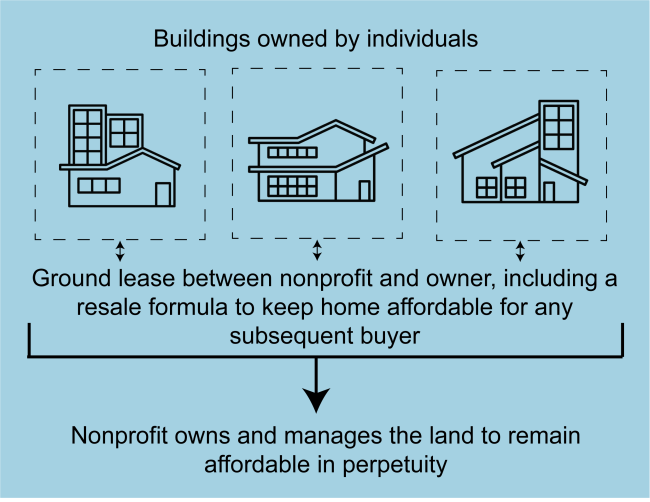
Who Owns The Building In A Ground Lease
Who Owns The Building In A Ground Lease - The lessee may own the building, but the land remains under the lessor’s control. The idea of the ground lease is that. A ground lease separates ownership of the land. Tenants assume responsibility for all the. A typical ground lease covers a period from 50 to 99 years. Under the terms of a ground lease, the tenant actually owns their building, but the landlord owns the ground it’s built on. With a ground lease, the landlord is not responsible for any buildings or other structures on the property. Ground leases are a type of lease that separates ownership of the land from ownership of the building and improvements constructed on the land. In this scenario, the lessee is the one who owns the building that is. With a ground lease, the land (ground) belongs to the title holder (landowner). A leasehold property means you own the building but not the land it sits on. Under the terms of a ground lease, the tenant actually owns their building, but the landlord owns the ground it’s built on. Sometimes a ground lease provides that the building is owned by the tenant during the term but ownership reverts to the landlord when the term of the lease ends. Ground leases typically involve separate ownership of the land and the buildings, so the lessor owns the land and the lessee owns the building. Tenants assume responsibility for all the. A ground lease, also known as a land lease, is a legal arrangement where a landowner leases the land to a tenant who constructs and owns buildings on that land. However, the lessee owns the building that is erected on the land and is responsible for its maintenance and upkeep. In this scenario, the lessee is the one who owns the building that is. Landlords use ground leases to retain ownership of the property for planning reasons, avoid capital gains, and generate revenue and income. With a ground lease, the land (ground) belongs to the title holder (landowner). Under the terms of a ground lease, the tenant actually owns their building, but the landlord owns the ground it’s built on. Instead, this responsibility lies with the tenant. However, the lessee owns the building that is erected on the land and is responsible for its maintenance and upkeep. A leasehold property means you own the building but not the. In a ground lease, the tenant typically owns the building and any improvements constructed on the leased land. Sometimes a ground lease provides that the building is owned by the tenant during the term but ownership reverts to the landlord when the term of the lease ends. Landlords use ground leases to retain ownership of the property for planning reasons,. The idea of the ground lease is that. Under the terms of a ground lease, the tenant actually owns their building, but the landlord owns the ground it’s built on. The lessee may own the building, but the land remains under the lessor’s control. Ground leases separate land ownership from ownership of structures built on the land. Who owns the. With a ground lease, the landlord is not responsible for any buildings or other structures on the property. A leasehold property means you own the building but not the land it sits on. Ground leases typically involve separate ownership of the land and the buildings, so the lessor owns the land and the lessee owns the building. The idea of. In a commercial real estate ground lease ownership structure, one party retains ownership of the ground and an investor/developer owns all of the improvements built on top of it. Sometimes a ground lease provides that the building is owned by the tenant during the term but ownership reverts to the landlord when the term of the lease ends. Under the. The ownership of any existing structures or newly constructed buildings on the property is subject to the lease. Instead, this responsibility lies with the tenant. A typical ground lease covers a period from 50 to 99 years. With a ground lease, the land (ground) belongs to the title holder (landowner). Tenants assume responsibility for all the. Under the terms of a ground lease, the tenant actually owns their building, but the landlord owns the ground it’s built on. A typical ground lease covers a period from 50 to 99 years. The lessee may own the building, but the land remains under the lessor’s control. Sometimes a ground lease provides that the building is owned by the. The lessee may own the building, but the land remains under the lessor’s control. The ownership of any existing structures or newly constructed buildings on the property is subject to the lease. Instead, you lease the land from the freeholder (landowner) for a set period, which could be anything. With a ground lease, the landlord is not responsible for any. Though the concept has certainly. The lessee may own the building, but the land remains under the lessor’s control. Tenants assume responsibility for all the. Ground leases are a type of lease that separates ownership of the land from ownership of the building and improvements constructed on the land. Ground leases typically involve separate ownership of the land and the. In a commercial real estate ground lease ownership structure, one party retains ownership of the ground and an investor/developer owns all of the improvements built on top of it. Who owns the building erected on land with a ground lease? The ownership of any existing structures or newly constructed buildings on the property is subject to the lease. A typical. A ground lease, also known as a land lease, is a legal arrangement where a landowner leases the land to a tenant who constructs and owns buildings on that land. The idea of the ground lease is that. Landlords use ground leases to retain ownership of the property for planning reasons, avoid capital gains, and generate revenue and income. In a ground lease, the tenant typically owns the building and any improvements constructed on the leased land. Who owns the building that is erected on land that has a ground lease? With a ground lease, the land (ground) belongs to the title holder (landowner). In this scenario, the lessee is the one who owns the building that is. Who owns the building erected on land with a ground lease? In a commercial real estate ground lease ownership structure, one party retains ownership of the ground and an investor/developer owns all of the improvements built on top of it. However, the lessee owns the building that is erected on the land and is responsible for its maintenance and upkeep. The lessee may own the building, but the land remains under the lessor’s control. Sometimes a ground lease provides that the building is owned by the tenant during the term but ownership reverts to the landlord when the term of the lease ends. Though the concept has certainly. Instead, this responsibility lies with the tenant. A leasehold property means you own the building but not the land it sits on. Ground leases separate land ownership from ownership of structures built on the land.Champlain Housing Trust Ground Lease ppt download
What Is a Ground Lease? USQ
What Is a Ground Lease? USQ
Free Printable Land Lease Agreement Templates [Word & PDF] Sample
Who Owns the Building in a Ground Lease?
Ground Lease Agreement Print & Download Legal Templates
How Ground Leases 2.0 Create Value And Avoid Disaster Real estate
What Is A Ground Lease Definition & Examples
Ground Lease AwesomeFinTech Blog
Community Land Trust
A Ground Lease Separates Ownership Of The Land.
The Ownership Of Any Existing Structures Or Newly Constructed Buildings On The Property Is Subject To The Lease.
Ground Leases Typically Involve Separate Ownership Of The Land And The Buildings, So The Lessor Owns The Land And The Lessee Owns The Building.
Ground Leases Are A Type Of Lease That Separates Ownership Of The Land From Ownership Of The Building And Improvements Constructed On The Land.
Related Post:



![Free Printable Land Lease Agreement Templates [Word & PDF] Sample](https://www.typecalendar.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Land-Lease-Agreement-1536x864.jpg)