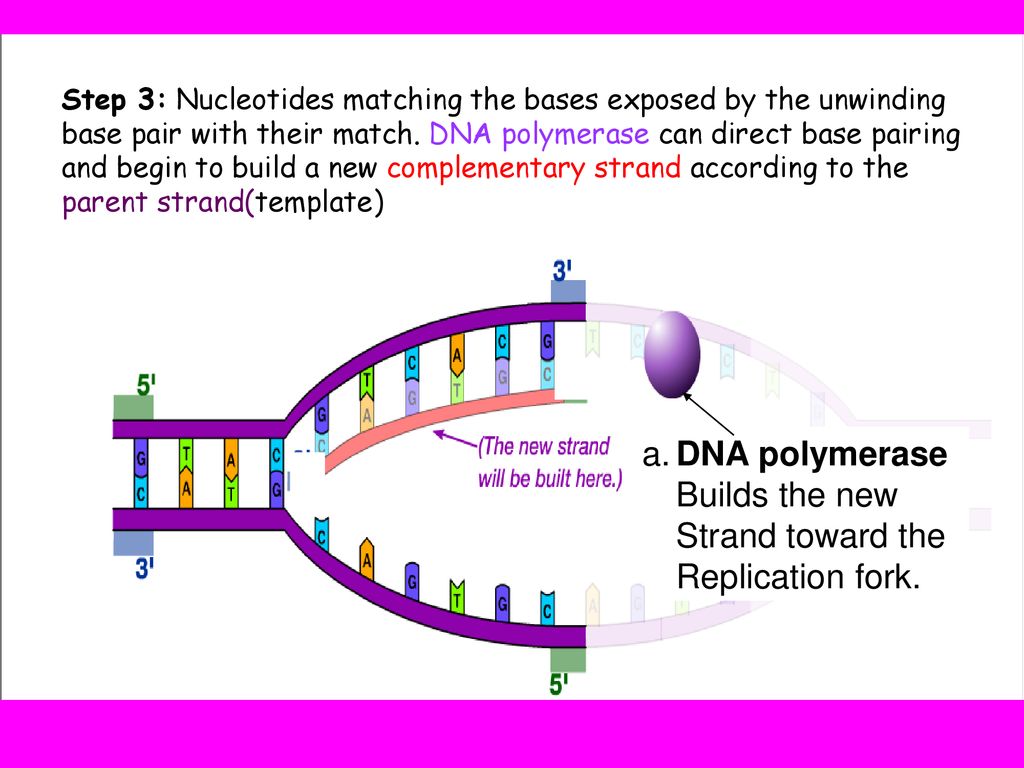
What Builds A New Dna Strand By Adding Complementary Bases
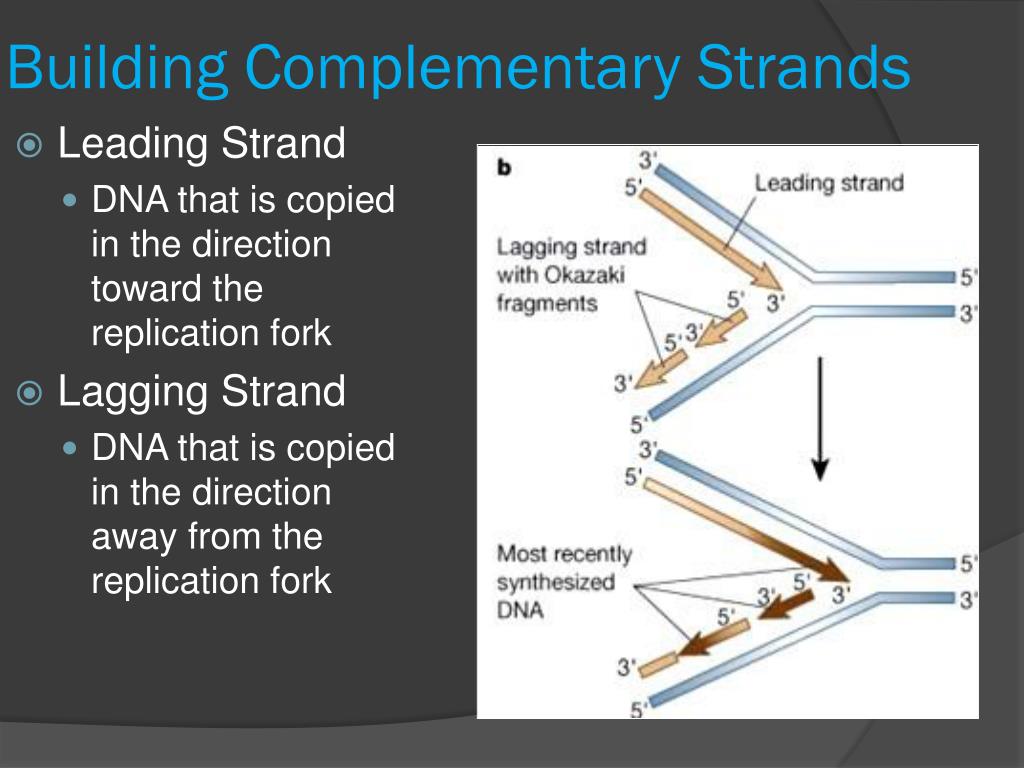
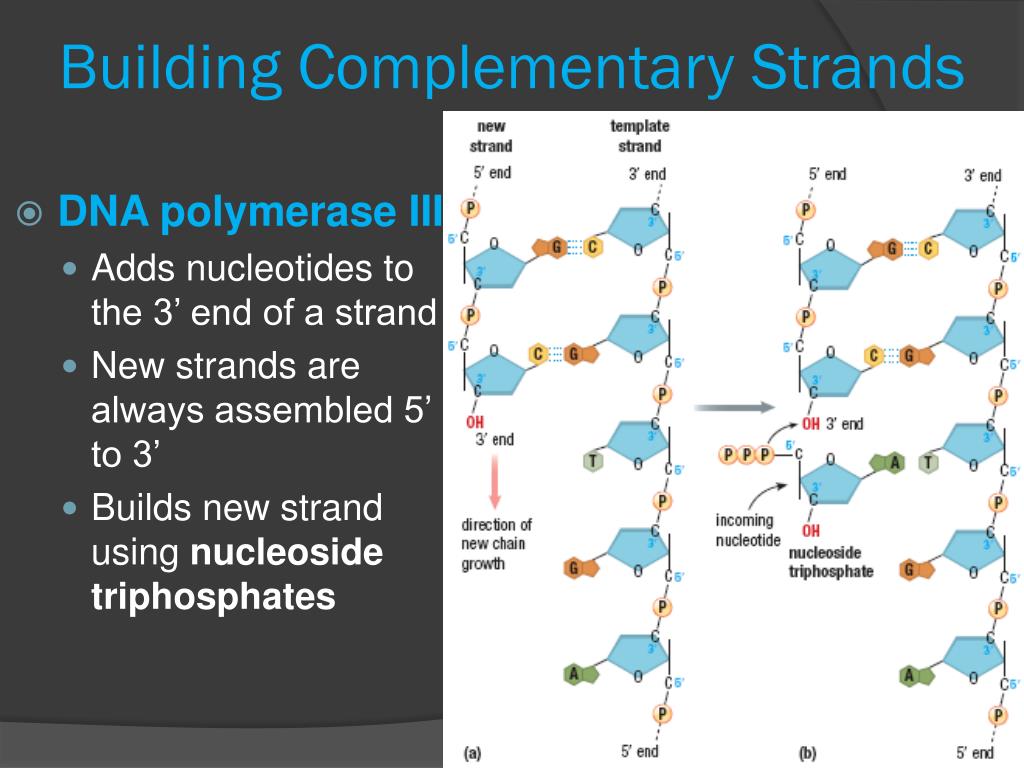
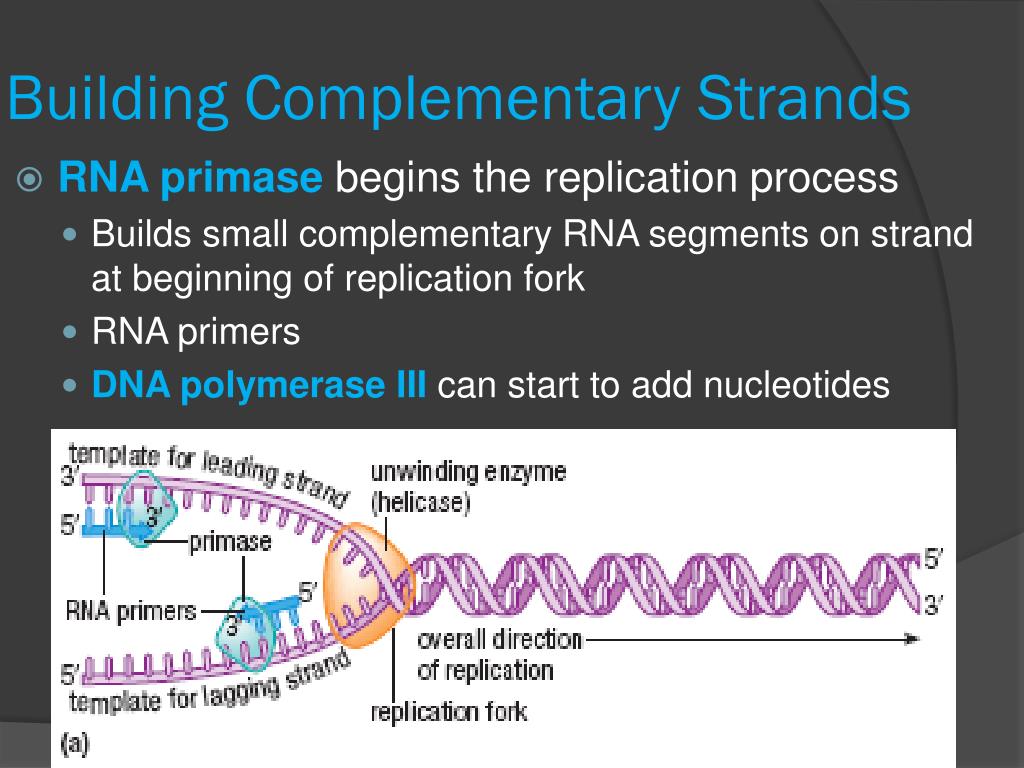
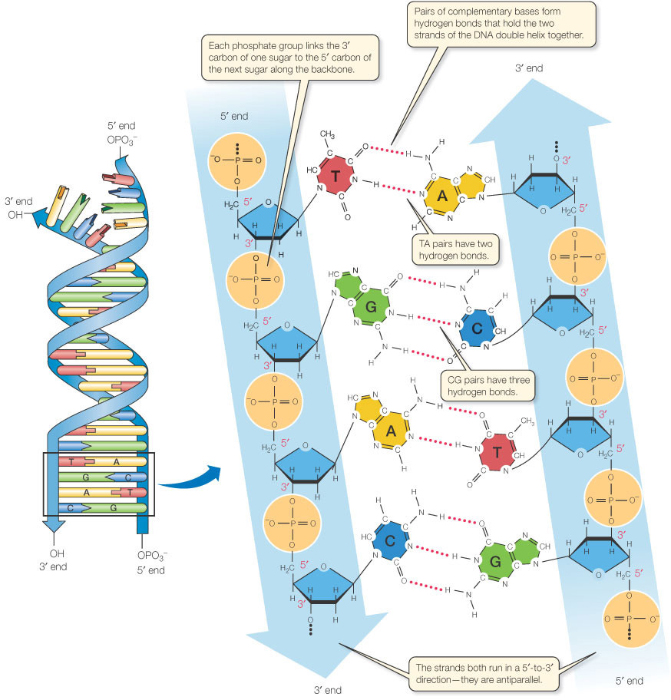
What Builds A New Dna Strand By Adding Complementary Bases - What builds a new dna strand by adding complementary bases? Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like enzyme that undwinds dna, fragments of copied dna created on the lagging strand, strand that is copied in a continuous. As discussed in chapter 3, dna replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. What stabalizes the dna molecule during replication? Dna polymerase iii builds a new strand by adding dna nucleotides one at a time. During this process, the dna molecule unwinds and separates into two strands. Okazaki fragments fragments of copied dna created. Dna replication relies on complementary base pairing. Hydrogen bonds are broken, the two strands separate to form a “bubble,” and bases are exposed. Dna ligase adds nucleotides to the lagging strand. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like enzyme that undwinds dna, fragments of copied dna created on the lagging strand, strand that is copied in a continuous. What strand is copied discontinously because it is traveling away. New nucleotides then line up on each strand in a complementary manner, a to t and g to c,. Dna polymerase, an enzyme, recognizes each base in a template strand and matches it to the complementary base in a free nucleotide. Dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments in the lagging strand, turning it into a continuous strand. Dna replication relies on complementary base pairing. The addition of nucleotides to form a complementary strand of dna is a process known as dna replication. During this process, the dna molecule unwinds and separates into two strands. It ensures the accurate copying of the original. Helicase stabilizes the dna molecule during replication. What builds a new dna strand by adding complementary bases? Dna polymerase controls the addition of dna nucleotides to the new strand of dna. All dna polymerases require a template strand against which to synthesize a new complementary strand. During replication, the dna strands separate, and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new. Dna polymerase. During this process, the dna molecule unwinds and separates into two strands. What stabalizes the dna molecule during replication? Dna polymerase is the enzyme that synthesizes new dna strands by adding complementary bases during dna replication. The addition of nucleotides to form a complementary strand of dna is a process known as dna replication. An enzyme called ‘dna polymerase’ drives. Dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments in the lagging strand, turning it into a continuous strand. Dna polymerase controls the addition of dna nucleotides to the new strand of dna. It requires a primer, a short rna. Okazaki fragments fragments of copied dna created. Helicase stabilizes the dna molecule during replication. The enzyme then catalyzes the. It ensures the accurate copying of the original. What stabalizes the dna molecule during replication? Dna replication relies on complementary base pairing. A strand of rna can form base pairs with a strand of dna, generating a dna/rna hybrid double helix if the two nucleotide sequences are complementary. As discussed in chapter 3, dna replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. What stabalizes the dna molecule during replication? The synthesis of rna primers is. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like enzyme that undwinds dna, fragments of copied dna created. A strand of rna can form base pairs with a strand of dna, generating a dna/rna hybrid double helix if the two nucleotide sequences are complementary. It ensures the accurate copying of the original. All dna polymerases require a template strand against which to synthesize a new complementary strand. The enzyme then catalyzes the. Done by the enzyme, dna polymerase. Hydrogen bonds are broken, the two strands separate to form a “bubble,” and bases are exposed. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what is the enzyme that unwinds dna, what are fragments of copied dna created on the lagging strand, what is the. A strand of rna can form base pairs with a strand of dna, generating. The enzyme then catalyzes the. Dna polymerase iii builds a new strand by adding dna nucleotides one at a time. What strand is copied discontinously because it is traveling away. New nucleotides then line up on each strand in a complementary manner, a to t and g to c,. A strand of rna can form base pairs with a strand. Dna polymerase iii builds a new strand by adding dna nucleotides one at a time. They all grow new dna by adding to the 3’ end of the growing dna chain in. What strand is copied discontinously because it is traveling away. The enzyme then catalyzes the. Done by the enzyme, dna polymerase. Hydrogen bonds are broken, the two strands separate to form a “bubble,” and bases are exposed. Helicase stabilizes the dna molecule during replication. All dna polymerases require a template strand against which to synthesize a new complementary strand. Dna polymerase is the enzyme that synthesizes new dna strands by adding complementary bases during dna replication. Dna polymerase plays a pivotal. Dna ligase adds nucleotides to the lagging strand. The synthesis of rna primers is. Hydrogen bonds are broken, the two strands separate to form a “bubble,” and bases are exposed. The enzyme then catalyzes the. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what is the enzyme that unwinds dna, what are fragments of copied dna created on the lagging strand, what is the. It ensures the accurate copying of the original. Okazaki fragments fragments of copied dna created. Dna replication relies on complementary base pairing. Dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments in the lagging strand, turning it into a continuous strand. Helicase stabilizes the dna molecule during replication. A strand of rna can form base pairs with a strand of dna, generating a dna/rna hybrid double helix if the two nucleotide sequences are complementary. As discussed in chapter 3, dna replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. What builds a new dna strand by adding complementary bases? Dna polymerase plays a pivotal role by adding nucleotides to the growing dna strand in a sequence complementary to the template strand. It requires a primer, a short rna. They all grow new dna by adding to the 3’ end of the growing dna chain in.PPT DNA Hereditary Molecules of Life PowerPoint Presentation, free
The Structure of DNA by Ron Vale
Original Template Dna Strand
DNA Replication SBI4U RESOURCE WEBSITE
PPT DNA Hereditary Molecules of Life PowerPoint Presentation, free
What is Complementary Bases in DNA
DNA. Structure and Replication Presentation Biology
Chapter 122 DNA Replication and Chromosomes ppt download
PPT DNA Hereditary Molecules of Life PowerPoint Presentation, free
Question Video Determining the Complementary Sequence of a DNA Strand
During This Process, The Dna Molecule Unwinds And Separates Into Two Strands.
The Addition Of Nucleotides To Form A Complementary Strand Of Dna Is A Process Known As Dna Replication.
All Dna Polymerases Require A Template Strand Against Which To Synthesize A New Complementary Strand.
Dna Polymerase Iii Builds A New Strand By Adding Dna Nucleotides One At A Time.
Related Post:


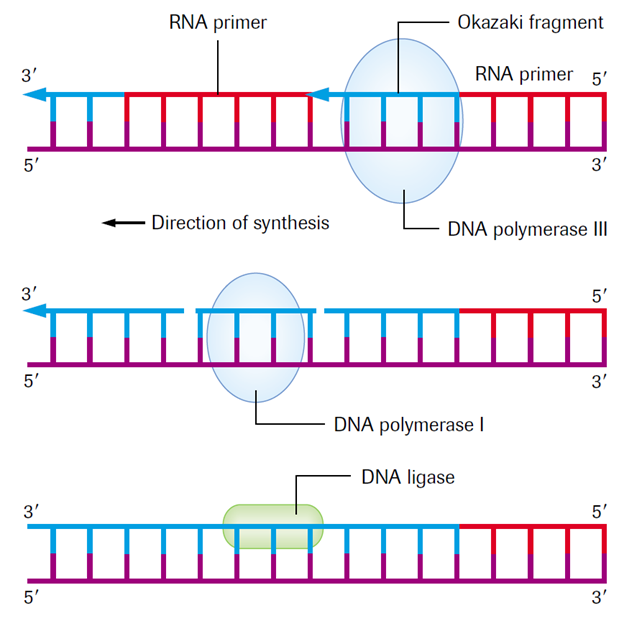
.PNG)