What Are The Building Blocks Of Glycogen
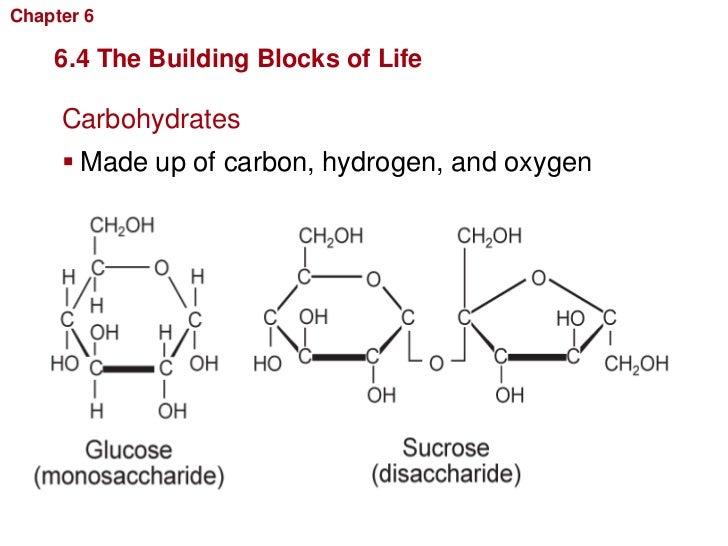
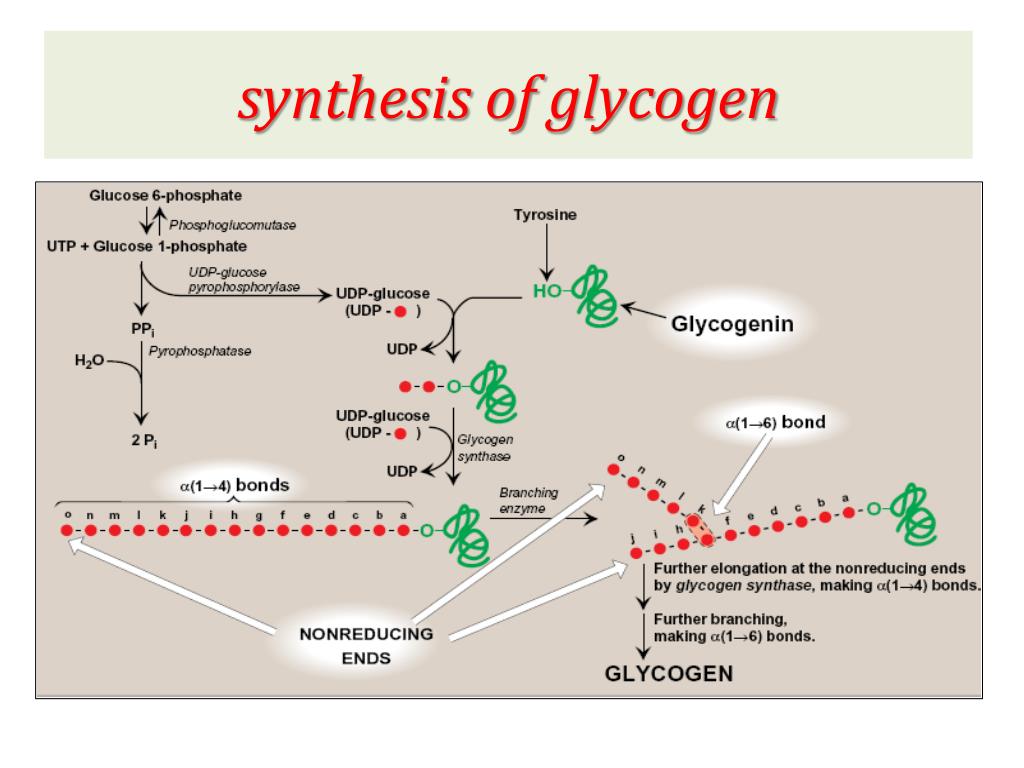
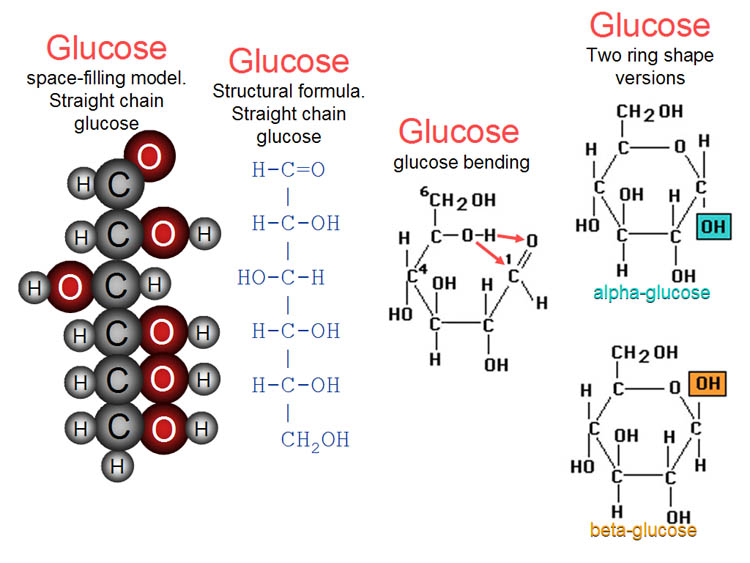
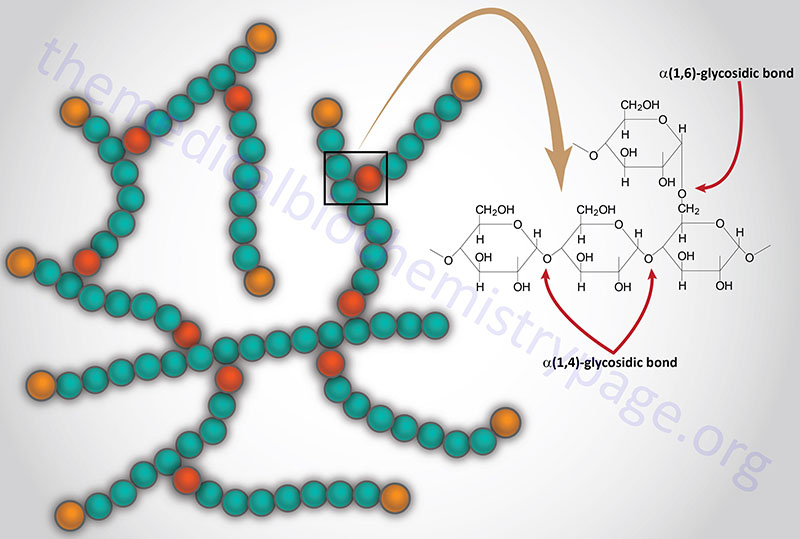
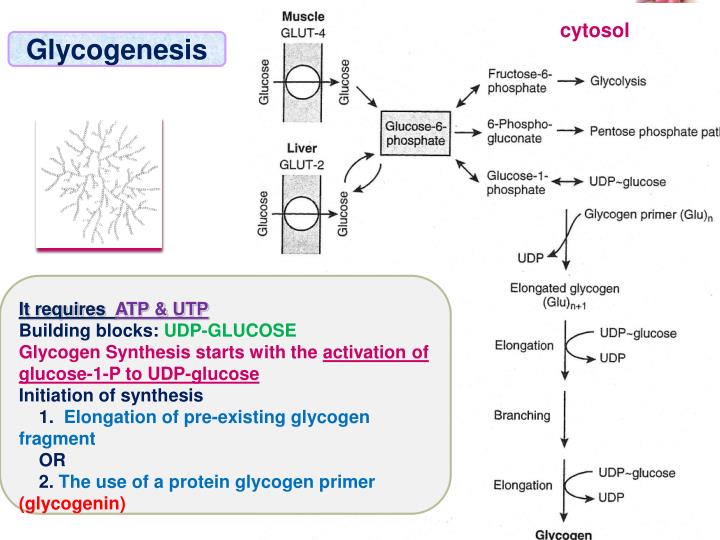
What Are The Building Blocks Of Glycogen - Glycogen is the stored form of glucose. In this article, let’s explore about these carbohydrates and their biological building blocks: It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body. The more complex carbohydrates, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides are composed of longer chains of monosaccharide units. It’s made of many connected glucose molecules. The biosynthesis of a glycogen molecule is primarily regulated by three proteins: The main building blocks of glycogen are monosaccharides, specifically glucose. Disaccharides, such as sucrose and lactose, consist of two monosaccharide units. The formation of glycogen from glucose is known as glycogenesis, and the breakdown of glycogen to form glucose is called glycogen metabolism or glycogenolysis. Its building blocks include glucose, the backbone monosaccharide, and glycosidic bonds,. Your body mainly stores glycogen in your liver and. Its building blocks include glucose, the backbone monosaccharide, and glycosidic bonds,. The glucose monomers link to form a primary linear polymer, and after an average of eight to ten. The biosynthesis of a glycogen molecule is primarily regulated by three proteins: Glycogen is the stored form of glucose. Glycogen, a branched polysaccharide, serves as a crucial energy source for cells. Disaccharides, such as sucrose and lactose, consist of two monosaccharide units. An activated form of glucose and the building block for glycogen synthesis and glycogenolysis; Glycogen is a complex carbohydrate, functioning as a storage form of glucose in animals,. It’s made of many connected glucose molecules. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body. Like amylopectin, its molecular chain has branches. They are the building blocks (monomers) for the synthesis of polymers or complex carbohydrates, as will be discussed further in this section. In this article, let’s explore about these carbohydrates and their biological building blocks: Glycogen, a branched polysaccharide, serves as. The formation of glycogen from glucose is known as glycogenesis, and the breakdown of glycogen to form glucose is called glycogen metabolism or glycogenolysis. The main building blocks of glycogen are monosaccharides, specifically glucose. Glycogen is the stored form of glucose. Glycogen is a polysaccharide, meaning it is made up of long chains of monosaccharides (simple sugars) connected by two. Its building blocks include glucose, the backbone monosaccharide, and glycosidic bonds,. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body. It’s made of many connected glucose molecules. The more complex carbohydrates, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides are composed of longer chains of monosaccharide units. Glycogen is a polysaccharide, meaning it is made up of long chains of monosaccharides (simple. Like amylopectin, its molecular chain has branches. Disaccharides, such as sucrose and lactose, consist of two monosaccharide units. It’s made of many connected glucose molecules. Glycogenin (gyg), glycogen synthase (gs), and glycogen branching enzyme (gbe). The main building blocks of glycogen are monosaccharides, specifically glucose. Your body mainly stores glycogen in your liver and. Glycogen is a polysaccharide, meaning it is made up of long chains of monosaccharides (simple sugars) connected by two glycosidic bonds: In this article, let’s explore about these carbohydrates and their biological building blocks: Disaccharides, such as sucrose and lactose, consist of two monosaccharide units. Carbohydrates are classified into three subtypes: Glycogenin (gyg), glycogen synthase (gs), and glycogen branching enzyme (gbe). The main building blocks of glycogen are monosaccharides, specifically glucose. Glycogen is a complex carbohydrate, functioning as a storage form of glucose in animals,. In this article, let’s explore about these carbohydrates and their biological building blocks: The glucose monomers link to form a primary linear polymer, and after an. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body. It’s made of many connected glucose molecules. Its building blocks include glucose, the backbone monosaccharide, and glycosidic bonds,. Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. The biosynthesis of a glycogen molecule is primarily regulated by. In this article, let’s explore about these carbohydrates and their biological building blocks: Carbohydrates are classified into three subtypes: Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, fungi, and bacteria. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body. The glucose monomers link to form a primary linear. Your body mainly stores glycogen in your liver and. The more complex carbohydrates, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides are composed of longer chains of monosaccharide units. Carbohydrates are classified into three subtypes: The formation of glycogen from glucose is known as glycogenesis, and the breakdown of glycogen to form glucose is called glycogen metabolism or glycogenolysis. Glycogen is a polysaccharide, meaning it. Disaccharides, such as sucrose and lactose, consist of two monosaccharide units. Monosaccharides, like glucose and fructose, are the simplest forms of carbohydrates and serve as the fundamental building blocks. Glycogen, a branched polysaccharide, serves as a crucial energy source for cells. The biosynthesis of a glycogen molecule is primarily regulated by three proteins: The glucose monomers link to form a. They are the building blocks (monomers) for the synthesis of polymers or complex carbohydrates, as will be discussed further in this section. Glycogen, a branched polysaccharide, serves as a crucial energy source for cells. The glucose monomers link to form a primary linear polymer, and after an average of eight to ten. It’s made of many connected glucose molecules. The main building blocks of glycogen are monosaccharides, specifically glucose. Glycogenin (gyg), glycogen synthase (gs), and glycogen branching enzyme (gbe). Your body mainly stores glycogen in your liver and. The formation of glycogen from glucose is known as glycogenesis, and the breakdown of glycogen to form glucose is called glycogen metabolism or glycogenolysis. It is the main storage form of glucose in the human body. Like amylopectin, its molecular chain has branches. In this article, let’s explore about these carbohydrates and their biological building blocks: The biosynthesis of a glycogen molecule is primarily regulated by three proteins: Glycogen is a polysaccharide, meaning it is made up of long chains of monosaccharides (simple sugars) connected by two glycosidic bonds: Glycogen is the stored form of glucose. The more complex carbohydrates, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides are composed of longer chains of monosaccharide units. Monosaccharides, like glucose and fructose, are the simplest forms of carbohydrates and serve as the fundamental building blocks.Glycogen Structure Diagram
Biochemistry notes students
Biochemistry notes students
Glycogen Metabolism Color Index Important Extra Information Doctors
PPT Energy to Skeletal Muscles Lecture1 Glycogen Metabolism
Building Organic Compounds
Glycogen Metabolism By Dr Reem M Sallam MD
Glycogen Metabolism Clinical Chemistry Unit Department of Pathology
Biochemical Properties of Carbohydrates The Medical Biochemistry Page
PPT Glycogen Metabolism PowerPoint Presentation ID7039540
Its Building Blocks Include Glucose, The Backbone Monosaccharide, And Glycosidic Bonds,.
Carbohydrates Are Classified Into Three Subtypes:
Glycogen Is A Multibranched Polysaccharide Of Glucose That Serves As A Form Of Energy Storage In Animals, Fungi, And Bacteria.
An Activated Form Of Glucose And The Building Block For Glycogen Synthesis And Glycogenolysis;
Related Post: