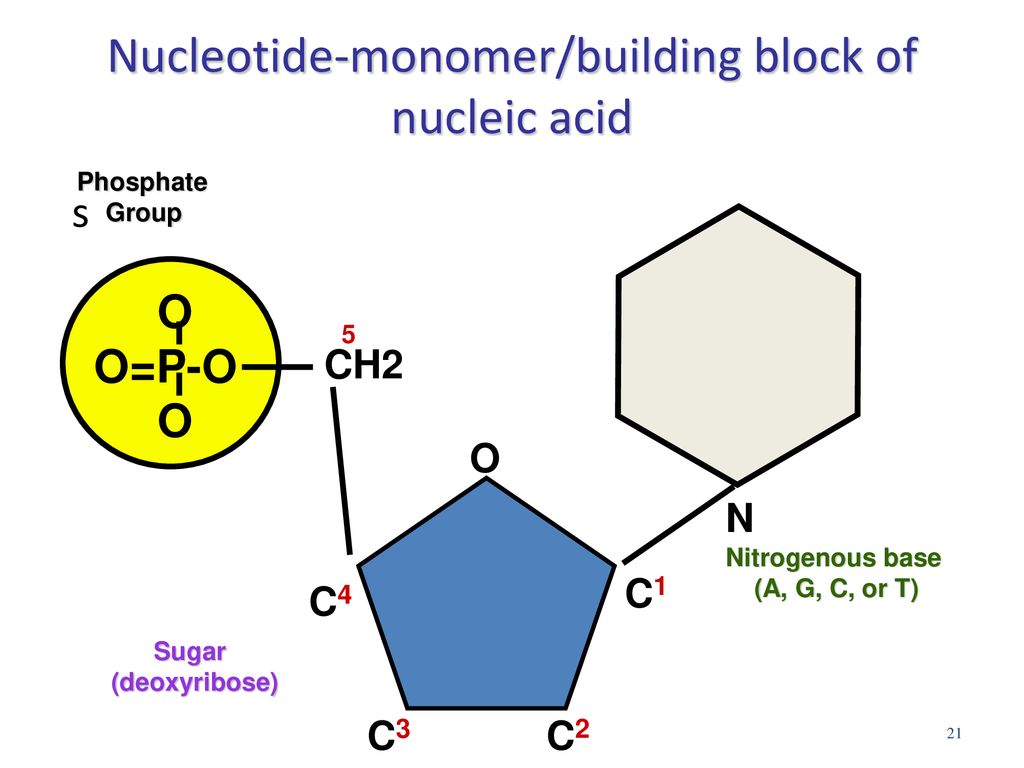
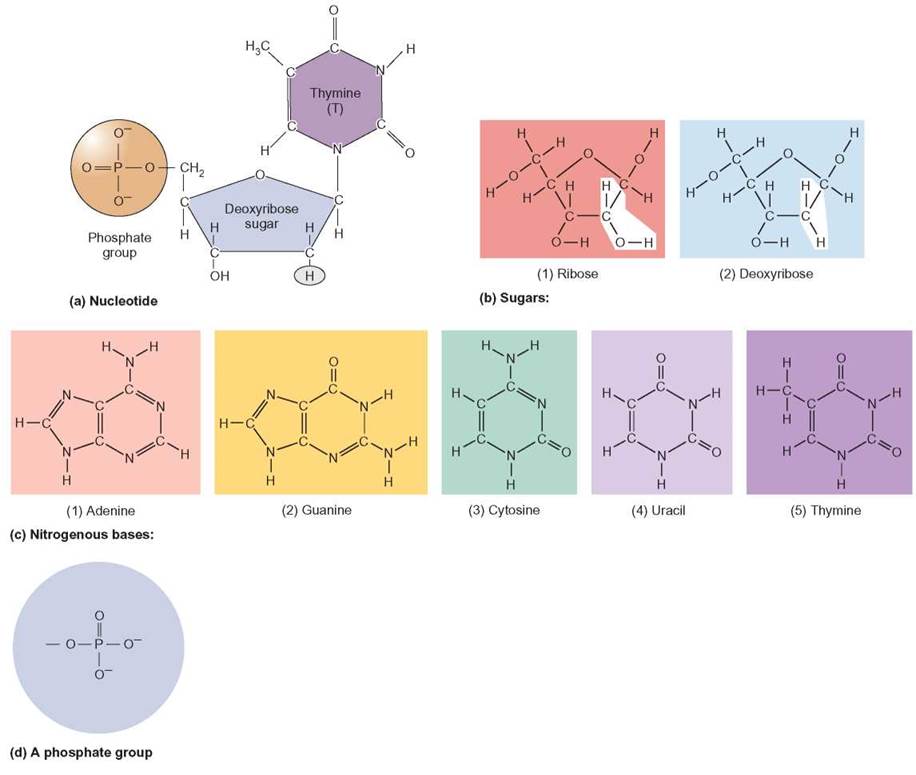
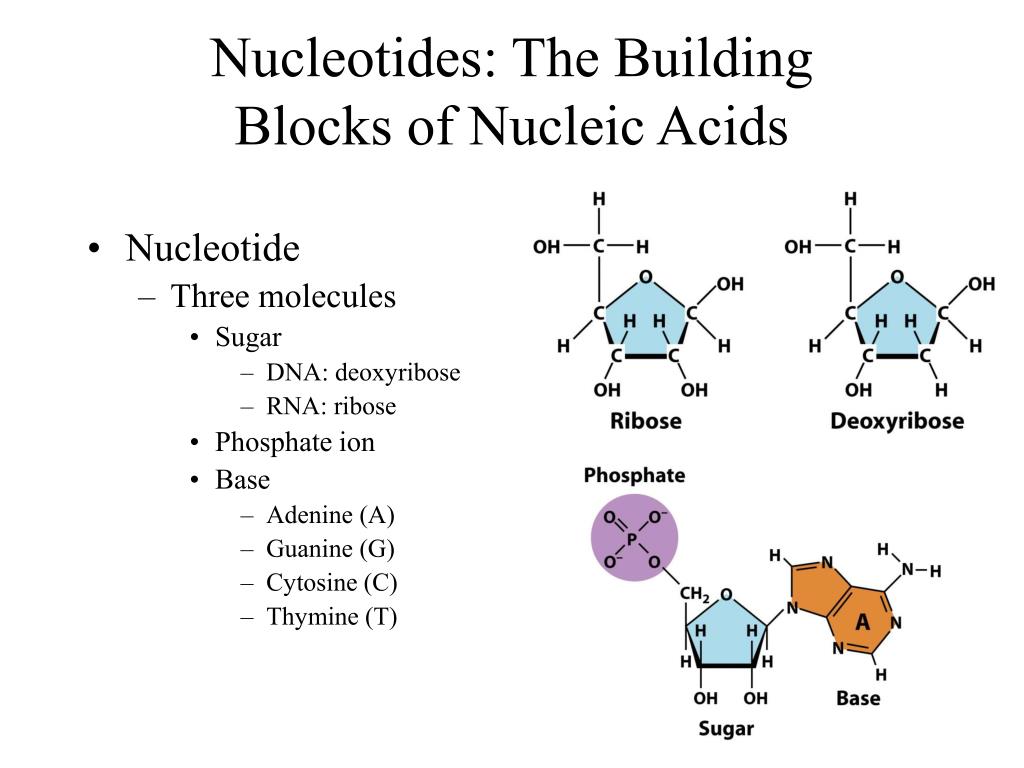
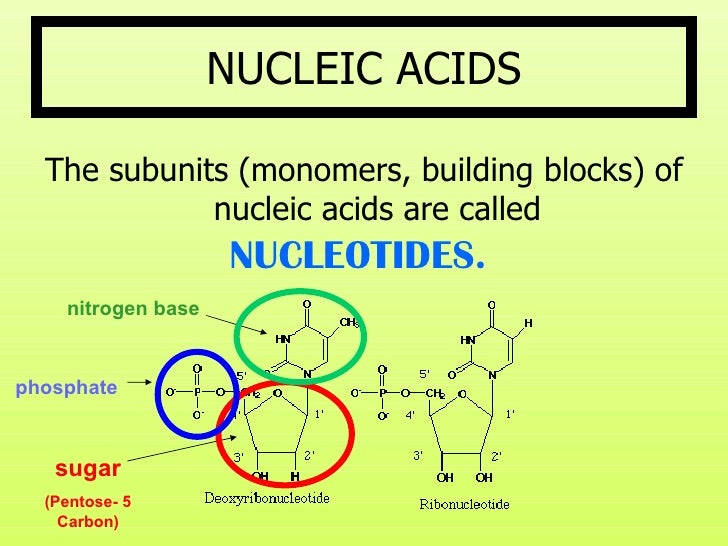
What Are The Monomers Building Blocks Of Nucleic Acids
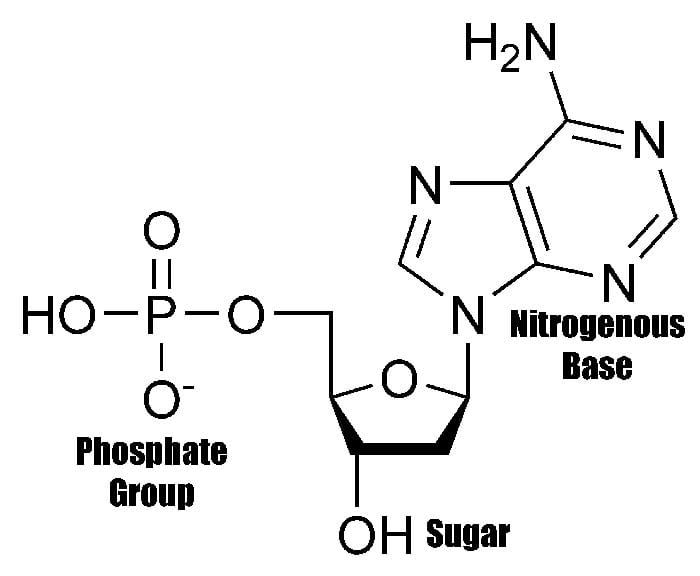
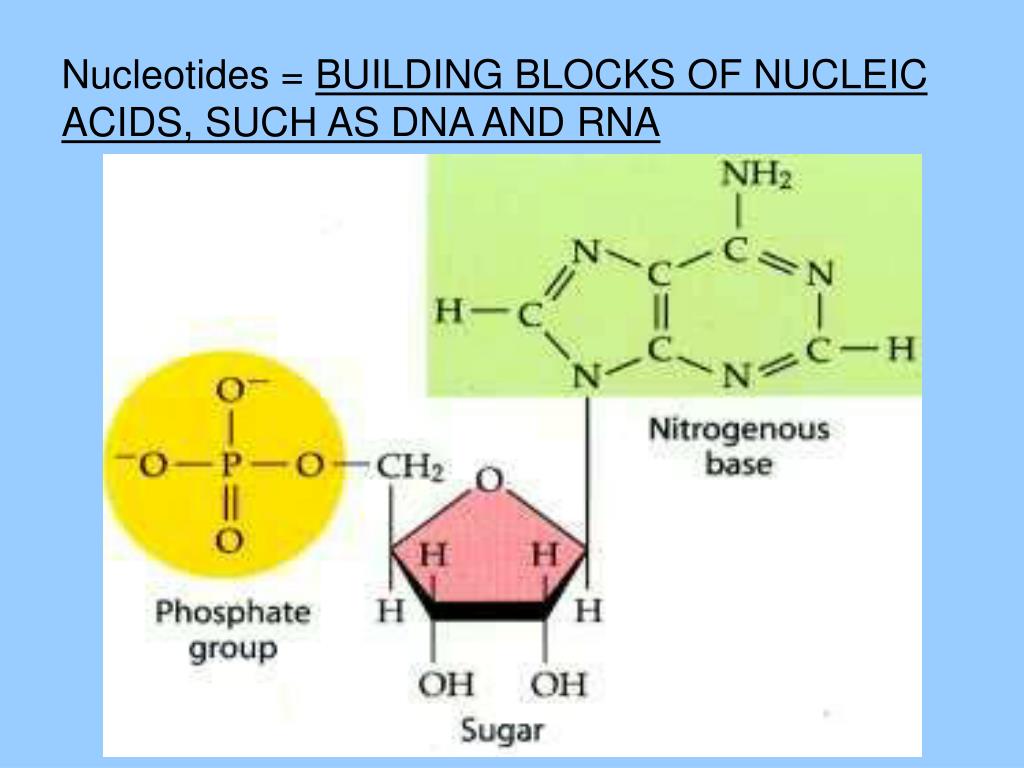
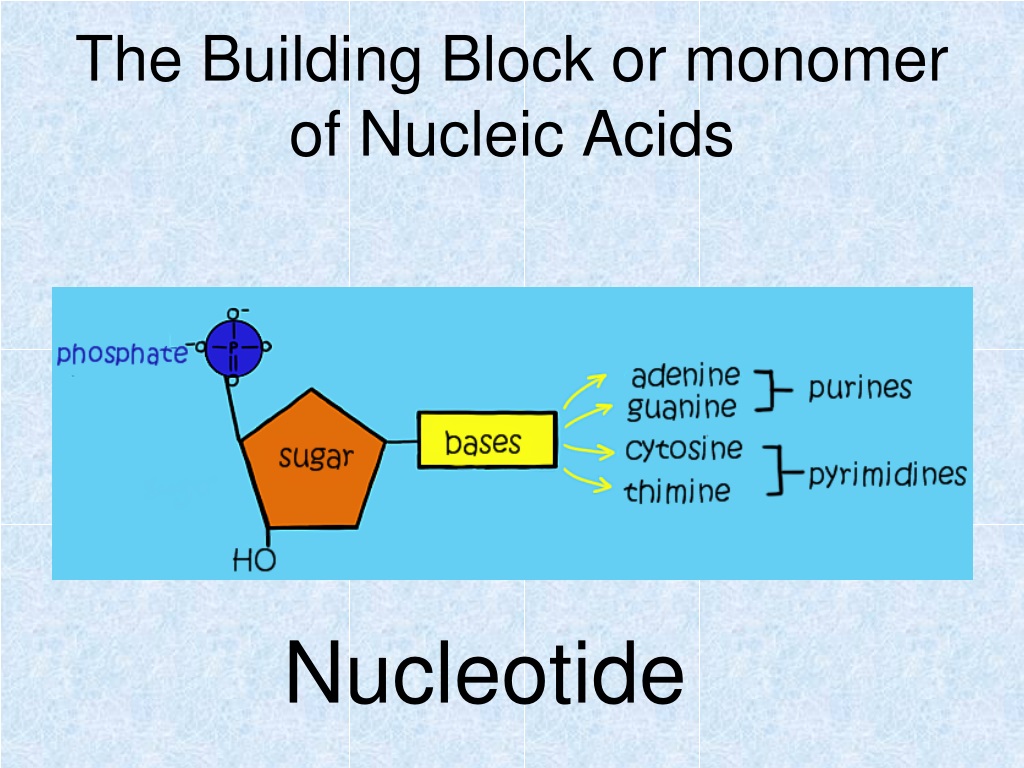
What Are The Monomers Building Blocks Of Nucleic Acids - Polymers of nucleic acids are created when monomers link together. Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a ribose or deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of dna and rna, two molecules essential for life as. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid. Discover the building blocks of dna, exploring its components and how they differ from rna nucleotides. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Nucleic acids (a.k.a dna and rna) are composed out of monomer units called nucleotides. The monomers of nucleic acids, also known as nucleotides, connect to form a polymer through a process termed polymerization, during which phosphodiester bonds are formed between the. Nucleic acids are polymers composed of monomers called nucleotides. These monomers consist of a sugar molecule, a. Nucleic acid monomers, or nucleotides, are the fundamental building blocks of the genetic material found in all living organisms. Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Like all macromolecules nucleic acids are made of building blocks or monomers. The monomers of nucleic acids, also known as nucleotides, connect to form a polymer through a process termed polymerization, during which phosphodiester bonds are formed between the. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid. Nucleic acids (a.k.a dna and rna) are composed out of monomer units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of dna and rna, two molecules essential for life as. These monomers consist of a sugar molecule, a. Nucleic acids are polymers composed of monomers called nucleotides. The site of the nitrogenous base attachment to the sugar residue (glycosidic bond) is shown in red. The deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) of a typical mammalian cell contains. Monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides: Nucleic acids are essential biomacromolecules that carry or contain genetic information. Sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e., phosphate (po3−4 po 4 3 −). Nucleic acids are polymers composed of monomers called nucleotides. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of dna and rna, two molecules essential for life as. The deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) of a typical mammalian cell contains. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are nucleic acids. Monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides: Dna and rna, the nucleic acids fundamental to life, are composed of monomers that serve as the building. The deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) of a typical mammalian cell contains. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: Polymers of nucleic acids are created when monomers link together. Figure 4.2 the monomer building blocks of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of dna and rna, two molecules essential for life as. Nucleic acids are polymers composed of monomers called nucleotides. Monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides: Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid. Discover the building blocks of dna, exploring its components and how they differ from rna nucleotides. The repeating, or monomer, units that are linked together to form nucleic acids are known as nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a ribose or deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are nucleic acids. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: The monomers of nucleic acids, also known as nucleotides, connect to form a. The site of the nitrogenous base attachment to the sugar residue (glycosidic bond) is shown in red. Figure 4.2 the monomer building blocks of nucleic acids. Sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base. These monomers consist of a sugar molecule, a. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid. Nucleic acid monomers, or nucleotides, are the fundamental building blocks of the genetic material found in all living organisms. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Figure 4.2 the monomer building blocks of nucleic acids. Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. The deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) of a typical mammalian cell contains. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a ribose or deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid. Dna and rna, the nucleic acids fundamental to life, are composed of monomers that serve as the building blocks of their respective structures. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of dna and rna, two molecules essential for life as. Sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Discover the. The monomers of nucleic acids, also known as nucleotides, connect to form a polymer through a process termed polymerization, during which phosphodiester bonds are formed between the. Nucleic acids (a.k.a dna and rna) are composed out of monomer units called nucleotides. Discover the building blocks of dna, exploring its components and how they differ from rna nucleotides. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e., phosphate (po3−4 po 4 3 −). Like all macromolecules nucleic acids are made of building blocks or monomers. Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a ribose or deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate. Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Polymers of nucleic acids are created when monomers link together. The site of the nitrogenous base attachment to the sugar residue (glycosidic bond) is shown in red. They can be separated primarily into two groups: Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid. Nucleic acids are essential biomacromolecules that carry or contain genetic information. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are nucleic acids. Nucleic acid monomers, or nucleotides, are the fundamental building blocks of the genetic material found in all living organisms. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids.Monomers Definition, Types, Structure, Examples
Proteins. ppt download
Nucleic Acids Organic Molecules—The Molecules of Life CORNERSTONES
PPT Classical and Modern PowerPoint Presentation ID143901
Biomolecules
Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids Structures & Functions
PPT DNA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5754268
PPT DNA and DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Macromolecules Biomolecules Building Blocks of Life Monomers Build
What Are the Monomer Building Blocks of Dna ElysekruwTyler
The Dna Monomer, Or Nucleotide, Comprises Three Components:
Nucleotides Are Like Building Blocks.
Figure 4.2 The Monomer Building Blocks Of Nucleic Acids.
Monomers Of Nucleic Acids Are Nucleotides:
Related Post: