What Are The Building Blocks Of Macromolecules
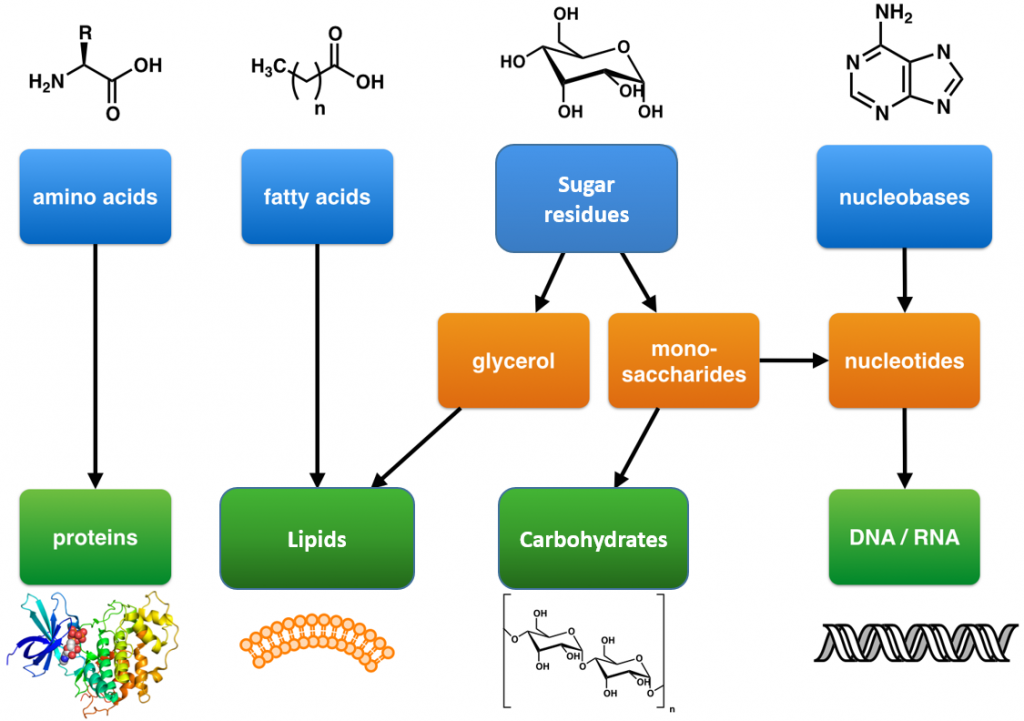
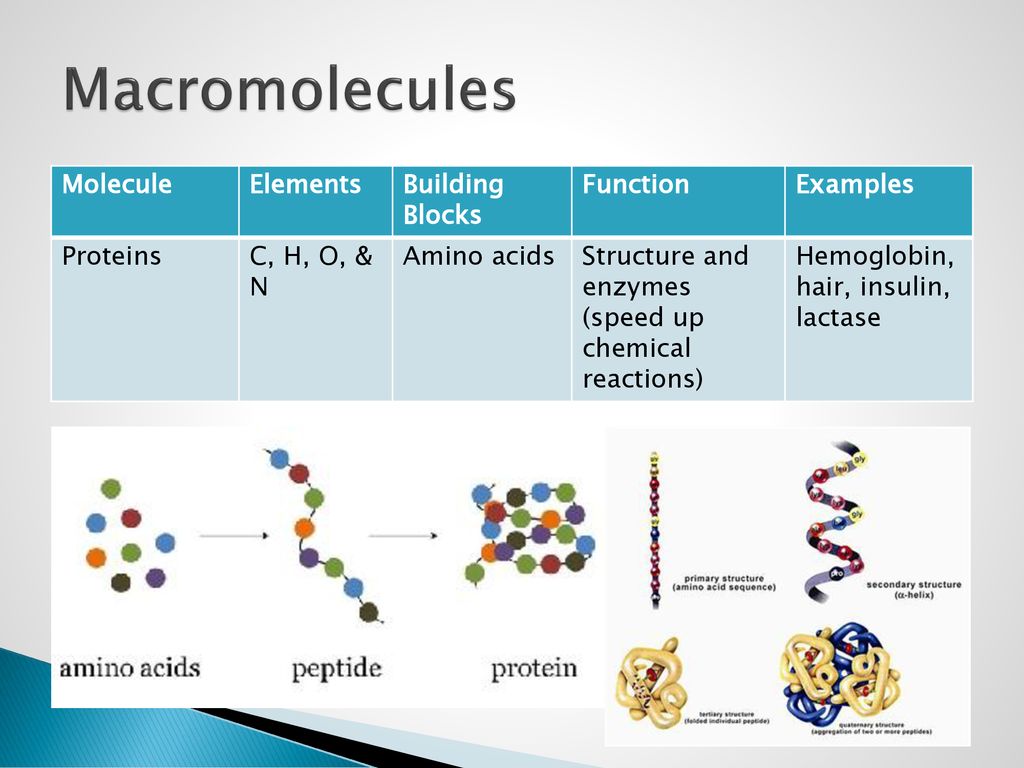
What Are The Building Blocks Of Macromolecules - •made up of smaller “building blocks” called monomers. Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are the 3 building blocks of all living things that we will focus on this unit. Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and more. Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Carbohydrates may bind to proteins and lipids that. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as. The four major classes of macromolecules are. Macromolecules form the building blocks of life and have immense potential in biotechnology. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen building blocks: These are called macromolecules because they are large. Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. The four major classes of macromolecules are. These macromolecules are proteins, nucleic acids (dna and rna), lipids (fats) and. Up to 24% cash back macromolecules •large organic molecules. Carbohydrates may bind to proteins and lipids that. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are important energy source required for various metabolic activities. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and more. These macromolecules are proteins, nucleic acids (dna and rna), lipids (fats) and. Just as a home is made from a variety of building materials, the human body is constructed from many cell. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are the 3 building blocks of all living things that we will. Living things are made of four types of molecules, known as macromolecules. These macromolecules are proteins, nucleic acids (dna and rna), lipids (fats) and. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as. Carbohydrates may bind to proteins and lipids that. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are important energy source required for. Living things are made of four types of molecules, known as macromolecules. Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. •made up of smaller “building blocks” called monomers. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as. Just as a home is made from a variety of building materials, the. Carbohydrates may bind to proteins and lipids that. Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. These macromolecules are proteins, nucleic acids (dna and rna), lipids (fats) and. They are involved in a wide range of biological processes, such as dna. Your body has many kinds of cells, each specialized for a specific purpose. These are called macromolecules because they are large. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen building blocks: These macromolecules are proteins, nucleic acids (dna and rna), lipids (fats) and. Your body has many kinds of cells, each specialized for a specific purpose. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are important energy source required for various metabolic activities. A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar. Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. •made up of smaller “building blocks” called monomers. These are called macromolecules because they are large. These macromolecules are the basic chemical building blocks from which all organisms are composed. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as. Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are the 3 building blocks of all living things that we will focus on this unit. These macromolecules are the basic chemical building blocks from which all organisms are. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger. Macromolecules form the building blocks of life and have immense potential in biotechnology. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as. Up to 24% cash back macromolecules •large organic molecules. Your body has many kinds of cells, each specialized for a. These macromolecules are proteins, nucleic acids (dna and rna), lipids (fats) and. Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as. Because these biological macromolecules all involve carbon. Living things are made of four types of molecules, known as macromolecules. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger. Living things are made of four types of molecules, known as macromolecules. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen building blocks: A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as. Carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins are the 3 building blocks of all living things that we will focus on this unit. The building blocks of these, respectively, are amino acids,. The monomers combine with each other using covalent bonds to form larger molecules known as. Up to 24% cash back macromolecules •large organic molecules. Because these biological macromolecules all involve carbon. These are called macromolecules because they are large. Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Living things are made of four types of molecules, known as macromolecules. •made up of smaller “building blocks” called monomers. The four major classes of macromolecules are. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are important energy source required for various metabolic activities. The remaining categories of biological macromolecules include proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides. They are built from smaller subunits, known as monomers, which combine to form polymers through chemical bonds. Carbohydrates may bind to proteins and lipids that. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen building blocks: Most macromolecules are made from single subunits, or building blocks, called monomers.Some examples of "building blocks" (BBs) in biological macromolecules
Four Macromolecules And Their Functions
CH103 Chapter 8 The Major Macromolecules Chemistry
PPT BIOCHEMISTRY COURSE Pharmacy biomedical preview program, Summer
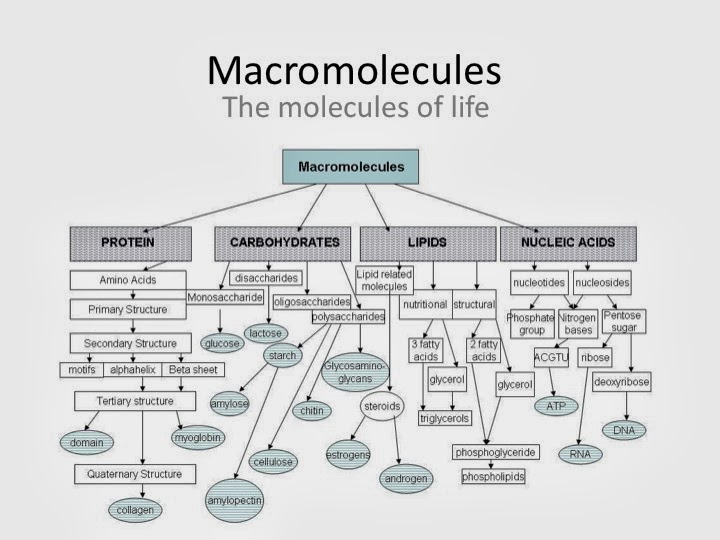
Mr. Maxey's Biology Blog The Building Blocks of Life Macromolecules
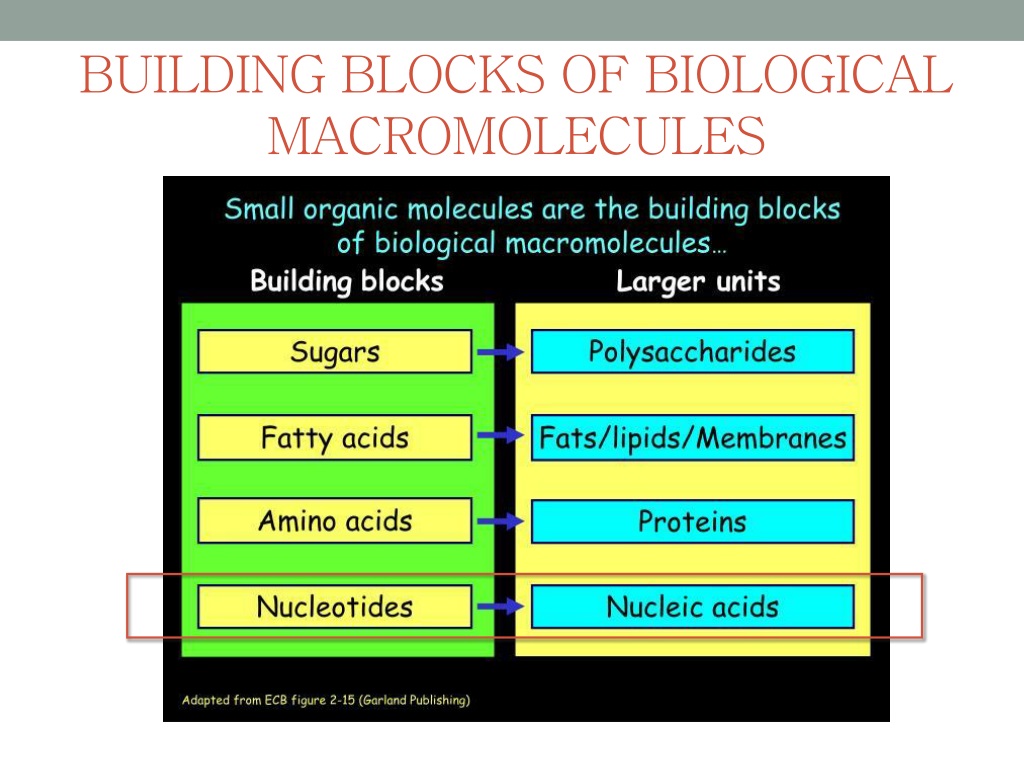
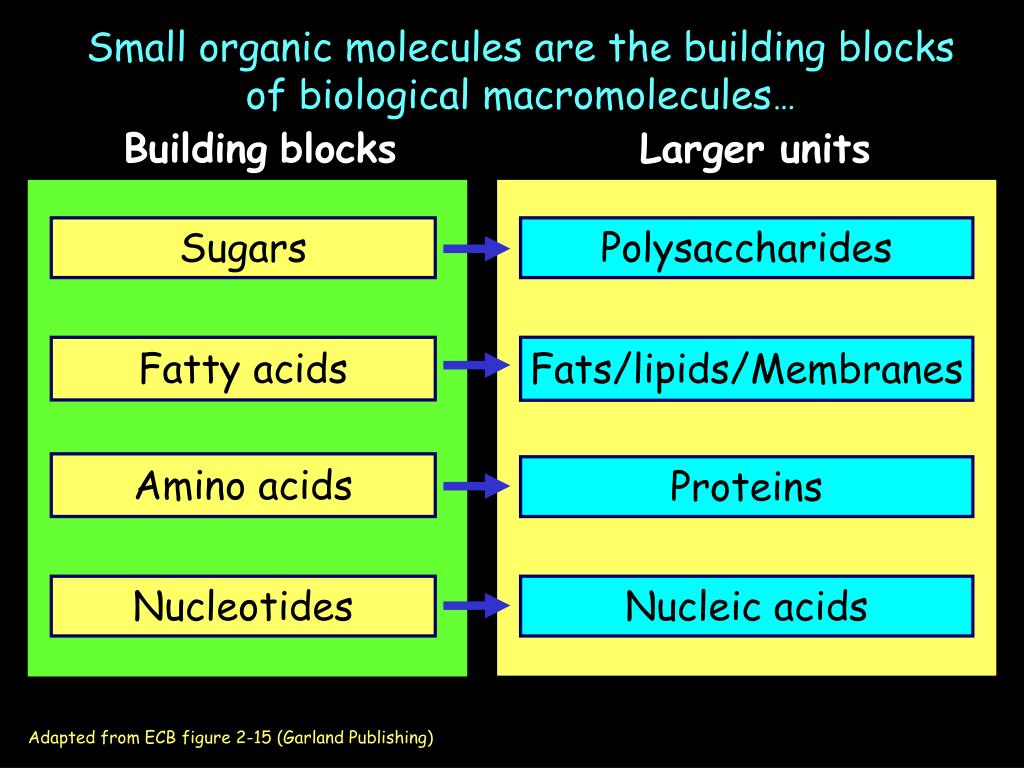
PPT Small organic molecules are the building blocks of biological
Unit 2 Biochemistry 2.4 Macromolecules. ppt download
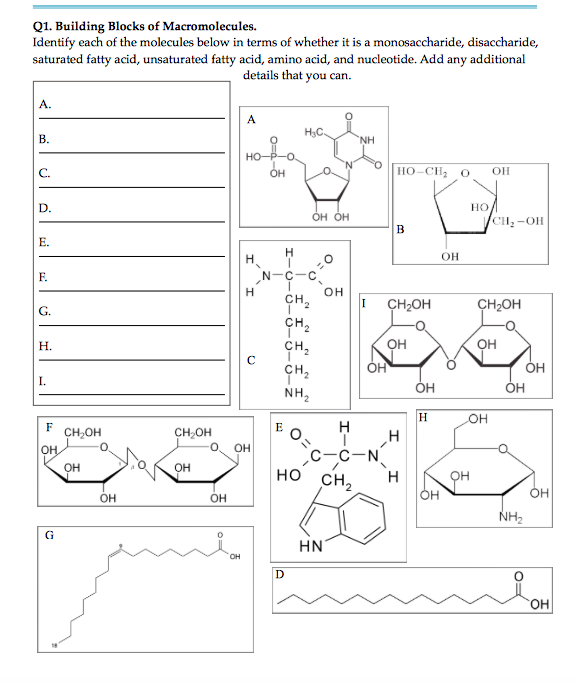
Solved Q1. Building Blocks of Macromolecules. Identify each
PPT Macromolecules Building blocks of life PowerPoint Presentation
Unit 2 Biochemistry 2.4 Macromolecules. ppt download
Your Body Has Many Kinds Of Cells, Each Specialized For A Specific Purpose.
Macromolecules Form The Building Blocks Of Life And Have Immense Potential In Biotechnology.
These Macromolecules Are Proteins, Nucleic Acids (Dna And Rna), Lipids (Fats) And.
Just As A Home Is Made From A Variety Of Building Materials, The Human Body Is Constructed From Many Cell.
Related Post: