna are two types. The term nucleotide refers to the building blocks of both dna (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, dntps) and rna (ribonucleoside triphosphates, ntps). Nucleotides are the basic units that assemble to form these intricate molecules. The structure of nucleic acids (i.e., dna) can be likened to a ladder that is made up of alternating steps that are symbolizing its three significant parts: Describe the. Dna carries the genetic code for traits. Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. Understand the function of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (rna and dna). The three components of a. Atp supply doesn't last very long, but can be regenerated from creatin phosphate via transfer of its phosphate group to adp. The structure of nucleic acids (i.e., dna) can be likened to a ladder that is made up of alternating steps that are symbolizing its three significant parts: Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the. Describe the secondary structure of dna. The term nucleotide refers to the building blocks of both dna (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, dntps) and rna (ribonucleoside triphosphates, ntps). Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. Dna and rna are two types. Dna carries the genetic code for traits. To truly understand nucleic acids, we must delve into the realm of their building blocks. Describe the secondary structure of dna. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides. Though only four different nucleotide bases can occur in a nucleic acid, each nucleic acid contains millions of bases bonded to it. Nucleotides are the basic units that assemble to form. The term nucleotide refers to the building blocks of both dna (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, dntps) and rna (ribonucleoside triphosphates, ntps). Define the basic building blocks of nucleic acids, including nucleotides, nitrogenous bases, the pentose sugar, and the phosphate group. Dna and rna are two types. Understand the function of nucleic acids. Here are some key roles of nucleic acids: Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. The order in which these nucleotide bases appear in the nucleic. Define the basic building blocks of nucleic acids, including nucleotides, nitrogenous bases, the pentose sugar, and the phosphate group. Dna and rna are two types. Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the mysteries. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. The order in which these nucleotide bases appear in the nucleic. Phosphocreatin is a storage form of energy in muscles. Here are some key roles of nucleic acids: The term nucleotide refers to the building blocks of both dna (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, dntps) and rna (ribonucleoside triphosphates, ntps). They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. Define the basic building blocks of nucleic acids, including nucleotides, nitrogenous bases, the pentose sugar, and the phosphate group. Understand the function of nucleic acids. Atp supply doesn't last very long, but can be regenerated from creatin phosphate via transfer of its phosphate group to adp. To truly understand nucleic acids, we must delve into the realm of their building blocks. The order in which these nucleotide bases appear in the nucleic. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in rna or deoxyribose in dna) attached. Pentose sugar, the phosphate group, and the nitrogenous base. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the mysteries. The structure of nucleic acids (i.e., dna) can be likened to a ladder that is made up of alternating steps that are symbolizing its three significant parts: Describe how nucleotides are linked together to form nucleic acids. The three components of a. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids.PPT Nucleic Acids The Ultimate Building Blocks PowerPoint
PPT Exploring Nucleic Acid Structures PowerPoint Presentation, free
PPT Nucleic Acids The Ultimate Building Blocks PowerPoint
Nucleotide Building Block of Nucleic Acid DNA & RNA KashiBiology
PPT DNA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5754268
PPT DNA and DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download
PPT Classical and Modern PowerPoint Presentation ID143901
Nucleic Acid Building Blocks AAT Bioquest
Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids Structures & Functions
FIGURE 3.15. The Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids
Dna Carries The Genetic Code For Traits.
In Order To Discuss This Important.
An Anion Of Phosphoric Acid, I.e.,.
Understanding Its Structure Is Vital As It Influences Rna’s Cellular Functions.
Related Post: