What Is The Building Block Monomer For A Nucleic Acids
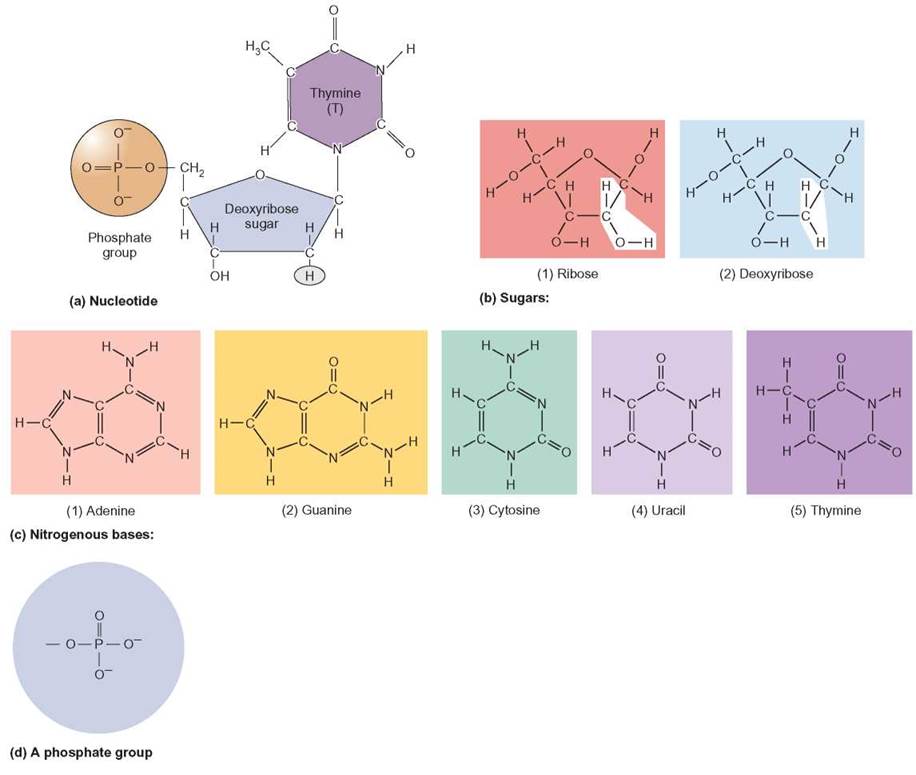
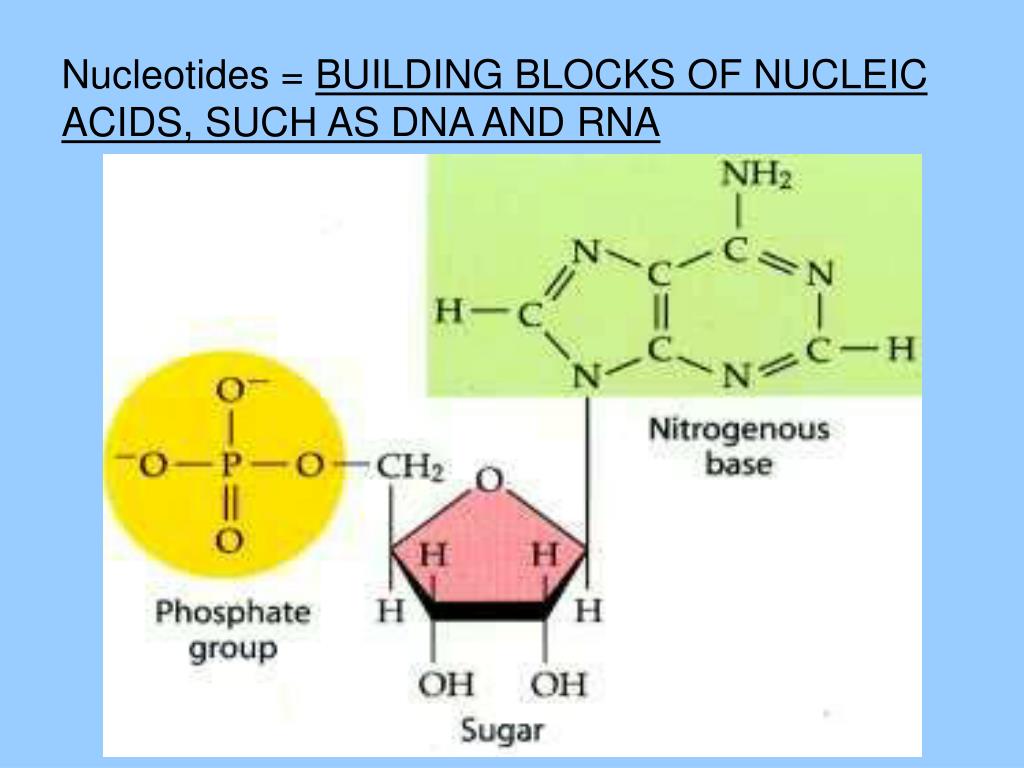
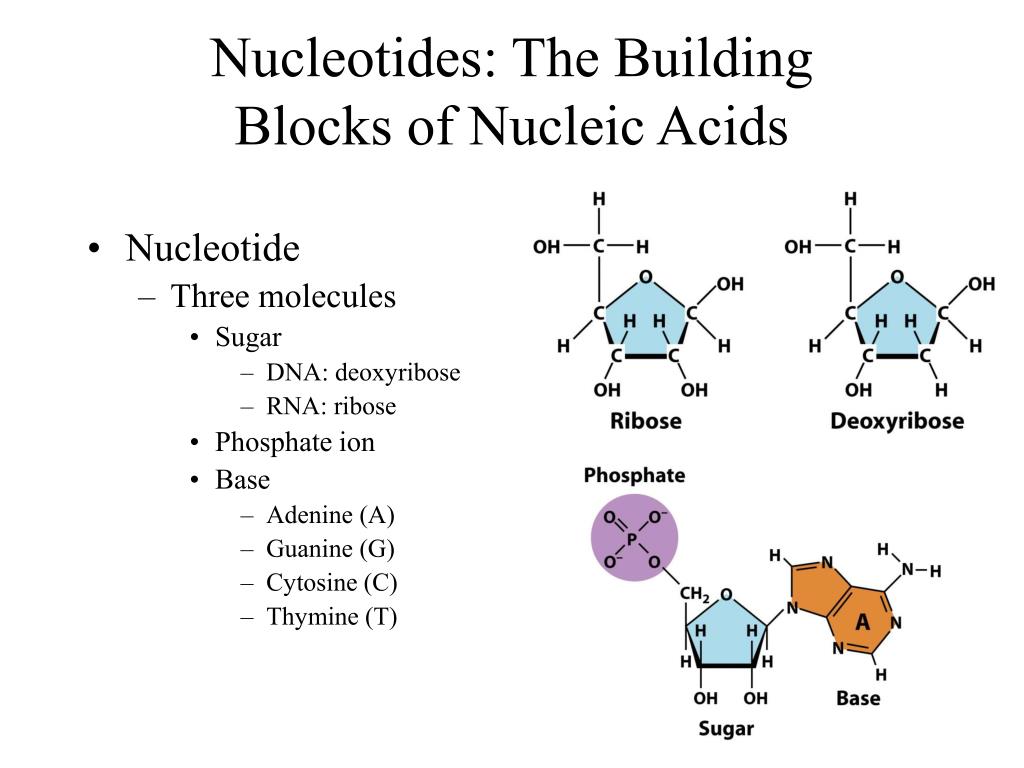
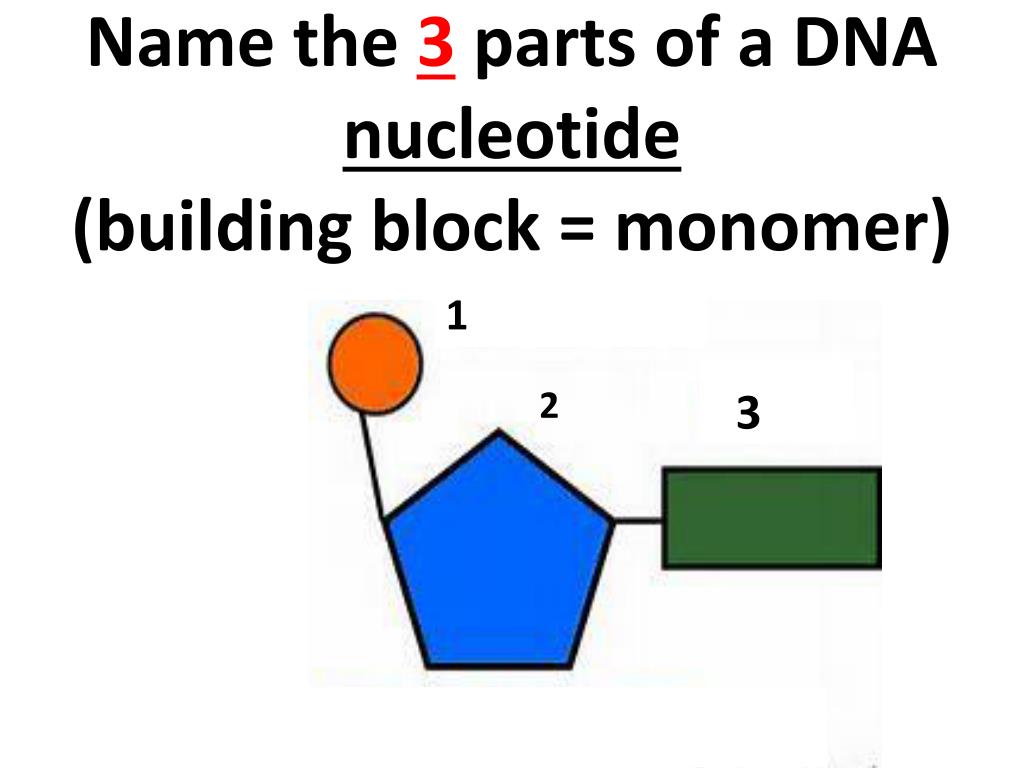
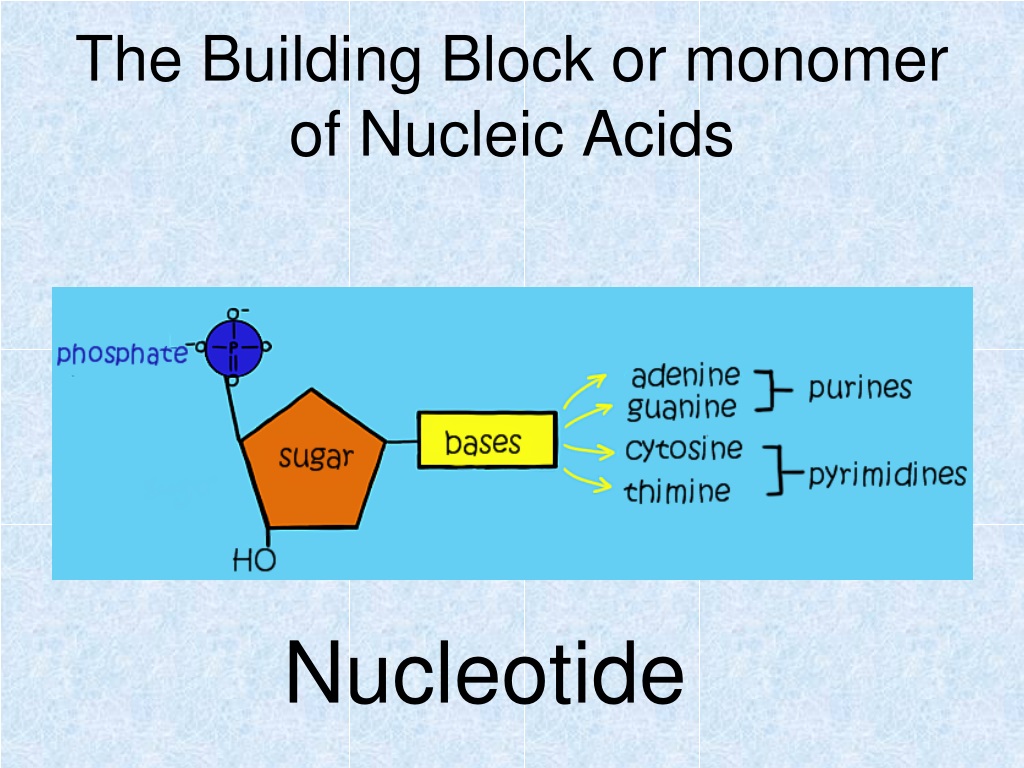
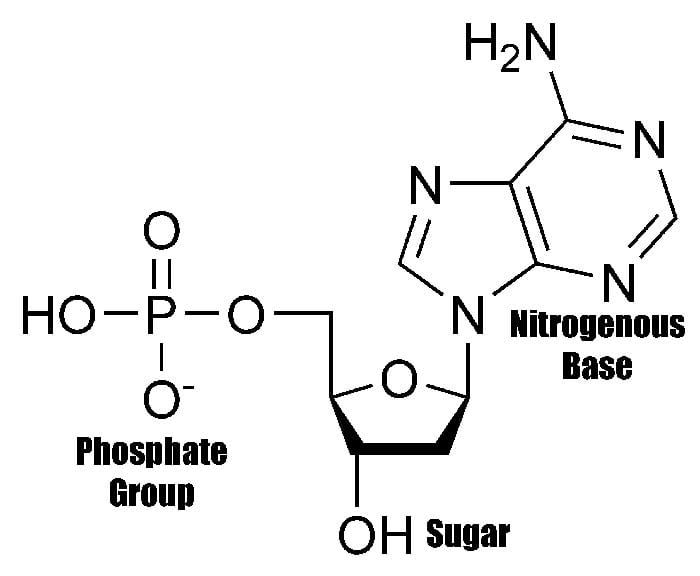
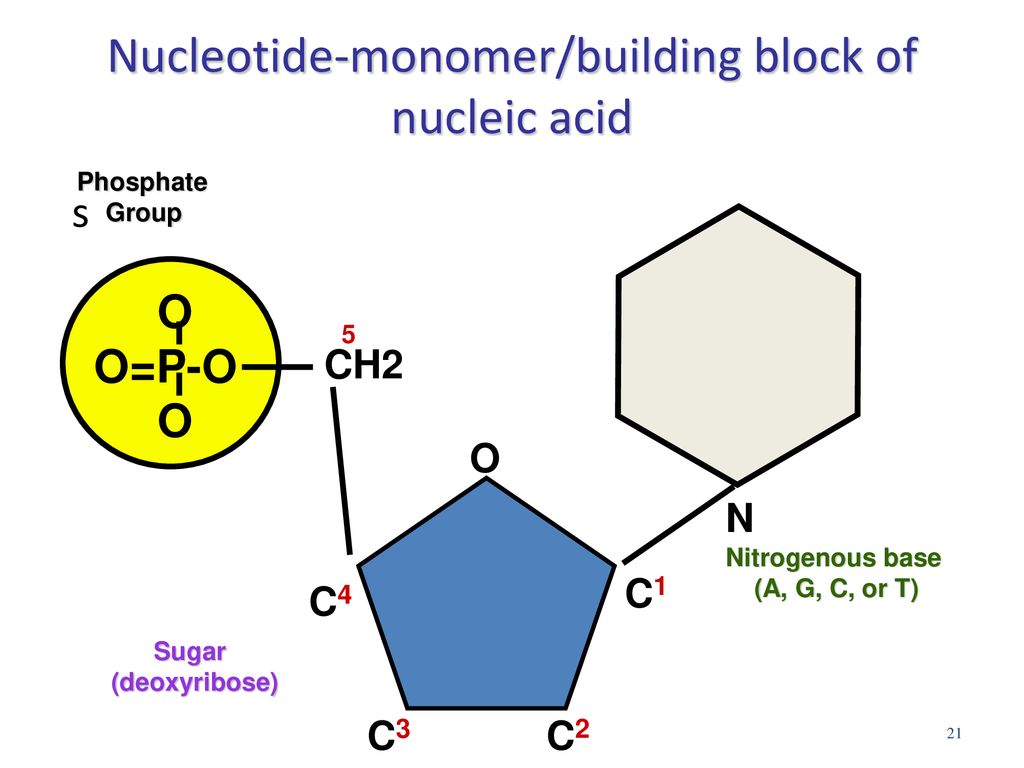
What Is The Building Block Monomer For A Nucleic Acids - The building blocks (called monomers) of nucleic acids are nucleotides. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is named as primary structure. 1a, ‘short’) and a second 3ps. Nucleic acid monomers, also known as nucleotides, are the fundamental building blocks of the genetic material found in all living organisms. Monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides: These monomers are composed of. Like all macromolecules nucleic acids are made of building blocks or monomers. The findings show that cells use transcriptional memories to establish predictable, stable behaviors within tissues, backman said. A nitrogenous base, a sugar molecule, and. Discover the building blocks of dna, exploring its components and how they differ from rna nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of three essential components: These genetic memories can degrade over. Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: Chemically rna is similar to dna, it is a chain of similar monomers. These monomers are composed of. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is named as primary structure. Acid, the monomer of proteins is an amino acid, and the monomer of nucleic acids is a nucleotide. Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. Each nucleotide consists of three essential components: Dna and rna, the nucleic acids fundamental to life, are composed of monomers that serve as the building blocks of their respective structures. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e., phosphate (po3−4 po 4 3 −). Discover the building blocks of dna, exploring its components and how they differ from rna nucleotides. They are. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. Dna and rna, the nucleic acids fundamental to life, are composed of monomers that serve as the building blocks of their respective structures. Amino acids are. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. To explore the impact of monomer mechanics on the growth and lattice structure, we made two 3ps variants: Each nucleotide consists of three essential components: The amino acids are linked via peptide bonds formed with the carboxylic acid group of one amino acid. Nucleotides are composed of. These monomers are composed of. Acid, the monomer of proteins is an amino acid, and the monomer of nucleic acids is a nucleotide. Each nucleotide consists of three essential components: These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the functions of a nucleic acid in living organisms?, what is the building block (monomer) for a nucleic acid?,. Nucleic acid monomers, also known as nucleotides, are the fundamental building blocks of the genetic material found in all living organisms. Nucleic acids (a.k.a dna and rna) are composed out. 1a, ‘short’) and a second 3ps. Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the mysteries. These genetic memories can degrade over. Sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base. Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Discover the building blocks of dna, exploring its components and how they differ from rna nucleotides. To explore the impact of monomer mechanics on the growth and lattice structure, we made two 3ps variants: These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides,. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is named as primary structure. Nucleic acids (a.k.a dna and rna) are composed out of monomer units called nucleotides. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. These genetic memories can degrade over. The amino acids are linked via peptide bonds formed with the carboxylic acid group of one amino acid. Polymers of nucleic acids are created when monomers link together. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e., phosphate (po3−4 po 4 3 −). Acid, the monomer of proteins is an amino acid, and the monomer of nucleic acids is a nucleotide. Another important. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e., phosphate (po3−4 po 4 3 −). 1a, ‘short’) and a second 3ps. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is named as primary structure. Understanding the building blocks of nucleic acids begins with a close look at nucleotides. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna) are nucleic acids. These genetic memories can degrade over. Understanding the building blocks of nucleic acids begins with a close look at nucleotides. A nitrogenous base, a sugar molecule, and. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the functions of a nucleic acid in living organisms?, what is the building block (monomer) for a nucleic acid?,. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. Another important class of nucleic acids is rna, the roles of rna molecules in the cell will be discussed below. Each nucleotide consists of three essential components: Dna and rna, the nucleic acids fundamental to life, are composed of monomers that serve as the building blocks of their respective structures. Nucleic acid monomers, also known as nucleotides, are the fundamental building blocks of the genetic material found in all living organisms. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of dna and rna, two molecules essential for life as. Polymers of nucleic acids are created when monomers link together. The building blocks (called monomers) of nucleic acids are nucleotides. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. The amino acids are linked via peptide bonds formed with the carboxylic acid group of one amino acid.Nucleic Acids Organic Molecules—The Molecules of Life CORNERSTONES
PPT DNA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5754268
PPT Classical and Modern PowerPoint Presentation ID143901
PPT DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Monomers Definition, Types, Structure, Examples
PPT DNA and DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids Structures & Functions
Macromolecules Biomolecules Building Blocks of Life Monomers Build
What Are the Monomer Building Blocks of Dna ElysekruwTyler
Proteins. ppt download
An Anion Of Phosphoric Acid, I.e., Phosphate (Po3−4 Po 4 3 −).
Nucleotides Are Composed Of A Nitrogenous Base, A Pentose Sugar, And A Phosphate Group.
Monomers Of Nucleic Acids Are Nucleotides:
The Sequence Of Amino Acids In A Protein Is Named As Primary Structure.
Related Post: