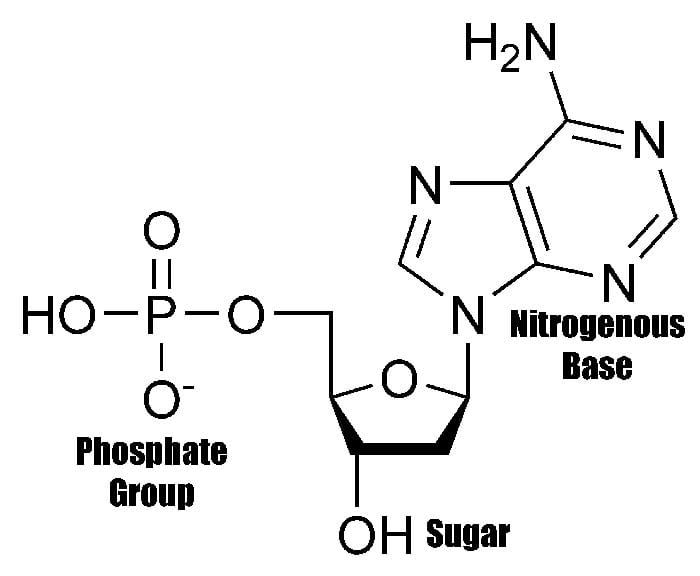
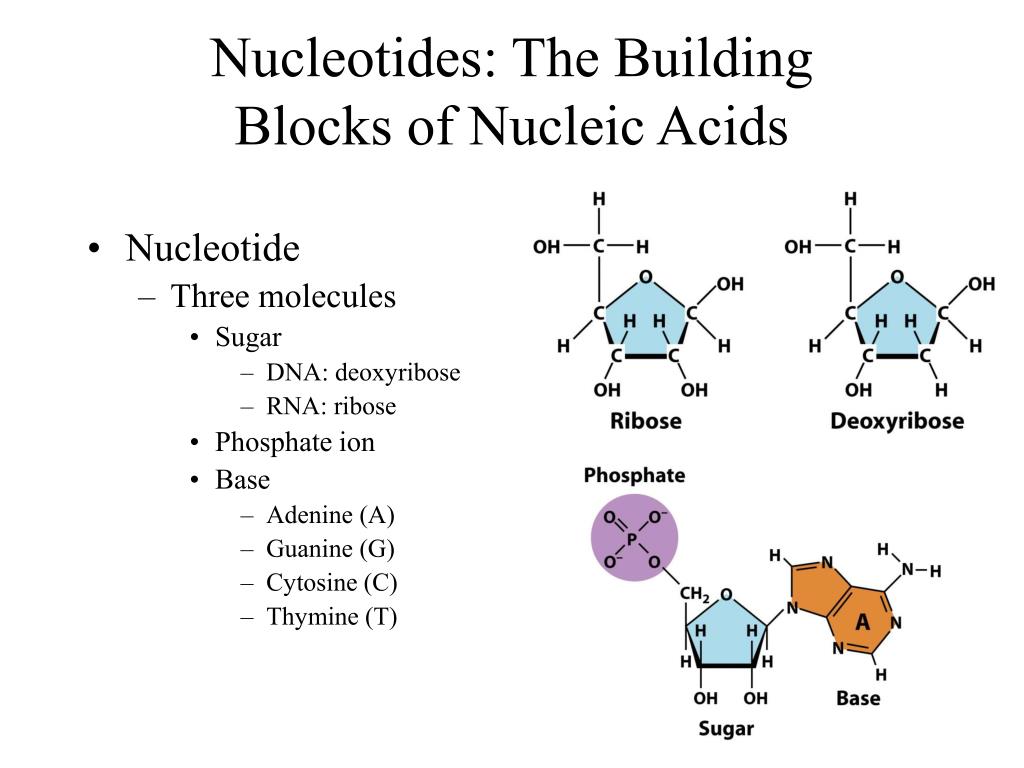
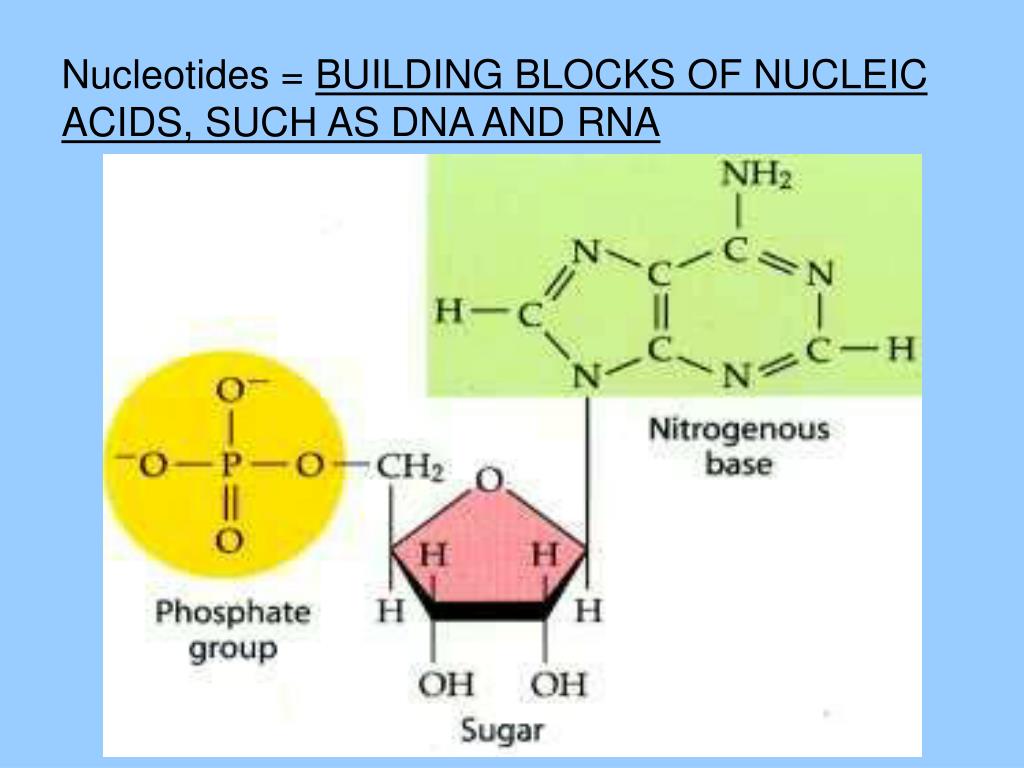
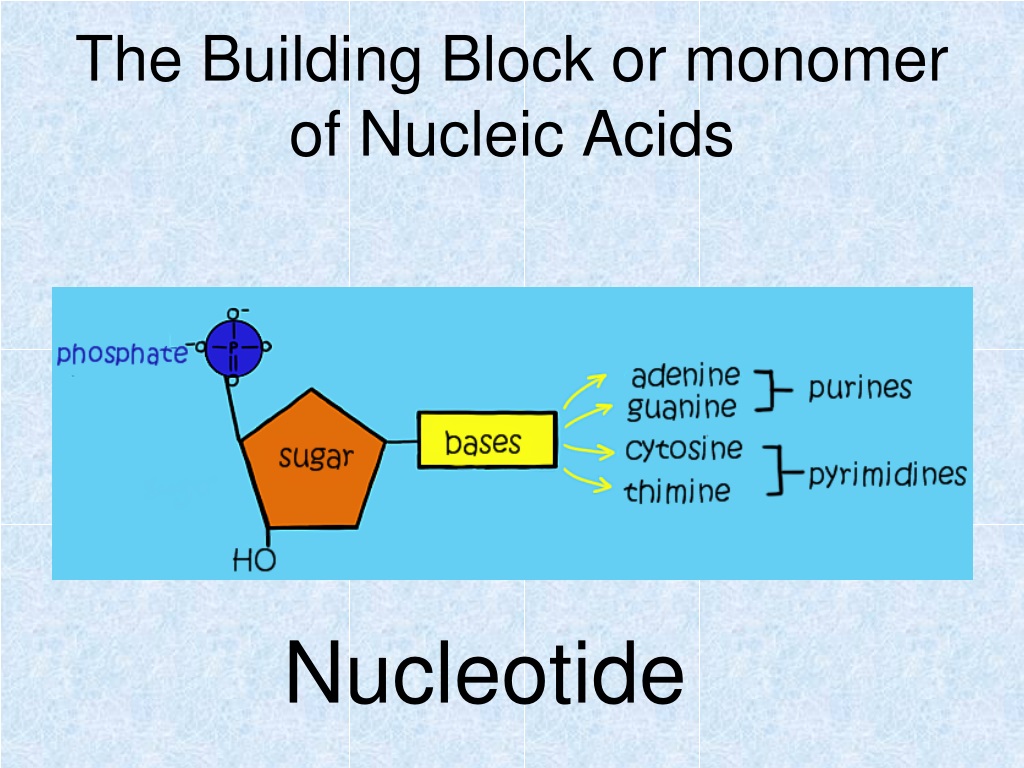
What Are The Buildings Blocks Of The Nuclic Acid
What Are The Buildings Blocks Of The Nuclic Acid - In order to discuss this important. Pentose sugar, the phosphate group, and the nitrogenous base. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. Nucleic acids, such as dna and rna, are composed of smaller units known as nucleotides. Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. The term nucleotide refers to the building blocks of both dna (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, dntps) and rna (ribonucleoside triphosphates, ntps). They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. Supramolecular ordered networks are formed through directional interactions of uniform macromonomer building blocks. To truly understand nucleic acids, we must delve into the realm of their building blocks. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides. Linear polymers of nucleotides that function in the storage & expression of genetic information, and its transfer from one generation to the next. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. Nucleotides that compose dna are called deoxyribonucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of three main components: The order in which these nucleotide bases appear in the nucleic. Each nucleotide is a composite organic molecule made up of a nitrogen base, five carbon sugars and at least one phosphate. Nucleotides are the basic units that assemble to form these intricate molecules. There are four types of. Nucleotides are the basic units that assemble to form these intricate molecules. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in rna or deoxyribose in dna) attached. The order in which these nucleotide bases appear in the nucleic. The three components of a. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Though only four different nucleotide bases can occur in a nucleic acid, each nucleic acid contains millions of bases bonded to. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in rna or deoxyribose in dna) attached. Linear polymers of nucleotides that function in the storage & expression of genetic information, and its transfer from one generation to the next. The order in which these nucleotide bases appear in the nucleic. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the. Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the mysteries. Supramolecular ordered networks are formed through directional interactions of uniform macromonomer building blocks. The three components of a. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Now it has been shown that, rather than. The term nucleotide refers to the building blocks of both dna (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, dntps) and rna (ribonucleoside triphosphates, ntps). They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (rna and dna). Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic. A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (rna and dna). Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. Supramolecular ordered networks are formed through directional interactions of uniform macromonomer building blocks. Rna, or ribonucleic acid, plays a crucial role in translating genetic information from dna into proteins. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule. Though only four different nucleotide bases can occur in a nucleic acid, each nucleic acid contains millions of bases bonded to it. Supramolecular ordered networks are formed through directional interactions of uniform macromonomer building blocks. The order in which these nucleotide bases appear in the nucleic. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate. Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. The structure of nucleic acids (i.e., dna) can be likened to a ladder that is made up of alternating steps that are symbolizing its three significant parts: Though only four different nucleotide bases can occur. Supramolecular ordered networks are formed through directional interactions of uniform macromonomer building blocks. Dna and rna are two types. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. There are four types of. Each nucleotide is a composite organic molecule made up of a nitrogen base, five carbon sugars and at least one phosphate. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. The three components of a. Now it has been shown that, rather than. Nucleotides that compose dna are called deoxyribonucleotides. The term nucleotide refers to the building blocks of both dna (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, dntps) and rna (ribonucleoside triphosphates, ntps). Nucleotides are the basic units that assemble to form these intricate molecules. Each nucleotide consists of three main components: A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in rna or deoxyribose in dna) attached. Linear polymers of nucleotides that function in the storage & expression of genetic information, and its transfer from one generation to the next. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. These molecular building blocks are fundamental to dna, encoding the information necessary for growth, development, and reproduction in living organisms. Supramolecular ordered networks are formed through directional interactions of uniform macromonomer building blocks. Now it has been shown that, rather than. The term nucleotide refers to the building blocks of both dna (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, dntps) and rna (ribonucleoside triphosphates, ntps). The phosphate is attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose and the. Pentose sugar, the phosphate group, and the nitrogenous base. In order to discuss this important. To truly understand nucleic acids, we must delve into the realm of their building blocks. Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the mysteries.What are the building blocks of nucleic acids Everdaily Review
Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids Structures & Functions
PPT Classical and Modern PowerPoint Presentation ID143901
PPT Nucleic Acids The Ultimate Building Blocks PowerPoint
Proteins and nucleic acids notes
PPT DNA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5754268
PPT DNA and DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download
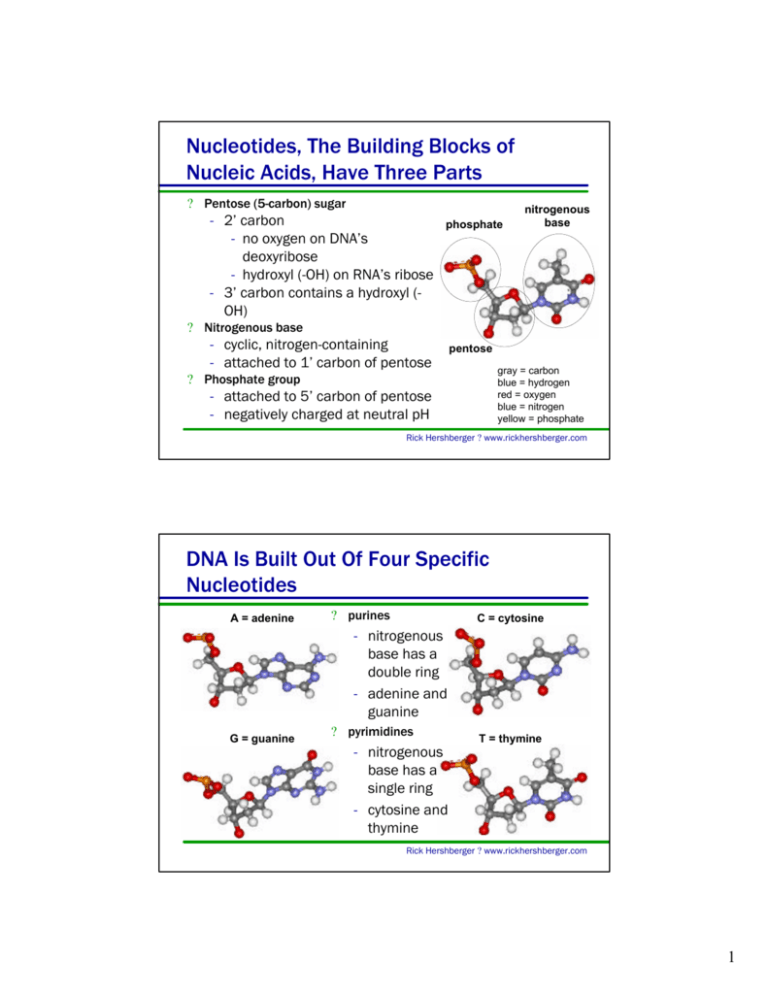
Nucleotides, The Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids, Have Three Parts
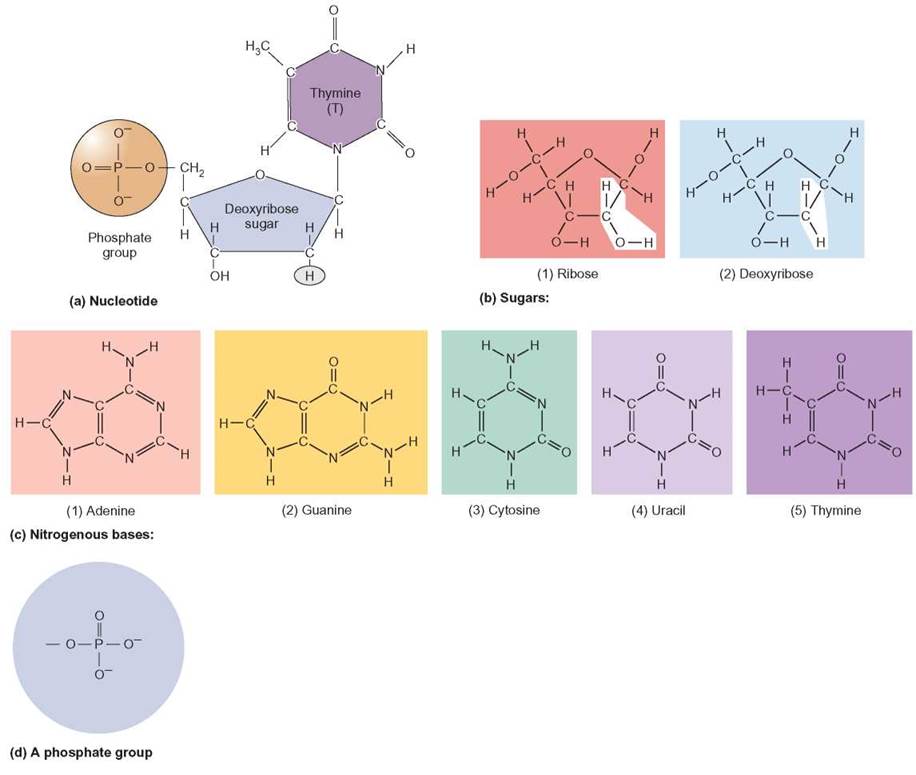
FIGURE 3.15. The Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids
PPT Exploring Nucleic Acid Structures PowerPoint Presentation, free
The Building Blocks Of Nucleic Acids Are Nucleotides.
Nucleotides That Compose Dna Are Called Deoxyribonucleotides.
Though Only Four Different Nucleotide Bases Can Occur In A Nucleic Acid, Each Nucleic Acid Contains Millions Of Bases Bonded To It.
They Are Major Components Of All Cells ~15% Of The Cells Dry Weight.
Related Post: