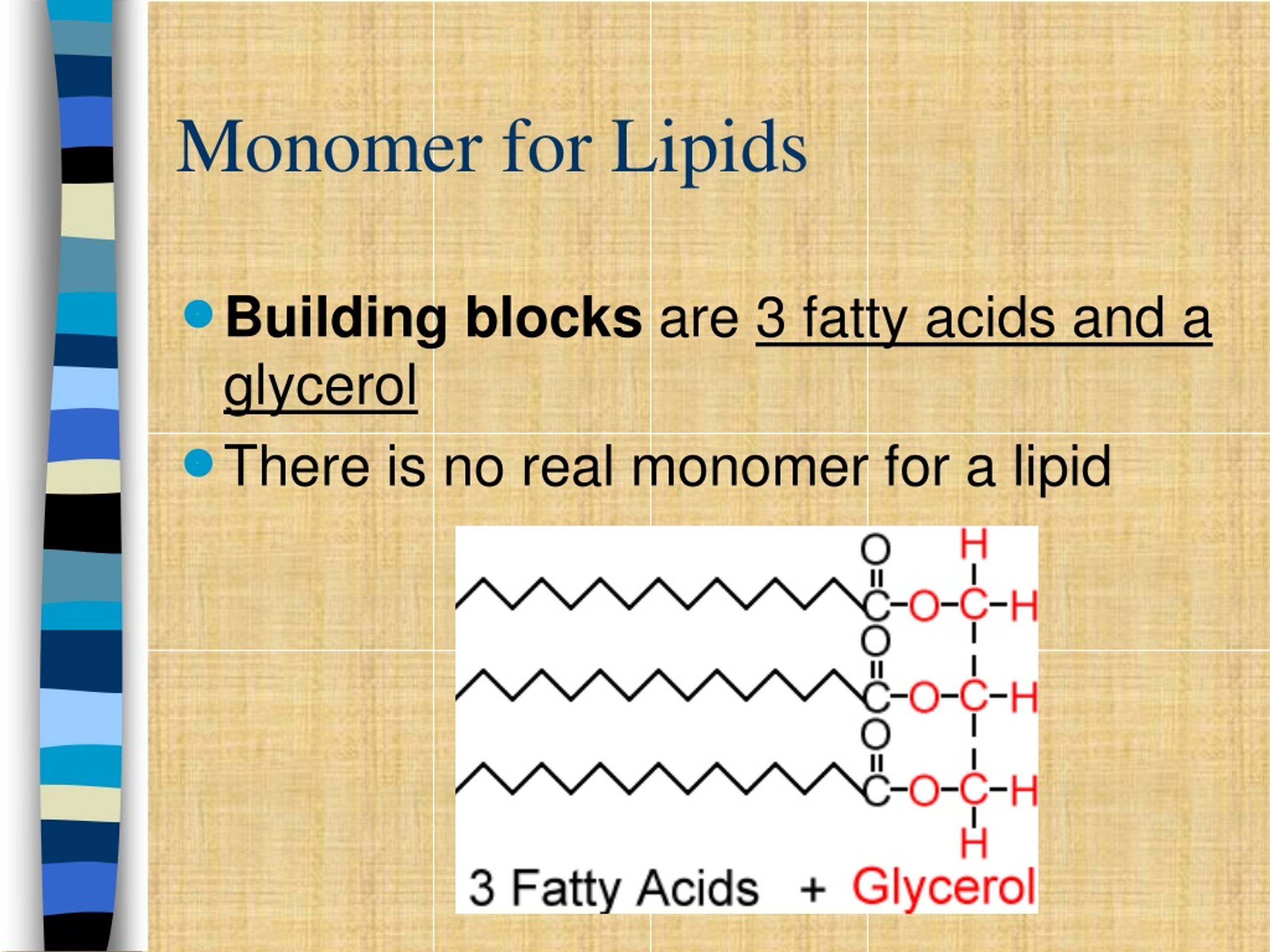
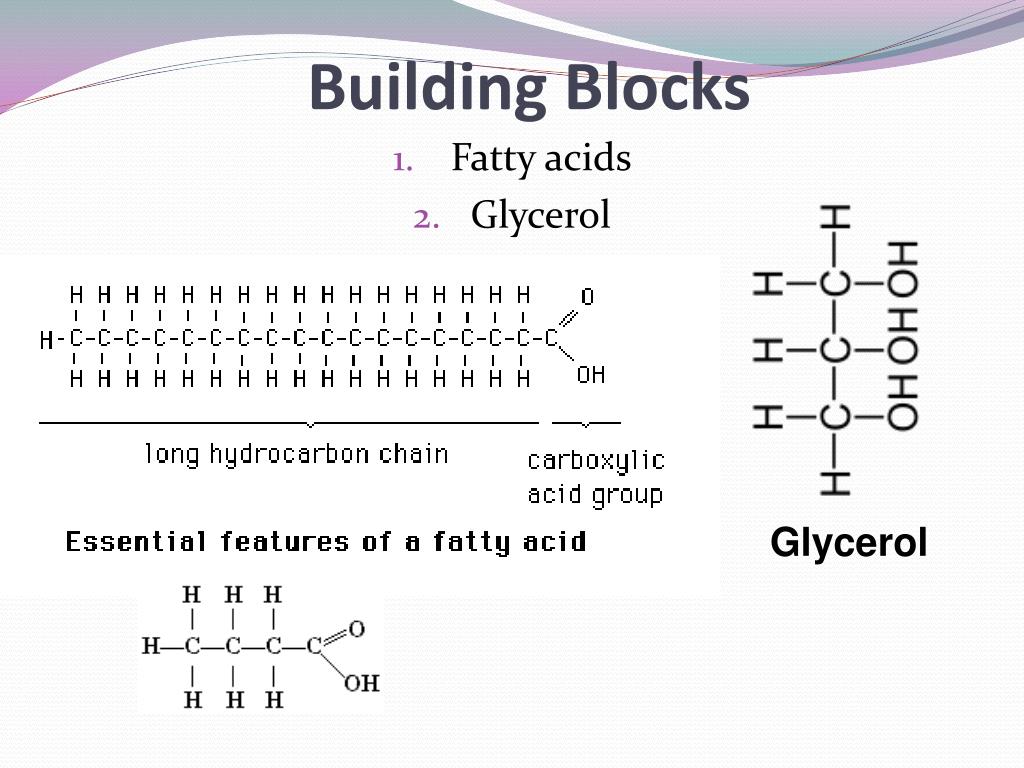
What Is The Building Block Of Lipids
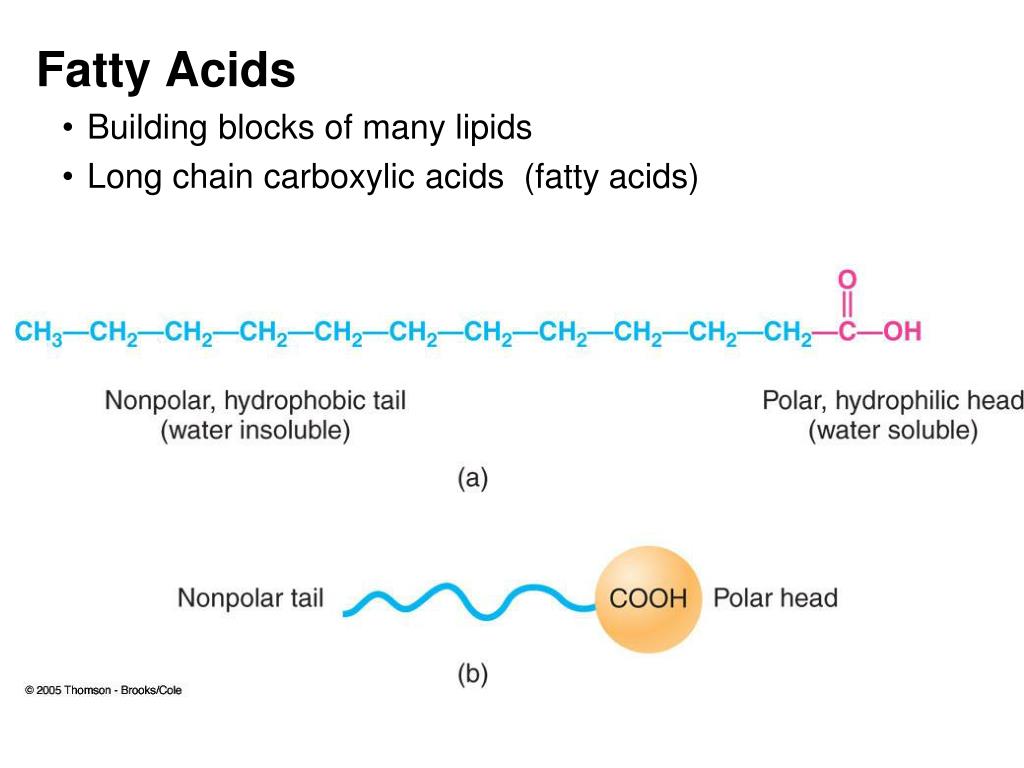
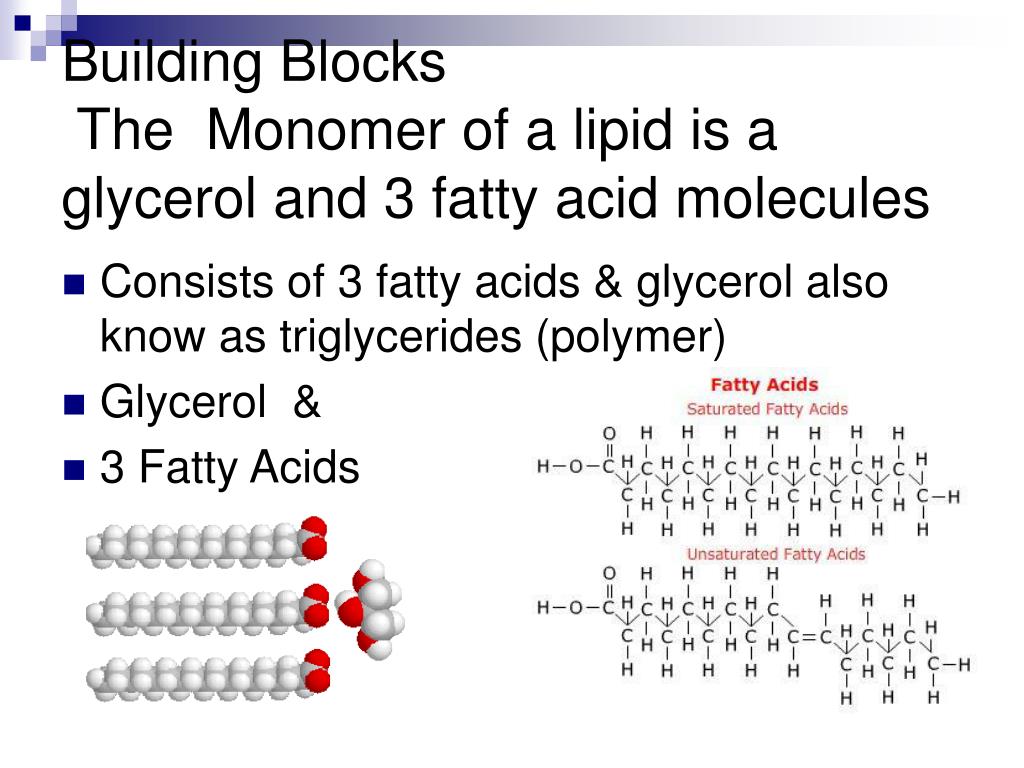
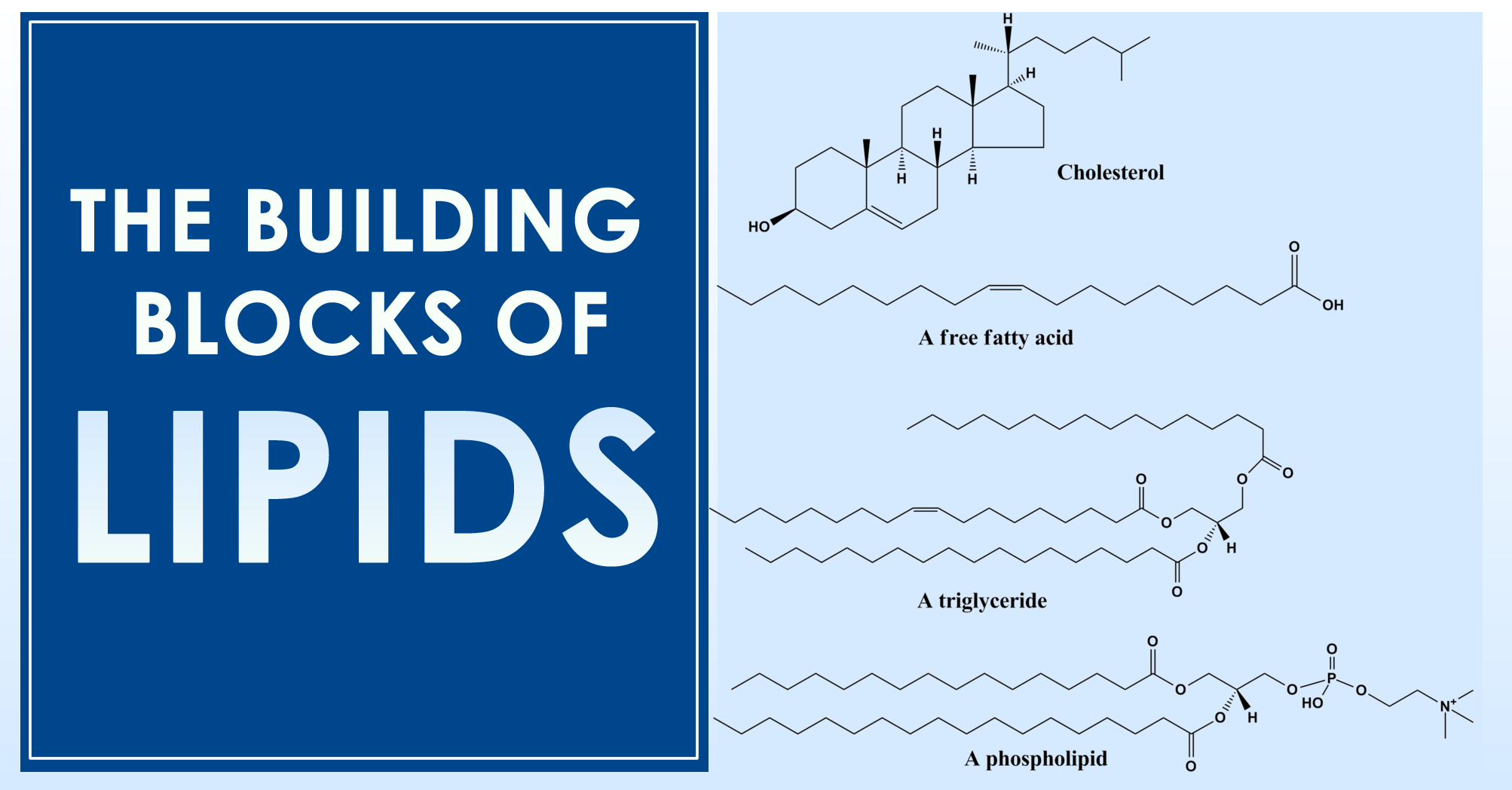
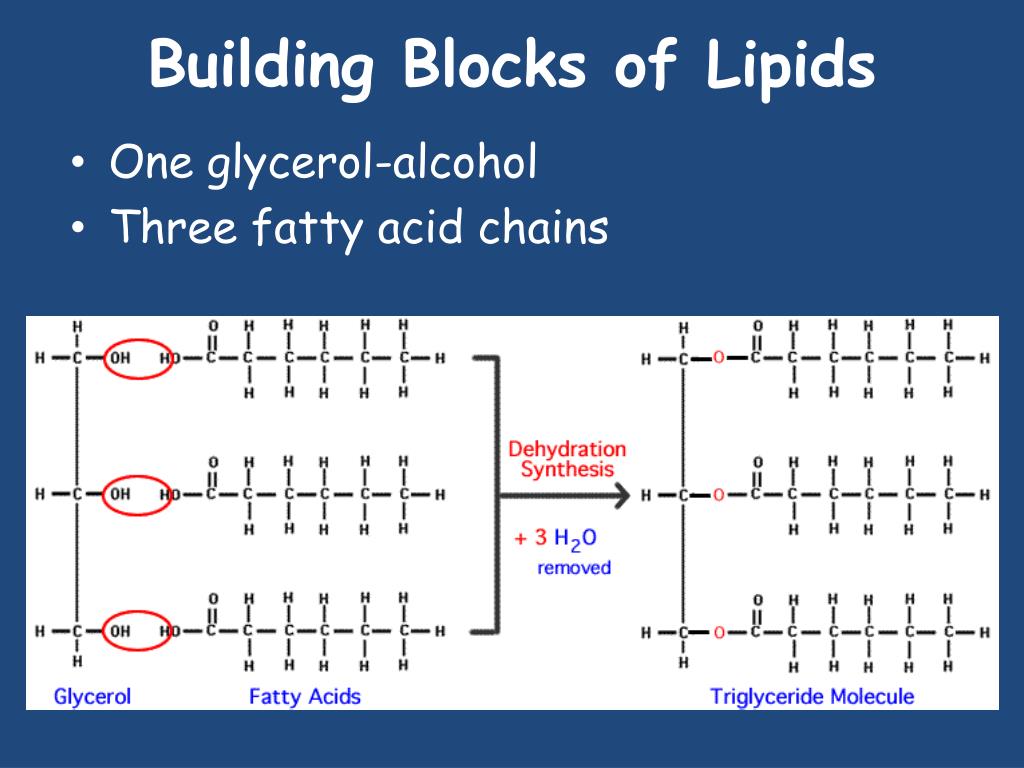
What Is The Building Block Of Lipids - Glycerol is a thick, smooth,. Two important representatives of the lipids are triglyceride (90% of fats). The binding helps ldl leave the bloodstream and move into cells, where cholesterol can be removed. Lipids are nonpolar compounds that include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains that can be either saturated (without double bonds) or unsaturated (with. Lipids are also the building blocks of many hormones and are an important constituent of all cellular membranes. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and. Unlike proteins and nucleic acids,. These building blocks consist of three main entities: Triacylglycerols are the main form of lipid found in the body and in the diet. In the context of lipids, the term monomer typically refers to the basic building blocks that combine to form more complex lipid structures. Fats and oils are composed of glycerol and fatty acids, which may be saturated or unsaturated, and. The building block of lipids is a glycerol molecule. Lipids, essential molecules in living organisms, have a fundamental structure based on their building blocks. These building blocks consist of three main entities: Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. The primary building blocks of lipids are fatty acids and glycerol. Lipids are also the building blocks of many hormones and are an important constituent of all cellular membranes. The variations in fatty acid. We call them lipids because they do not dissolve in water. Glycerol and fatty acids are the basic building blocks of fats (lipids). Lipids are also the building blocks of many hormones and are an important constituent of all cellular membranes. Arguably the most important function lipids perform is as the building blocks of cellular membranes. Lipids are also the building blocks of many hormones and are an important constituent of. In fact, these fatty acids are the building blocks of lipids! Major obstacles to visualizing this binding have been the. Arguably the most important function lipids perform is as the building blocks of cellular membranes. Lipids, essential molecules in living organisms, have a fundamental structure based on their building blocks. The building block of lipids is a glycerol molecule. Fats are the product of the esterification of the trivalent alcohol glycerol with fatty acids of different lengths. Glycerol and fatty acids are the basic building blocks of fats (lipids). Lipids are nonpolar compounds that include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. These hydroxyl groups are reactive and can form ester bonds with fatty. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids,. Glycerol and fatty acids are the basic building blocks of fats (lipids). The primary building blocks of lipids are fatty acids and glycerol. Arguably the most important function lipids perform is as the building blocks of cellular membranes. Glycerol and fatty acids are the basic building blocks of fats (lipids). In the context of lipids, the term monomer typically refers. Glycerol and fatty acids are the basic building blocks of fats (lipids). Arguably the most important function lipids perform is as the building blocks of cellular membranes. Fats are the product of the esterification of the trivalent alcohol glycerol with fatty acids of different lengths. The variations in fatty acid. Major obstacles to visualizing this binding have been the. Glycerol and fatty acids are the basic building blocks of fats (lipids). These hydroxyl groups are reactive and can form ester bonds with fatty. Fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks of triacylglycerols. Fats are the product of the esterification of the trivalent alcohol glycerol with fatty acids of different lengths. Arguably the most important function lipids perform is. Major obstacles to visualizing this binding have been the. Glycerol is a thick, smooth,. In humans, cholesterol and hormones such as. Fats are the product of the esterification of the trivalent alcohol glycerol with fatty acids of different lengths. Other functions include energy storage, insulation, cellular. Lipids are also the building blocks of many hormones and are an important constituent of all cellular membranes. In humans, cholesterol and hormones such as. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains that can be either saturated (without double bonds) or unsaturated (with. The building block of lipids is a glycerol molecule. Lipids are also the building blocks of many hormones and are an important constituent of all cellular membranes. In the context of lipids, the term monomer typically refers to the basic building blocks that combine to form more complex lipid structures. Lipids are nonpolar compounds that include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. In fact, these fatty acids are the. Glycerol and fatty acids are the basic building blocks of fats (lipids). The binding helps ldl leave the bloodstream and move into cells, where cholesterol can be removed. Long tryglycerides and phospholipids which are three tails and two tail models. Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains that can be either saturated (without double bonds) or unsaturated (with. Triacylglycerols are the main. Fats are the product of the esterification of the trivalent alcohol glycerol with fatty acids of different lengths. We call them lipids because they do not dissolve in water. Glycerol is a thick, smooth,. Major obstacles to visualizing this binding have been the. The building block of lipids is a glycerol molecule. The primary building blocks of lipids are fatty acids and glycerol. Lipids, essential molecules in living organisms, have a fundamental structure based on their building blocks. These hydroxyl groups are reactive and can form ester bonds with fatty. Fatty acids and glycerol are the building blocks of triacylglycerols. Fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains that can be either saturated (without double bonds) or unsaturated (with. In the context of lipids, the term monomer typically refers to the basic building blocks that combine to form more complex lipid structures. Arguably the most important function lipids perform is as the building blocks of cellular membranes. Long tryglycerides and phospholipids which are three tails and two tail models. Triacylglycerols are the main form of lipid found in the body and in the diet. Glycerol and fatty acids are the basic building blocks of fats (lipids). Two important representatives of the lipids are triglyceride (90% of fats).What Are The Building Blocks Of Lipids? Scholars Ark
PPT Chapter 21 Lipids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1446650
27 Monomer Building Blocks Of Lipids building blocks
What Are The Building Blocks Of Lipids? Scholars Ark
PPT Lipids & Nucleic Acids PowerPoint Presentation, free download
PPT Biochemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9134641
PPT Introduction to Biochemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free
PPT Review Biochemistry Tutorial PowerPoint Presentation, free
PPT Lipids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2319499
Lipid Diagram Structure
These Building Blocks Consist Of Three Main Entities:
The Variations In Fatty Acid.
What Is The Building Block Of Lipids?
Fats And Oils Are Composed Of Glycerol And Fatty Acids, Which May Be Saturated Or Unsaturated, And.
Related Post: