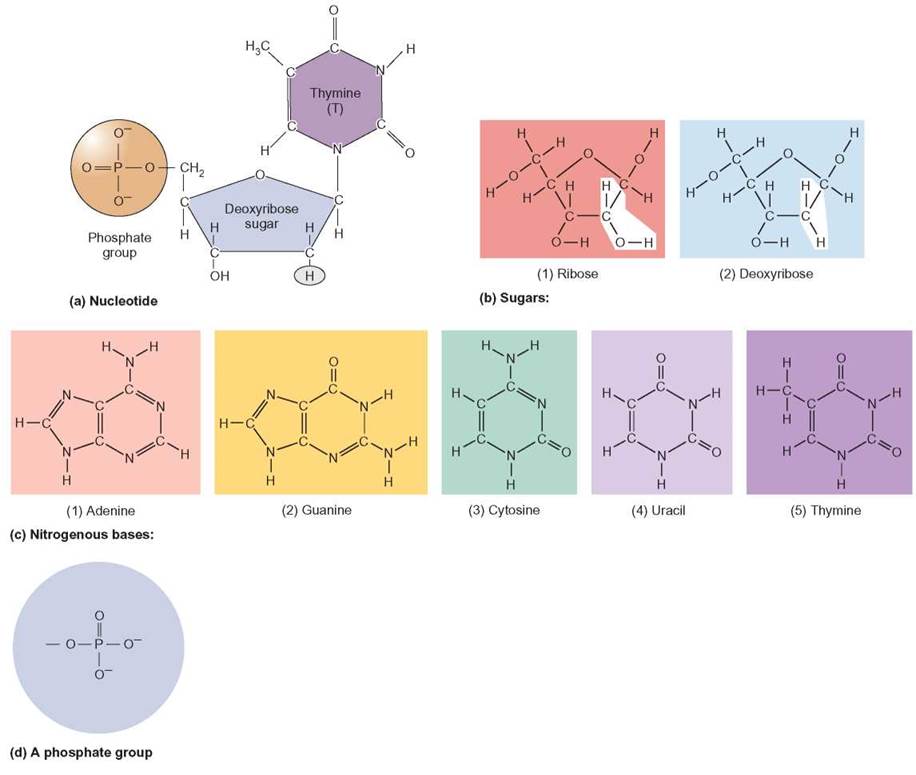
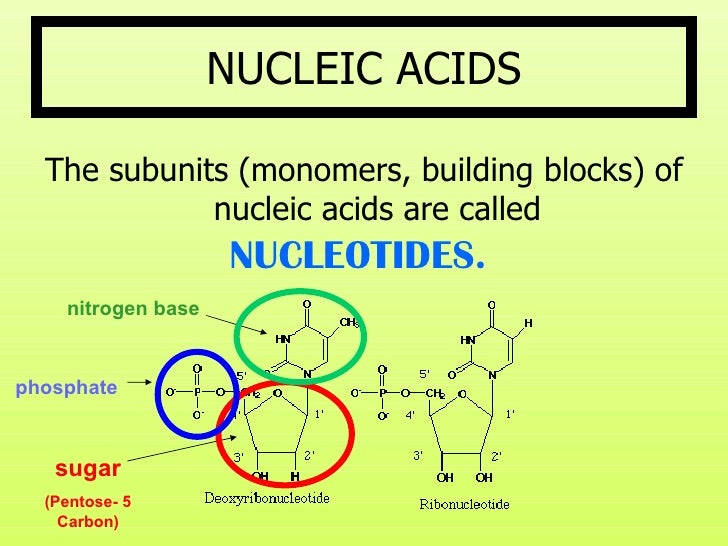
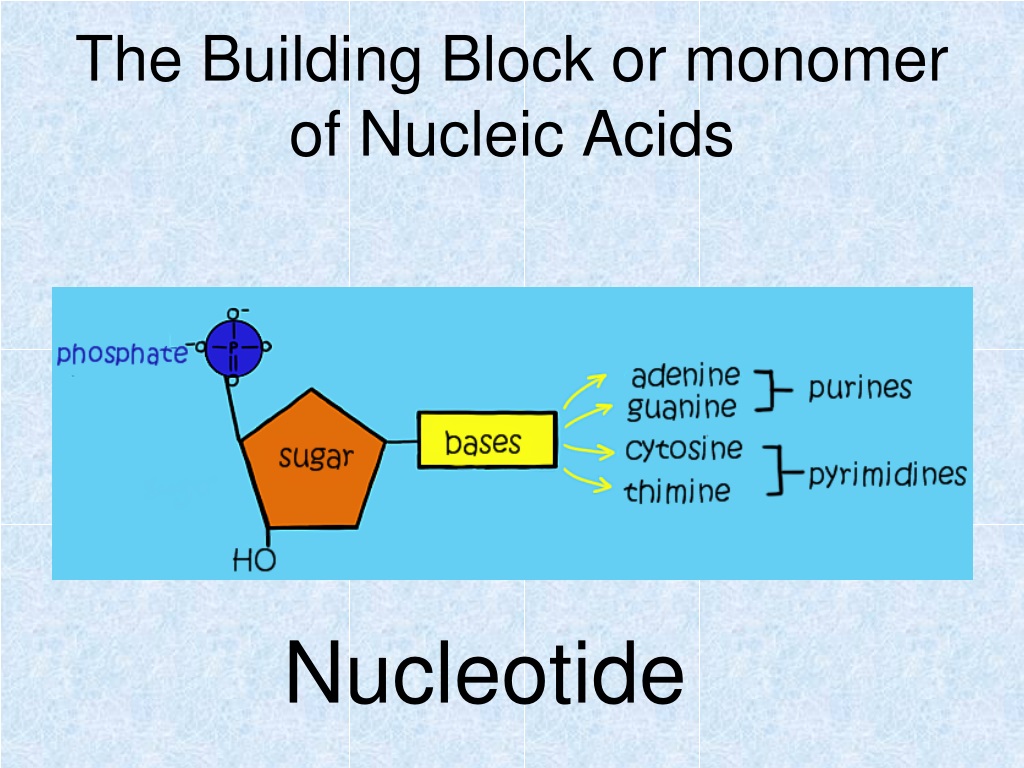
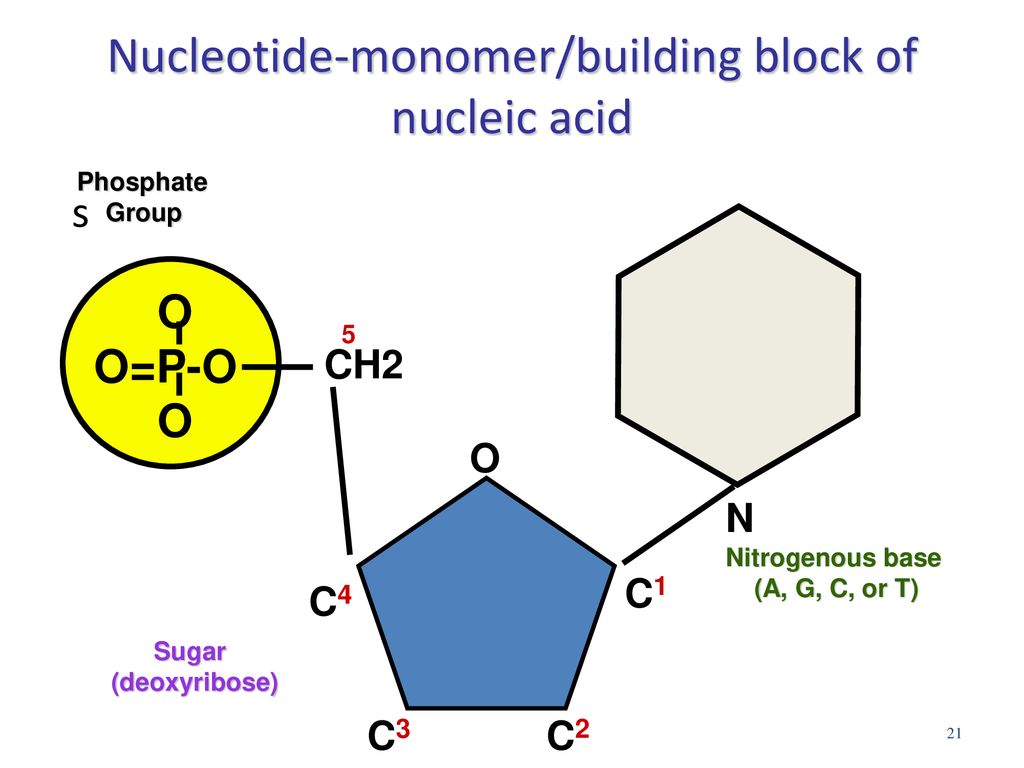
What Is The Building Block Monomer Of Nucleic Acids
What Is The Building Block Monomer Of Nucleic Acids - Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. The deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) of a typical mammalian cell contains. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. [1] [2] [3] the chromosome of a typical prokaryote. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: Expert answers info the building blocks of nucleic acids are called nucleotides. The three components of a. These monomers consist of a sugar molecule, a. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of dna and rna, two molecules essential for life as. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the functions of a nucleic acid in living organisms?, what is the building block (monomer) for a nucleic acid?,. These elements bind to form monosaccharides, phosphate. Both groups are made up of monomers called nucleotides. Discover the building blocks of dna, exploring its components and how they differ from rna nucleotides. Chemically rna is similar to dna, it is a chain of similar monomers. Nucleic acid monomers, or nucleotides, are the fundamental building blocks of the genetic material found in all living organisms. Another important class of nucleic acids is rna, the roles of rna molecules in the cell will be discussed below. The three components of a. Nucleic acids (a.k.a dna and rna) are composed out of monomer units called nucleotides. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides, which consist of a sugar molecule (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine,. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. These elements bind to form monosaccharides, phosphate. These monomers consist of a sugar molecule, a. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of dna and rna, two molecules essential for life as. The image below shows the general structure of these nucleotides which contain a phosphate group, a pentose sugar and a base. Nucleic acid monomers, or nucleotides, are the fundamental. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of dna and rna, two molecules essential for life as. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the functions of a. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. The repeating, or monomer, units that are linked together to form nucleic acids are known as nucleotides. Nucleic acids (a.k.a dna and rna) are composed out of monomer units. Nucleic acids (a.k.a dna and rna) are composed out of monomer units called nucleotides. [1] [2] [3] the chromosome of a typical prokaryote. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what are the functions of a nucleic acid in living organisms?, what is the. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of dna and rna, two molecules essential for life as. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna. Understanding them is crucial for unraveling the mysteries. The deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) of a typical mammalian cell contains. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of dna and rna, two molecules essential for life as. Nucleotides that compose dna are called deoxyribonucleotides. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of dna and rna, two molecules essential for life as. The deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) of a typical mammalian cell contains. Both groups are made up of monomers called nucleotides. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides, which consist of a sugar molecule (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine,.. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides. Expert answers info the building blocks of nucleic acids are called nucleotides. Both groups are made up of monomers called nucleotides. Chemically rna is similar to dna, it is a chain of similar monomers. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: These elements bind to form monosaccharides, phosphate. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e., phosphate (po3−4 po 4 3 −). They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. Both groups are made up of monomers called nucleotides. These monomers consist of a sugar molecule, a. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides. The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e.,. Each nucleotide is a composite organic molecule made up of a nitrogen base, five carbon sugars and at least one phosphate. Another important class of nucleic acids is rna, the roles of rna molecules in the cell will be discussed below. Nucleic acids (a.k.a dna and rna) are composed out of monomer units called nucleotides. Dna and rna are chainlike macromolecules that function in the storage and transfer of genetic information. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides. The building blocks of nucleic acids are nucleotides, which consist of a sugar molecule (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine,. Each nucleotide monomer, and therefore each nucleic acid polymer, is composed of a group of five elements. Nucleic acid monomers, or nucleotides, are the fundamental building blocks of the genetic material found in all living organisms. The deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) of a typical mammalian cell contains. These elements bind to form monosaccharides, phosphate. An anion of phosphoric acid, i.e., phosphate (po3−4 po 4 3 −). The dna monomer, or nucleotide, comprises three components: Discover the building blocks of dna, exploring its components and how they differ from rna nucleotides. They are major components of all cells ~15% of the cells dry weight. Nucleotides are the building blocks, i.e., the repeat units or monomers of nucleic acids. These molecules, known as nucleosides and nucleotides, are the building blocks of nucleic acids like dna and rna.Monomers Definition, Types, Structure, Examples
PPT Classical and Modern PowerPoint Presentation ID143901
Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids Structures & Functions
PPT DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis PowerPoint Presentation, free download
PPT DNA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5754268
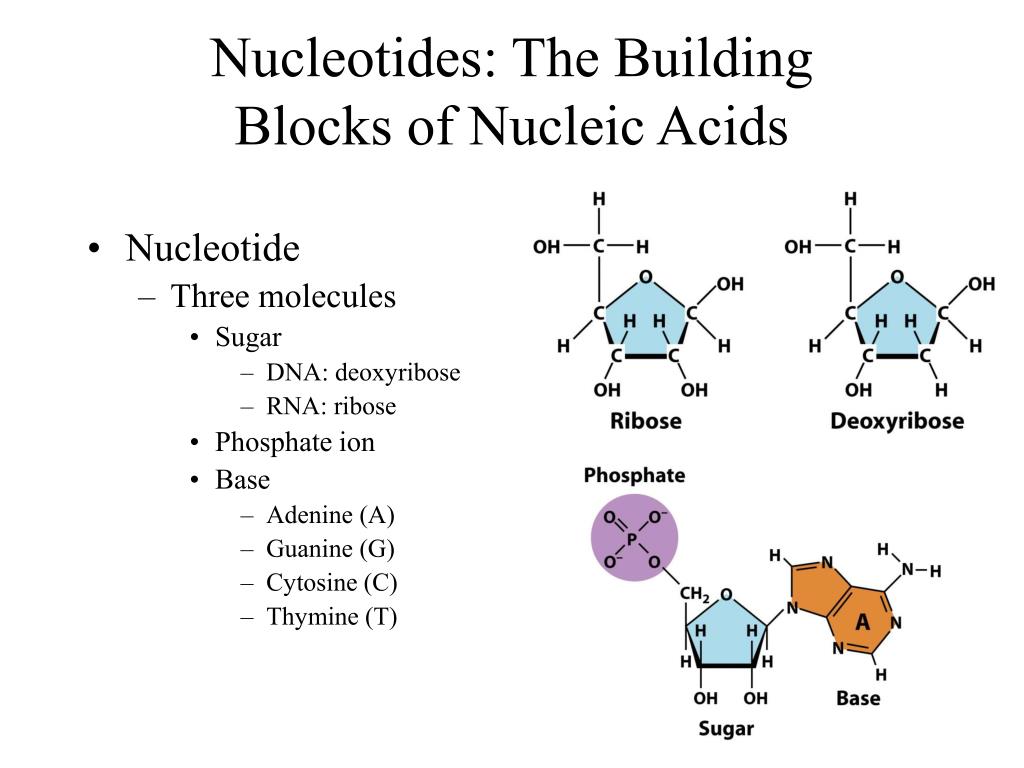
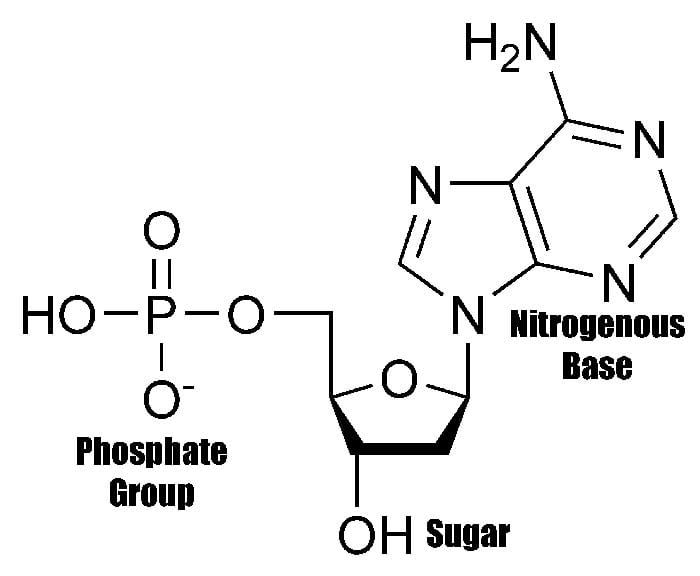
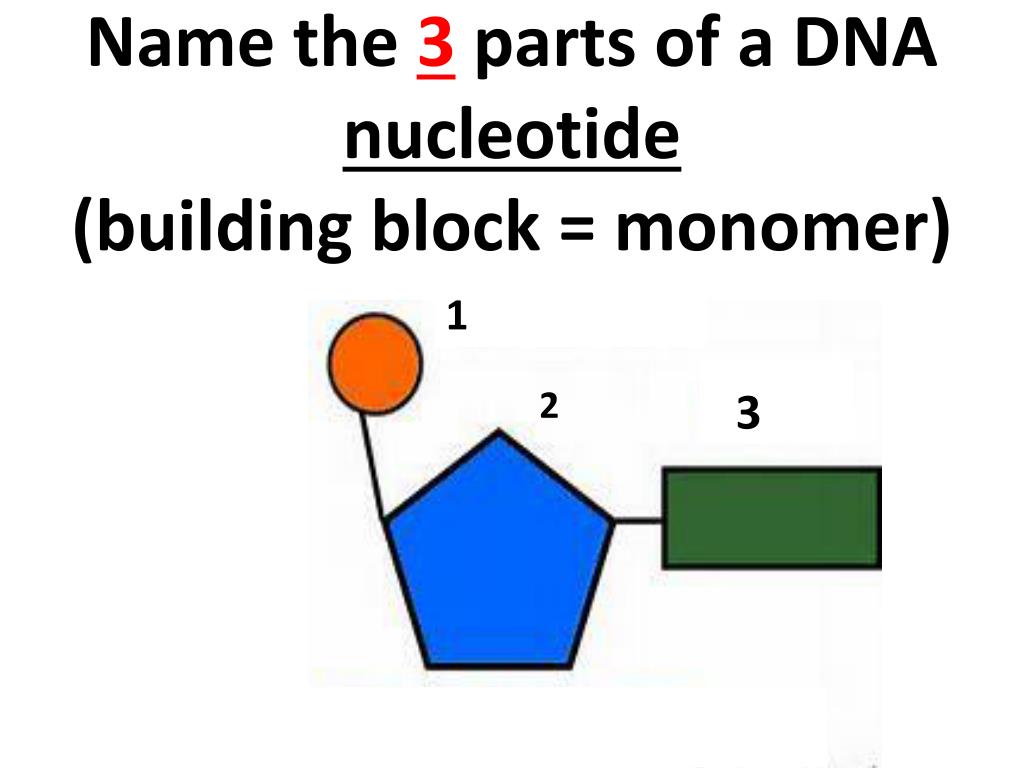
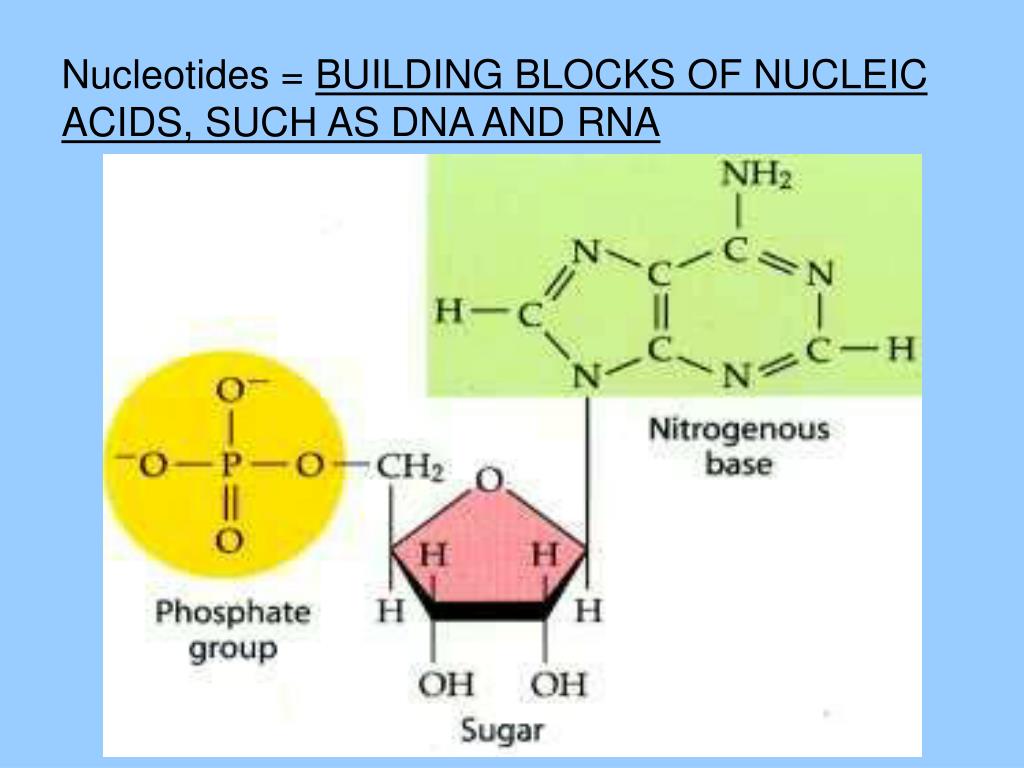
FIGURE 3.15. The Building Blocks of Nucleic Acids
Biomolecules
PPT DNA and DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Proteins. ppt download
What Are the Monomer Building Blocks of Dna ElysekruwTyler
Nucleotides Are The Building Blocks, I.e., The Repeat Units Or Monomers Of Nucleic Acids.
Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like What Are The Functions Of A Nucleic Acid In Living Organisms?, What Is The Building Block (Monomer) For A Nucleic Acid?,.
The Image Below Shows The General Structure Of These Nucleotides Which Contain A Phosphate Group, A Pentose Sugar And A Base.
Understanding Them Is Crucial For Unraveling The Mysteries.
Related Post: