What Is The Basic Building Block Of Nucleic Acids
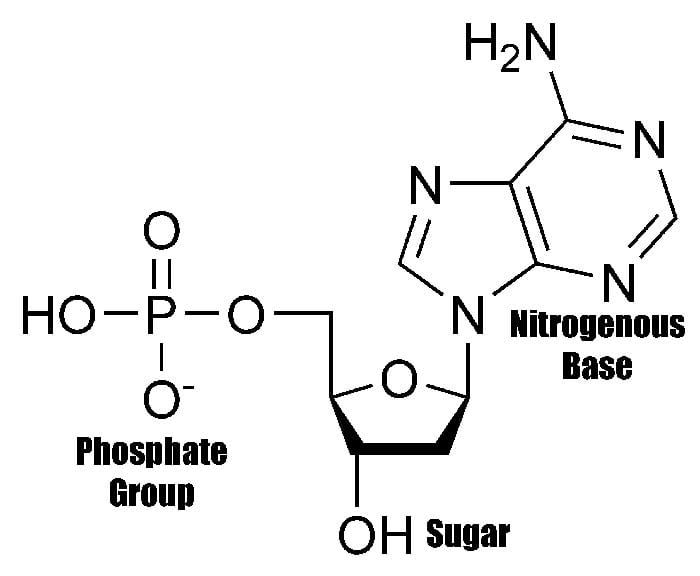
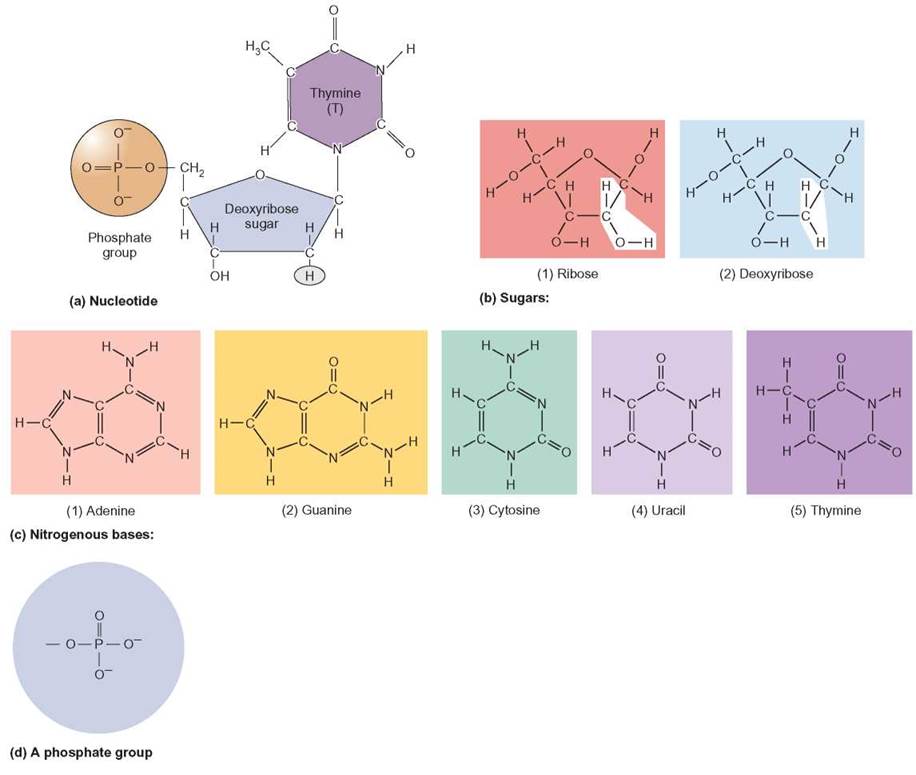
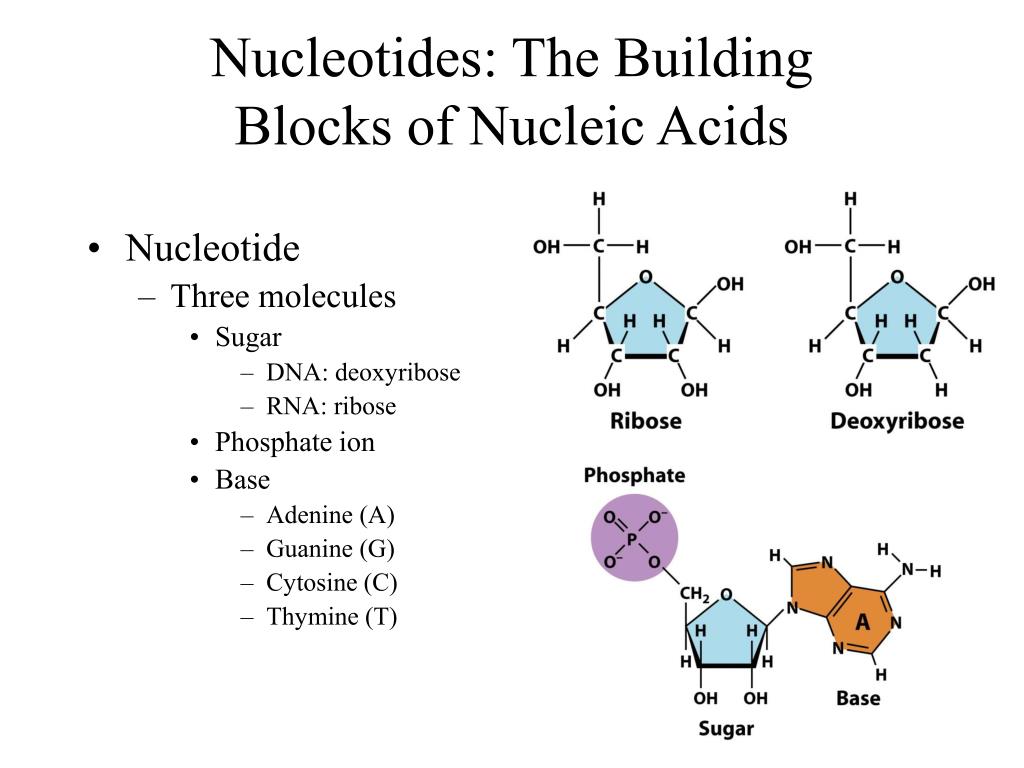
What Is The Basic Building Block Of Nucleic Acids - A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of dna and rna. The phosphate is attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose and the. What are the building blocks of nucleic acids? Humans have two types of nucleic acids in their bodies: Nucleic acids are large polymers formed by linking nucleotides together and are found in every cell. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. Each nucleotide is a composite organic molecule made up of a nitrogen base, five carbon sugars and at least one phosphate. Understand the function of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are nucleosides with one or more phosphate groups attached, forming nucleotide monophosphates, diphosphates, or triphosphates. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. Nucleotides are nucleosides with one or more phosphate groups attached, forming nucleotide monophosphates, diphosphates, or triphosphates. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Each nucleotide is a composite organic molecule made up of a nitrogen base, five carbon sugars and at least one phosphate. Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in rna or deoxyribose in dna) attached. They determine who and what we are. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. These molecules contain the set of instructions for our cells: Humans have two types of nucleic acids in their bodies: Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the elements contained in nucleic acids?, what is the basic structural building blocks of nucleic acids?,. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. A nucleotide is the basic building block of. Each nucleotide is a composite organic molecule made up of a nitrogen base, five carbon sugars and at least one phosphate. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of. What are the building blocks of nucleic acids? Each nucleotide is a composite organic molecule made up of a nitrogen base, five carbon sugars and at least one phosphate. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Molecules that contain only a sugar and a. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides, which consist of a sugar molecule (ribose or deoxyribose),. A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of dna and rna. Molecules that contain only a sugar and a. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Nucleotides contain three primary structural components. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in rna or deoxyribose in dna) attached. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. Rna, or ribonucleic acid, plays a crucial role in translating genetic information from dna into proteins. These molecules contain the set of instructions for our cells: Nucleotides contain three primary structural components. Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the elements contained in nucleic acids?, what is the basic structural building blocks of nucleic acids?,. A nucleotide is an organic molecule that is the building block of dna and rna. Nucleotides are nucleosides with one or more. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides, which consist of a sugar molecule (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate. Nucleotides contain three primary structural components. A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (rna and dna). They determine who and what we are. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in rna or deoxyribose in dna) attached. Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides, which consist of. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) is the nucleic acid that stores genetic. Understanding its structure is vital as it influences rna’s cellular functions. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. These molecules contain the set of instructions for our cells: Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. What are the building blocks of nucleic acids? These molecules contain the set of instructions for our cells: An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Molecules that contain only a sugar and a. A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in rna or deoxyribose in dna) attached. Rna, or ribonucleic acid, plays a crucial role in translating genetic information from dna into proteins. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (rna and dna). They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. Understand the function of nucleic acids. These molecules contain the set of instructions for our cells: The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides, which consist of a sugar molecule (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate. Nucleic acids are large polymers formed by linking nucleotides together and are found in every cell. Humans have two types of nucleic acids in their bodies: These are a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and at least one phosphate. The phosphate is attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose and the. Molecules that contain only a sugar and a. They also have functions related to cell signaling, metabolism, and enzyme reactions. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Each nucleotide is a composite organic molecule made up of a nitrogen base, five carbon sugars and at least one phosphate.PPT Exploring Nucleic Acid Structures PowerPoint Presentation, free
PPT DNA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5754268
PPT DNA and DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Nucleic Acids Function, Examples, and Monomers
Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids Structures & Functions
Pin on Macromolecules
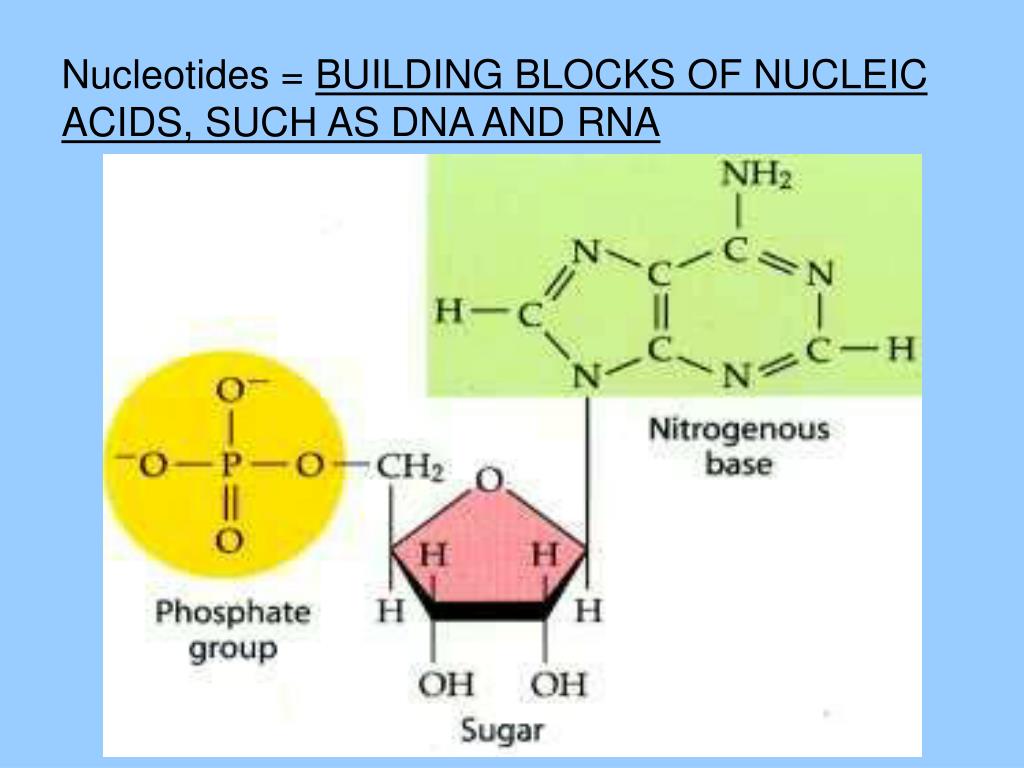
FIGURE 3.15. The Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids
Basic Nucleic Acid Chemical Structure
PPT Classical and Modern PowerPoint Presentation ID143901
PPT Nucleic Acids The Ultimate Building Blocks PowerPoint
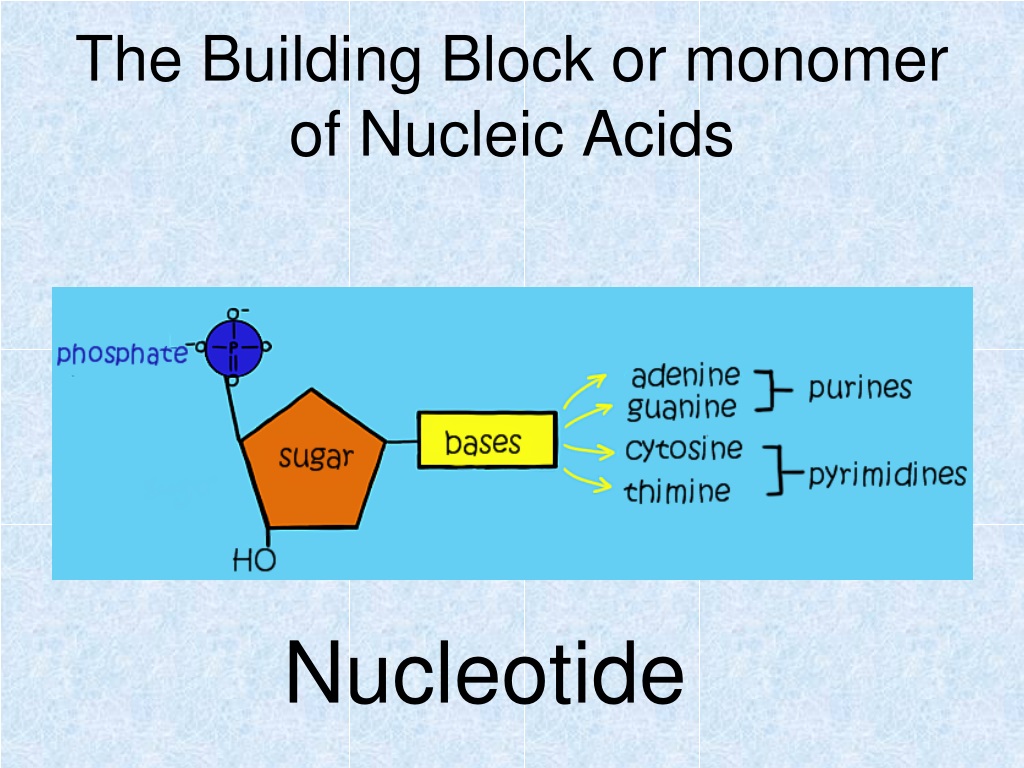
Nucleotides Contain Three Primary Structural Components.
What Are The Building Blocks Of Nucleic Acids?
A Nucleotide Is An Organic Molecule That Is The Building Block Of Dna And Rna.
They Determine Who And What We Are.
Related Post:
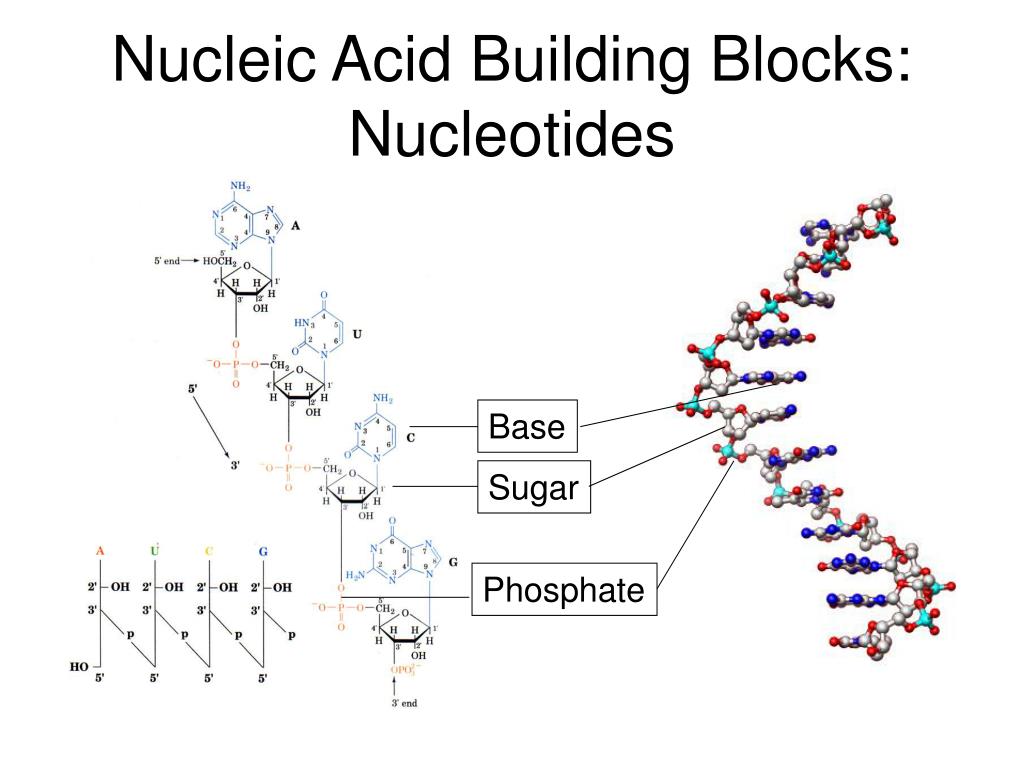
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotide_base-5b6335bdc9e77c002570743e.jpg)