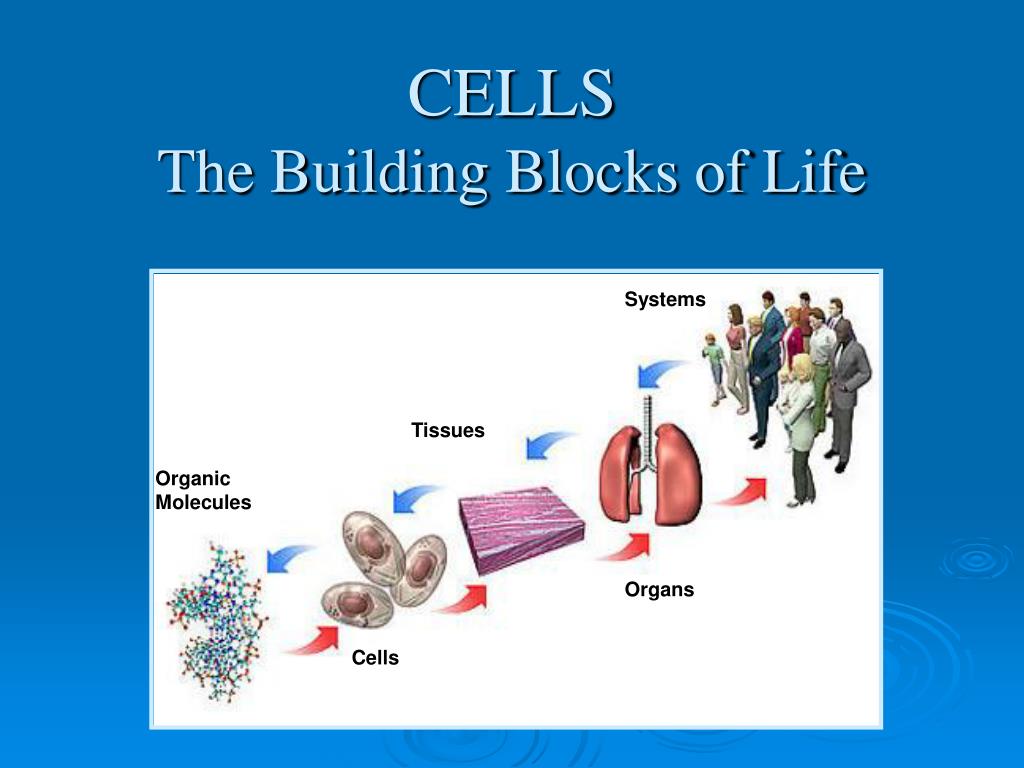
What Are The Building Blocks Of Tissues
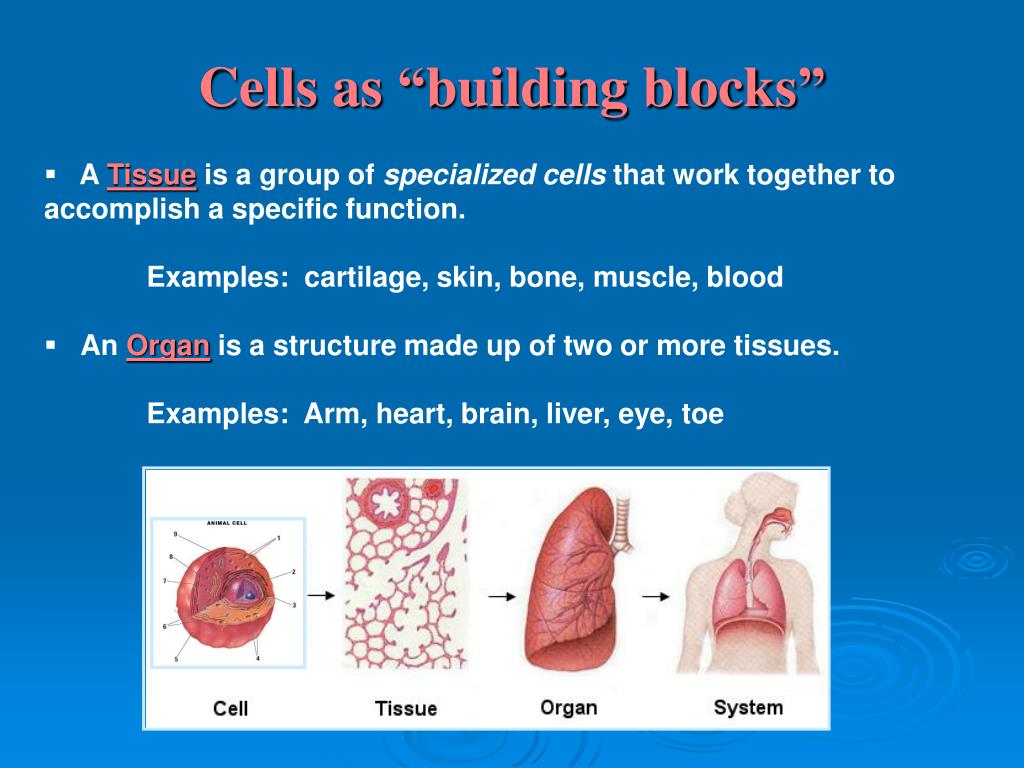
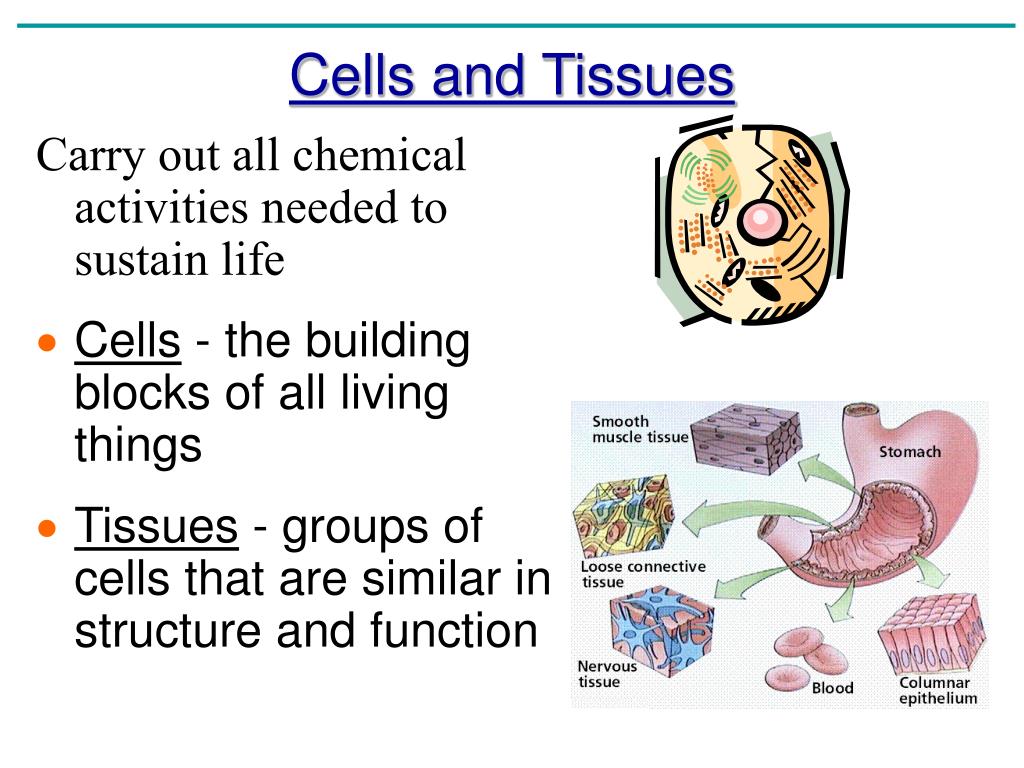
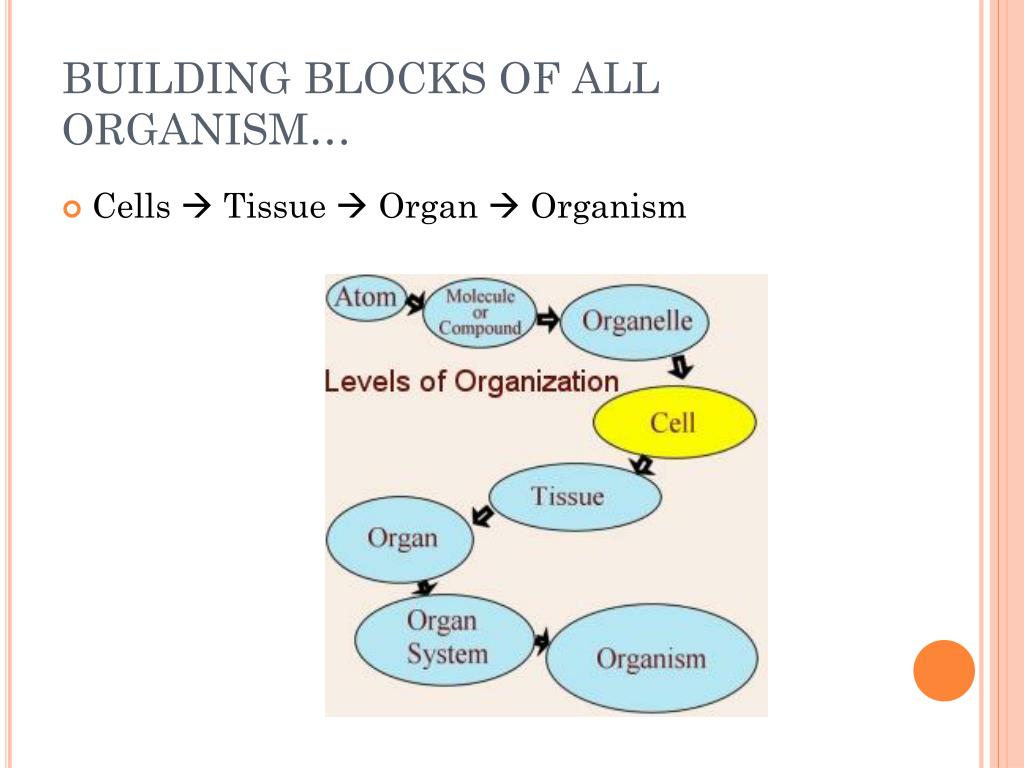
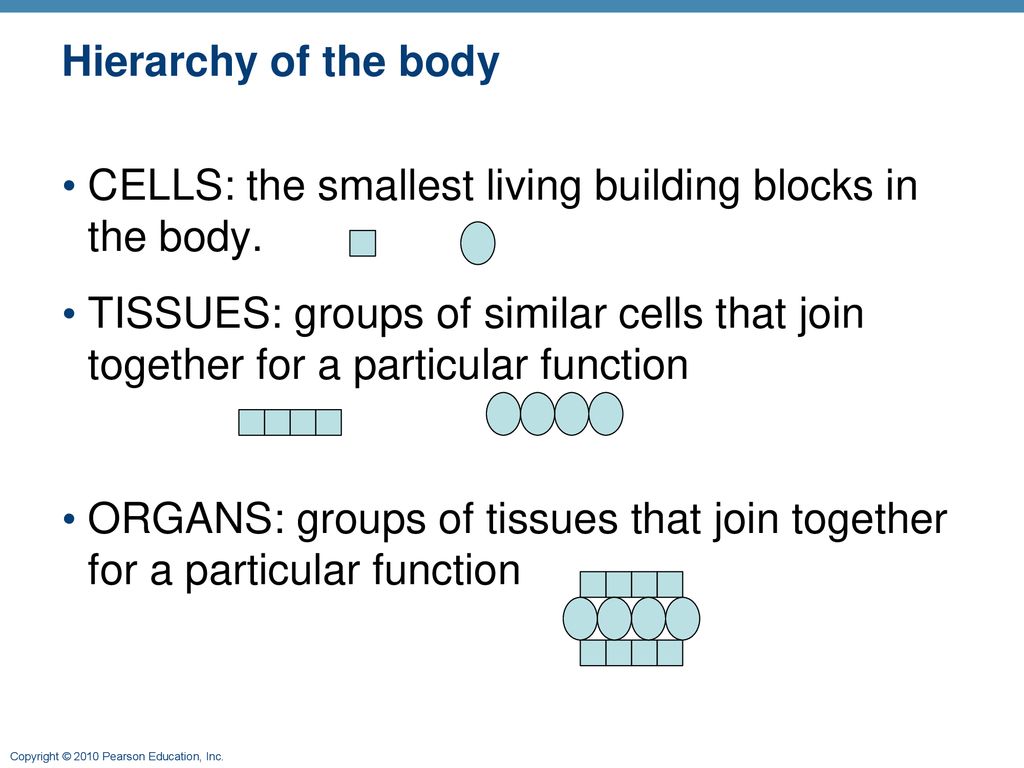
What Are The Building Blocks Of Tissues - Getting to know these most basic parts to see how their functions affect the rest of the parts of. Cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms. Find out more from bitesize ks3 biology ccea. In fact, everything is made from building blocks including living things. Cell is the structural and functional unit of life. The findings show that cells use transcriptional memories to establish predictable, stable behaviors within tissues, backman said. Animal cells and plant cells can form tissues, such. Building blocks of cellular support. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like six levels of structural organization, first level of structural organization, what do bonded molecules form? These genetic memories can degrade over. Connective tissue supports and protects body. Each tissue type has a characteristic role in the body: Northwestern medicine scientists have discovered. Animal cells and plant cells can form tissues, such. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the building blocks of body structures, groups of cells that have a common origin and function, what are the four. All kinds of cells, whether in plants or in animals, contain the same basic structures. Epithelium covers the body surface and lines body cavities. Each tissue type plays a role in maintaining homeostasis,. A generalized cell consists of three main parts:. The findings contradict the classic view that microtubules are typically similar building blocks in every cell, while regulatory proteins confer unique structure and function,. Atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems are the body's building blocks. Functional tissue units (ftus) form the basic building blocks of organs and are important for understanding and modeling their healthy physiological function and disease. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like six levels of structural organization, first level of structural organization, what do bonded molecules. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like epitheal tissue, epithelial tissue (functions), cilia and more. Several cells of one kind that interconnect with each other and perform a shared function form tissues; Getting to know these most basic parts to see how their functions affect the rest of the parts of. Northwestern medicine scientists have discovered. These genetic. Find out more from bitesize ks3 biology ccea. Functional tissue units (ftus) form the basic building blocks of organs and are important for understanding and modeling their healthy physiological function and disease. Atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems are the body's building blocks. These genetic memories can degrade over. Several cells of one kind that interconnect with each. Animal cells and plant cells can form tissues, such. Epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous, and adipose. Tissues are the building blocks of life, forming a tapestry that supports and maintains the body’s systems. Cell is the structural and functional unit of life. Explore the essential roles of structural proteins in cellular support, their interactions, and the factors influencing their. Cell is the structural and functional unit of life. Functional tissue units (ftus) form the basic building blocks of organs and are important for understanding and modeling their healthy physiological function and disease. The findings contradict the classic view that microtubules are typically similar building blocks in every cell, while regulatory proteins confer unique structure and function,. Each such structure. Each such structure also has the same basic function. If you take a look at your home you will notice it is enclosed by outer. Epithelial tissue serve as a protective covering for all internal and external surfaces. The building blocks of tissues are proteins, which consist of long chains of amino acids. In fact, everything is made from building. If you take a look at your home you will notice it is enclosed by outer. In fact, everything is made from building blocks including living things. Getting to know these most basic parts to see how their functions affect the rest of the parts of. Functional tissue units (ftus) form the basic building blocks of organs and are important. The findings show that cells use transcriptional memories to establish predictable, stable behaviors within tissues, backman said. There are four main types of tissues: All kinds of cells, whether in plants or in animals, contain the same basic structures. In fact, everything is made from building blocks including living things. Animal cells and plant cells can form tissues, such. A typical cell includes a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material either within the nucleus or in. Each contain an amino group, an acid group, a hydrogen atom, and a distinctive side group, all attached to a central carbon atom. Cultured meat aims to produce meat mass by culturing cells and tissues based on the muscle regeneration mechanism, and is. Vadim backman, phd, the sachs family professor of biomedical engineering and medicine, was senior author of the study. Cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms. Functional tissue units (ftus) form the basic building blocks of organs and are important for understanding and modeling their healthy physiological function and disease. Cell is the. What are the building blocks of a cell like? Each tissue type plays a role in maintaining homeostasis,. A generalized cell consists of three main parts:. Building blocks of life cell and tissues when a small wall is built, a number of bricks are arranged end to end. Tissues are the building blocks of life, forming a tapestry that supports and maintains the body’s systems. Similarly cells are arranged variously to build the bodies of living. Cultured meat aims to produce meat mass by culturing cells and tissues based on the muscle regeneration mechanism, and is considered an alternative to raising and. Building blocks of cellular support. Connective tissue supports and protects body. Each such structure also has the same basic function. Find out more from bitesize ks3 biology ccea. Atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems are the body's building blocks. Each tissue type has a characteristic role in the body: The findings contradict the classic view that microtubules are typically similar building blocks in every cell, while regulatory proteins confer unique structure and function,. Vadim backman, phd, the sachs family professor of biomedical engineering and medicine, was senior author of the study. Epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous, and adipose.CELLS AND TISSUES.. Tissue A Definition A group of connected
Tissues Class 9 Notes Understanding the Building Blocks of Life
Tissues The Building Blocks of Life ICSE CLASS 9 BIOLOGY Part 3
PPT CELLS The Building Blocks of Life PowerPoint Presentation, free
PPT Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Cell Anatomy PowerPoint
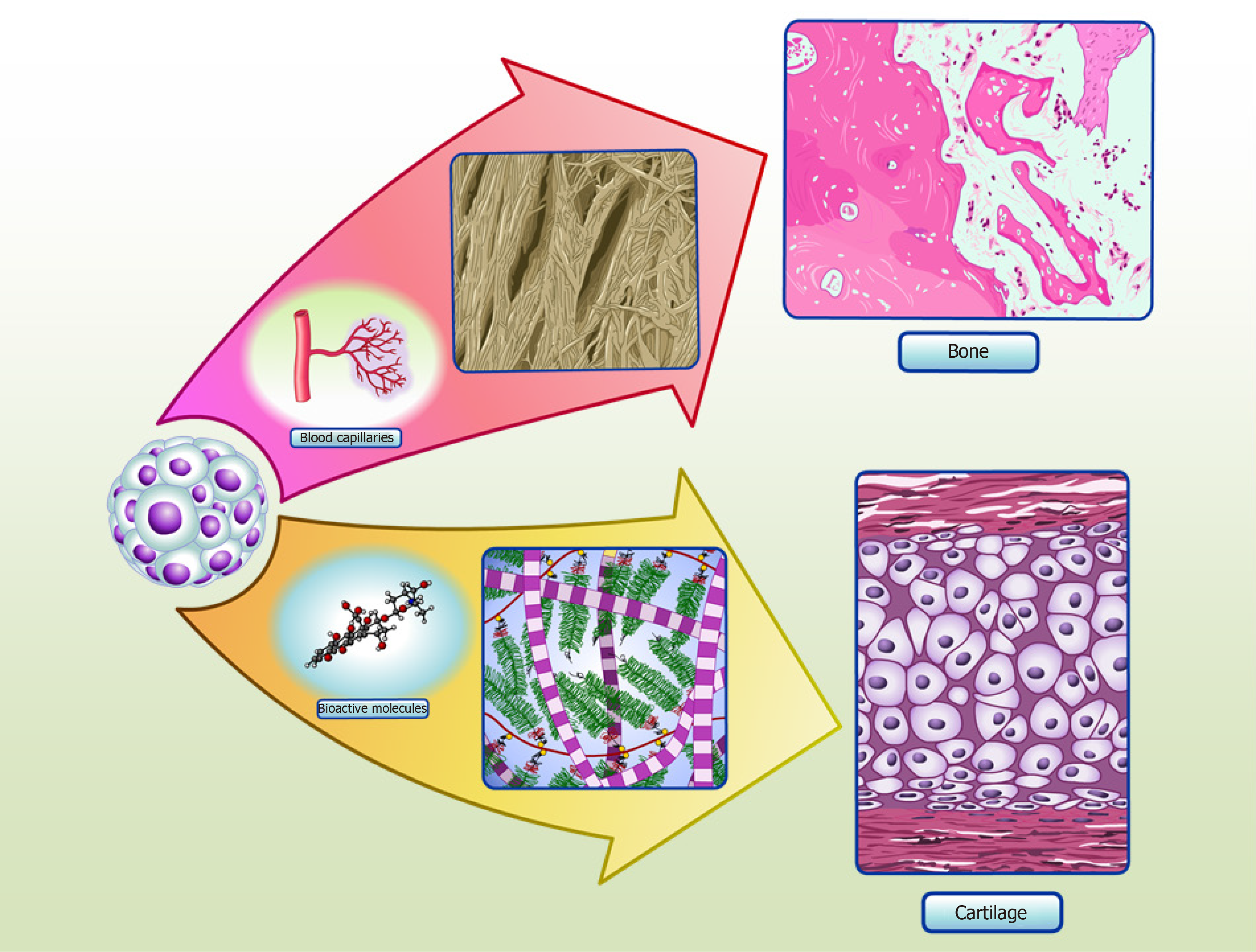
Cartilage and bone tissue engineering using adipose stromal/stem cells
The Building Blocks of Life Cells, Tissues, and Organs YouTube
PPT PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6932211
PPT CELLS The Building Blocks of Life PowerPoint Presentation, free
Histology Dr. Nichols Coronado HS. ppt download
Epithelial Tissue Serve As A Protective Covering For All Internal And External Surfaces.
Epithelium Covers The Body Surface And Lines Body Cavities.
All Kinds Of Cells, Whether In Plants Or In Animals, Contain The Same Basic Structures.
These Genetic Memories Can Degrade Over.
Related Post: