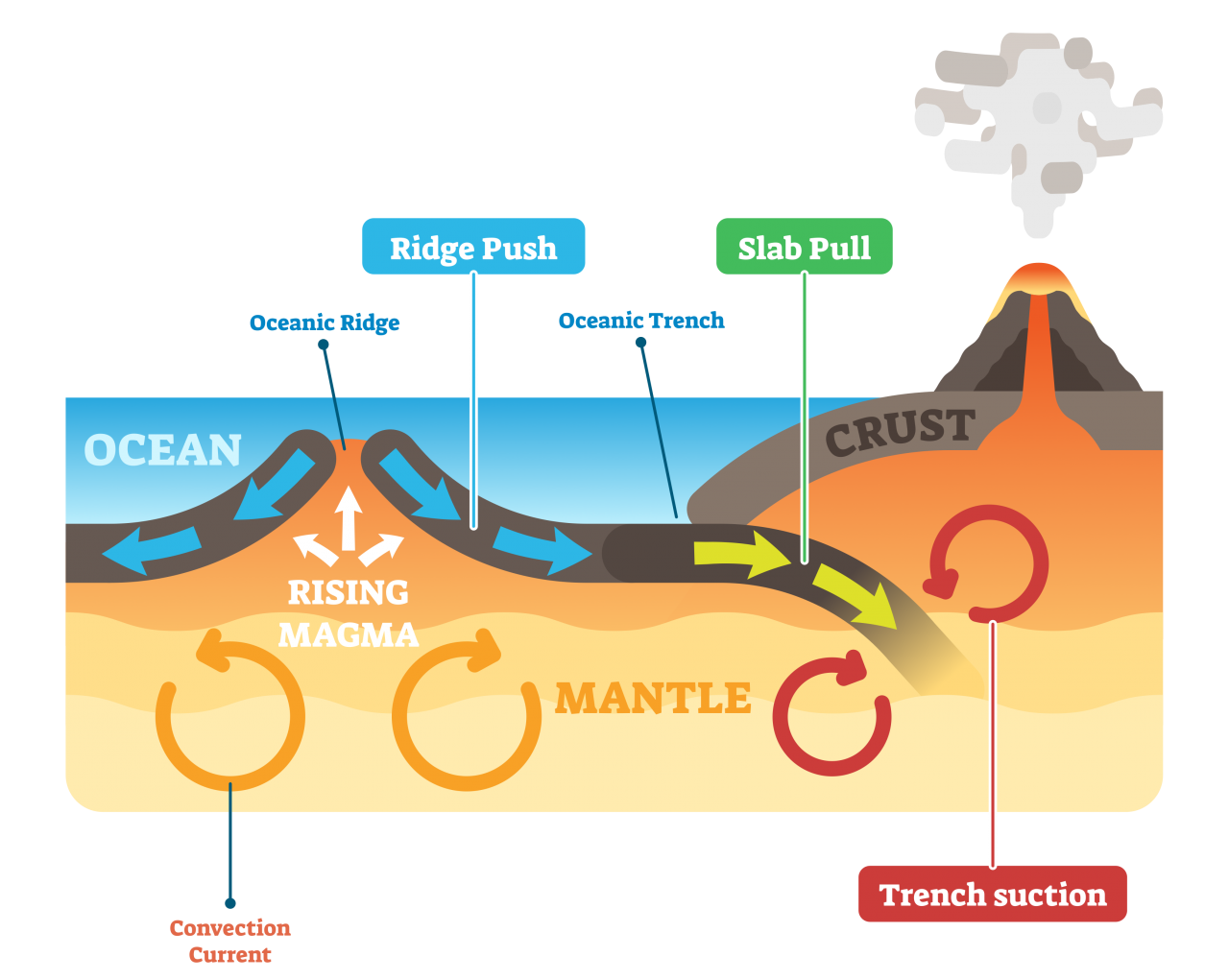
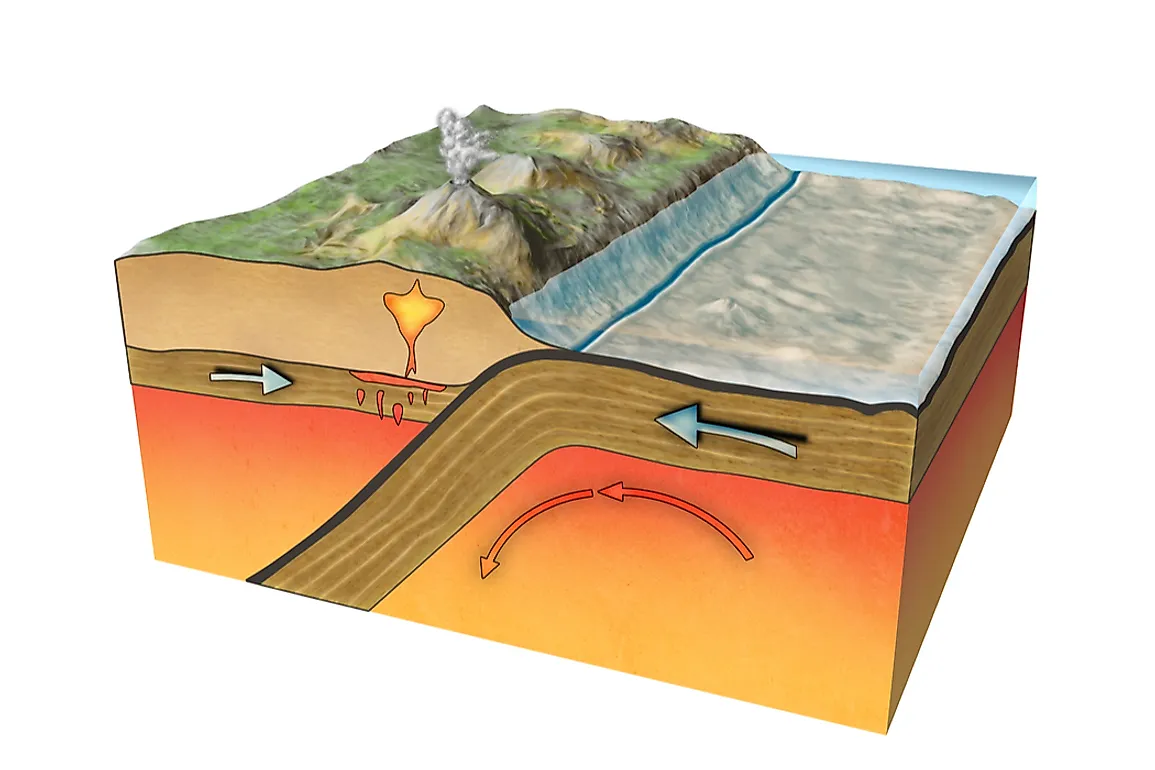
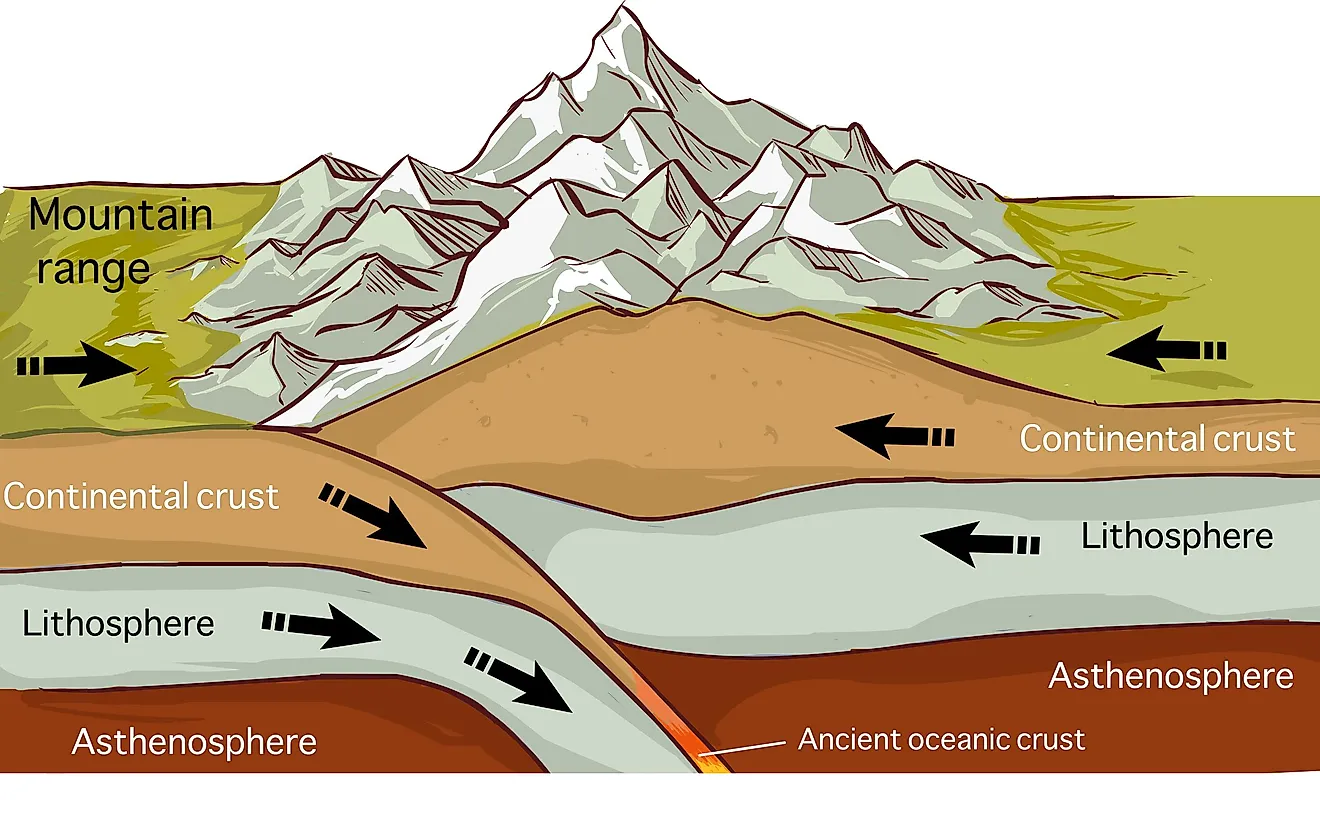
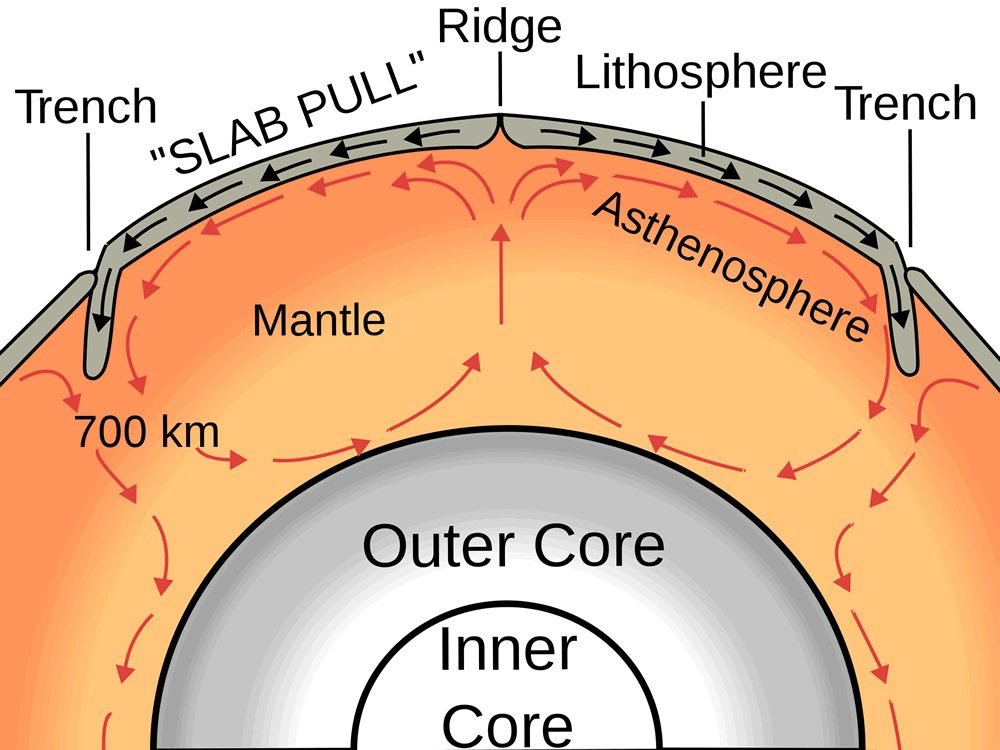
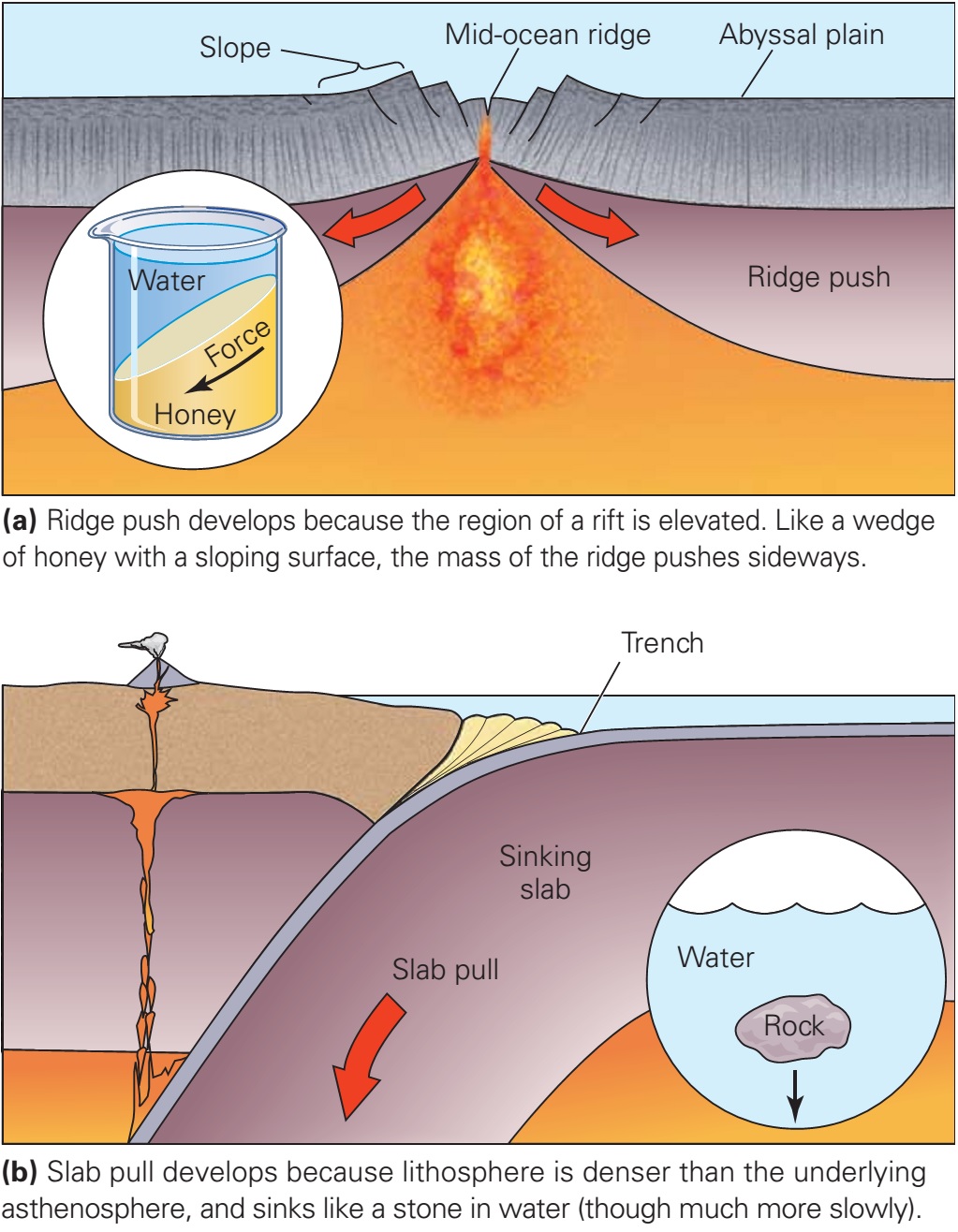
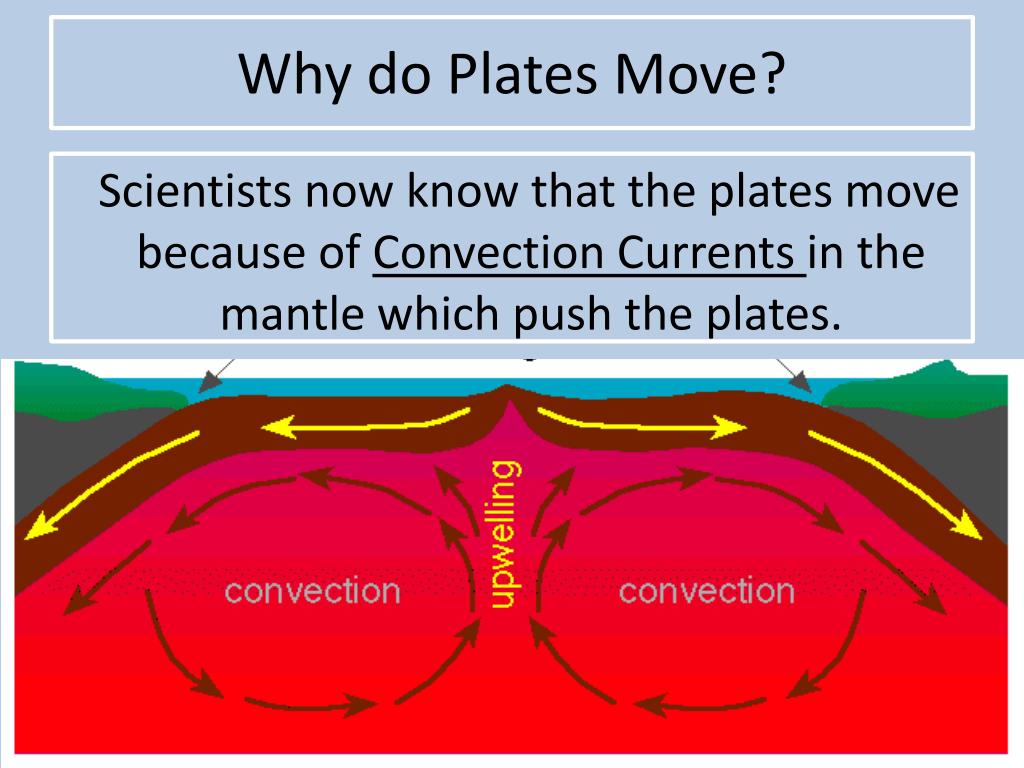
When Moving Plates Get Hung Up This Builds Up
When Moving Plates Get Hung Up This Builds Up - Individual plates of varying size move about the surface of the earth at varying speeds. As the plates move, their rough edges can get stuck on each other. Watch a video clip from nova: Earth’s thin outer layer of cold, rigid rock is made up of interlocking tectonic plates that float, or ride, on an underlying layer of hot, slowly moving rock inside earth. When the plates finally give and slip due to the increased pressure, energy is. When the plates move toward each other and collide, the crust crunches together and piles up. Plate movement builds up pressure in faults until the two sides of the fault suddenly shift to release the pressure. A slippery layer about 416 miles (670 kilometers) deep stops chunks of crust in their tracks,. This stops movement at the boundary while the rest of the plates keep moving. Learn how tectonic plates move, collide, or spread apart, and how they cause earthquakes, volcanoes, mountains, and trenches. Watch a video clip from nova: Individual plates of varying size move about the surface of the earth at varying speeds. Plates get locked together and pressure builds up. When this stress is realeased. Deadliest earthquakes and see how scientists. Earthquakes occur along fault lines as the plates converge, separate or slide past one another. This web page explains how scientists measure the motion of the earth's plates using magnetic stripes and gps satellites. When two tectonic plates rub against each other, they can create earthquakes, as the pressure builds up and is released along the fault line. But there are some hitches in this system, and new research reveals why: Plate movement builds up pressure in faults until the two sides of the fault suddenly shift to release the pressure. When two tectonic plates rub against each other, they can create earthquakes, as the pressure builds up and is released along the fault line. A slippery layer about 416 miles (670 kilometers) deep stops chunks of crust in their tracks,. Plate boundary at which plates slide past one another this type of current found within earth's mantle is strong enough. When two tectonic plates rub against each other, they can create earthquakes, as the pressure builds up and is released along the fault line. When the plates finally give and slip due to the increased pressure, energy is. Learn how tectonic plates move, collide, or spread apart, and how they cause earthquakes, volcanoes, mountains, and trenches. As the plates move,. Plates get locked together and pressure builds up. Today you will learn more about what causes. Plate boundary at which plates slide past one another this type of current found within earth's mantle is strong enough to move. When the indian plate hit the eurasian plate and formed the himalayan mountains. As the plates move, their rough edges can get. This web page explains how scientists measure the motion of the earth's plates using magnetic stripes and gps satellites. As the plates move, their rough edges can get stuck on each other. Deadliest earthquakes and see how scientists. As this happens slowly over time, mountains are formed on earth’s surface. Today you will learn more about what causes. Deadliest earthquakes and see how scientists. Watch a video clip from nova: When the plates move toward each other and collide, the crust crunches together and piles up. But there are some hitches in this system, and new research reveals why: When this stress is realeased. Learn how tectonic plates move, collide, or spread apart, and how they cause earthquakes, volcanoes, mountains, and trenches. As the plates move, their rough edges can get stuck on each other. This causes pressure to build up. When the plates move toward each other and collide, the crust crunches together and piles up. Earth’s thin outer layer of cold, rigid. This stops movement at the boundary while the rest of the plates keep moving. Individual plates of varying size move about the surface of the earth at varying speeds. Find out why they move, what is released. When the plates finally give and slip due to the increased pressure, energy is. When two tectonic plates rub against each other, they. As the plates move past each other, they sometimes get caught and pressure builds up. A slippery layer about 416 miles (670 kilometers) deep stops chunks of crust in their tracks,. This stops movement at the boundary while the rest of the plates keep moving. As the plates move, their rough edges can get stuck on each other. This causes. This causes pressure to build up. Earthquakes happen quickly, but the pressures that build up to cause them happen over a long period of time as tectonic plates shift. It does not mention anything about what happens. Learn how tectonic plates move, collide, or spread apart, and how they cause earthquakes, volcanoes, mountains, and trenches. When the plates move toward. When this stress is realeased. This stops movement at the boundary while the rest of the plates keep moving. Plates get locked together and pressure builds up. This causes pressure to build up. Individual plates of varying size move about the surface of the earth at varying speeds. 【solved】click here to get an answer to your question : When the plates move toward each other and collide, the crust crunches together and piles up. When this stress is realeased. This causes pressure to build up. When the indian plate hit the eurasian plate and formed the himalayan mountains. Watch a video clip from nova: This stops movement at the boundary while the rest of the plates keep moving. Friction causes the plates to get stuck. Find out why they move, what is released. When two tectonic plates rub against each other, they can create earthquakes, as the pressure builds up and is released along the fault line. Earthquakes occur along fault lines as the plates converge, separate or slide past one another. When the plates finally give and slip due to the increased pressure, energy is. This movement is known as plate tectonics. Deadliest earthquakes and see how scientists. This web page explains how scientists measure the motion of the earth's plates using magnetic stripes and gps satellites. Earth’s thin outer layer of cold, rigid rock is made up of interlocking tectonic plates that float, or ride, on an underlying layer of hot, slowly moving rock inside earth.Mechanisms of Plate Movement PBS LearningMedia
Why do tectonic plates move? Geography
Plate Movement Real World Examples at Leanna Weise blog
Plate tectonics 101—what happens when plates move toward each other
What Causes Tectonic Plates To Move? WorldAtlas
How tectonic plates move? Electrical
Learning Geology What Drives Plate Motion, and How Fast Do Plates Move?
How Do Tectonic Plates Move Ks2 at Bernard Coe blog
PPT Tectonic Plates PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2281109
How Do The Plates Move At A Convergent Boundary at Jai Reid blog
Two Raw Spaghetti Noodles (One.
As This Happens Slowly Over Time, Mountains Are Formed On Earth’s Surface.
A Slippery Layer About 416 Miles (670 Kilometers) Deep Stops Chunks Of Crust In Their Tracks,.
But There Are Some Hitches In This System, And New Research Reveals Why:
Related Post: