Cube Shaped Building Floating On Water Physics
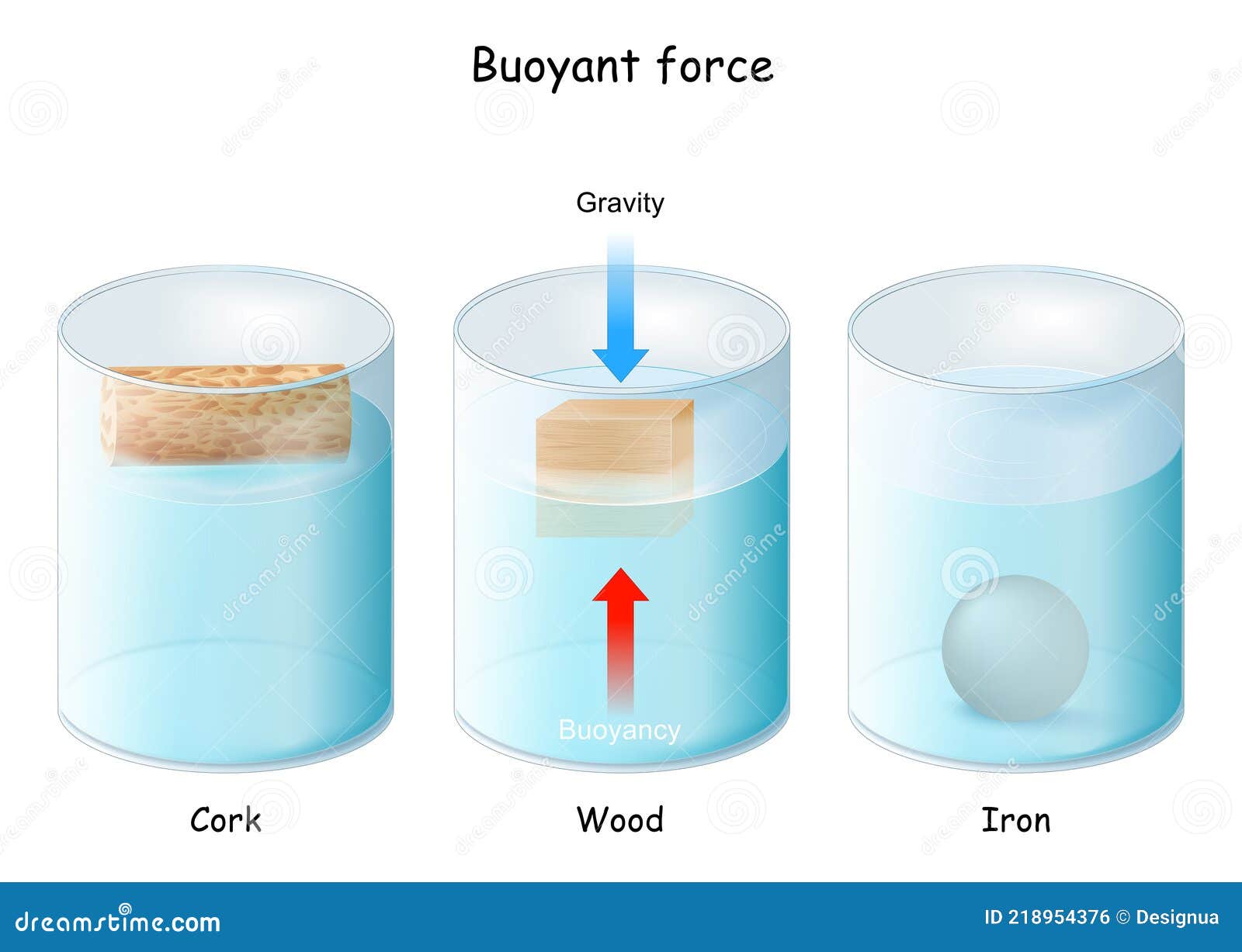
Cube Shaped Building Floating On Water Physics - In an ice cube, water molecules are frozen in a crystalline structure, with molecules held together by hydrogen bonds. The walls, roof and ceiling of the “water cube” are covered — indeed, made from — enormous bubbles that seem to have drifted into place randomly, as if floating on the. We'll conduct experiments with different objects like wood spheres, rubber spheres, and even water balloons, examining their densities and how they interact with water. This solid form has a lower density than the liquid form,. Topological structures in the interference patterns of three water waves. Archimedes example a cube of plastic 4.0 cm on a side with density = 0.8 g/cm3 is floating in the water. Any object, totally or partially immersed in a fluid or liquid, is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. In on floating bodies, archimedes suggested that (c. But throw a heavy metal anchor off the deck, and it sinks. When a 9 gram coin is placed on the block, how much sinks below water surface? The downward force on the object is simply its weight. The walls, roof and ceiling of the “water cube” are covered — indeed, made from — enormous bubbles that seem to have drifted into place randomly, as if floating on the. Archimedes example a cube of plastic 4.0 cm on a side with density = 0.8 g/cm3 is floating in the water. When a 9 gram coin is placed on the block, how much sinks below water surface? But throw a heavy metal anchor off the deck, and it sinks. In an ice cube, water molecules are frozen in a crystalline structure, with molecules held together by hydrogen bonds. Any object, totally or partially immersed in a fluid or liquid, is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. Determine the maximum mass that can be suspended from this cubic. In on floating bodies, archimedes suggested that (c. Show why objects float in a preferred orientation and why one hull shape is more stable than another. The walls, roof and ceiling of the “water cube” are covered — indeed, made from — enormous bubbles that seem to have drifted into place randomly, as if floating on the. Any object, totally or partially immersed in a fluid or liquid, is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. The. But throw a heavy metal anchor off the deck, and it sinks. Cruise ships and aircraft carriers are built from hundreds of thousands of tons of material, yet they float. Show why objects float in a preferred orientation and why one hull shape is more stable than another. In on floating bodies, archimedes suggested that (c. Topological structures in the. This solid form has a lower density than the liquid form,. But throw a heavy metal anchor off the deck, and it sinks. Cruise ships and aircraft carriers are built from hundreds of thousands of tons of material, yet they float. In on floating bodies, archimedes suggested that (c. Any object, totally or partially immersed in a fluid or liquid,. Determine the maximum mass that can be suspended from this cubic. We'll conduct experiments with different objects like wood spheres, rubber spheres, and even water balloons, examining their densities and how they interact with water. Archimedes' principle allows the buoyancy of any floating object partially or fully immersed in a fluid to be calculated. In on floating bodies, archimedes suggested. Archimedes example a cube of plastic 4.0 cm on a side with density = 0.8 g/cm3 is floating in the water. This solid form has a lower density than the liquid form,. Determine the maximum mass that can be suspended from this cubic. Show why objects float in a preferred orientation and why one hull shape is more stable than. In an ice cube, water molecules are frozen in a crystalline structure, with molecules held together by hydrogen bonds. Topological structures in the interference patterns of three water waves. Any object, totally or partially immersed in a fluid or liquid, is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. Show why objects. We'll conduct experiments with different objects like wood spheres, rubber spheres, and even water balloons, examining their densities and how they interact with water. In an ice cube, water molecules are frozen in a crystalline structure, with molecules held together by hydrogen bonds. Show why objects float in a preferred orientation and why one hull shape is more stable than. Any object, totally or partially immersed in a fluid or liquid, is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. When a 9 gram coin is placed on the block, how much sinks below water surface? The walls, roof and ceiling of the “water cube” are covered — indeed, made from —. The downward force on the object is simply its weight. Any object, totally or partially immersed in a fluid or liquid, is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. Archimedes' principle allows the buoyancy of any floating object partially or fully immersed in a fluid to be calculated. The walls, roof. We'll conduct experiments with different objects like wood spheres, rubber spheres, and even water balloons, examining their densities and how they interact with water. In on floating bodies, archimedes suggested that (c. Topological structures in the interference patterns of three water waves. But throw a heavy metal anchor off the deck, and it sinks. Determine the maximum mass that can. Archimedes example a cube of plastic 4.0 cm on a side with density = 0.8 g/cm3 is floating in the water. This solid form has a lower density than the liquid form,. The walls, roof and ceiling of the “water cube” are covered — indeed, made from — enormous bubbles that seem to have drifted into place randomly, as if floating on the. Cruise ships and aircraft carriers are built from hundreds of thousands of tons of material, yet they float. Show why objects float in a preferred orientation and why one hull shape is more stable than another. In an ice cube, water molecules are frozen in a crystalline structure, with molecules held together by hydrogen bonds. Any object, totally or partially immersed in a fluid or liquid, is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. Determine the maximum mass that can be suspended from this cubic. Archimedes' principle allows the buoyancy of any floating object partially or fully immersed in a fluid to be calculated. In on floating bodies, archimedes suggested that (c. The downward force on the object is simply its weight. Topological structures in the interference patterns of three water waves.Buoyant Force. Archimedes` Principle Stock Vector Illustration of
a solid cube floats in water half immersed and has small vertical
SOLVED Four cubeshaped blocks are floating in equilibrium in a tank
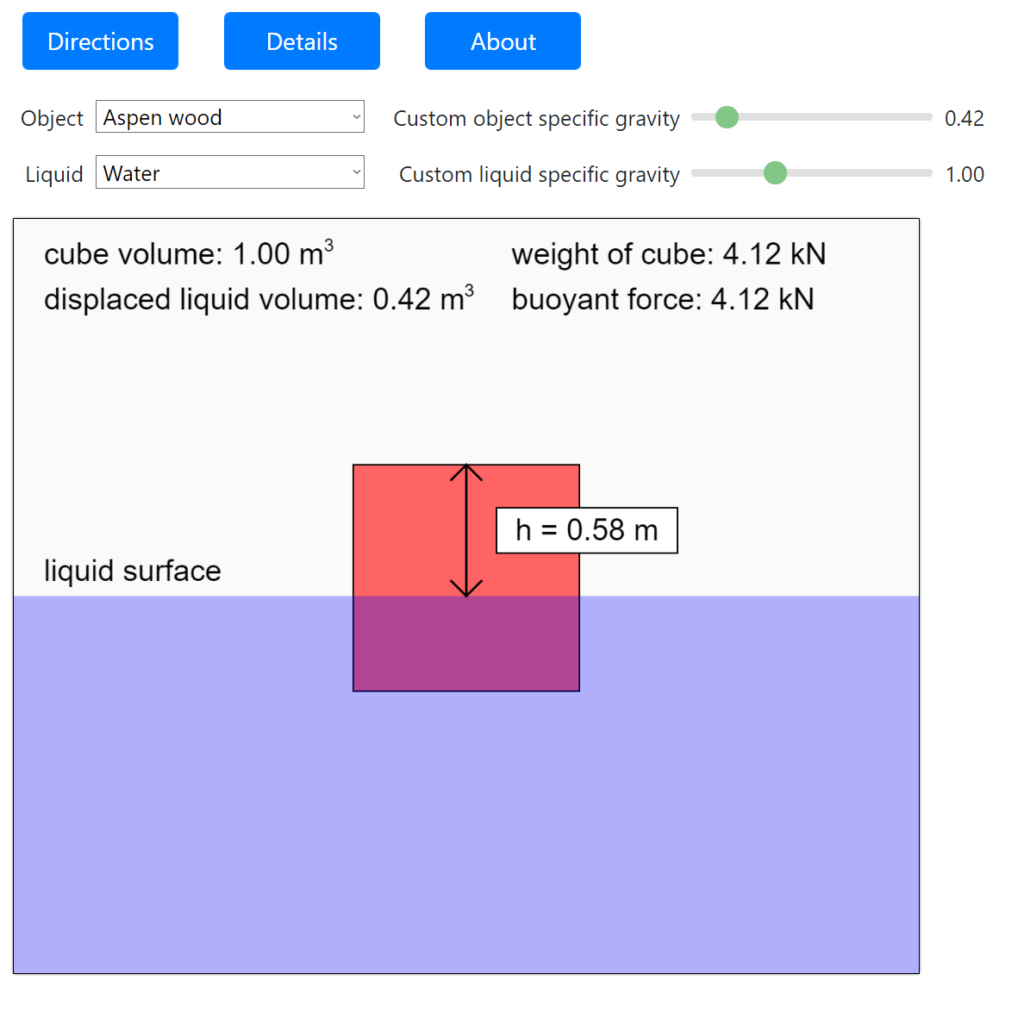
bouyancyofafloatingcube LearnChemE
Physics. Ice Cube Floating in a Glass of Water Stock Illustration
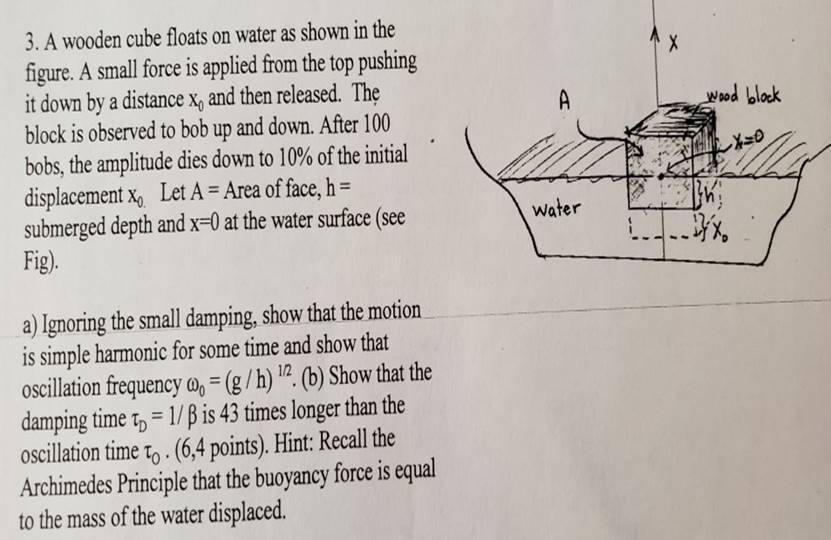
(Solved) 3. A Wooden Cube Floats On Water As Shown In The Figure. A
Vektor Stok Principle Floatation On Wooden Cube Water (Tanpa Royalti
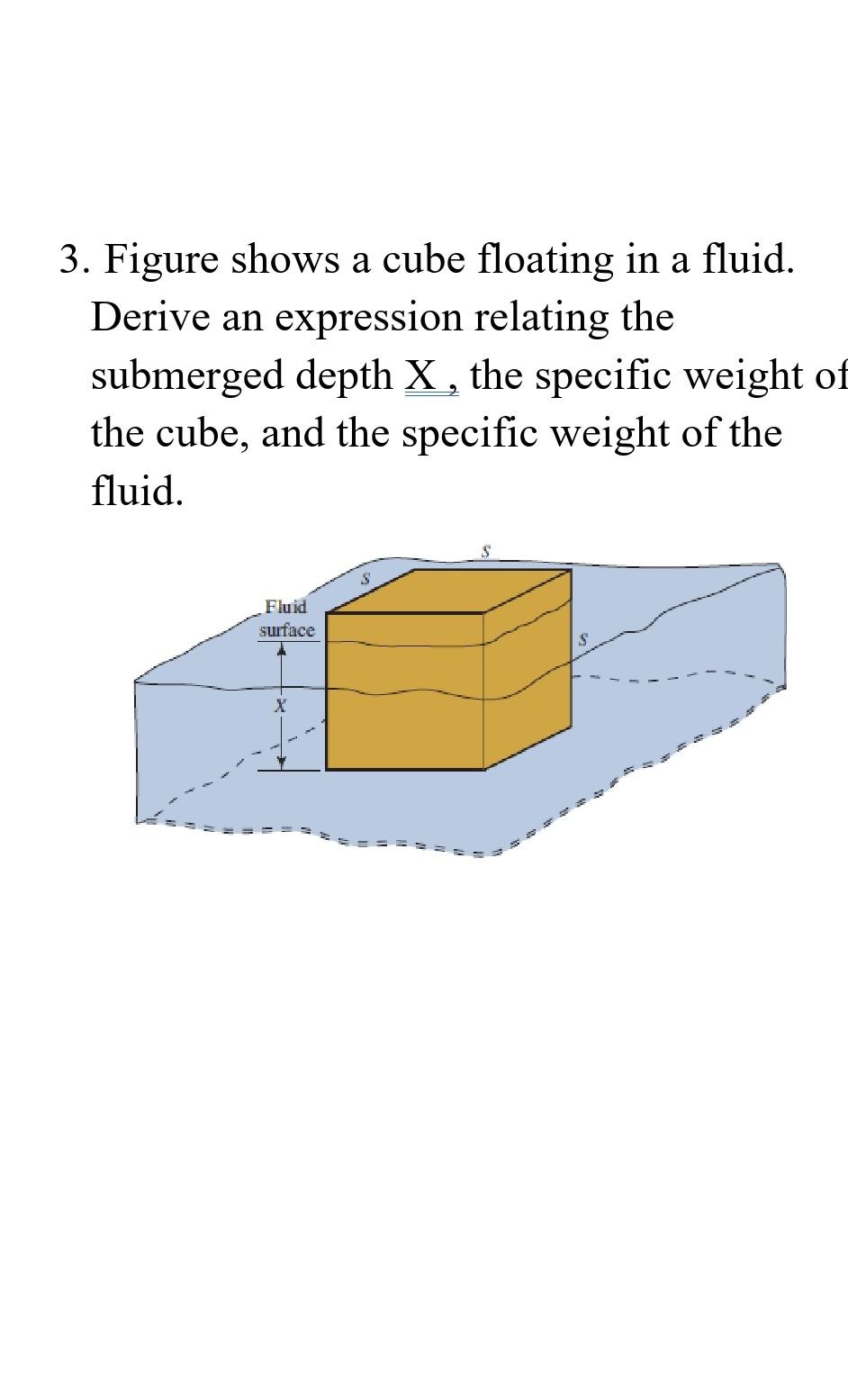
Solved 3. Figure shows a cube floating in a fluid. Derive an
A wooden cube just floats inside water when a 0.2 kg mass is placed on
A plastic cube floats in a liquid while remaining fully submerged the
When A 9 Gram Coin Is Placed On The Block, How Much Sinks Below Water Surface?
We'll Conduct Experiments With Different Objects Like Wood Spheres, Rubber Spheres, And Even Water Balloons, Examining Their Densities And How They Interact With Water.
But Throw A Heavy Metal Anchor Off The Deck, And It Sinks.
Related Post: